Mastering AC Power Source Procurement: A Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ac power source
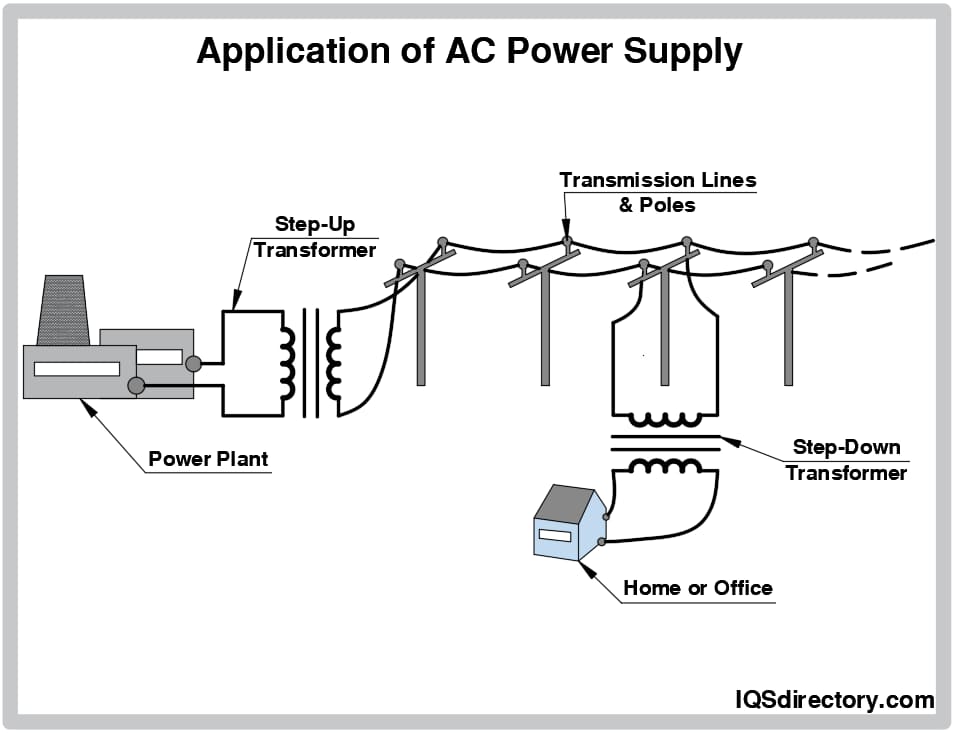
In today’s interconnected world, AC power sources are pivotal to the seamless operation of various industries, from manufacturing to telecommunications. As businesses increasingly rely on stable and efficient power supply systems, understanding the nuances of AC power sources becomes essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The market for AC power sources is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2030, reflecting the rising demand for reliable energy solutions.
This guide aims to empower buyers with a comprehensive understanding of AC power sources, covering critical aspects such as types of AC power sources, materials used, manufacturing and quality control processes, supplier evaluations, and cost considerations. Additionally, we will explore market trends and frequently asked questions, ensuring that buyers are well-equipped to make informed sourcing decisions.
By delving into these elements, this resource will not only enhance your knowledge but also streamline your procurement processes. Whether you are sourcing for a new project or optimizing existing operations, our insights will help you navigate the complexities of the global market, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and competitive advantage. Embrace the opportunity to leverage this guide and transform your sourcing strategy in the dynamic landscape of AC power sources.
Understanding ac power source Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase AC | Utilizes one alternating current waveform, typically 120V or 240V | Residential and small commercial use | Pros: Simple installation, cost-effective. Cons: Limited power capacity, less efficient for large loads. |
| Three-Phase AC | Comprises three alternating current waveforms, providing a more stable power supply | Industrial machinery, large commercial setups | Pros: Higher efficiency, better load balancing. Cons: More complex installation, higher initial costs. |
| Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) | Adjusts frequency and voltage to control motor speeds | Manufacturing, HVAC systems | Pros: Energy savings, improved control. Cons: Initial investment can be high, requires technical expertise. |
| Inverter-Based AC | Converts DC to AC, often used in renewable energy systems | Solar power systems, backup power | Pros: Flexibility in power sources, suitable for off-grid applications. Cons: Can be less efficient than direct AC sources, potential for higher maintenance costs. |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) | Provides backup power during outages, often includes battery storage | Data centers, hospitals, critical systems | Pros: Ensures continuous operation, protects against power surges. Cons: Limited backup time, higher upfront costs. |
Single-Phase AC
Single-phase AC is the most common type of power supply used in residential and small commercial settings. It operates on a single alternating current waveform, typically at voltages of 120V or 240V. This type of power source is suitable for small appliances and lighting systems. When purchasing single-phase AC systems, buyers should consider the load requirements and the simplicity of installation, as well as the potential limitations in power capacity for larger operations.
Three-Phase AC
Three-phase AC power is characterized by three alternating current waveforms, which allows for a more stable and efficient power supply. This system is primarily used in industrial environments and large commercial applications due to its ability to handle heavier loads and provide better load balancing. When considering a three-phase AC system, B2B buyers should evaluate the specific energy demands of their operations and the complexity of installation, as well as the potential for long-term energy savings despite higher initial costs.
Variable Frequency Drive (VFD)
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are specialized devices that adjust the frequency and voltage supplied to electric motors, enabling precise control over motor speeds. Commonly used in manufacturing and HVAC systems, VFDs can lead to significant energy savings and enhanced operational efficiency. B2B buyers should assess the compatibility of VFDs with existing systems and consider the initial investment versus the potential for reduced energy costs and improved process control.
Inverter-Based AC
Inverter-based AC systems convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), making them ideal for renewable energy applications, such as solar power systems. These systems offer flexibility in power sources and are suitable for both grid-tied and off-grid applications. When evaluating inverter-based solutions, buyers should consider efficiency ratings, compatibility with renewable energy sources, and potential maintenance requirements, which can be higher compared to traditional AC sources.
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) provide backup power during electrical outages, making them critical for data centers, hospitals, and other facilities where continuous operation is essential. UPS systems typically include battery storage and can protect sensitive equipment from power surges. Buyers should evaluate the required backup time, the total load capacity, and the total cost of ownership when selecting a UPS, as these systems can involve significant upfront and maintenance costs.
Key Industrial Applications of ac power source
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ac power source | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering machinery and production lines | Enhanced operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Voltage compatibility, energy efficiency, and reliability |
| Telecommunications | Base station power supply | Continuous service uptime and network reliability | Load capacity, scalability, and environmental resilience |
| Healthcare | Operating medical equipment and devices | Critical for patient safety and operational reliability | Compliance with health standards and power stability |
| Construction | Temporary power supply for construction sites | Ensures uninterrupted operations and worker safety | Portability, fuel type, and ease of installation |
| Transportation | Charging electric vehicles and powering depots | Supports sustainable transport solutions and reduces costs | Compatibility with existing infrastructure and energy source availability |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, AC power sources are crucial for powering various machinery and production lines. These systems require consistent and reliable power to operate effectively, minimizing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing AC power sources that meet local voltage standards and energy efficiency regulations is vital. Additionally, buyers should consider the reliability of the power supply to prevent disruptions in production schedules.
Telecommunications
AC power sources are integral to telecommunications, particularly for base station power supply. These stations require a steady power supply to ensure continuous service uptime and network reliability, especially in remote areas where power interruptions can significantly impact connectivity. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing AC power sources with adequate load capacity and scalability to accommodate future growth. Environmental resilience is also a key consideration, given the varying climate conditions in these regions.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AC power sources are essential for operating medical equipment and devices, which are critical for patient safety and operational reliability. Hospitals and clinics must ensure that their power supply systems comply with stringent health standards to avoid any risks associated with power outages. International buyers should focus on sourcing AC power sources that provide stable voltage and are equipped with backup solutions to maintain operations during emergencies, particularly in regions with less reliable power infrastructure.
Construction
The construction industry often relies on temporary power supplies at job sites to ensure uninterrupted operations. AC power sources provide the necessary energy for tools, lighting, and equipment, directly contributing to worker safety and project timelines. When sourcing these power solutions, buyers should consider factors such as portability, fuel type, and ease of installation. For projects in remote locations, especially in Africa and South America, the ability to quickly set up and dismantle power sources is crucial.
Transportation
In the transportation sector, AC power sources play a pivotal role in charging electric vehicles (EVs) and powering depots. As the shift towards sustainable transport solutions accelerates, businesses must invest in reliable AC power sources to support their EV infrastructure. Buyers should focus on compatibility with existing charging infrastructure and the availability of renewable energy sources to optimize costs. In markets like Europe and the Middle East, where EV adoption is rapidly increasing, sourcing efficient AC power solutions can provide a competitive advantage.
Related Video: 01 – Instantaneous Power in AC Circuit Analysis (Electrical Engineering)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ac power source
When selecting materials for AC power sources, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in AC power sources, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and exhibits excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and is resistant to corrosion, particularly when anodized.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is favored for its low weight and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for portable AC power sources. However, its lower tensile strength compared to other metals can lead to mechanical failures under high stress.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is compatible with various media, including air and water, making it versatile for different applications. However, it may not perform well in high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM and DIN. Additionally, the availability of aluminum may vary by region, impacting supply chain logistics.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, with a temperature rating of up to 200°C. It also has good resistance to corrosion, particularly in dry environments.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for electrical components, enhancing efficiency. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated.
Impact on Application:
Copper is suitable for applications requiring high electrical performance, such as transformers and power distribution systems. Its compatibility with various insulating materials is a significant advantage.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Copper is subject to price fluctuations, which can affect project budgets. Buyers should also consider sourcing from regions with stable supply chains to avoid disruptions.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is a robust material with high tensile strength and a temperature rating of up to 300°C. It is also resistant to deformation under stress but can be prone to corrosion if not treated.
Pros & Cons:
Steel’s durability makes it suitable for heavy-duty applications, such as structural components in power systems. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in portable applications, and it may require additional coatings for corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application:
Steel is ideal for applications requiring structural integrity and durability, such as enclosures for AC power sources. Its compatibility with various environmental conditions is a plus.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with standards like JIS and ASTM is crucial. Buyers should also evaluate local regulations regarding the use of steel, particularly in regions with stringent environmental policies.
Plastic Composites
Key Properties:
Plastic composites can withstand temperatures up to 120°C and offer good electrical insulation properties. They are lightweight and resistant to corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
These materials are cost-effective and can be molded into complex shapes, making them suitable for various applications. However, they may not withstand high temperatures or mechanical stresses as well as metals.
Impact on Application:
Plastic composites are ideal for insulating components and housing in AC power sources. Their compatibility with various media makes them versatile, although they may not be suitable for high-load applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that plastic composites meet local standards for fire resistance and environmental impact. Understanding regional preferences for materials can also guide procurement decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for AC Power Source | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Portable AC power sources | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower tensile strength | Low |
| Copper | Electrical components | Excellent electrical conductivity | Higher cost and oxidation risk | High |
| Steel | Structural components | High durability and tensile strength | Heavier and requires corrosion treatment | Medium |
| Plastic Composites | Insulating components and housings | Cost-effective and moldable | Limited temperature and stress tolerance | Low |
In conclusion, selecting the right material for AC power sources involves a careful assessment of performance characteristics, application suitability, and regional compliance requirements. By understanding these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ac power source
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance for AC power sources are crucial for ensuring reliability and performance in various applications. International B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, need to understand these processes to make informed purchasing decisions. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing stages, key techniques, relevant quality standards, and actionable insights for verifying supplier quality control.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of AC power sources typically involves several main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the quality and performance of the final product.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. Material Preparation
Material preparation is the first step in the manufacturing process. This stage involves sourcing high-quality materials such as copper for windings, silicon for semiconductors, and various alloys for housing. Key techniques include:
- Material Selection: Ensuring that materials meet specific electrical and thermal conductivity requirements.
- Inspection and Testing: Conducting tests on raw materials to verify compliance with industry standards (e.g., IEC, ASTM).
2. Forming
In the forming stage, raw materials are shaped into components necessary for the AC power source. This can include:
- Winding: Copper wire is wound around a core to create inductors and transformers.
- Stamping: Metal sheets are stamped to create enclosures and internal components.
Key techniques used during forming include precision machining and automated winding machines, which enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage involves integrating all components into a complete AC power source. This includes:
- Component Integration: Assembly of transformers, rectifiers, filters, and control circuits.
- Soldering and Connection: Ensuring all electrical connections are secure through soldering and use of connectors.
Automation plays a significant role here, with robotics often used for repetitive tasks, improving consistency and speed.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the durability and aesthetic appeal of the AC power source. Key activities include:
- Coating and Painting: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and improve insulation.
- Final Assembly Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure all components function correctly and meet specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in manufacturing AC power sources to ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with international standards. The QA process typically involves several checkpoints and testing methods.
International Standards
For AC power sources, adherence to international standards is essential. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for manufacturers to ensure consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety standards, crucial for products sold in the European market.
- API Standards: Relevant for AC power sources used in oil and gas applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials before they enter the production line to ensure they meet required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring processes during manufacturing to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive tests on the finished product to ensure it meets performance standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is a critical component of quality assurance, and common methods include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying voltage, current, and frequency output to ensure compliance with specifications.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing the thermal performance under operational conditions to prevent overheating.
- Durability Testing: Subjecting the product to environmental conditions (e.g., humidity, temperature variations) to evaluate its resilience.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to ensure their suppliers adhere to quality standards. Here are actionable insights for verifying supplier QC:
1. Conduct Audits
Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. Focus on:
- Process Documentation: Ensure suppliers have documented their quality control processes.
- Facility Inspection: Visit manufacturing sites to observe practices and equipment used.
2. Request Quality Reports
Buyers should request quality assurance reports that detail:
- Testing Results: Documentation of tests conducted on raw materials and finished products.
- Compliance Certifications: Proof of compliance with relevant international standards.
3. Engage Third-Party Inspectors
Consider hiring third-party inspectors for an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control processes. They can:
- Perform Random Inspections: Conduct unannounced inspections during manufacturing.
- Provide Detailed Reports: Offer insights into areas for improvement and verify compliance with standards.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers must navigate specific challenges related to quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality perceptions may differ across regions; establish clear expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarize yourself with local regulations in the supplier’s country to ensure compliance with export standards.
- Communication Barriers: Leverage technology to maintain clear communication regarding quality expectations and standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and implementing robust quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can ensure they procure reliable and high-quality AC power sources. This diligence not only enhances operational efficiency but also builds trust and long-term relationships with suppliers.
Related Video: 18650 Cell Manufacturing Process, Automatic Production Line
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ac power source Sourcing
In the B2B landscape for AC power sources, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for effective sourcing. This analysis will focus on the various cost components involved in manufacturing AC power sources, the factors influencing pricing, and actionable tips for international buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
The total cost of sourcing AC power sources can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The primary materials include copper, aluminum, and various electronic components. Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by regional wage standards and the skill level of the workforce. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but could also affect quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for customized products. Buyers should consider how these costs are amortized over production volumes.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability is vital. Investments in QC processes can lead to higher upfront costs but lower long-term costs due to reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on the distance, mode of transport, and shipping terms. Buyers must factor in these costs to understand the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary widely based on market conditions and supplier strategies.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of AC power sources:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized solutions may incur additional costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected charges.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect costs. Buyers should be aware of the trade-offs between cost and performance.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality standards and certifications can lead to increased costs but may be necessary for regulatory compliance or specific market requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can impact pricing. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can greatly affect shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms is essential for accurately calculating total costs.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the complexities of sourcing AC power sources, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in thorough negotiations with suppliers. Understand their cost structure and be prepared to discuss pricing based on volume and specifications.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate suppliers not just on price, but also on their ability to deliver quality products consistently. A slightly higher price may result in lower total costs due to fewer defects and warranty claims.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider all costs associated with the product, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime. This holistic view can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations and market conditions. Understanding local economic factors can help in negotiating better terms.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed here are indicative and can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain the best possible pricing and terms for your AC power source needs.
Spotlight on Potential ac power source Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ac power source’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ac power source
Key Technical Properties of AC Power Sources
Understanding the essential technical specifications of AC power sources is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical properties to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
– Definition: The maximum voltage the AC power source can output, typically expressed in volts (V).
– Importance: Voltage ratings are vital for ensuring compatibility with electrical systems. Mismatched voltage can lead to equipment failure or safety hazards. -
Frequency
– Definition: The frequency at which the AC power source operates, measured in hertz (Hz).
– Importance: Different regions operate at different frequencies (e.g., 50 Hz in Europe and 60 Hz in the Americas). Understanding frequency is essential for ensuring equipment operates efficiently and effectively. -
Power Output
– Definition: The maximum power the AC power source can deliver, typically measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW).
– Importance: Buyers must assess their power requirements to avoid under-specifying or overloading the power source, which can lead to performance issues or equipment damage. -
Load Regulation
– Definition: The ability of the AC power source to maintain a stable output voltage despite variations in load conditions.
– Importance: Good load regulation ensures consistent performance and reliability, which is crucial in industrial applications where equipment sensitivity is high. -
Efficiency
– Definition: The ratio of useful power output to the total power input, often expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: High efficiency reduces energy costs and minimizes heat generation, leading to longer equipment life and reduced operational costs. -
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
– Definition: A measure of the distortion of the output waveform compared to a pure sine wave, expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: Low THD is critical for sensitive electronic equipment, as excessive distortion can lead to malfunctions or reduced performance.
Common Trade Terminology
In addition to technical specifications, familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the AC power source market. Here are several common terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify quality standards and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for smaller businesses.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs facilitate competitive bidding, helping buyers secure the best price and terms for their purchases. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) related to international shipping and freight.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities and risks in the shipping process, aiding in negotiation and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring timely availability of equipment. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Industry-specific standards that products must meet to ensure safety and performance, such as ISO or IEC standards.
– Importance: Awareness of certification requirements helps buyers ensure compliance and quality assurance for their equipment.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ac power source Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global AC power source market is poised for steady growth, projected to expand at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2030. Key drivers include the increasing demand for reliable power supply systems across various industries, such as telecommunications, aerospace, and automotive. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing significant investments in infrastructure development, leading to heightened demand for AC power sources.
International B2B buyers are increasingly focusing on digital transformation within their supply chains. Technologies such as IoT, machine learning, and advanced analytics are revolutionizing the sourcing process, enabling companies to optimize inventory management and demand forecasting. In regions like Africa and South America, where traditional power infrastructure may be lacking, innovative AC power solutions, including portable and renewable options, are gaining traction. Furthermore, European markets are emphasizing the need for high-quality, reliable power sources, prompting suppliers to enhance product specifications and customer service.
Buyers should also be aware of the geopolitical dynamics affecting sourcing strategies. Trade agreements, tariffs, and regional regulations can significantly impact supply chain operations. Engaging with suppliers who have a robust understanding of these dynamics can mitigate risks associated with sourcing AC power sources, ensuring timely delivery and compliance with local regulations.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration for businesses in the AC power source sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of emissions and waste, is under scrutiny. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon footprints and utilizing eco-friendly materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally vital; companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. This includes ensuring that materials are sourced responsibly, labor practices are fair, and environmental standards are met. Buyers should seek suppliers with recognized certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management or the Energy Star label, which indicates energy-efficient products.
Incorporating sustainable practices not only enhances a company’s reputation but can also lead to cost savings. For instance, investing in energy-efficient AC power sources can reduce operational costs over time. Furthermore, as regulatory pressures increase globally, adhering to sustainability standards can help companies avoid penalties and secure a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of AC power sources has been marked by significant technological advancements since the late 19th century. Initially dominated by conventional power generation methods, the sector has gradually integrated more sophisticated technologies, such as inverter systems and renewable energy sources.
In recent years, the shift towards digitalization and automation has transformed how AC power sources are designed and utilized. Modern systems not only provide power but also feature integrated monitoring and control systems that enhance efficiency and reliability. This evolution is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers who seek to leverage the latest technologies to improve their operations and meet growing energy demands sustainably.
Overall, understanding these dynamics equips buyers with the insights needed to make informed sourcing decisions in a competitive and rapidly changing market landscape.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ac power source
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for AC power sources?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, production capacity, and quality assurance processes. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 to ensure compliance with international standards. Check for customer reviews and ask for references from existing clients. Conduct a factory audit if possible to assess their operations and capabilities. Additionally, inquire about their experience with international shipping and customs clearance to minimize delays. -
Can I customize AC power sources to meet specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for AC power sources, including voltage, power ratings, and form factors. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance requirements. Ensure the supplier has the capability and resources for your specific needs. It’s advisable to request prototypes for testing before finalizing your order to ensure the product meets your expectations. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for AC power sources?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and depend on the complexity of the product. Generally, expect MOQs to range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard products. Lead times can also vary based on the supplier’s location and production capabilities, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. Always discuss your requirements upfront to negotiate favorable terms, especially if you need smaller quantities or shorter lead times. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted for international orders?
Payment terms can vary based on the supplier and your negotiation. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. For large orders, consider negotiating partial payments—such as a deposit upfront with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and provide recourse in case of disputes, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification for AC power sources?
Request copies of relevant quality assurance certifications, such as CE, UL, or IEC, which demonstrate compliance with international safety standards. It’s also wise to establish a quality control process, including inspections at various production stages. Consider hiring a third-party inspection service to verify product quality before shipment, especially for large orders. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of receiving defective products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing AC power sources?
Logistics planning is crucial when sourcing internationally. Understand the shipping options available, including air freight for faster delivery or sea freight for cost savings. Be aware of customs regulations in your country and the supplier’s location to avoid unexpected delays. Additionally, discuss packaging requirements with your supplier to ensure products arrive safely and undamaged. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
To effectively handle disputes, start by maintaining open communication with your supplier to resolve issues amicably. If problems arise, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, including dispute resolution procedures. Consider using mediation or arbitration to settle disputes without resorting to legal action, as these methods can save time and costs. Document all communications and agreements related to the dispute for reference. -
What are the key factors affecting the total cost of ownership (TCO) for AC power sources?
The TCO includes not just the initial purchase price but also factors like shipping, customs duties, installation, maintenance, and energy consumption. Evaluate the efficiency and longevity of the AC power sources, as these can impact operational costs over time. Request detailed quotes from suppliers that include all associated costs, and compare them to assess the true value of the investment before making a decision.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ac power source
The global AC power source market is poised for steady growth, projected to expand at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2030. This trend underscores the importance of strategic sourcing for international B2B buyers. By leveraging a well-defined sourcing strategy, companies can not only reduce costs but also enhance supply chain resilience and responsiveness to market changes.
Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the necessity of data-driven decision-making. Utilizing advanced analytics to forecast demand and optimize procurement processes can significantly enhance operational efficiency. Furthermore, segmenting supply chain strategies allows firms to tailor their approaches, aligning them with specific regional market needs, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with reliable suppliers and invest in modernizing their supply chain frameworks. This proactive approach will not only safeguard against potential disruptions but also position businesses for sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive landscape. Engage with strategic partners today to harness the full potential of AC power sources and drive your business forward in the global marketplace.