Unlock Cost-Effective Sourcing Strategies for Vee Belt
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vee belt
V-belts are essential components in the machinery and automotive sectors, serving as the backbone of power transmission systems. Their ability to efficiently transfer power between rotating shafts makes them indispensable in various applications, from industrial equipment to agricultural machinery. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of V-belt selection and sourcing can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of V-belts, covering critical aspects such as types, materials, manufacturing standards, quality control measures, and cost considerations. We delve into the diverse applications of V-belts across different industries, highlighting their versatility and performance advantages over alternative power transmission methods.
Moreover, this resource offers insights into the global market landscape, identifying reputable suppliers and manufacturers, along with best practices for sourcing these vital components. By addressing frequently asked questions, we empower buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, ensuring they choose the right V-belt solutions for their specific needs.
In an increasingly competitive environment, leveraging this guide will enhance your sourcing strategy, streamline your procurement processes, and ultimately contribute to the success of your operations.
Understanding vee belt Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classical V-Belts | Trapezoidal cross-section; standard design | Automotive, industrial machinery | Pros: Cost-effective, widely available. Cons: Limited in high-speed applications. |
| Narrow V-Belts | Compact design; higher power transmission capacity | High-speed machinery, robotics | Pros: Space-efficient, high torque. Cons: May require specific pulleys. |
| Double V-Belts | V-shaped on both sides; allows multi-shaft power | Complex machinery, conveyor systems | Pros: Versatile for multiple drives. Cons: Higher cost and complexity in installation. |
| Ribbed V-Belts | Multiple longitudinal ribs; flexible design | Small pulleys, HVAC systems | Pros: Reduced bending stress, flexible. Cons: Limited power transmission capacity. |
| Poly-V Belts | Slim ribbed design; high-speed applications | Automotive engines, compact machinery | Pros: Excellent grip, space-saving. Cons: More expensive, specific installation requirements. |
Classical V-Belts
Classical V-belts are the most commonly used type, featuring a trapezoidal cross-section that allows for effective power transmission between rotating shafts. Their design offers a balance between performance and cost, making them suitable for a variety of applications, including automotive and industrial machinery. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include compatibility with existing pulleys and the expected load conditions, as these belts are generally not recommended for high-speed applications.
Narrow V-Belts
Narrow V-belts have a more compact profile than classical V-belts, which enables them to transmit higher power in limited spaces. They are particularly suited for high-speed machinery and robotics where torque requirements are elevated. Buyers should consider the specific pulley specifications and installation conditions, as these belts may necessitate more precise alignment and configuration.
Double V-Belts
Double V-belts feature a V-shape on both sides, allowing them to transmit power between three or more shafts simultaneously. This design is ideal for complex machinery and conveyor systems that require robust power distribution. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of versatility against the higher costs and potential complexities in installation, as well as ensure compatibility with multi-grooved sheaves.
Ribbed V-Belts
Ribbed V-belts are characterized by their multiple longitudinal ribs, which enhance flexibility and reduce bending stress. This makes them particularly effective for small pulleys and serpentine drive systems, such as those found in HVAC applications. Buyers should consider their power transmission capacity, which is generally lower than traditional V-belts, and ensure that the application requirements align with this design’s strengths.
Poly-V Belts
Poly-V belts are designed with a slim, ribbed profile that allows for high-speed applications while saving space. They are commonly used in automotive engines and compact machinery where efficiency and performance are critical. For B2B buyers, the considerations include the initial cost, as they tend to be more expensive than traditional V-belts, along with the need for specific installation practices to ensure optimal performance.
Related Video: Large Language Models (LLMs) – Everything You NEED To Know
Key Industrial Applications of vee belt
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Vee Belt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Power transmission in engines | Efficient power transfer reduces fuel consumption | Ensure compatibility with engine specifications and torque requirements |
| Industrial Equipment | Driving conveyor systems | Increased operational efficiency and reduced downtime | Consider the load capacity and length requirements for specific machinery |
| Agricultural Machinery | Powering tractors and harvesters | Enhances productivity and reliability in farming operations | Look for belts designed for high torque and resistance to environmental factors |
| HVAC Systems | Operating fans and compressors | Improves energy efficiency and extends equipment lifespan | Focus on belt flexibility and resistance to wear in high-temperature environments |
| Mining and Construction | Powering heavy machinery like excavators | Ensures consistent performance under heavy loads | Prioritize durability and strength to withstand harsh conditions |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, V-belts are critical for transmitting power from the engine to various components such as the alternator, water pump, and air conditioning compressor. They help maintain efficient engine operation, contributing to better fuel economy. International buyers should ensure that the V-belts they source meet the specific torque and compatibility requirements of different vehicle models, especially in regions like Africa and South America where vehicle diversity is high.
Industrial Equipment
V-belts are extensively used in industrial machinery, particularly in conveyor systems and manufacturing equipment. They facilitate the smooth operation of lathes, milling machines, and other tools by effectively transmitting power between rotating shafts. Buyers in this sector must consider the load capacity, belt length, and compatibility with existing machinery to optimize performance and reduce maintenance costs. In Europe, where precision engineering is paramount, sourcing high-quality V-belts that meet stringent standards is essential.
Agricultural Machinery
In agriculture, V-belts are employed in tractors, combines, and other farming equipment to transfer power between various components. Their ability to handle high torque makes them ideal for demanding applications, enhancing productivity and reliability in farming operations. Buyers should look for V-belts that are specifically designed to withstand the rigors of agricultural environments, including resistance to dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures, particularly in regions like Egypt and South America.
HVAC Systems
V-belts play a vital role in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems by powering fans, blowers, and compressors. Their efficient power transmission contributes to improved energy efficiency and prolonged equipment lifespan. When sourcing V-belts for HVAC applications, international buyers should prioritize flexibility and wear resistance, especially in high-temperature environments, to ensure consistent performance and minimize operational disruptions.
Mining and Construction
In the mining and construction sectors, V-belts are used to power heavy machinery, such as excavators and drills. They provide reliable power transmission under extreme load conditions, ensuring consistent performance. Buyers in these industries should focus on sourcing durable V-belts that can withstand harsh environments and heavy-duty applications. This includes considering factors such as material strength, temperature resistance, and compatibility with specific machinery models to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Related Video: Calculating Power Transmitted Using Flat Belts and Vee Belts
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vee belt
When selecting materials for V-belts, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in V-belt manufacturing, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in different regions.
1. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber V-belts are known for their excellent flexibility and elasticity. They typically have a temperature rating of up to 70°C and can handle moderate pressures. Rubber also provides good frictional properties, which enhances grip on pulleys.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber is relatively inexpensive and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for standard applications. However, it can degrade under extreme temperatures and may not be suitable for high-torque applications. Its susceptibility to ozone and UV light can also limit its lifespan.
Impact on Application:
Rubber belts are ideal for automotive and light industrial applications where moderate power transmission is required. They are not suitable for environments with high heat or chemical exposure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM D2000 for rubber materials. In regions like Africa and South America, where environmental conditions may vary, it’s crucial to assess the rubber’s durability against local factors like humidity and temperature fluctuations.
2. Polyurethane
Key Properties:
Polyurethane V-belts offer superior abrasion resistance and can operate effectively at temperatures ranging from -30°C to 80°C. They are also resistant to oils and chemicals, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of polyurethane belts is a significant advantage, as they often outlast rubber belts in demanding applications. However, they are generally more expensive and can be more complex to manufacture, which may affect lead times.
Impact on Application:
These belts are well-suited for heavy-duty industrial machinery and applications involving exposure to oils or chemicals. Their flexibility allows for use in compact spaces with tight pulley arrangements.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should look for compliance with DIN 2215 standards, particularly in Europe. The higher cost may be justified in applications where longevity and performance are critical, especially in the Middle East where harsh conditions prevail.
3. Polyester Reinforced Rubber
Key Properties:
This composite material combines the elasticity of rubber with the strength of polyester fibers. It can withstand temperatures up to 100°C and offers enhanced tensile strength and resistance to wear.
Pros & Cons:
The inclusion of polyester significantly increases the belt’s durability and load-bearing capacity. However, the manufacturing process is more complex, which can lead to increased costs and longer production times.
Impact on Application:
Ideal for high-torque applications in heavy machinery, this material is commonly used in agricultural and industrial settings where reliability is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that the belts meet relevant standards such as ISO 14890. In regions like Poland and Egypt, where agricultural machinery is prevalent, the advantages of polyester reinforced belts can lead to reduced maintenance costs over time.
4. Fiberglass Reinforced Rubber
Key Properties:
Fiberglass reinforced V-belts provide exceptional strength and stability, with temperature ratings similar to polyester. They can handle high loads and are resistant to stretching.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage is their ability to maintain tension over long periods, which translates to less frequent replacements. However, they are typically more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Application:
These belts are particularly effective in high-performance applications, such as in HVAC systems and heavy industrial equipment, where consistent performance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with JIS B 1851 standards is essential for buyers in Asia. The higher initial investment may be offset by lower operational costs, making them a viable option for long-term projects in Europe and the Middle East.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vee belt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Automotive, light industrial | Cost-effective and flexible | Degrades under extreme conditions | Low |
| Polyurethane | Heavy-duty industrial machinery | High durability and chemical resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Polyester Reinforced Rubber | High-torque agricultural machinery | Enhanced strength and load capacity | More complex manufacturing process | Medium |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Rubber | HVAC systems, heavy industrial | Maintains tension and reduces replacements | Higher initial investment | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides valuable insights for B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on application requirements, environmental conditions, and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vee belt
The manufacturing of V-belts is a complex process that requires precision and adherence to strict quality control standards. For B2B buyers, particularly in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can inform better purchasing decisions and ensure that they source reliable products. This section will provide an overview of the typical manufacturing processes, quality assurance protocols, and ways buyers can verify supplier quality.
Manufacturing Process
Material Preparation
The first stage in V-belt manufacturing is material preparation. High-quality materials are crucial for the performance and durability of V-belts. The primary materials used include:
- Rubber Compounds: Natural and synthetic rubber compounds are blended to achieve specific properties such as flexibility, strength, and resistance to wear.
- Reinforcement Fibers: To enhance tensile strength, fibers like polyester, aramid, or steel are embedded into the rubber. This reinforcement is critical for high-load applications.
- Fabric Linings: The outer surface may be coated with fabric to improve grip and reduce wear on pulleys.
Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next step is the forming process. This typically involves:
- Extrusion: The rubber compound is extruded into the desired V-shaped profile. This step ensures uniformity in thickness and cross-section.
- Curing: After extrusion, the belts are cured in molds at high temperatures. Curing solidifies the rubber and enhances its elasticity and durability. The curing process may vary based on the type of rubber and intended application.
Assembly
In the assembly stage, various components are integrated to form the final product:
- Belt Joining: For belts requiring specific lengths, the ends may be joined using methods like vulcanization or adhesive bonding.
- Quality Checks: Initial inspections are performed to ensure that the dimensions and surface finishes meet specifications before proceeding to the finishing stage.
Finishing
The finishing stage includes:
- Trimming and Sizing: Any excess material is trimmed, and the belt is cut to the specified length.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to verify that the belts meet all design specifications and quality standards. This may include visual checks for defects, dimensional checks, and surface quality evaluations.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of V-belt manufacturing. International standards and industry-specific guidelines govern the quality processes to ensure that products are reliable and safe for use.
International Standards
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to internationally recognized quality management systems, such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures consistent quality in products and services. Compliance indicates a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 14001: For environmentally conscious buyers, this standard addresses effective environmental management practices during manufacturing.
Industry-Specific Standards
In addition to general quality standards, certain industry-specific certifications may be relevant, including:
- CE Marking: Indicates that the product meets European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for V-belts used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically implemented at several key checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive evaluation of the finished product, including tests for dimensional accuracy, tensile strength, and surface quality.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the testing methods used to ensure the reliability of V-belts:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and elasticity of the belt to ensure it can handle specified loads.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses the durability of the belt under cyclic loading conditions.
- Dynamic Testing: Evaluates performance under actual operating conditions to ensure effective power transmission without slippage.
Verification of Supplier Quality
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can implement several strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports from suppliers, including information on testing results and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to conduct independent assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
When sourcing V-belts from suppliers in different regions, international buyers should consider the following nuances:
- Certification Recognition: Ensure that the certifications and standards recognized in the supplier’s region are acknowledged in the buyer’s market. For example, CE marking is crucial for European buyers.
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Be aware of varying manufacturing practices and regulatory requirements across regions, which may impact product specifications and quality assurance processes.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is vital; ensure that documentation and quality reports are available in a language that the buyer can understand.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for V-belts, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure products that meet their performance and durability requirements. This knowledge is particularly valuable for international buyers navigating diverse markets and standards.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vee belt Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of V-belts is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will provide insights into the key cost components, price influencers, and practical tips for optimizing sourcing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary raw materials for V-belts include rubber, polymers, and sometimes reinforced fibers. The choice of material significantly affects the cost. For instance, high-performance belts made from premium materials will command higher prices than standard options.
-
Labor: Manufacturing V-belts involves skilled labor, especially in the processes of cutting, molding, and quality testing. Labor costs can vary widely depending on the country of production. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but this can sometimes come at the expense of quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, rent, and other operational costs associated with the manufacturing facility. Overhead costs will differ based on the location of the manufacturer and the efficiency of their processes.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific V-belt designs can be a significant upfront cost. Buyers seeking specialized products may need to factor in these expenses as part of their total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures product reliability and performance. While this adds to the overall cost, it is a necessary investment, especially for applications in critical industries like automotive and industrial machinery.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, the mode of transportation, and current fuel prices. Additionally, customs duties and tariffs may apply, particularly for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a profit margin on top of their costs, which can vary by market and competition. Understanding the margin expectations of suppliers can help in negotiating better prices.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should aim to meet or negotiate minimum order quantities to secure better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom V-belts tailored to specific applications can incur higher costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (like ISO or industry-specific standards) can justify higher prices. Buyers in regions with strict compliance requirements should prioritize certified suppliers.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better quality assurance and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery is crucial. Incoterms dictate who bears the cost and risk at various stages of transportation, impacting overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing. Leverage your purchasing power by comparing quotes from multiple suppliers to drive down costs.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. Opt for belts that offer longevity and reliability to minimize long-term expenses.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of regional market dynamics, including currency fluctuations and local demand, which can impact pricing. Additionally, understanding local import regulations can help avoid unexpected costs.
Disclaimer
Prices for V-belts are subject to fluctuation based on market conditions, raw material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. It is recommended to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential vee belt Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘vee belt’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vee belt
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with V-belts is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge enables informed purchasing decisions and enhances operational efficiency in various applications.
Critical Technical Properties of V-Belts
-
Material Composition
– V-belts are typically made from rubber or polymer materials, often reinforced with fibers for added strength. The choice of material impacts durability and performance. For high-torque applications, selecting a reinforced belt is essential to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Belt Dimensions
– V-belts come in various sizes, including width and height measurements that dictate their fit in specific pulleys. Common dimensions are classified under standards such as SPZ, SPA, SPB, and SPC. Accurate measurements are vital to prevent slippage and ensure optimal power transmission. -
Power Rating
– The power rating indicates the maximum load a V-belt can handle under specific conditions. Buyers should consider the application requirements, including the service factor, which varies based on usage intensity. Understanding this metric helps in selecting the right belt for both light and heavy-duty applications. -
Belt Length and Length Factor
– V-belts are measured in internal lengths (e.g., Z, A, B, C) or external lengths (e.g., SPZ, SPA). The length factor adjusts based on the specific application and pulley configuration. Accurate length measurement ensures that the belt fits correctly, reducing wear and enhancing performance. -
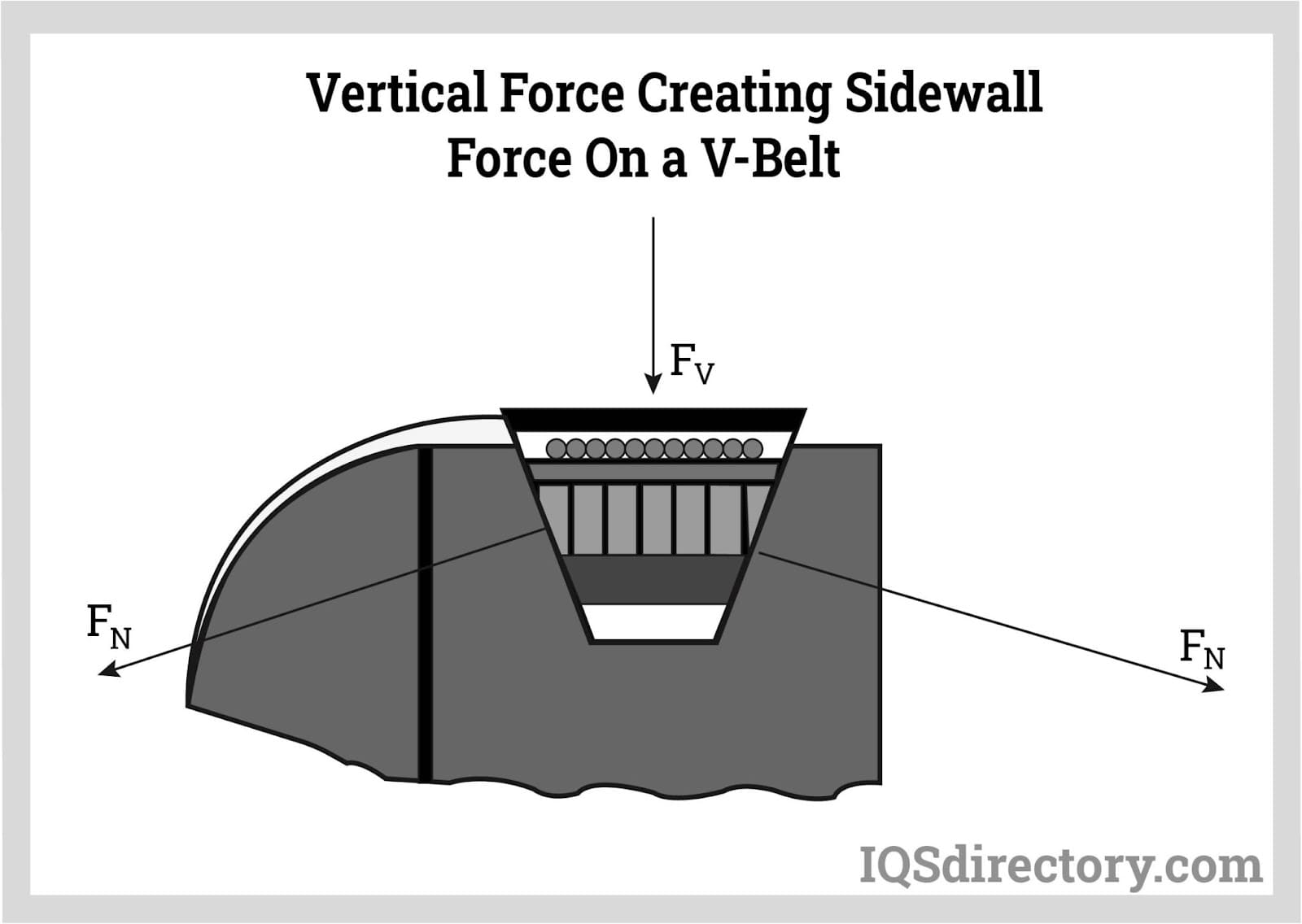
Angle of Contact
– This refers to the contact area of the V-belt with the pulley. A larger angle of contact improves power transmission efficiency. When designing a drive system, maximizing this angle can lead to better performance, especially in high-load scenarios. -
Tensile Strength
– The tensile strength of a V-belt determines its ability to withstand tension without breaking. This property is crucial for high-speed applications where significant forces are at play. Understanding tensile strength aids in selecting belts that match the operational demands of specific machinery.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications ensures that buyers procure compatible V-belts that meet the original design standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term specifies the smallest amount of product a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess inventory needs and manage costs, especially for smaller operations that may not require large quantities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. For V-belt purchases, submitting an RFQ ensures that buyers receive competitive pricing and clear terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better negotiation. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized terms used in international trade to define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and costs associated with importing V-belts. -
Lead Time
– This refers to the time taken from placing an order to delivery. Understanding lead times is crucial for operational planning, particularly in industries that rely on timely maintenance and production schedules.
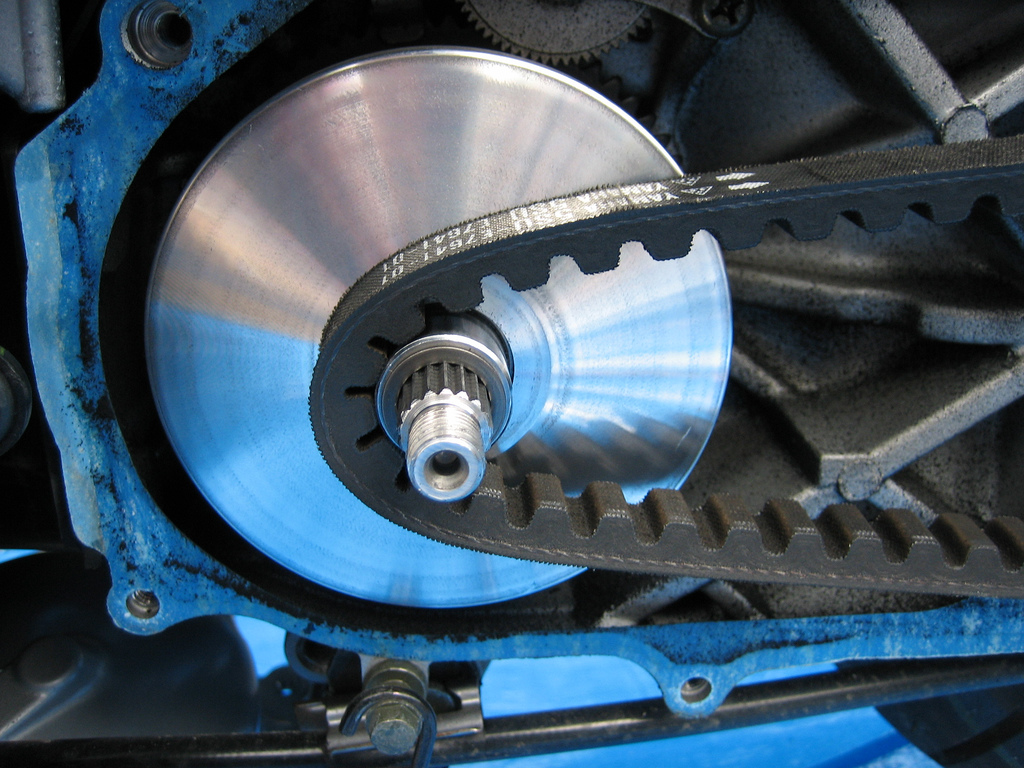

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Belt Efficiency
– This term describes the ratio of useful power transmitted by the belt to the total power input. Higher belt efficiency indicates better performance and lower energy consumption, which is essential for cost management in industrial applications.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions that enhance productivity and minimize operational risks. Understanding the technical specifications of V-belts ensures that the right products are selected for specific applications, leading to improved performance and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vee belt Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global V-belt market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing industrial automation, rising demand for energy-efficient systems, and the expansion of the automotive sector. V-belts are essential for power transmission in machinery across diverse applications, from automotive engines to industrial equipment. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the dynamics of this market is crucial for strategic sourcing.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT and predictive maintenance, are reshaping how V-belt systems are monitored and maintained. Smart manufacturing processes are increasingly integrating V-belts with sensors that provide real-time data on performance and wear, allowing for proactive management of equipment. This trend not only extends the lifespan of V-belts but also enhances operational efficiency.
Additionally, buyers should be aware of the shift towards narrow V-belts and ribbed V-belts, which are becoming popular due to their compact design and improved power transmission capabilities. The growing focus on energy efficiency is pushing manufacturers to innovate, leading to the introduction of belts that can operate at higher speeds with reduced slippage. For buyers, this translates into the need for continuous evaluation of suppliers and products to ensure they are obtaining the most advanced and efficient solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing V-belts, as companies face increasing pressure from regulators and consumers to minimize their environmental impact. The production of V-belts typically involves synthetic rubber and polymers, which pose environmental concerns. Hence, buyers should prioritize suppliers that implement eco-friendly manufacturing processes and use sustainable materials.
Ethical supply chains are also essential. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and transparency in their sourcing processes. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Global Recycled Standard can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of bio-based materials for V-belts is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also enhance the sustainability profile of the product. Buyers should actively seek out products that highlight their use of recycled or renewable materials, as this can improve their own corporate sustainability initiatives and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of V-belts has transformed the landscape of power transmission since their introduction in the early 20th century. Originally, flat belts dominated the market, but V-belts emerged due to their superior efficiency and compact design, allowing for higher power transmission in smaller spaces. Over the decades, advancements in materials science have led to the development of reinforced belts that offer greater durability and performance, catering to the demands of various industrial applications.
As industries continue to evolve, V-belts are adapting to meet the needs of modern machinery and energy-efficient systems. This historical context is essential for buyers, as understanding the advancements in V-belt technology can guide them in selecting the most suitable products for their applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vee belt
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for V-belts?
When vetting suppliers, consider their experience, reputation, and manufacturing capabilities. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Request references from other international buyers, and assess their responsiveness to inquiries. Additionally, ask for samples to evaluate product quality and ensure they have the capacity to meet your specific requirements in terms of volume and customization. -
Are V-belts customizable to fit specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for V-belts. This can include variations in size, material composition, and design features tailored to specific operational needs. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications regarding your application, including load requirements and environmental conditions. This will help manufacturers recommend the most suitable options for your needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for V-belts?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the type and customization of the V-belts. Generally, standard V-belts may have lower MOQs, while specialized or custom belts might require larger orders. When negotiating, clarify your volume needs and explore options for smaller trial orders if you are testing a new supplier or product. -
What are the common lead times for ordering V-belts internationally?
Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors such as supplier location, manufacturing capabilities, and order complexity. For international shipping, customs clearance can also affect delivery times. To avoid delays, confirm lead times upfront and factor in potential shipping and customs processing times when planning your procurement. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from V-belt suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should implement stringent quality assurance processes, including material inspections, in-process checks, and final product testing. Ask for documentation proving compliance with international standards and any relevant certifications. Additionally, inquire about their return and warranty policies, which can provide insight into their commitment to product quality and customer satisfaction.
-
How should I handle disputes with V-belt suppliers?
To effectively manage disputes, maintain clear and open communication with your supplier. Document all agreements, specifications, and correspondence. If issues arise, address them promptly and seek a resolution through dialogue. If necessary, refer to contractual agreements and consider mediation or arbitration as a means of resolving disputes without escalating to legal action. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing V-belts?
When sourcing V-belts, consider shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Evaluate whether the supplier can handle logistics or if you need to coordinate shipping yourself. Understand the import regulations and duties applicable in your country. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides proper packaging to prevent damage during transit, as well as tracking information for shipment monitoring. -
What payment terms are commonly offered for international V-belt orders?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. For large orders, consider negotiating favorable terms that may include partial payments based on milestones. Always ensure that payment methods are secure and that you have a clear understanding of currency exchange rates and potential fees, especially when dealing with international transactions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vee belt
As the demand for efficient power transmission continues to grow across various industries, the strategic sourcing of V-belts becomes increasingly critical for international B2B buyers. Understanding the different types of V-belts—such as classical, narrow, double, and ribbed—enables buyers to select the most suitable option for their specific applications, whether in automotive, industrial equipment, or agricultural machinery.
Key Takeaways:
– Performance vs. Cost: Buyers must balance performance requirements with cost considerations, as reinforced V-belts may offer better longevity and efficiency in high-torque applications.
– Supplier Relationships: Establishing strong partnerships with reliable manufacturers ensures access to quality products and timely deliveries, which is essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
– Regional Insights: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage regional supply chains and local manufacturing capabilities to optimize sourcing strategies.
Looking ahead, the V-belt market is poised for growth, driven by advancements in materials and manufacturing processes. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about technological innovations and emerging trends in power transmission solutions. By adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, organizations can enhance their competitive edge and ensure long-term operational success.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)