Master Sourcing Level Switches: Essential Insights for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for level switch
In today’s interconnected industrial landscape, the level switch plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient management of various liquids and solids across diverse sectors. From manufacturing and water treatment to food and beverage processing, these devices are crucial for maintaining optimal levels and preventing costly overflows or dry runs. As international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of level switches can significantly enhance your sourcing strategy and operational efficiency.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of level switches, detailing the various types—including mechanical, capacitive, and ultrasonic—as well as the materials used in their construction, such as stainless steel and plastic. We delve into the manufacturing and quality control processes that guarantee reliability and performance, ensuring that you partner with suppliers who meet stringent industry standards.
Moreover, we provide insights into potential suppliers, cost considerations, and the latest market trends. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) will clarify common doubts, enabling you to make informed decisions tailored to your specific needs.
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, particularly in regions like the UAE and France, this guide serves as an essential resource. It empowers you to navigate the global market with confidence, ensuring that you select the right level switches that align with your operational requirements and budgetary constraints. As you embark on this journey, let this guide be your trusted companion in optimizing your sourcing process.
Understanding level switch Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Float Switch | Operates using a buoyant float that rises and falls with liquid levels. | Water tanks, chemical processing | Pros: Simple design, low cost; Cons: Limited to specific applications, can be affected by turbulence. |
| Capacitive Level Switch | Senses changes in capacitance caused by the presence of a liquid. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Non-contact measurement, versatile; Cons: Sensitive to environmental changes, may require calibration. |
| Ultrasonic Level Switch | Uses ultrasonic waves to detect liquid levels without contact. | Wastewater treatment, oil & gas | Pros: Accurate over long distances, suitable for various liquids; Cons: Performance can be affected by temperature and pressure variations. |
| Pressure Level Switch | Measures the pressure exerted by a liquid to determine its level. | Tanks, boilers, refrigeration systems | Pros: Suitable for high-pressure environments, reliable; Cons: Requires maintenance, can be more expensive. |
| Optical Level Switch | Utilizes light reflection to detect the presence of a liquid. | Chemical storage, food industry | Pros: Highly accurate, effective for clear liquids; Cons: Not suitable for opaque or turbulent liquids. |
Float Switch
Float switches are among the most traditional types of level switches. They rely on a buoyant float that moves with the liquid level, activating a switch at predetermined levels. These switches are particularly suitable for applications in water tanks and chemical processing due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, buyers should consider their limitations, such as susceptibility to turbulence and the need for specific installation conditions.
Capacitive Level Switch
Capacitive level switches work by measuring changes in capacitance that occur with the presence of a liquid. This type is highly versatile and can be used across various industries, including food processing and pharmaceuticals. They are non-contact devices, which reduces wear and tear. However, potential buyers should note that capacitive switches can be sensitive to environmental conditions, necessitating careful calibration and installation.
Ultrasonic Level Switch
Ultrasonic level switches utilize sound waves to detect liquid levels without making contact. They are ideal for applications in wastewater treatment and the oil and gas industry due to their accuracy and ability to work over long distances. While they offer significant advantages, including versatility across different liquid types, buyers must be aware that their performance can be influenced by temperature and pressure variations, which may necessitate additional adjustments.
Pressure Level Switch
Pressure level switches operate by measuring the pressure exerted by a liquid, making them suitable for high-pressure environments such as tanks and refrigeration systems. They are known for their reliability and durability. However, these switches may require regular maintenance and can be more costly than other types. Buyers should weigh these factors when considering pressure level switches for their applications.
Optical Level Switch
Optical level switches detect liquid levels by utilizing light reflection. They are particularly effective for clear liquids and are commonly used in chemical storage and food industry applications. Their high accuracy is a significant advantage; however, they are not suitable for opaque or turbulent liquids. Buyers should consider their specific application needs when evaluating optical level switches, ensuring they match the operational environment and the types of liquids being monitored.
Key Industrial Applications of level switch
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of level switch | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Monitoring oil and water levels in storage tanks | Ensures safety and regulatory compliance, prevents overflows | Look for switches with high durability and resistance to harsh environments. |
| Water Treatment | Level detection in sewage treatment plants | Optimizes treatment processes and prevents equipment damage | Consider switches that offer accurate readings in varying conditions. |
| Food and Beverage | Monitoring liquid levels in processing tanks | Improves efficiency, reduces waste, and maintains product quality | Seek switches that meet hygiene standards and are easy to clean. |
| Pharmaceuticals | Ensuring proper levels in chemical storage | Maintains safety, compliance, and operational efficiency | Focus on switches with certifications for use in controlled environments. |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Level monitoring in reactors and storage units | Enhances safety, prevents spills, and optimizes production | Evaluate the compatibility of materials with various chemicals. |
In the Oil & Gas sector, level switches are crucial for monitoring oil and water levels in storage tanks. These devices help prevent overflows and ensure compliance with safety regulations. For international buyers, sourcing switches that are durable and resistant to harsh environmental conditions is essential, especially in regions with extreme temperatures or corrosive substances.
In Water Treatment, level switches are employed to detect levels in sewage treatment plants. By accurately monitoring water levels, these switches help optimize treatment processes and prevent damage to equipment caused by overflows or dry running. Buyers should focus on switches that provide precise readings even in variable conditions, as this can significantly impact operational efficiency.
The Food and Beverage industry utilizes level switches to monitor liquid levels in processing tanks. This application enhances operational efficiency by minimizing waste and ensuring consistent product quality. B2B buyers should prioritize switches that comply with hygiene standards, as cleanliness is paramount in food processing environments. Ease of maintenance is also a critical consideration.
In the Pharmaceuticals sector, level switches are vital for ensuring the proper levels of chemicals in storage. This application is crucial for maintaining safety and compliance with stringent regulations. Buyers should look for switches that have certifications for use in controlled environments, ensuring they meet industry standards and can operate under precise conditions.
Finally, in Chemical Manufacturing, level switches are used for monitoring levels in reactors and storage units. These devices enhance safety by preventing spills and optimizing production processes. Buyers in this sector need to evaluate the compatibility of level switches with various chemicals to ensure they can withstand the operational demands without compromising safety or performance.
Related Video: Float Operated Level Switch Operation | Float Level Switch Working Principle | Level Switch.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for level switch
When selecting materials for level switches, international B2B buyers must consider a range of factors, including the specific application, environmental conditions, and regulatory compliance. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in level switches, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures. Common grades like 304 and 316 are often used, with 316 offering better resistance to chlorides and other corrosive substances.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for harsh environments, ensuring a long lifespan. However, it can be more expensive than other materials, and its manufacturing process can be complex, potentially increasing lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and chemicals, making it versatile for various industries.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like the UAE and France, certifications may be required for specific applications, particularly in food and pharmaceutical industries.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is lightweight, resistant to many chemicals, and has a lower temperature rating compared to metals. It is typically rated for use in environments up to 60°C (140°F).
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of PVC makes it a popular choice for applications where budget constraints are significant. However, its lower temperature and pressure ratings limit its use in high-demand environments.
Impact on Application: PVC is ideal for applications involving water and some chemicals, but it may not be suitable for high-temperature or high-pressure scenarios.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with local regulations regarding chemical handling and environmental impact, especially in regions with strict environmental laws.
Teflon (PTFE)
Key Properties: Teflon is renowned for its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction properties. It can operate effectively in a wide temperature range, from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of Teflon is its ability to handle aggressive chemicals without degrading. However, it is relatively expensive and can be more challenging to manufacture due to its unique properties.
Impact on Application: Teflon is particularly suited for applications involving corrosive chemicals, making it a preferred choice in the chemical processing industry.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers must consider the availability of Teflon components in their region and any specific certifications required for chemical applications, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, especially when anodized. It typically has a moderate temperature rating, suitable for many industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: The lightweight nature of aluminum makes it easy to handle and install. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well in highly corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications involving water and some mild chemicals but may not be ideal for aggressive substances.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet relevant standards, such as JIS in Japan or ASTM in the United States, to ensure quality and compliance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for level switch | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Harsh environments, chemical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| PVC | Water and mild chemical applications | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited temperature and pressure ratings | Low |
| Teflon (PTFE) | Chemical processing, aggressive media | Exceptional chemical resistance | Expensive and challenging to manufacture | High |
| Aluminum | Mild chemical applications | Lightweight and easy to handle | Less durable in corrosive environments | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for level switches, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights needed to make informed decisions based on their specific applications and market conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for level switch
Manufacturing Processes for Level Switches
The manufacturing of level switches involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing level switches.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– The first step involves selecting appropriate materials, which may include metals, plastics, and ceramics, depending on the application.
– Materials must be assessed for their chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical properties.
– Suppliers often conduct tests to ensure the quality of raw materials, which can include spectroscopic analysis and tensile testing. -
Forming
– This stage includes processes such as machining, molding, and die casting.
– Precision machining techniques like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) are commonly employed to create intricate components with tight tolerances.
– Molding techniques, especially for plastic components, might involve injection molding, where molten plastic is injected into a mold to form the desired shape. -
Assembly
– After forming, components are assembled, which may include the integration of electronic sensors, mechanical parts, and housing.
– Automated assembly lines are often used to enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
– Each assembly process should be documented, ensuring traceability of components. -
Finishing
– The final stage involves surface treatments such as coating, polishing, or anodizing to enhance durability and appearance.
– This stage may also include the application of protective coatings to improve resistance to corrosion and wear.
– Final inspections are critical to ensure that the finishing meets the required aesthetic and functional standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing process of level switches, ensuring that products meet international and industry-specific standards. Here are some key aspects of QA that B2B buyers should consider:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS) and is applicable to any organization. It emphasizes customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For level switches used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical.
QC Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint occurs at the receipt of materials, ensuring that they meet the specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early. Techniques may include visual inspections and measurements.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducted after assembly and before shipping, this involves rigorous testing to ensure that the product operates correctly and meets all standards.
Common Testing Methods
- Functional Testing: Verifies that the level switch operates as intended under specified conditions.
- Electrical Testing: Ensures that electronic components function correctly, checking for issues such as short circuits or incorrect voltage levels.
- Environmental Testing: Simulates conditions like temperature extremes and humidity to ensure reliability in various environments.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable steps to consider:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control systems. This can include on-site visits and reviews of their QMS documentation. -
Request Quality Reports
– Ask suppliers for quality reports that demonstrate compliance with international standards and internal quality metrics. These reports should include results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent assessments of suppliers’ facilities and processes. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding product quality. -
Certifications Verification
– Ensure that suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) and verify their authenticity through the issuing bodies. This can provide confidence in the supplier’s commitment to quality.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
International buyers must be aware of certain nuances regarding quality control and certification when dealing with suppliers from different regions:
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality perceptions may vary across cultures. Buyers should communicate their quality expectations clearly and ensure they are understood.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have distinct regulatory requirements. For instance, CE marking is mandatory for products in Europe, while different standards may apply in Africa or South America.
- Adaptability: Suppliers should demonstrate adaptability in their quality control processes, allowing for modifications based on specific buyer requirements or industry standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the production of level switches, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies, ensuring that they procure reliable and high-quality products tailored to their operational needs.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for level switch Sourcing
When sourcing level switches, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for effective negotiation and cost management.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver for level switches is the materials used in their construction. Common materials include plastics, metals, and electronic components, each with fluctuating market prices influenced by global supply and demand.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly based on geographical location. For instance, manufacturing in regions with lower labor costs (e.g., parts of South America and Africa) can reduce overall expenses, but may also impact quality and lead times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, equipment maintenance, and utilities. Efficient production processes can minimize overhead, but buyers should be aware that these costs are often embedded in the pricing of the finished product.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is required for specific designs, which can lead to higher upfront costs. Buyers should assess whether the investment in tooling is justified by the expected volume and customization.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product reliability involves QC processes that contribute to costs. Certifications such as ISO or industry-specific standards can also add to expenses, reflecting the commitment to quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping, handling, and storage costs are critical, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and tariffs can significantly impact the final cost.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely based on competition, brand reputation, and perceived value. Understanding these margins can aid in negotiating better prices.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders typically reduce the unit price. Buyers should evaluate their demand forecasts to leverage this effectively.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized products may incur additional costs. Clear communication of specifications can help avoid unexpected price hikes.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications often lead to increased costs. Buyers must balance quality needs with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Establishing a strong relationship with reliable suppliers can lead to better terms.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing logistics costs. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) affect who bears shipping costs and risks, impacting overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your cost structure. Leverage volume commitments and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A cheaper product may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, be aware of regional pricing differences. Currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions can affect costs.
-
Due Diligence: Conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, including their financial health and production capabilities. This can prevent costly disruptions and ensure quality.
Conclusion
While indicative pricing for level switches can vary, understanding the underlying cost components and price influencers equips buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. By employing strategic negotiation techniques and considering the TCO, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing effectiveness and ultimately drive better business outcomes.
Spotlight on Potential level switch Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘level switch’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for level switch
Key Technical Properties of Level Switches
When evaluating level switches for industrial applications, it’s crucial to understand specific technical properties that can significantly impact performance and compatibility with your systems. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The grade of material used in the construction of the level switch, often specified in terms of corrosion resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate material is vital for applications involving aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures. For instance, stainless steel is commonly used for its resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for chemical processing industries. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: The range of temperatures within which the level switch can function effectively, typically expressed in degrees Celsius.
– Importance: Ensuring that the level switch can operate in the specific temperature conditions of your application is critical to prevent failure. A switch that cannot withstand high temperatures could lead to inaccurate readings or equipment damage. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: The maximum pressure that the level switch can handle, often measured in psi (pounds per square inch) or bar.
– Importance: This is particularly important in industries such as oil and gas, where equipment may be subjected to high pressures. Choosing a level switch with an appropriate pressure rating ensures safety and reliability. -
Electrical Rating
– Definition: The specifications for voltage and current that the level switch can handle, often expressed in volts (V) and amperes (A).
– Importance: Understanding the electrical rating is essential for compatibility with existing control systems. A mismatch can lead to operational failures or safety hazards. -
Switching Mechanism
– Definition: The method by which the level switch detects and responds to changes in liquid levels, such as float, capacitive, or ultrasonic.
– Importance: The choice of switching mechanism affects sensitivity, accuracy, and the suitability of the switch for various types of liquids, whether conductive or non-conductive.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the procurement process. Here are some key terms relevant to level switches:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces components that are used in another company’s end products.
– Relevance: Understanding whether a level switch is sourced from an OEM can impact quality assurance and the reliability of components in your systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ can help in budgeting and inventory management. It can also influence the decision to source from multiple suppliers to meet demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other details for a specific quantity of products.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ is a standard practice in B2B procurement that allows buyers to compare options and negotiate better terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), used in international trade.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for determining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, risk, and costs, which can significantly affect overall project budgets. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Relevance: Knowing the lead time helps in planning and scheduling operations, ensuring that production timelines are met without delays.
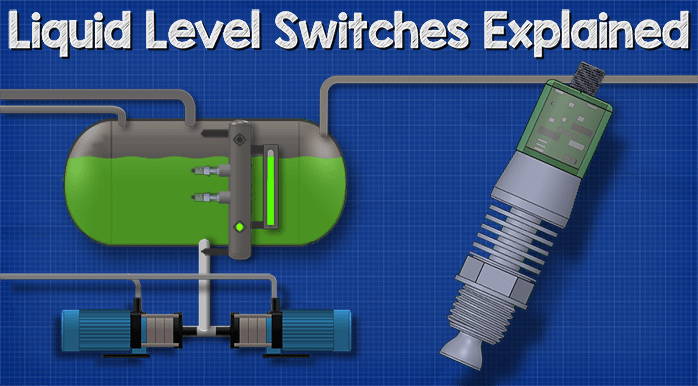
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing level switches, ultimately enhancing their procurement strategies and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the level switch Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The level switch sector is experiencing significant evolution driven by technological advancements and changing market dynamics. Key global drivers include the increasing demand for automation in industrial processes, the growth of smart manufacturing, and the need for improved accuracy in liquid level measurement. As industries in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for operational efficiency, the adoption of advanced level switch technologies is becoming imperative.
Emerging B2B tech trends in this sector include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities, enabling real-time monitoring and data analytics for predictive maintenance. This shift is being supported by a growing emphasis on digital transformation initiatives across various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing. International buyers should also note the trend towards dual sourcing strategies, which allow companies to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions by diversifying their supplier base.
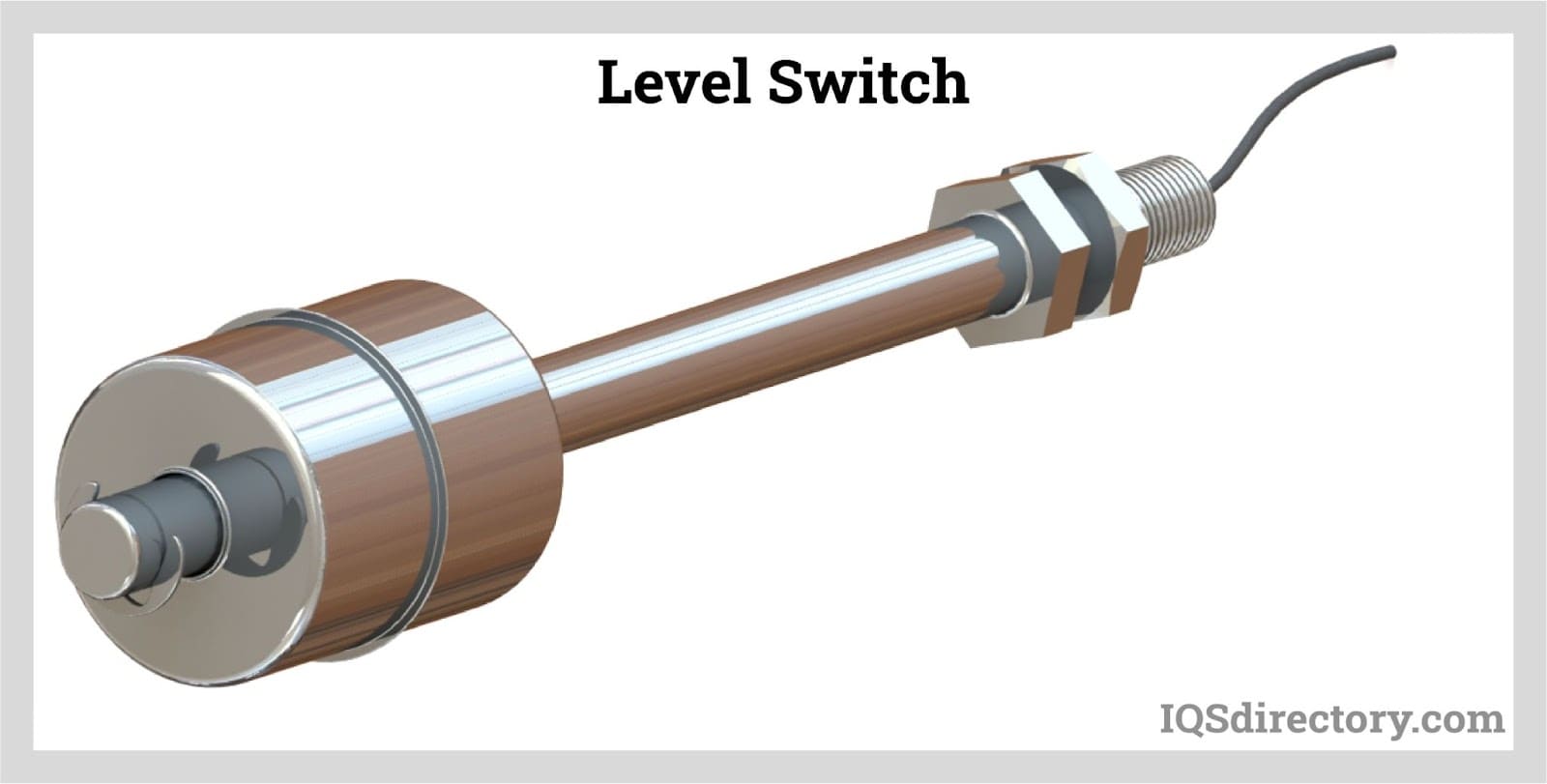
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In addition, buyers from Africa and South America may find opportunities in local manufacturing partnerships, which can reduce lead times and costs while supporting regional economies. The market dynamics are further influenced by regulatory standards that prioritize safety and efficiency, compelling manufacturers to innovate continually. As a result, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the level switch sector, particularly as industries face increasing pressure from consumers and regulatory bodies to adopt environmentally friendly practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable sourcing practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and utilizing renewable resources.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. International B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices, promoting fair working conditions and compliance with international labor standards. This commitment not only enhances brand reputation but also fosters long-term partnerships based on trust and accountability.
Buyers should look for ‘green’ certifications and materials in their sourcing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and products made from recycled or sustainably sourced materials can significantly enhance a company’s sustainability profile. By integrating these practices into their procurement strategies, buyers can contribute to a circular economy while meeting the growing demand for sustainable solutions in the marketplace.
Brief Evolution/History
The level switch technology has evolved significantly since its inception, driven by the need for precise liquid level measurement in various industries. Initially, mechanical devices such as floats were commonly used. However, advancements in electronics and materials science have led to the development of more sophisticated electronic and ultrasonic level switches. These modern solutions offer enhanced accuracy, reliability, and the ability to operate in challenging environments, making them essential in sectors like petrochemicals, water treatment, and food processing.
As industries continue to embrace automation and digitalization, the level switch sector is poised for further innovation, enabling businesses to optimize processes and enhance operational efficiency. Understanding this evolution helps international buyers appreciate the technological advancements that can influence their sourcing decisions today.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of level switch
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers for level switches?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in manufacturing level switches and their reputation in the industry. Request references from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to gauge reliability. Additionally, check certifications relevant to your industry standards, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Conduct on-site visits if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes. -
Can I customize level switches to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for level switches, including size, material, and operational specifications. Discuss your exact needs with potential suppliers, such as the type of media being measured (liquid, solid, etc.) and the required sensitivity. Be prepared to provide technical specifications and any regulatory standards your product must meet. Ensure that the supplier has the capacity to handle custom orders and ask for prototypes or samples before finalizing your order. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for level switches?
MOQs for level switches can vary widely depending on the manufacturer and the complexity of the switch. Generally, MOQs can range from 50 to several hundred units. Lead times also differ, often ranging from 4 to 12 weeks based on the supplier’s workload and customization needs. It’s crucial to discuss these details upfront to align your project timelines and avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing level switches internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region. Common methods include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Negotiate terms that provide you with security, such as a partial upfront payment followed by the balance after inspection. Be aware of currency exchange rates and international transaction fees. Consider using escrow services for larger orders to mitigate risk. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes from your suppliers, including testing procedures and certification compliance. Ensure that the level switches meet international standards relevant to your industry, such as CE marking in Europe or UL certification in the United States. Regular audits and inspections can help maintain quality. Consider third-party quality control services to verify compliance before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing level switches?
Logistics play a critical role in the timely delivery of level switches. Assess the supplier’s shipping methods, including options for air or sea freight, and their ability to handle customs clearance. Discuss delivery timelines and potential delays, particularly in regions with stringent import regulations. Additionally, factor in local logistics providers in your area who can facilitate last-mile delivery to ensure a smooth process. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements, including specifications, timelines, and payment terms. In the event of a disagreement, attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication. If necessary, refer to your contract and consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to legal action. Having a clear dispute resolution process outlined in your contract can help prevent escalation. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing level switches internationally?
Common challenges include language barriers, cultural differences, and varying regulatory standards. To overcome these issues, engage with suppliers who have experience working with international clients. Building strong relationships and clear communication can help navigate these challenges. Additionally, stay informed about the political and economic climate in the supplier’s country, as this can impact production and shipping timelines.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for level switch
In today’s competitive landscape, effective strategic sourcing for level switches is critical for businesses aiming to optimize operations and drive profitability. Key takeaways highlight the importance of understanding various sourcing strategies—whether single, dual, or multi-sourcing—to mitigate risks and enhance supply chain resilience. B2B buyers must prioritize thorough supplier evaluations, focusing on quality, compliance, and technological capabilities to ensure reliable performance and service continuity.
As industries continue to evolve, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for innovative and adaptable level switch solutions will only grow. Embracing a strategic sourcing approach allows businesses to not only secure the best products but also build strong partnerships that can withstand market fluctuations.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should actively explore opportunities for collaboration and diversification in their sourcing strategies. By leveraging global networks and staying informed about technological advancements, companies can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected market. Engage with suppliers who align with your strategic goals, and take proactive steps to future-proof your operations.