Master the Art of Sourcing Transformer Parts for Optimal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for transformer parts
In the dynamic landscape of global energy infrastructure, transformer parts play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliable transmission and distribution of electrical power. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate the complexities of procurement, understanding the nuances of transformer parts becomes essential. These components not only influence the efficiency and longevity of transformer systems but also impact overall operational resilience and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide is designed to empower buyers with actionable insights into the multifaceted world of transformer parts. It covers critical topics such as various transformer types, material selection, and manufacturing quality control practices, ensuring that you are well-equipped to make informed sourcing decisions. Additionally, it delves into supplier assessment strategies, providing a framework for identifying trustworthy partners amidst diverse logistical challenges.
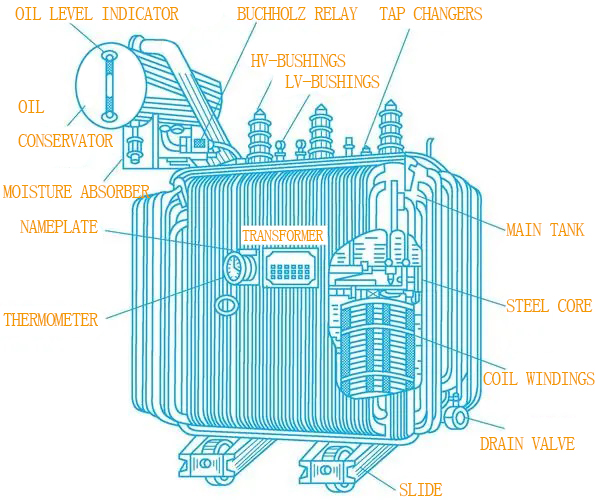
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Moreover, the guide explores pricing structures and market trends, enhancing your negotiation capabilities to secure favorable terms. It addresses common frequently asked questions, clarifying essential aspects such as lead times, warranties, and compliance with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards.
By synthesizing global best practices with regional insights, this guide serves as a vital resource for B2B buyers seeking to optimize their sourcing strategies and achieve sustainable growth in their respective markets.
Understanding transformer parts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Transformer | High voltage, large capacity, typically oil-filled | Transmission grids, substations | High efficiency but costly; requires skilled maintenance |
| Distribution Transformer | Lower capacity, step-down voltages, easy installation | Utility distribution networks, commercial facilities | Widely available and easy to deploy; may incur losses at low load |
| Dry-Type Transformer | Air-cooled, no oil, uses resin insulation | Indoor applications, renewable energy installations | Safer and low maintenance; limited capacity and higher cost |
| Instrument Transformer | Precision scaling (CTs and VTs), small/medium size | Metering, protection, and control systems | Highly accurate; limited to measurement, not power conversion |
| Autotransformer | Single winding with tap, compact design | Voltage regulation, industrial drives | Economical and smaller footprint; lacks electrical isolation |
Power Transformer
Power transformers are designed for high-voltage applications, playing a crucial role in bulk power transmission. Their oil-filled construction enhances cooling and operational efficiency, making them suitable for large-scale energy infrastructure, particularly in Africa and the Middle East where grid reliability is paramount. B2B buyers must prioritize supplier reliability, factory certifications, and after-sales support, given the substantial upfront investment and the need for skilled maintenance. Long lead times are common, so early engagement with suppliers is advisable to mitigate project delays.
Distribution Transformer
Distribution transformers are essential for stepping down voltage for local energy delivery, making them indispensable in urban and rural electrification projects. Their simpler installation and scalability make them ideal for rapidly growing markets in South America and Africa. Buyers should assess efficiency ratings and local regulatory compliance while considering the balance between initial costs and potential operational losses. They are typically more accessible and easier to maintain than power transformers, providing a reliable solution for utility networks and commercial facilities.
Dry-Type Transformer
Dry-type transformers are characterized by their air-cooled design and resin insulation, making them a safer option for indoor installations, such as data centers and hospitals. They eliminate the risk of oil leaks, which is crucial in urban environments with stringent safety regulations, especially in Europe and the Middle East. While they offer low maintenance and environmental benefits, they come with higher initial costs and limited power capacity. B2B buyers should consider the specific application requirements and seek suppliers with expertise in dry-type solutions.
Instrument Transformer
Instrument transformers, including current transformers (CTs) and voltage transformers (VTs), are vital for metering and protection in electrical systems. Their small to medium size and high accuracy make them suitable for control systems across various industries, including manufacturing and energy. While they do not convert power, their reliability in measurement and protection is critical for system integrity. Buyers should focus on manufacturers that offer proven accuracy and compliance with industry standards, ensuring that the transformers meet specific operational requirements.
Autotransformer
Autotransformers feature a single winding with taps, allowing for voltage regulation in a compact design. They are cost-effective and occupy less space, making them suitable for industrial drives and certain voltage applications. However, the lack of electrical isolation can pose risks, particularly in safety-critical environments. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific application needs and potential safety implications when considering autotransformers, ensuring that they align with operational requirements and regulatory standards.
Related Video: Attention is all you need (Transformer) – Model explanation (including math), Inference and Training
Key Industrial Applications of transformer parts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Transformer Parts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Step-down transformers for drilling operations | Ensures reliable power supply for remote operations | Need for rugged, high-efficiency designs with local support |
| Renewable Energy | Transformers for wind and solar farms | Optimizes energy conversion and grid integration | Compliance with environmental standards and scalability |
| Manufacturing | Custom transformers for machinery control | Enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime | Importance of precision engineering and long-term reliability |
| Mining | Heavy-duty transformers for mineral processing | Supports continuous operation in harsh environments | Supplier reputation in providing durable solutions for extreme conditions |
| Data Centers | Dry-type transformers for power distribution | Increases safety and reliability in critical facilities | Focus on energy efficiency, low maintenance, and compliance with safety standards |
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas sector, transformer parts are crucial for powering drilling rigs and associated equipment in remote locations. Step-down transformers are commonly used to reduce high transmission voltages to usable levels, ensuring a steady and reliable power supply. B2B buyers in this industry must focus on sourcing rugged designs that can withstand harsh environmental conditions and provide high efficiency. Local support and service capabilities are also critical, as rapid maintenance can minimize costly downtimes.
Renewable Energy
Transformers play a vital role in renewable energy applications, particularly in wind and solar farms. They facilitate the conversion of generated electricity to appropriate voltage levels for grid integration, which is essential for maximizing energy efficiency. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that comply with environmental standards and can offer scalable solutions, as the demand for renewable energy sources continues to grow. Understanding the specific grid requirements and operational conditions is also essential for effective sourcing.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, custom transformers are often employed to control machinery and provide the necessary power for various processes. These transformers enhance operational efficiency by ensuring that machinery operates at optimal voltage levels, reducing energy waste and downtime. B2B buyers should seek suppliers with expertise in precision engineering to guarantee that the transformers meet specific operational needs. Long-term reliability is critical, as any failure could lead to significant production losses.
Mining
The mining industry relies heavily on heavy-duty transformers to support mineral processing operations. These transformers are designed to operate continuously in harsh environments, providing the necessary power for extraction and processing equipment. When sourcing transformer parts, buyers must assess the supplier’s reputation for durability and reliability in extreme conditions. Ensuring that the transformers can handle high loads without failure is a key consideration for maintaining operational continuity.
Data Centers
In data centers, dry-type transformers are preferred for power distribution due to their safety and reliability. These transformers eliminate fire risks associated with oil-filled units, making them ideal for critical infrastructure where uptime is paramount. B2B buyers should focus on energy-efficient designs that require minimal maintenance, as well as compliance with stringent safety standards. The ability to integrate seamlessly with existing power systems while providing redundancy is crucial for ensuring uninterrupted service.
Related Video: Transformer Parts and Functions
Strategic Material Selection Guide for transformer parts
When selecting materials for transformer parts, B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, cost, and compliance. Here’s an analysis of four common materials used in transformer manufacturing, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international buyers.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has a low thermal expansion coefficient, making it stable under varying conditions.
Pros & Cons:
Copper is highly durable and offers superior performance in terms of efficiency and energy loss reduction. However, it is relatively expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum, and its high cost can impact the overall budget for large-scale projects. Additionally, the manufacturing process can be complex, requiring skilled labor and advanced technology.
Impact on Application:
Copper is ideal for high-power applications where efficiency is critical, such as in power transformers and high-voltage transmission. Its compatibility with various insulating materials enhances its performance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as IEC and ASTM, as well as consider the availability of copper in local markets, which may be subject to price volatility.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, has good electrical conductivity (about 60% that of copper), and is resistant to corrosion. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 150°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and lower weight, making it easier to handle and install. However, it has higher resistive losses than copper, which can affect efficiency in high-load applications. The manufacturing process for aluminum can also be less complex, resulting in shorter lead times.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is commonly used in distribution transformers and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as portable or mobile transformers.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Africa and South America should be aware of local standards and regulations that may affect aluminum use. Compliance with standards like JIS in Japan or DIN in Germany is crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety.
Silicon Steel
Key Properties:
Silicon steel, particularly grain-oriented silicon steel, is used for transformer cores due to its magnetic properties. It has low hysteresis losses and can operate efficiently at high flux densities.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of silicon steel is its ability to minimize energy losses, which enhances the overall efficiency of transformers. However, it can be more brittle than other materials, requiring careful handling during manufacturing and installation. The cost of high-grade silicon steel can also be significant.
Impact on Application:
Silicon steel is essential for power transformers, where efficiency is paramount. Its properties make it suitable for applications with high magnetic flux, such as in large-scale energy distribution.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that silicon steel meets international quality standards (like ASTM A677) and consider sourcing from suppliers with a reputation for quality to ensure long-term performance.
Insulation Materials (e.g., Resin)
Key Properties:
Insulation materials, such as resin or oil, provide electrical insulation and thermal management. They can withstand high temperatures and have excellent dielectric properties.
Pros & Cons:
Resin insulation is non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and provides good thermal stability. However, it can be more expensive than traditional oil insulation and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
Insulation materials are critical in ensuring the safety and efficiency of transformers, especially in applications exposed to harsh environmental conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers should ensure that insulation materials comply with relevant safety and environmental standards, such as RoHS in Europe, to avoid regulatory issues.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for transformer parts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings in power transformers | Excellent conductivity and durability | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Aluminum | Windings in distribution transformers | Cost-effective and lightweight | Higher resistive losses | Medium |
| Silicon Steel | Transformer cores | Minimizes energy losses | Brittle and can be expensive | High |
| Insulation (Resin) | Electrical insulation in transformers | Environmentally friendly and stable | Higher cost and specialized handling | Medium |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the materials used in transformer parts, aiding in making informed procurement decisions that align with their specific operational needs and compliance requirements.
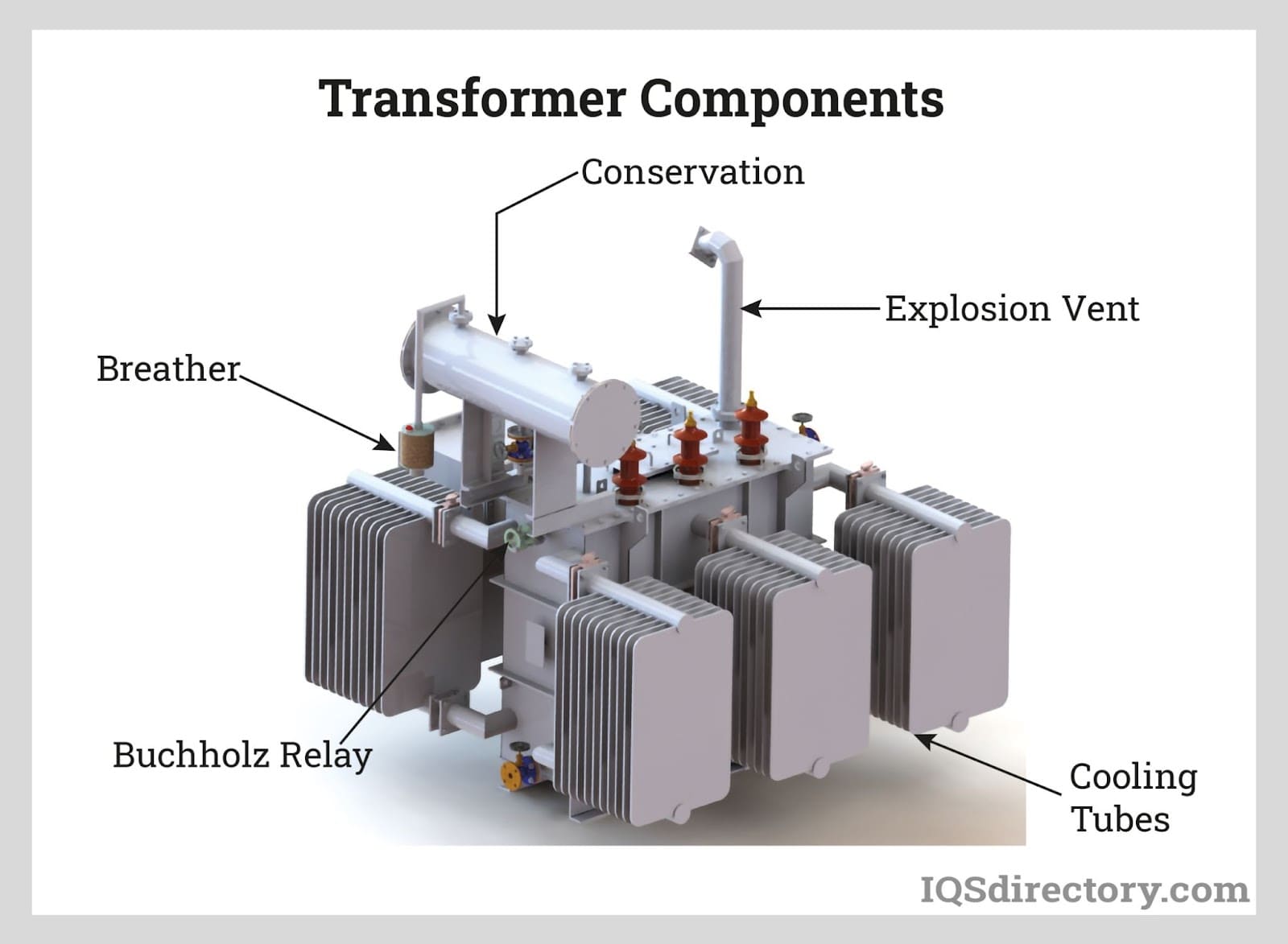
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for transformer parts
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for transformer parts are critical for ensuring reliability, efficiency, and safety in their operation. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can significantly impact sourcing decisions and long-term partnerships. Below is a detailed exploration of the typical manufacturing stages, quality control (QC) measures, and actionable insights for verifying supplier quality.
Manufacturing Processes for Transformer Parts
The manufacturing of transformer parts involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets the necessary specifications and performance standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing transformer parts is selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials include:
- Copper and Aluminum: Used for windings due to their excellent conductivity.
- Silicon Steel: Used for cores, chosen for its magnetic properties to minimize losses.
- Insulation Materials: Such as resin or paper, essential for safety and efficiency.
During material preparation, suppliers must ensure that all materials meet specified industry standards. This may involve testing for conductivity, tensile strength, and thermal resistance.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the prepared materials into the necessary components:
- Winding Process: Copper or aluminum wire is wound around a core to create the primary and secondary coils. The winding technique can significantly affect the transformer’s efficiency.
- Core Assembly: The core is constructed by stacking sheets of silicon steel to minimize energy losses. Precision in this stage is essential to ensure optimal magnetic performance.
Manufacturers may employ automated winding machines and core stacking equipment to enhance consistency and reduce human error during this stage.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This includes:
- Coil Installation: The wound coils are positioned on the core.
- Insulation Application: Insulation materials are applied between the windings and the core to prevent electrical shorts and enhance safety.
- Enclosure Fabrication: The transformer is housed in a protective casing, which may be made from steel or other durable materials, ensuring robustness against environmental factors.
During assembly, manufacturers must adhere to strict guidelines to ensure that all components fit correctly and are securely fastened.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves applying finishing touches to the transformer parts:
- Surface Treatment: Coatings may be applied to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.
- Testing Setup: Preliminary testing setups are installed to prepare for quality assurance checks.
Finishing processes are critical for extending the lifespan of transformer components and ensuring they can operate under various environmental conditions.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance in transformer manufacturing is vital for maintaining high standards and ensuring compliance with international regulations. B2B buyers must be familiar with the following key aspects of quality control:
International Standards
Several internationally recognized standards govern the quality and safety of transformer parts, including:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for transformers used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring they meet industry-specific requirements.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process at various stages to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting comprehensive testing on the finished product to ensure it meets performance and safety standards.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure the quality of transformer parts, manufacturers employ various testing methods, including:
- Electrical Testing: Verifying insulation resistance, power factor, and load testing to ensure electrical integrity.
- Thermal Testing: Assessing the heat dissipation capabilities of transformers under load conditions.
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating the strength and durability of materials used in the transformers.
Verifying Supplier Quality
B2B buyers must implement strategies to verify the quality assurance processes of potential suppliers:
Conducting Audits
Regular audits of manufacturing facilities can provide insights into the supplier’s quality management practices. Buyers should focus on:
- Process Documentation: Ensuring that the supplier maintains detailed records of manufacturing processes and quality checks.
- Compliance Certifications: Verifying that the supplier holds relevant certifications that align with international standards.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request quality reports, including:
- Test Results: Documentation of testing outcomes for key parameters.
- Non-Conformance Reports: Records of any deviations from quality standards and corrective actions taken.
Engaging Third-Party Inspectors
Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control processes. This can include:
- Factory Inspections: On-site evaluations of manufacturing practices and compliance with safety standards.
- Random Sampling: Testing samples from production runs to ensure they meet specified criteria.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers face unique challenges regarding quality assurance:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding regional practices and expectations in manufacturing can help buyers navigate supplier relationships effectively.
- Logistical Challenges: Buyers must consider the complexities of international shipping and customs, which can impact delivery timelines and product condition.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying standards, and buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet local regulatory requirements.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for transformer parts, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their sourcing strategies. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also contributes to the successful implementation of transformer solutions tailored to specific operational needs.
Related Video: Extreme Power Transformer Manufacturing Process – How It’s Made
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for transformer parts Sourcing
In the intricate landscape of sourcing transformer parts, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis focuses on the primary cost components and influencers that affect pricing, as well as actionable tips for effective procurement.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost of transformer parts. Key materials include copper or aluminum for windings, silicon steel for cores, and various insulation materials. The fluctuating prices of these raw materials can lead to variations in the final cost, making it essential for buyers to stay informed about market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs are influenced by the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs may provide competitive pricing, but this must be balanced against potential quality concerns. Skilled labor is necessary for the precision assembly of transformer components, which can lead to higher costs in regions with stringent labor regulations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to the operation of manufacturing facilities, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes and advanced manufacturing technologies can help mitigate these costs, allowing suppliers to offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, especially for custom or specialized transformer parts. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling already in place, as this can affect lead times and upfront costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with international standards (such as ISO, CE, or UL) requires investment in quality control processes. Suppliers that prioritize QC may charge higher prices, but this investment is crucial for ensuring reliability and performance.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary significantly based on the geographical distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms used. Buyers should consider the total logistics expenses when evaluating supplier quotes, as these can impact the overall cost structure.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and the complexity of the transformer parts. Understanding typical margin percentages in the industry can help buyers assess whether pricing is fair.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order volumes often lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their project needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom transformers or specialized parts typically incur higher costs due to the additional design and manufacturing efforts required. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the associated costs.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: High-quality materials and certifications can drive up costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these factors based on their specific application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Engaging with well-established suppliers may come at a premium but often ensures better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can significantly affect the pricing structure, as they determine the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping, insurance, and logistics. Understanding these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing flexibility. Leveraging volume commitments or long-term contracts can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors such as reliability, maintenance costs, and energy efficiency when assessing overall value.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international buyers may face additional costs related to tariffs, customs duties, and currency fluctuations. Incorporating these factors into the budgeting process is essential for accurate financial planning.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Regularly analyze market pricing trends and benchmark against similar products. This practice can provide insights into fair pricing and help negotiate better deals.
-
Supplier Diversity: Consider sourcing from multiple suppliers to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and pricing volatility.
Disclaimer
Prices are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential transformer parts Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘transformer parts’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for transformer parts
Key Technical Properties of Transformer Parts
Understanding the essential technical properties of transformer parts is vital for B2B buyers aiming to make informed procurement decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: The choice of material impacts the transformer’s efficiency and durability. Common materials include copper and aluminum for windings, and grain-oriented electrical steel for cores. Higher-grade materials generally offer better conductivity and lower losses, which are crucial for reducing operational costs over the transformer’s lifespan.
-
Tolerance Levels: Tolerance refers to the permissible variation in the dimensions of transformer components. Strict tolerance specifications ensure that parts fit correctly, which is essential for optimal performance and reliability. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can meet tight tolerances, as this minimizes the risk of failures and enhances overall system efficiency.
-
Power Rating (kVA/MVA): This indicates the maximum load a transformer can handle. It’s essential for buyers to select a transformer with an appropriate power rating to match their operational requirements. Underestimating power needs can lead to overheating and operational failures, while overestimating can result in unnecessary costs.
-
Insulation Class: Insulation class defines the maximum temperature a transformer can operate without degrading its components. Higher insulation classes (e.g., Class H) offer better thermal performance, which is crucial in high-load environments. Understanding insulation ratings can help buyers anticipate maintenance needs and lifespan.
-
Cooling Method: Transformers can be air-cooled or oil-cooled, with each method having implications for efficiency and installation requirements. Buyers should evaluate their operational environment and determine the most suitable cooling method to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
-
Efficiency Ratings: Efficiency ratings indicate how well a transformer converts input power to output power, with higher percentages reflecting lower energy losses. For B2B buyers, selecting high-efficiency transformers can lead to significant cost savings in energy consumption over time, making this a critical factor in procurement decisions.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are several commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the OEM landscape helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensures compatibility with existing systems.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, particularly for buyers in regions with fluctuating demand.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from potential suppliers. It is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate terms effectively.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, which is crucial for international sourcing.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is important for project planning and ensuring that transformers are available when needed.
-
Warranty: A warranty is a promise made by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the transformer and the terms under which repairs or replacements will be made. Buyers should carefully review warranty terms to ensure adequate protection against defects and failures.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring they procure the right transformer parts that meet their operational and financial objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the transformer parts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The transformer parts sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by global energy demands, technological advancements, and regulatory frameworks aimed at enhancing efficiency. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are facing a dynamic market characterized by several key trends.
One major driver is the increasing focus on renewable energy integration. As countries strive to meet sustainability targets, there is a growing demand for transformers that can efficiently manage variable power sources like wind and solar. This shift is prompting manufacturers to innovate transformer designs and components that enhance performance and adaptability.
Furthermore, the digitalization of the energy sector is reshaping sourcing strategies. Advanced technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are being utilized to monitor transformer health, optimize maintenance schedules, and improve supply chain visibility. B2B buyers must adapt to these technological shifts by partnering with suppliers who offer smart components and data-driven solutions.
Supply chain resilience is another critical factor. The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting buyers to seek local suppliers or diversify their sourcing strategies to mitigate risks. This trend is especially relevant for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where logistics and infrastructure can pose significant challenges.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of fluctuating raw material costs, particularly copper and aluminum, which directly impact transformer parts pricing. Understanding these market dynamics will empower B2B buyers to negotiate better terms and secure reliable supply sources.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the transformer parts sector. The environmental impact of transformer manufacturing and operation necessitates a shift towards ethical sourcing practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to minimizing their carbon footprint and adhering to environmental regulations.
The use of sustainable materials, such as recycled metals and eco-friendly insulation, is gaining traction. Buyers should seek out suppliers who can provide certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) to ensure that their sourcing aligns with global sustainability standards.
Moreover, ethical supply chains are critical for fostering transparency and accountability. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence on suppliers to verify their sourcing practices and labor conditions. This not only mitigates reputational risks but also supports the growth of responsible businesses in developing regions.
Adopting ‘green’ certifications and materials can also enhance a company’s brand value and market positioning. As consumers and stakeholders increasingly demand sustainability, B2B buyers who prioritize ethical sourcing can differentiate themselves and foster long-term relationships with eco-conscious partners.
Brief Evolution/History
The transformer parts sector has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from basic, manually assembled components to highly engineered, precision-manufactured systems. Early transformers primarily utilized copper windings and iron cores, focusing on functionality and reliability.
With the advent of electricity and the expansion of power grids in the early 20th century, the demand for more efficient and durable transformers surged. Innovations such as oil-immersed transformers and advanced insulation materials emerged, enabling higher voltage capacities and improved thermal management.
Today, the sector is characterized by a strong emphasis on technology and sustainability. The integration of smart technologies and materials science into transformer design is reshaping the industry, making it imperative for B2B buyers to remain informed about these advancements to stay competitive in the global market.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of transformer parts
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for transformer parts?
Vetting suppliers requires a multi-faceted approach. Begin by researching potential suppliers’ backgrounds, including their manufacturing capabilities, financial stability, and industry reputation. Request references from previous clients and check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates adherence to quality management standards. Additionally, consider conducting site visits to assess facilities and quality control processes. Engaging in thorough due diligence helps mitigate risks associated with poor-quality components or unreliable delivery schedules. -
What customization options should I consider when sourcing transformer parts?
Customization options can significantly enhance the performance and compatibility of transformer parts with your specific applications. Identify key specifications, such as voltage ratings, insulation materials, and cooling methods. Collaborate with suppliers early in the design phase to ensure that your requirements are met without compromising on efficiency or safety. Be aware that custom solutions may lead to longer lead times and higher costs, so weigh the benefits against these factors before proceeding. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for transformer parts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary widely depending on the supplier and the specific transformer parts being sourced. Standard parts may have lower MOQs, while custom components often require larger orders to justify production costs. Lead times typically range from a few weeks to several months based on complexity, customization, and supplier capacity. When negotiating, ensure you clarify these aspects to align your project timelines with supplier capabilities, especially in markets with fluctuating demand. -
How important are quality assurance certifications when sourcing transformer parts?
Quality assurance certifications are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to maintaining high manufacturing standards. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and compliance with industry-specific standards like UL or CE. These certifications assure that the components meet rigorous safety and performance benchmarks. Request documentation for these certifications during the procurement process to ensure that the parts sourced will perform reliably and meet regulatory requirements in your region. -
What logistical challenges should I anticipate when importing transformer parts?
Importing transformer parts may present various logistical challenges, including customs regulations, shipping delays, and transportation costs. Understand the import regulations in your country, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where customs processes can be complex. Additionally, consider partnering with experienced freight forwarders who can navigate these challenges and provide insight into optimal shipping methods and routes. Proper planning can help mitigate delays and additional costs, ensuring timely delivery to your projects. -
How can I handle disputes with suppliers regarding transformer parts?
Disputes with suppliers can arise from quality issues, delivery delays, or contractual misunderstandings. To minimize conflicts, establish clear communication channels and detailed contracts that outline expectations, timelines, and recourse measures. If a dispute occurs, attempt to resolve it amicably through negotiation and direct communication. Should that fail, refer to the contract for dispute resolution procedures, which may include mediation or arbitration. Maintaining a professional relationship with suppliers can also facilitate more favorable outcomes during conflicts. -
What payment terms are commonly used in international B2B transactions for transformer parts?
Payment terms in international transactions often vary based on supplier trust and order size. Common arrangements include upfront payments, letters of credit, or staggered payments upon milestones such as order confirmation or shipment. Always negotiate terms that safeguard your interests, especially when dealing with new suppliers. Consider the implications of currency fluctuations and payment processing fees, which can affect overall costs. Clear payment terms can enhance trust and ensure smoother transactions throughout the procurement process. -
What role does sustainability play in sourcing transformer parts?
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important for B2B buyers, particularly in regions prioritizing environmental responsibility. When sourcing transformer parts, assess suppliers’ adherence to environmental standards and their practices regarding material sourcing, waste management, and energy efficiency. Look for certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management. By prioritizing sustainable suppliers, you not only comply with regulations but also enhance your brand’s reputation and align with global trends toward more responsible industrial practices.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for transformer parts
As the global demand for efficient power solutions continues to grow, strategic sourcing of transformer parts emerges as a crucial factor for success in diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers must focus on quality assurance, supplier reliability, and compliance with industry standards to mitigate risks associated with procurement. Understanding the unique requirements of different transformer types, coupled with a thorough supplier assessment, can lead to cost-effective and sustainable solutions.
Investing time in early collaboration with manufacturers can streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that transformers are tailored to specific operational needs. Moreover, staying informed about market trends and technological advancements will empower buyers to make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and reduce lifecycle costs.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace a proactive sourcing strategy that prioritizes sustainability and innovation. By aligning procurement practices with evolving industry demands, buyers can secure a competitive edge in their respective markets. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore custom solutions, and position your organization for long-term success in the dynamic transformer parts landscape.