Master Sourcing Hydraulic Lifts: Key Insights for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic lift
In an increasingly interconnected global market, hydraulic lifts play a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and safety across diverse industries. From manufacturing and logistics to construction and automotive sectors, these versatile devices enable businesses to handle heavy loads with precision, significantly reducing the risk of workplace injuries and improving overall productivity. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Poland and Spain—look to optimize their operations, understanding the nuances of hydraulic lift technology becomes essential.
This comprehensive guide is tailored to empower you with the critical insights needed for informed sourcing decisions. We will delve into various types of hydraulic lifts, including mobile, low-profile, and high-capacity options, while examining the materials and manufacturing quality that influence performance and durability. Additionally, we will navigate the landscape of key suppliers, cost considerations, and essential market trends, ensuring you are equipped to make strategic choices that align with your business objectives.
By addressing frequently asked questions and providing actionable recommendations, this guide aims to simplify your procurement process. With the right knowledge at your fingertips, you can confidently invest in hydraulic lifts that not only meet your operational needs but also drive your business forward in a competitive global marketplace.
Understanding hydraulic lift Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Hydraulic Lift Tables | Basic design with hydraulic cylinders and scissor mechanism | Manufacturing, Warehousing | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to use; Cons: Limited load capacity compared to specialized types |
| Mobile Hydraulic Lift Tables | Equipped with wheels for portability and maneuverability | Assembly lines, Shipping docks | Pros: Flexible and easy to relocate; Cons: Stability may vary under heavy loads |
| Rotating Hydraulic Lift Tables | Features a rotating platform for easy access to loads | Automotive repair, Packaging | Pros: Improves workflow efficiency; Cons: More complex, may require maintenance |
| Low Profile Hydraulic Lift Tables | Designed with a low height for easy loading/unloading | Electronics assembly, Material handling | Pros: Ideal for low-clearance environments; Cons: Limited height range |
| High Capacity Hydraulic Lift Tables | Built to handle extremely heavy loads, often with reinforced structures | Heavy manufacturing, Aerospace | Pros: Capable of lifting very heavy items; Cons: Higher cost and may require more space |
Standard Hydraulic Lift Tables
Standard hydraulic lift tables are characterized by their straightforward design, featuring hydraulic cylinders and a scissor mechanism. They are suitable for general manufacturing and warehousing applications, often lifting loads between 1,000 to 6,000 pounds. Buyers should consider factors such as lift height and load capacity, as these will directly influence operational efficiency and safety. Their cost-effectiveness makes them a popular choice for businesses looking to streamline processes without significant investment.
Mobile Hydraulic Lift Tables
Mobile hydraulic lift tables are designed for flexibility, equipped with wheels that allow for easy relocation within workspaces. This mobility is particularly beneficial in dynamic environments like assembly lines and shipping docks. When purchasing, it’s crucial to assess the table’s stability under load, as this can vary based on weight distribution. Additionally, consider the floor conditions in the operational area to ensure safety and functionality, as uneven surfaces can compromise performance.
Rotating Hydraulic Lift Tables
Rotating hydraulic lift tables enhance operational efficiency by allowing users to rotate loads for optimal access without needing to move the entire table. This feature is especially advantageous in industries such as automotive repair and packaging. Buyers should evaluate the reliability of the rotation mechanism and ease of operation, as these factors will affect maintenance and usability. While they offer significant workflow improvements, the added complexity may necessitate a higher level of expertise for operators.
Low Profile Hydraulic Lift Tables
Low profile hydraulic lift tables are specifically designed for environments with low clearance, making them ideal for applications in electronics assembly and material handling. Their design allows for easy loading and unloading without excessive lifting, which can enhance workplace ergonomics. Buyers should focus on the height range and load capacity to ensure compatibility with existing workflows. Durability is also a key consideration, particularly in high-use environments where wear and tear can occur rapidly.
High Capacity Hydraulic Lift Tables
High capacity hydraulic lift tables are engineered to handle exceptionally heavy loads, often exceeding 6,000 pounds. These tables are essential in heavy manufacturing and aerospace sectors, where large components need to be moved safely. When purchasing, it’s vital to assess structural integrity and safety features to prevent accidents. While they provide significant lifting capabilities, buyers should also factor in the higher cost and potential need for more extensive maintenance protocols to ensure longevity and performance.
Related Video: Hydraulic and Traction Lift Comparison
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic lift
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Hydraulic Lift | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Assembly Line Operations | Increases efficiency and reduces manual labor risks | Assess load capacity, lift height, and durability for frequent use. |
| Automotive | Vehicle Maintenance and Repair | Enhances safety and accessibility for technicians | Ensure compatibility with vehicle types and check maintenance support. |
| Warehousing | Loading and Unloading Goods | Optimizes space utilization and improves throughput | Consider mobility features and stability under heavy loads. |
| Construction | Elevating Materials for Installation | Facilitates safer work at height and improved workflow | Evaluate height range and weight capacity for specific projects. |
| Aviation | Passenger and Cargo Handling | Streamlines operations and enhances service quality | Focus on custom solutions that meet safety regulations and accessibility needs. |
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, hydraulic lifts are integral to assembly line operations where they facilitate the movement of heavy components. These lifts enable workers to position items at ergonomic heights, significantly reducing the risk of injury associated with manual lifting. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, sourcing durable models that can withstand high-frequency use is crucial. Buyers should also evaluate the lift’s load capacity and height adjustment features to ensure they meet specific operational requirements.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, hydraulic lifts are essential for vehicle maintenance and repair tasks. They allow technicians to easily access undercarriages and other hard-to-reach areas, enhancing safety and efficiency. For B2B buyers in the Middle East and Europe, it’s vital to consider the lift’s compatibility with various vehicle types and sizes. Additionally, maintenance support and the availability of replacement parts should be prioritized to minimize downtime and ensure continuous operation.
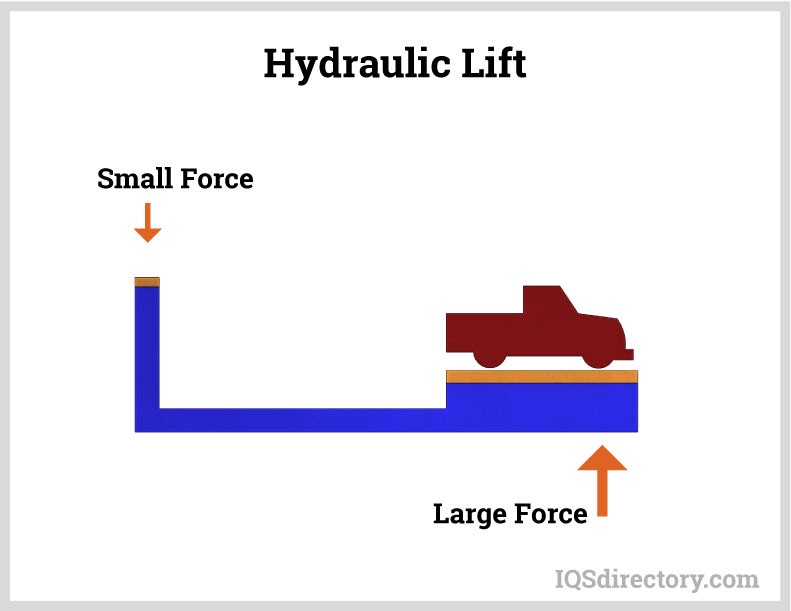
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Warehousing
Hydraulic lifts play a critical role in warehousing by streamlining the loading and unloading of goods. They enable efficient movement of heavy items, which optimizes space utilization and increases throughput. Buyers from Europe, particularly in countries like Poland and Spain, should focus on models that offer mobility and stability, as these factors can significantly impact operational efficiency in dynamic warehouse environments. Ensuring that the lifts can handle the specific weights and dimensions of the goods being moved is also essential.
Construction
In the construction industry, hydraulic lifts are used to elevate materials for installation, making the process safer and more efficient. They allow workers to access elevated areas without the risks associated with ladders or scaffolding. For international buyers, especially in regions with varying construction regulations, it is important to evaluate the lift’s height range and load capacity to ensure compliance and effectiveness for specific projects. Additionally, sourcing from reputable manufacturers that adhere to safety standards is critical.
Aviation
Hydraulic lifts are essential in the aviation sector for handling passengers and cargo. They streamline operations by providing safe and efficient access to aircraft, enhancing the overall service quality. For B2B buyers in this industry, particularly in the Middle East, focusing on custom solutions that comply with international safety regulations and accessibility standards is crucial. Buyers should also consider the lift’s adaptability to different aircraft types and the availability of training for operators to ensure safe usage.
Related Video: Hydraulic lift with animation
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic lift
When selecting materials for hydraulic lifts, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in hydraulic lift manufacturing, along with considerations for international B2B buyers.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high strength and durability, with a temperature rating that can withstand extreme conditions. It offers excellent corrosion resistance when treated or alloyed, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength-to-weight ratio, which allows for the construction of robust hydraulic lift structures. However, it can be relatively heavy, increasing shipping costs and requiring more energy for operation. The manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for precise fabrication and welding.
Impact on Application: Steel is compatible with various hydraulic fluids, making it versatile for different applications. Its durability ensures long-term performance in heavy-duty environments, such as manufacturing and construction.
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or EN 10025 for structural steel. Additionally, they should consider local availability and the cost implications of sourcing treated steel to enhance corrosion resistance in humid or saline environments.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, particularly in non-oxidizing environments. It has a lower temperature tolerance compared to steel but is still effective in moderate conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which facilitates easier transport and installation. However, it has a lower load-bearing capacity than steel, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. The manufacturing process can be more complex due to the need for specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is ideal for mobile hydraulic lifts where weight reduction is crucial. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for applications in industries like food processing and pharmaceuticals, where cleanliness is paramount.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers in regions with high humidity or exposure to chemicals should ensure that the aluminum alloy meets relevant standards, such as ASTM B221. Understanding local recycling capabilities is also important, as aluminum is highly recyclable and can reduce overall material costs.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as fiberglass or carbon fiber, offer high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can withstand a range of temperatures but may be less effective under extreme pressure conditions.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to environmental degradation. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized skills for repairs. Their use in hydraulic lifts is still relatively niche compared to metals.
Impact on Application: Composites are particularly useful in applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or portable hydraulic lifts. They can also be tailored for specific media compatibility, enhancing their utility in specialized environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with industry standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. The initial cost may be higher, but the long-term savings in maintenance and durability can offset this.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel combines the strength of steel with enhanced corrosion resistance due to its chromium content. It performs well in a wide range of temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive than regular steel and can be challenging to machine and fabricate.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for hydraulic lifts used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical. Its durability ensures long-lasting performance even in challenging conditions.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, they should evaluate the cost implications of sourcing high-quality stainless steel, especially in regions where it may not be readily available.
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic lift | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty manufacturing lifts | High strength and durability | Heavy, higher shipping costs | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile lifts in food processing | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower load capacity | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace and portable lifts | Excellent strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing and marine lifts | Corrosion resistance and durability | Expensive and difficult to fabricate | High |
This material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions that align with operational needs and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic lift
Hydraulic lifts are critical components in various industries, and understanding their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. This section provides an in-depth examination of the manufacturing processes involved in hydraulic lifts, as well as the quality assurance measures that ensure these products meet international standards.
Manufacturing Processes for Hydraulic Lifts
The manufacturing of hydraulic lifts involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product’s performance, reliability, and safety.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing involves selecting and preparing the right materials. Common materials include:
- Steel and Aluminum: Used for their strength and lightweight properties.
- Hydraulic Fluids: Essential for the operation of hydraulic systems.
- Seals and Gaskets: Critical for preventing leaks in hydraulic systems.
During this phase, materials are sourced from reputable suppliers, and their quality is assessed. B2B buyers should inquire about the suppliers’ material certifications, which can indicate adherence to industry standards.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This can include processes such as:
- Cutting: Steel and aluminum sheets are cut to specific dimensions.
- Bending and Shaping: Using hydraulic presses or CNC machines, materials are bent into required shapes for lift components.
- Welding: Critical components are welded together to form the structural framework of the lift.
Advanced techniques such as laser cutting and robotic welding are often employed to enhance precision and strength. Buyers should consider suppliers that utilize modern technology to ensure high-quality manufacturing.
3. Assembly
After forming the individual components, the assembly process begins. This phase involves:
- Integration of Hydraulic Systems: Hydraulic cylinders, pumps, and valves are installed to create the lift mechanism.
- Electrical Integration: For lifts with electronic controls, wiring and control systems are integrated during assembly.
- Final Assembly: All components, including the lift platform and safety features, are assembled.
Quality at this stage is crucial, as any misalignment can affect the lift’s performance. B2B buyers should request information on the assembly protocols and any automated systems used to ensure precision.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which includes:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as powder coating or galvanizing are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Final Inspections: Each lift undergoes rigorous inspections to check for defects or issues.
Buyers should ensure that the finishing processes meet their operational requirements, especially in harsh environments.
Quality Assurance in Hydraulic Lift Manufacturing
Quality assurance is integral to the manufacturing process of hydraulic lifts, ensuring that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: A globally recognized standard for quality management systems, focusing on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for hydraulic lifts used in oil and gas applications, ensuring safety and reliability.
These certifications are crucial for B2B buyers, as they indicate that the manufacturer adheres to strict quality and safety guidelines.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are critical in the manufacturing process. Common checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of the finished product before shipment.
B2B buyers should ask about the frequency and methods used for these inspections to gauge the manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
Common Testing Methods
To verify the quality and safety of hydraulic lifts, various testing methods are employed, including:
- Load Testing: Ensures the lift can handle its rated load capacity without failure.
- Leak Testing: Checks for leaks in hydraulic systems, which can compromise safety.
- Operational Testing: Simulates actual working conditions to assess performance.
Understanding these testing methods can help buyers ensure that the lifts will perform reliably in their specific applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are some strategies:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help assess their adherence to quality standards. This may include reviewing their ISO certifications and quality management systems.
- Requesting Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and testing results.
- Third-party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality standards and practices.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers must be aware of specific nuances regarding QC and certifications when sourcing hydraulic lifts internationally. Factors to consider include:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have unique regulations concerning hydraulic lifts. Buyers should ensure that products comply with local laws in their respective markets.
- Cultural Expectations: Buyers from different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service. Understanding these cultural differences can facilitate smoother negotiations and partnerships.
- Logistics and Lead Times: International sourcing can introduce challenges related to logistics, lead times, and customs clearance. Buyers should factor these into their procurement strategies.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with hydraulic lifts is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant standards, quality control checkpoints, and strategies for verifying supplier quality, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and safety.
Related Video: Most Satisfying Factory Production Processes And Heavy-Duty Factory Machines!
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic lift Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of hydraulic lifts is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed sourcing decisions. This analysis delves into the various components influencing costs and pricing strategies, especially for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used in hydraulic lift production significantly impact costs. Common materials include steel for structural components and hydraulic fluid, which can vary in price based on specifications. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to reduce costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on geographical location and the complexity of manufacturing processes. Regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, may lead to increased overall pricing. Understanding local labor markets can help buyers anticipate these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can minimize overhead costs, making it essential for buyers to evaluate suppliers’ operational efficiencies.
-
Tooling: The cost of specialized tools and equipment required for production can be substantial. Custom hydraulic lifts necessitate additional tooling, which can increase initial costs but may yield better long-term value through enhanced functionality.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investment in quality assurance processes ensures that hydraulic lifts meet safety and performance standards. Suppliers who prioritize QC may charge a premium, but this often translates to lower maintenance and replacement costs over time.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping methods, and regional tariffs. Buyers should factor in logistics when assessing total costs, especially for international purchases where freight charges may significantly impact pricing.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market conditions, competition, and demand. Understanding these margins can provide insight into potential negotiation strategies.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Buying in bulk often leads to significant discounts. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better prices, especially when sourcing from manufacturers.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized hydraulic lifts tailored to specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against its impact on price.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can enhance product reliability but also raise prices. Buyers should ensure that the quality justifies the cost.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and reliability can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record, while new entrants might offer competitive pricing to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for managing shipping responsibilities and costs. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift financial responsibilities and affect overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage multiple quotes to negotiate better pricing. Don’t hesitate to discuss bulk orders or long-term contracts for potential discounts.
-
Cost Efficiency: Assess not only the purchase price but also the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, costs may differ significantly between suppliers in Europe and those in Africa or South America due to local economic conditions.
-
Disclaimer on Prices: Prices for hydraulic lifts can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable to obtain specific quotes and assess them in the context of your unique requirements and market conditions.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints, ultimately enhancing their competitive advantage in the market.
Spotlight on Potential hydraulic lift Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘hydraulic lift’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic lift
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology related to hydraulic lifts is essential for international B2B buyers, especially when making informed purchasing decisions. Below are key specifications and commonly used terms in the hydraulic lift industry.
Key Technical Properties
-
Load Capacity
– Definition: This refers to the maximum weight a hydraulic lift can safely handle, usually measured in pounds or kilograms.
– Importance: Understanding the load capacity is critical for ensuring that the lift can accommodate the specific needs of your operations. Exceeding this limit can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and costly downtime. -
Lift Height
– Definition: The maximum vertical distance a hydraulic lift can raise a load, typically measured from the floor to the top of the platform.
– Importance: Different applications require varying lift heights. Buyers should assess their workspace and the items being lifted to ensure the selected lift meets operational requirements. -
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the quality and strength of the materials used in the construction of the hydraulic lift, such as steel or aluminum.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials contribute to durability and safety. Buyers should look for lifts made from materials that can withstand their specific operating conditions, especially in demanding environments. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value, which is critical for components like hydraulic cylinders.
– Importance: Precise tolerances ensure that all parts fit together correctly, contributing to the lift’s overall functionality and safety. Poor tolerances can lead to operational inefficiencies and increased maintenance costs. -
Hydraulic Fluid Type
– Definition: The kind of fluid used in the hydraulic system, which can affect performance, temperature range, and lubrication.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate hydraulic fluid is essential for optimal performance and longevity of the hydraulic system. Buyers should ensure compatibility with the manufacturer’s specifications. -
Cycle Time
– Definition: The time it takes for a hydraulic lift to complete a full lifting and lowering operation.
– Importance: A shorter cycle time increases operational efficiency, which is crucial for high-volume environments such as warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM products can help buyers identify quality components and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ can help buyers plan their purchases effectively, especially in budget-sensitive scenarios. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing for specific goods or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare costs and terms from multiple suppliers, aiding in informed decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, facilitating smoother international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Relevance: Knowing the lead time is crucial for planning operations and managing inventory effectively, especially for businesses that rely on timely deliveries.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the product and the terms of repair or replacement.
– Relevance: A solid warranty can provide peace of mind for buyers, ensuring support in case of defects or failures in the hydraulic lift.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms will empower international B2B buyers to make better-informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic lifts, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and safety.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hydraulic lift Sector
In the hydraulic lift sector, several global drivers are shaping market dynamics and influencing sourcing trends for international B2B buyers. Growing urbanization and the rapid expansion of industrial sectors across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions. Additionally, the rise of e-commerce has heightened logistics and warehousing needs, further pushing the adoption of hydraulic lifts to streamline operations.
Technological advancements in hydraulic systems, including the integration of IoT and automation, are revolutionizing how these lifts are sourced and utilized. Buyers are increasingly looking for smart hydraulic lifts that can provide real-time data on performance and maintenance needs, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced downtime. Furthermore, the ongoing shift towards digital procurement platforms allows buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and products, facilitating better pricing and supply chain transparency.
Another significant trend is the focus on customization. As industries vary in their specific needs, hydraulic lift manufacturers are offering tailored solutions to meet diverse requirements, from load capacities to operational environments. This trend underscores the importance for buyers to engage closely with suppliers to ensure that the selected hydraulic lifts align perfectly with their operational demands.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a critical consideration in the hydraulic lift sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of hydraulic lifts necessitates a shift towards eco-friendly practices. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that utilize sustainable materials and practices, such as recycled metals and energy-efficient hydraulic systems, to minimize their carbon footprint.
Moreover, ensuring an ethical supply chain is vital. This involves vetting suppliers for their labor practices and commitment to social responsibility. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Buyers should actively seek out products that meet these standards, as they not only contribute to a cleaner environment but also enhance brand reputation and compliance with increasingly stringent regulations.
Brief Evolution/History
The hydraulic lift sector has evolved significantly since its inception in the late 19th century. Originally designed for basic lifting tasks, hydraulic systems have undergone transformative advancements, driven by engineering innovations and industrial demands. The introduction of scissor lift technology in the mid-20th century revolutionized material handling, making it safer and more efficient. Today, hydraulic lifts are integral to various industries, including manufacturing, logistics, and construction, reflecting a continuous evolution toward enhanced performance and adaptability. B2B buyers must recognize this historical context to better appreciate the advancements and innovations available in today’s market, positioning themselves strategically for future procurement decisions.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic lift
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for hydraulic lifts?
When vetting suppliers, start by researching their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Request references from past clients to gauge their reliability. Verify certifications related to safety and quality standards, such as ISO or CE marks, which demonstrate compliance with international regulations. Additionally, consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if feasible, or request a virtual tour. Engaging with multiple suppliers can also provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness, crucial factors in maintaining a long-term relationship. -
What customization options are typically available for hydraulic lifts?
Most manufacturers offer various customization options for hydraulic lifts, including size, load capacity, and specific features tailored to your operational needs. You can request modifications such as additional safety features, unique lifting heights, or mobile configurations. Ensure you communicate your requirements clearly and inquire about the design process, lead times, and any potential impact on costs. It’s advisable to collaborate closely with the supplier’s engineering team to ensure that all specifications are met effectively. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for hydraulic lifts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) vary by supplier and can depend on the type of hydraulic lift and customization level. Generally, for standard models, MOQs might range from 1 to 10 units, while customized solutions may require larger orders. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks depending on the complexity of the design and the supplier’s production schedule. Always discuss these aspects upfront to align your procurement timeline with your operational needs and avoid delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic lifts?
Payment terms can vary significantly among suppliers, but common arrangements include a deposit (often 30% to 50%) at the time of order, with the balance due prior to shipment. It’s crucial to clarify payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or PayPal, especially for international transactions. Additionally, inquire about any financing options available or discounts for bulk purchases. Ensure all terms are documented in the purchase agreement to prevent misunderstandings later. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification for hydraulic lifts?
To ensure quality assurance, ask suppliers for their quality control processes and relevant certifications. Look for compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request test reports for the hydraulic lifts, including load testing and safety evaluations. Furthermore, consider arranging for third-party inspections or audits if sourcing from unfamiliar suppliers, as this can provide additional assurance regarding product quality and reliability. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing hydraulic lifts?
Logistics plays a critical role in importing hydraulic lifts. Evaluate shipping methods, costs, and transit times based on your location. Understand customs regulations in your country, as specific documentation may be required for heavy machinery imports. Partner with a reliable freight forwarder familiar with industrial equipment to navigate these complexities effectively. Additionally, factor in potential duties and taxes, and ensure that your supplier provides all necessary shipping documents to facilitate smooth customs clearance. -
How can I handle disputes or issues with suppliers?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels with your supplier from the outset. Document all interactions, agreements, and transactions to provide a clear record if issues arise. In case of a dispute, try to resolve it amicably through direct negotiation. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Building a solid relationship with your supplier can also help mitigate conflicts and foster a collaborative problem-solving approach. -
What are the common applications for hydraulic lifts in different industries?
Hydraulic lifts are utilized across various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and automotive maintenance. In manufacturing, they facilitate the movement of heavy components, improving efficiency and safety. In warehousing, hydraulic lifts assist in loading and unloading goods, optimizing space utilization. The automotive industry relies on hydraulic lifts for vehicle servicing and inspections. Understanding these applications can help you choose the right type of hydraulic lift that aligns with your specific operational needs and industry standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic lift
As you conclude your journey through the intricacies of sourcing hydraulic lifts, it’s essential to underscore the pivotal role that strategic sourcing plays in enhancing operational efficiency and safety. Key takeaways include the importance of understanding the diverse types of hydraulic lift tables available, evaluating supplier reliability, and considering cost implications in relation to your specific operational needs. Each of these factors can significantly impact productivity and workplace safety, making informed decisions crucial.
International B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must adopt a proactive approach to sourcing. This means leveraging global supplier networks, engaging in thorough market research, and considering partnerships that offer both innovation and reliability.
Looking forward, the hydraulic lift market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various sectors. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your operations and remain competitive in the marketplace. Take the next step—evaluate your current lifting solutions, assess your needs, and connect with trusted suppliers to secure the best hydraulic lift solutions tailored for your business.