Master Sourcing Grating Steel: Your Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for grating steel
In an increasingly interconnected world, the demand for grating steel has surged, driven by its vital role in various industrial applications. From construction and infrastructure to manufacturing and energy sectors, grating steel is essential for ensuring safety, accessibility, and durability. As international B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek reliable sourcing solutions, understanding the nuances of the grating steel market becomes paramount.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of grating steel, covering critical aspects that empower buyers to make informed decisions. Key topics include:
- Types of Grating Steel: Explore the various forms and applications, including welded, riveted, and swaged options.
- Materials and Manufacturing: Gain insights into the materials used, such as carbon steel and stainless steel, and the manufacturing processes involved.
- Quality Control Standards: Learn about the essential quality checks and certifications that ensure safety and performance.
- Supplier Landscape: Identify reputable suppliers and manufacturers across different regions, facilitating effective partnerships.
- Cost Considerations: Understand the factors influencing pricing to optimize budget allocations.
- Market Trends and Insights: Stay ahead of the curve with the latest market dynamics and forecasts.
- FAQs: Address common queries to streamline the procurement process.
By leveraging the insights provided in this guide, international B2B buyers will be better equipped to navigate the global market for grating steel, ensuring they secure high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Understanding grating steel Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel Bar Grating | Made from flat steel bars, often welded; high load capacity | Platforms, walkways, and drainage covers | Pros: High strength; customizable sizes. Cons: Heavier, potentially higher costs. |
| Expanded Metal Grating | Created by stretching metal sheets; diamond-shaped openings | Security fencing, walkways, and vents | Pros: Lightweight; good airflow. Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity. |
| Fiberglass Grating | Made from fiberglass-reinforced plastic; corrosion-resistant | Chemical processing, wastewater treatment | Pros: Non-corrosive; lightweight. Cons: Lower load capacity compared to steel. |
| Heavy-Duty Grating | Thicker bars for increased strength; often used in industrial settings | Heavy machinery access, industrial platforms | Pros: High load capacity; durable. Cons: More expensive; heavier. |
| Architectural Grating | Aesthetic designs; can include decorative elements | Commercial buildings, public spaces | Pros: Enhances aesthetics; versatile. Cons: May compromise on load capacity. |
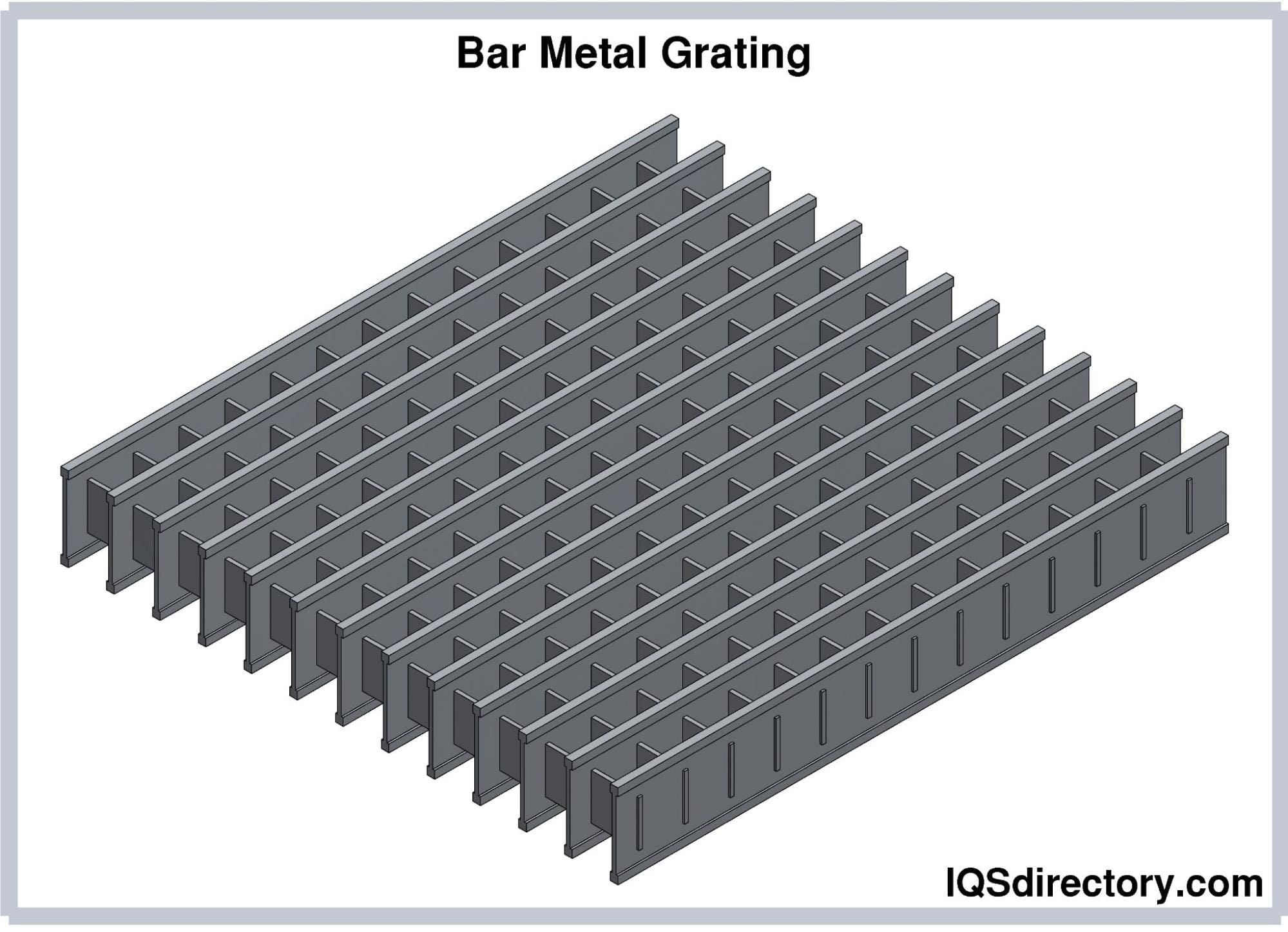
Steel Bar Grating
Steel bar grating is constructed from flat steel bars that are welded together to form a grid. This type of grating is known for its high load-bearing capacity, making it ideal for applications such as platforms, walkways, and drainage covers. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific load requirements and environmental factors, such as exposure to corrosive substances, that may affect longevity. Customization options are available, allowing for tailored solutions to fit specific project needs.
Expanded Metal Grating
Expanded metal grating is manufactured by stretching metal sheets to create a diamond pattern. This design allows for excellent airflow and visibility, making it suitable for applications like security fencing and walkways. Buyers appreciate its lightweight nature, which can facilitate easier installation. However, it has a limited load-bearing capacity compared to other types, which should be a critical consideration in high-load scenarios.
Fiberglass Grating
Fiberglass grating consists of fiberglass-reinforced plastic, providing exceptional resistance to corrosion and chemicals. This makes it particularly suitable for environments such as chemical processing plants and wastewater treatment facilities. Its lightweight nature simplifies installation, but buyers should note that it generally offers lower load-bearing capacity compared to metal alternatives. When choosing fiberglass grating, consider the specific environmental conditions and load requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Heavy-Duty Grating
Heavy-duty grating features thicker bars designed for increased strength and durability, making it a popular choice in industrial settings. It is commonly used for heavy machinery access and industrial platforms where high load capacity is essential. While this type of grating is robust, it is also heavier and more expensive, which may impact project budgets. Buyers should evaluate their load requirements and consider the trade-off between cost and durability when selecting heavy-duty grating.
Architectural Grating
Architectural grating is designed with aesthetics in mind, often incorporating decorative elements suitable for commercial buildings and public spaces. While it enhances the visual appeal of a structure, buyers need to be aware that it may compromise on load capacity compared to more utilitarian options. When considering architectural grating, businesses should balance aesthetic desires with the functional requirements of their projects, ensuring that it meets both design and safety standards.
Related Video: What Makes Large Language Models Expensive?
Key Industrial Applications of grating steel
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of grating steel | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Walkways and Platforms | Enhanced safety and durability for pedestrian traffic | Local regulations, load-bearing specifications, and corrosion resistance requirements. |
| Oil & Gas | Drilling Platforms and Offshore Structures | Provides structural integrity in harsh environments | Compliance with industry standards, resistance to chemicals and extreme temperatures. |
| Manufacturing | Machine Guards and Safety Barriers | Protects personnel and equipment, reducing downtime | Customization options for sizes, load ratings, and surface treatments. |
| Water Treatment | Grating for Wastewater Treatment Plants | Facilitates efficient filtration and maintenance access | Resistance to corrosion and chemicals, ease of cleaning. |
| Transportation | Rail and Road Bridges | Supports heavy loads while ensuring safety and longevity | Material specifications, weight restrictions, and environmental impact considerations. |
Construction
In the construction industry, grating steel is widely used for walkways and platforms, ensuring safe pedestrian access across job sites. Its open design allows for efficient drainage and reduces the accumulation of water, which can pose slip hazards. Buyers in this sector must consider local building regulations and specific load-bearing requirements, especially in regions prone to heavy rainfall or flooding, such as parts of Africa and South America.
Oil & Gas
The oil and gas sector utilizes grating steel in drilling platforms and offshore structures, where it must withstand harsh environmental conditions. The material’s strength and durability are crucial for maintaining structural integrity in these demanding settings. International buyers should prioritize sourcing grating that meets rigorous industry standards for chemical resistance and can endure extreme temperatures, particularly in regions like the Middle East where such conditions are prevalent.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing facilities, grating steel serves as machine guards and safety barriers, providing essential protection for workers and machinery. This application helps to minimize accidents and downtime by creating a safer working environment. Buyers should look for customizable options that fit specific machine configurations, ensuring compliance with safety regulations while also considering load ratings and surface treatments to prevent wear over time.
Water Treatment
Grating steel is integral to wastewater treatment plants, where it is used for filtration systems and maintenance access points. Its design allows for efficient water flow while providing structural support. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the grating sourced is resistant to corrosion and chemicals, which are common in wastewater environments, facilitating easier maintenance and longevity of the infrastructure.
Transportation
In the transportation industry, grating steel is employed in the construction of rail and road bridges, where it must support significant loads. This application ensures safety and durability over time, especially in high-traffic areas. Key considerations for international buyers include material specifications to meet local weight restrictions and environmental impact assessments, particularly in Europe, where regulatory standards can be stringent.
Related Video: Standard Steel Grating 101:Materials, Design, and Applications
Strategic Material Selection Guide for grating steel
When selecting grating steel materials for various applications, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including performance characteristics, cost implications, and compliance with regional standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in grating steel, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is known for its strength and durability. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it has limited corrosion resistance unless treated.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: High strength-to-weight ratio, cost-effective, and easy to fabricate.
– Cons: Susceptible to rust and corrosion without protective coatings, which can lead to increased maintenance costs over time.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is ideal for environments where exposure to moisture is limited. It is commonly used in industrial settings, such as manufacturing plants and warehouses.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36 or equivalent. In regions with high humidity, additional protective measures like galvanization may be necessary to prolong lifespan.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance due to its chromium content. It can withstand a variety of chemicals and is suitable for both high and low-temperature applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Exceptional durability, low maintenance, and aesthetic appeal.
– Cons: Higher initial cost compared to carbon steel and more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is particularly effective in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and other industries where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for Buyers:
International buyers should look for compliance with standards like ASTM A304 or A316, which specify material quality. The choice of grade can affect pricing and suitability, so understanding local market preferences is essential.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It is not as strong as steel but compensates with its low weight and ease of handling.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Lightweight, resistant to rust, and easy to install.
– Cons: Lower load-bearing capacity compared to steel, which may limit its use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum grating is often used in environments where weight is a concern, such as in transportation and temporary structures.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with standards like ASTM B221. In regions with high temperatures, aluminum may perform better than steel, making it a preferred choice in hot climates.
4. Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP)
Key Properties:
FRP is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and non-conductive. It can withstand harsh chemicals and is suitable for various environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, low weight, and high strength-to-weight ratio.
– Cons: Higher cost and potential for UV degradation if not properly treated.
Impact on Application:
FRP is ideal for chemical processing plants, water treatment facilities, and other applications where corrosion is a significant concern.
Considerations for Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with industry-specific standards and consider the local climate’s impact on material longevity. Understanding the specific chemical compatibility is crucial for effective application.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for grating steel | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Industrial settings, manufacturing plants | High strength-to-weight ratio | Susceptible to rust without coating | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Exceptional durability and hygiene | Higher initial cost | High |
| Aluminum | Transportation, temporary structures | Lightweight and easy to install | Lower load-bearing capacity | Medium |
| Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic | Chemical processing, water treatment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, potential UV degradation | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with a comprehensive understanding of the options available for grating steel. By considering the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific regional factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for grating steel
Manufacturing Processes for Grating Steel
The manufacturing process for grating steel involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards. Understanding these stages is vital for B2B buyers, as it impacts product reliability and performance.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. High-quality steel, typically carbon steel or stainless steel, is selected based on the specific application requirements. The materials are then cut to size using precision cutting methods, such as shearing or sawing, to ensure uniformity. Buyers should inquire about the source of the raw materials, as reputable suppliers often provide traceability documentation, ensuring compliance with international standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Forming
In the forming stage, the cut steel is processed into the desired shapes. This can involve various techniques such as:
- Welding: This is a common method used to create the grids and frames of grating steel. It is crucial to use qualified welders and appropriate welding techniques to ensure structural integrity.
- Punching: Holes are punched into the steel to create openings for drainage or ventilation. The punching process needs to be precise to maintain the grating’s load-bearing capacity.
- Bending: Depending on design requirements, steel may be bent to achieve specific shapes. The bending process should be controlled to prevent material fatigue.
Assembly
After forming, the next phase is assembly. This involves combining different components of the grating, such as the bars and frames, into a final product. Assembly can involve mechanical fastening methods like bolts or additional welding. It is essential for buyers to confirm that the assembly process adheres to relevant engineering standards to ensure the product’s reliability.
Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the durability and aesthetics of grating steel. Common finishing techniques include:
- Hot-Dip Galvanization: This process involves coating the steel with zinc to prevent corrosion, which is particularly important for outdoor applications or environments exposed to moisture.
- Powder Coating: This provides a protective layer and can add color to the grating, enhancing its visual appeal.
- Passivation: For stainless steel grating, passivation is used to enhance corrosion resistance by removing free iron from the surface.
Quality Assurance in Grating Steel Production
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the manufacturing of grating steel, ensuring that the products meet both international and industry-specific standards. B2B buyers should be well-versed in these standards to make informed purchasing decisions.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This is a globally recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). Suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking is mandatory for construction products, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that the products can withstand harsh conditions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet predefined specifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers maintain thorough records of IQC results.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitoring the manufacturing process itself is critical. Regular inspections should be conducted to identify and rectify any deviations from the established procedures.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, finished products undergo comprehensive testing and inspection. This step ensures that the final product adheres to all relevant standards and specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to verify the quality of grating steel, including:
- Load Testing: This assesses the load-bearing capacity of the grating, ensuring it can withstand the intended application.
- Corrosion Testing: For galvanized or stainless steel, corrosion resistance tests determine the longevity of the protective coatings.
- Visual Inspections: Regular visual checks can identify surface defects, weld quality, and overall finish.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must adopt proactive strategies to verify supplier quality control measures:
- Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality management systems. Buyers should consider conducting both announced and unannounced audits to get a true picture of operations.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their QC practices and outcomes. This includes documentation of IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices. This is particularly important for international buyers who may face challenges in assessing local suppliers.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must be aware of specific nuances that may affect their procurement processes:
- Local Standards: Each region may have its own set of standards that suppliers must meet. Buyers should ensure that the products comply with both local and international standards to avoid potential legal and operational issues.
- Logistics and Shipping: Quality can also be affected during shipping. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust packaging and transport protocols to prevent damage during transit.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural differences in business practices can enhance communication and expectations regarding quality. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better quality outcomes.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices is essential for B2B buyers of grating steel. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can ensure they procure high-quality products that meet their specific needs and standards.
Related Video: Amazing Scale! Process of Making I-Beam with Metal Scrap. Korean Steel Factory
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for grating steel Sourcing
When sourcing grating steel, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is critical for international B2B buyers, especially from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and offers actionable buyer tips to ensure effective procurement.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the raw material itself, typically carbon steel or stainless steel. Prices can fluctuate based on global demand, supply chain disruptions, and the volatility of metal markets. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with stable pricing.
-
Labor: This includes wages for skilled workers involved in the manufacturing process. In regions with high labor costs, such as Europe, this can significantly affect the overall price. Conversely, sourcing from areas with lower labor costs may yield savings but may compromise quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead costs, such as utilities, maintenance, and facility expenses, are essential to factor in. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce these costs, which is why evaluating the supplier’s operational efficiency is vital.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specific tooling, which can add to the cost. It is crucial to assess whether the supplier has the necessary tools or if additional investments are needed.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures product reliability but adds to the cost. Suppliers that are certified (e.g., ISO 9001) may charge a premium for their products, reflecting their commitment to quality.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and the complexity of delivery. Understanding the logistics involved, including potential tariffs and duties, is essential for accurate cost assessment.
- Margin: Finally, suppliers will add their profit margin, which can vary widely depending on market conditions and competitive landscape.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of grating steel:
- Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk purchases often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their consumption needs to negotiate better terms.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications may incur higher costs due to additional tooling and processing requirements.
- Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials affects pricing. Stainless steel, for example, is typically more expensive than carbon steel.
- Quality/Certifications: Higher quality and certified products usually come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certification against potential cost savings.
- Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their proven track record.
- Incoterms: Understanding the shipping terms (Incoterms) can significantly impact the final cost. Different terms shift responsibilities for costs and risks between buyer and seller.
Buyer Tips
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing grating steel, consider the following strategies:
- Negotiate Effectively: Leverage volume commitments to negotiate better pricing. Establish long-term relationships with suppliers for favorable terms.
- Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider costs associated with maintenance, installation, and potential downtime.
- Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, European suppliers might have higher compliance costs, while suppliers in South America may offer more competitive rates due to lower labor costs.
- Conduct Market Research: Regularly assess market trends and fluctuations in material costs. This knowledge can empower buyers during negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices for grating steel can vary based on numerous factors, and the information provided is indicative. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential grating steel Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘grating steel’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for grating steel
Grating steel is a vital component in various industrial applications, providing safety, support, and durability. Understanding its essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing materials from different regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section outlines key specifications and commonly used trade terms to facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Key Technical Properties of Grating Steel
-
Material Grade
– Grating steel is often categorized by material grade, which indicates the chemical composition and mechanical properties of the steel. Common grades include carbon steel (e.g., ASTM A36), stainless steel (e.g., ASTM A304), and aluminum. Each grade has specific strength, corrosion resistance, and weldability characteristics. Buyers should select the grade that aligns with their application requirements, such as load-bearing capacity and environmental conditions. -
Load Capacity
– The load capacity of grating steel refers to the maximum weight the grating can support without failure. This property is crucial for applications in industrial flooring, walkways, and platforms. Load capacity is typically expressed in pounds per square foot (PSF) or kilograms per square meter (KSM). Understanding load specifications ensures safety and compliance with industry standards. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the permissible limits of variation in dimensions and weight of grating steel. It includes specifications for thickness, width, and length, which are essential for ensuring proper fit and functionality in the intended application. Tight tolerances are critical in projects where precision is required, such as in machinery or structural components. -
Finish Type
– The finish type describes the surface treatment of the grating steel, which can affect its durability and aesthetic appeal. Common finishes include hot-dip galvanized, powder-coated, and painted. Each finish offers different levels of corrosion resistance and visual characteristics, impacting maintenance needs and longevity in various environments. -
Bar Spacing
– Bar spacing refers to the distance between the steel bars in the grating. It is a critical design factor that influences both safety and drainage. Wider spacing may be suitable for pedestrian traffic, while narrower spacing is often required for heavy machinery. Buyers must consider the intended use to select appropriate bar spacing.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications helps buyers identify suppliers capable of providing high-quality grating steel that meets specific design and performance criteria. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for B2B buyers as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with project sizes and budget constraints. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications, quantities, and delivery requirements. For international buyers, a well-structured RFQ is essential for obtaining competitive pricing and ensuring clarity in communication with suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are a set of globally recognized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and freight costs. Familiarity with Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for B2B transactions, as they help mitigate risks and clarify obligations in international trade. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the period between placing an order and receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to ensure timely delivery, especially when sourcing materials across international borders.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement processes for grating steel, ensuring they meet safety standards and project specifications while optimizing costs and logistics.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the grating steel Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global grating steel market is experiencing a notable shift driven by several key factors. Urbanization and infrastructure development across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are propelling demand for durable and versatile materials like grating steel. The construction industry is particularly robust in these regions, with projects ranging from commercial buildings to public infrastructure, necessitating reliable flooring solutions.
Emerging technologies are also reshaping sourcing trends in the grating steel sector. Innovations such as 3D printing and advanced manufacturing techniques are enabling suppliers to create customized solutions that meet specific client needs. Additionally, the rise of digital procurement platforms is streamlining the sourcing process, allowing buyers to compare prices, quality, and delivery times more efficiently. This tech-driven approach is particularly beneficial for international buyers, as it minimizes time zone barriers and enhances transparency.
Furthermore, supply chain resilience has become a priority due to recent global disruptions. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer flexible logistics and consistent quality despite potential geopolitical tensions or supply shortages. Companies that can demonstrate their ability to adapt to changing market conditions will have a competitive edge.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a secondary consideration; it is at the forefront of decision-making for B2B buyers in the grating steel sector. The environmental impact of steel production is significant, with high carbon emissions associated with traditional manufacturing processes. As a result, many companies are seeking sustainable alternatives, such as recycled steel or products made with lower carbon footprints.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical supply chains are equally critical. Buyers are increasingly demanding transparency regarding the sourcing of raw materials and the working conditions in production facilities. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) standards are becoming essential for suppliers looking to build credibility in the market. By prioritizing suppliers with robust sustainability practices, buyers can enhance their own brand’s reputation and align with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Additionally, exploring green certifications can provide buyers with a competitive advantage. Products that meet stringent environmental criteria not only appeal to eco-conscious consumers but can also qualify for government incentives or tax breaks, further incentivizing sustainability in sourcing.
Brief Evolution/History
The grating steel industry has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from basic utility applications to sophisticated architectural and industrial solutions. Historically, grating steel was primarily used in industrial settings for safety and efficiency. However, advancements in design and manufacturing have expanded its applications into commercial and residential spaces, where aesthetics and versatility are equally important.
In recent years, the rise of modular construction techniques has further propelled the use of grating steel. This evolution reflects broader trends in the construction industry, where speed, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability are paramount. As international buyers navigate this dynamic market, understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into current trends and future opportunities.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of grating steel
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of grating steel?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in the grating steel sector. Request references from previous clients and check online reviews. Additionally, evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, quality assurance processes, and compliance with international standards. For international buyers, ensure the supplier can navigate export regulations specific to your region, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
Can I customize grating steel products to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for grating steel. This can include variations in size, material, and load capacity. When discussing customization, be clear about your requirements and specifications. It’s also advisable to request samples to assess the quality of the customized product before placing a large order. Ensure that the supplier can accommodate your customization requests within your project timelines. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for grating steel?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can vary significantly based on the supplier and product specifications. Commonly, MOQs range from a few tons to several hundred, depending on the type of grating. Lead times can also vary, often ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s crucial to communicate your timelines with suppliers early in the negotiation process. If you require smaller orders, inquire about flexibility or alternatives like stock items. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing grating steel?
Payment terms for grating steel typically include options like upfront payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. International transactions may involve additional complexities, such as currency fluctuations and banking fees. Negotiate terms that protect both parties, ensuring you understand the implications of each option. Always review payment conditions in the contract, and consider using escrow services for large transactions to mitigate risks. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for grating steel products?
To ensure quality, request documentation of certifications that meet international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Suppliers should provide test reports for the materials used and evidence of compliance with safety and performance standards relevant to your industry. Conducting an on-site audit of the supplier’s facilities can also provide insights into their quality control processes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing grating steel?
Logistics are critical when importing grating steel, particularly regarding shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Work with a logistics partner experienced in handling industrial materials to streamline the import process. Understand the costs associated with shipping, insurance, and duties, and factor these into your budget. Ensure that the supplier is familiar with exporting to your country and can provide necessary documentation for customs. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
Disputes can arise over quality, delivery, or payment issues. To mitigate risks, establish clear terms in your contract, including dispute resolution mechanisms such as mediation or arbitration. Maintain open communication with your supplier and document all interactions. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it amicably before escalating it. Having a legal framework in place, tailored to international trade laws, can also help protect your interests. -
How do I stay informed about market trends in the grating steel industry?
Staying informed about market trends requires ongoing research and engagement with industry networks. Subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and join professional associations related to steel and manufacturing. Networking with other B2B buyers and suppliers can provide insights into emerging trends, pricing fluctuations, and innovations in grating steel products. Utilize online platforms and forums to exchange knowledge and experiences with peers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for grating steel
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of grating steel presents a pivotal opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key takeaways from this guide highlight the importance of establishing reliable supplier relationships, leveraging local and global market insights, and optimizing procurement processes to enhance cost-efficiency.
Investing in quality grating steel not only ensures compliance with safety and performance standards but also fosters long-term operational efficiency. Diversifying sourcing options can mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and price volatility, particularly in an increasingly interconnected global market.
Looking ahead, B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace innovative sourcing strategies, such as integrating digital procurement tools and fostering partnerships with local manufacturers to capitalize on regional advantages. Act now to align your sourcing strategies with future trends, ensuring your operations are resilient and competitive in the dynamic landscape of grating steel procurement. Your proactive approach today can secure a stronger foundation for your business tomorrow.