Master Sourcing Strategies for Spring Lock Mechanism: A B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for spring lock mechanism
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing, the spring lock mechanism stands out as a crucial component that ensures the reliability and safety of countless applications. From automotive systems to industrial machinery, these mechanisms play a pivotal role in enhancing product functionality and user safety. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Colombia and France—understanding the intricacies of spring lock mechanisms is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of spring lock mechanisms, exploring their materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. It also provides valuable insights into the selection of reputable suppliers, offering a detailed analysis of cost factors and market trends. By addressing common questions and concerns, the guide empowers buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing these essential components effectively.
Armed with this knowledge, international buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, mitigate risks, and foster strong supplier relationships. Whether you are looking to optimize your supply chain or ensure compliance with industry standards, this guide serves as an indispensable resource for making well-informed decisions in the global market for spring lock mechanisms.
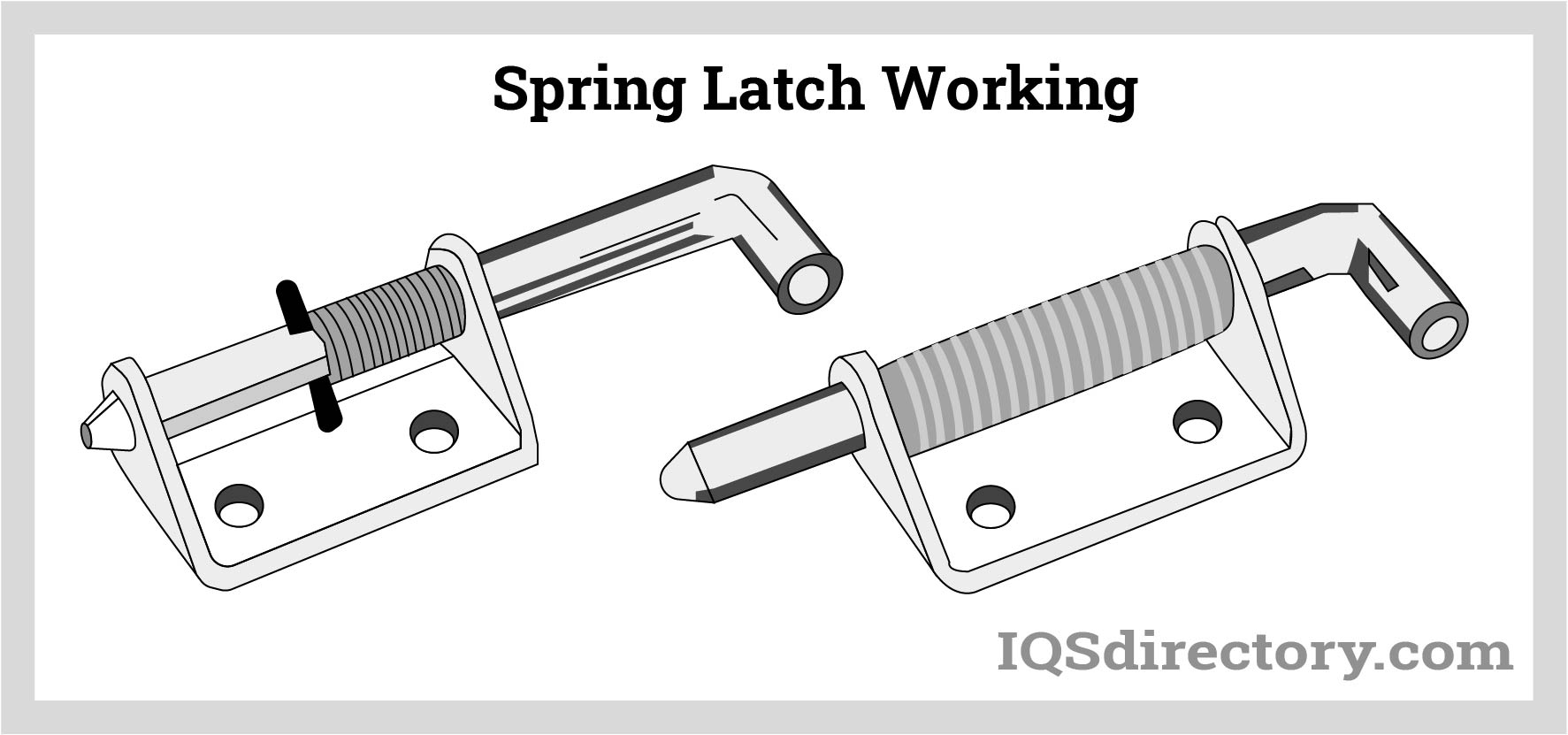
Understanding spring lock mechanism Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compression Spring Lock | Utilizes a coil spring to maintain tension; compact design | Automotive, machinery, electronics | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective; Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Tension Spring Lock | Operates under tension, providing a strong hold; suitable for dynamic loads | Industrial equipment, safety devices | Pros: High strength, good for dynamic loads; Cons: Requires precise installation. |
| Gas Spring Lock | Uses gas pressure for locking; adjustable force options | Furniture, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Smooth operation, adjustable; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Locking Pin Mechanism | Features a pin that secures components in place; often manually operated | Construction equipment, machinery assembly | Pros: Reliable locking, easy to operate; Cons: Manual operation can be inconvenient. |
| Magnetic Spring Lock | Uses magnetic force for locking; often integrated into electronic systems | Consumer electronics, security systems | Pros: Quick release, minimal wear; Cons: May be affected by external magnetic fields. |
Compression Spring Lock
Compression spring locks are characterized by their use of a coil spring that maintains tension within a compact design. These locks are prevalent in automotive applications, machinery, and electronic devices where space constraints are a consideration. B2B buyers should note that while compression spring locks are cost-effective and simple to manufacture, they may have limitations in load capacity, making them less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Tension Spring Lock
Tension spring locks operate under tension, providing a robust hold that can withstand dynamic loads. This type of lock is commonly found in industrial equipment and safety devices, where reliability is crucial. For B2B buyers, the strength of tension spring locks is a significant advantage; however, precise installation is necessary to ensure optimal performance, which may require specialized knowledge or tools.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Gas Spring Lock
Gas spring locks utilize gas pressure to achieve locking mechanisms and often come with adjustable force options. They are widely used in furniture, automotive applications, and aerospace industries. The smooth operation and adjustability of gas spring locks make them appealing to B2B buyers. However, the higher initial cost may be a barrier for some businesses, particularly in cost-sensitive markets.
Locking Pin Mechanism
Locking pin mechanisms feature a pin that secures components in place, often requiring manual operation. These locks are extensively used in construction equipment and machinery assembly, where reliable locking is essential. B2B buyers appreciate the straightforward operation and reliability of locking pin mechanisms, but the manual nature of their operation can be inconvenient in fast-paced environments.
Magnetic Spring Lock
Magnetic spring locks employ magnetic force to secure items, making them ideal for integration into electronic systems. Common applications include consumer electronics and security systems. B2B buyers benefit from the quick release and minimal wear associated with magnetic spring locks; however, they should consider the potential impact of external magnetic fields on performance, which could affect reliability in certain environments.
Related Video: 1. Risk Communication. Models. Definitions
Key Industrial Applications of spring lock mechanism
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of spring lock mechanism | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine assembly and panel fastening | Enhances assembly speed, reduces component failure. | Quality certifications, compatibility with existing systems, and availability of custom sizes. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft door and hatch locking systems | Increases safety and reliability in critical operations. | Compliance with aviation standards, weight considerations, and corrosion resistance. |
| Construction | Scaffolding and temporary structures | Provides secure and adjustable connections for safety. | Load capacity, durability, and ease of installation. |
| Furniture | Adjustable furniture mechanisms | Offers flexibility and ease of use for end-users. | Aesthetic design, strength, and integration with various materials. |
| Electronics | Device casing and battery compartments | Ensures secure assembly and user safety. | Precision in dimensions, material properties, and thermal resistance. |
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, spring lock mechanisms are crucial for engine assembly and panel fastening. These mechanisms enhance assembly speed and reduce the risk of component failure, which is vital in high-performance vehicles. International B2B buyers must ensure that the spring locks meet stringent quality certifications and are compatible with existing systems. Additionally, buyers should consider the availability of custom sizes to fit specific automotive designs.
Aerospace Applications
In aerospace, spring locks are utilized in aircraft door and hatch locking systems. They play a critical role in enhancing safety and reliability during flight operations. Buyers in this sector need to prioritize compliance with aviation standards, ensuring that the mechanisms can withstand extreme conditions. Weight considerations are also essential, as is the need for corrosion-resistant materials that can endure harsh environments.
Construction Applications
The construction industry employs spring lock mechanisms in scaffolding and temporary structures. These mechanisms provide secure and adjustable connections that are vital for worker safety. When sourcing these components, businesses should focus on load capacity and durability to ensure they can withstand various environmental conditions. Ease of installation is another crucial factor, as it can significantly impact project timelines.
Furniture Applications
In the furniture sector, spring lock mechanisms are used in adjustable furniture designs, such as height-adjustable desks and modular seating. These mechanisms provide flexibility and ease of use, enhancing user experience. Buyers should consider the aesthetic design of the locks, ensuring they complement the overall look of the furniture. Additionally, the strength of the mechanism is essential to support varying weights and usage scenarios.
Electronics Applications
Within the electronics industry, spring locks are essential for securing device casings and battery compartments. They ensure the safe assembly of components, which is crucial for user safety and product longevity. Buyers should focus on precision in dimensions to facilitate seamless integration into electronic devices. Furthermore, material properties such as thermal resistance can be critical, especially in devices that generate heat during operation.
Related Video: Self locking expanding mechanism 1 outer spring
Strategic Material Selection Guide for spring lock mechanism
When selecting materials for spring lock mechanisms, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in spring lock mechanisms, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 800°C). It is also non-magnetic, which can be advantageous in certain applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it ideal for environments exposed to moisture or corrosive substances. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for applications where hygiene is critical, such as in food processing or medical devices. Its resistance to rust and staining ensures longevity in these environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 or DIN 1.4301 for stainless steel grades. Import regulations may vary, so understanding local standards is crucial.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel offers a good balance of strength and ductility, with temperature ratings up to 400°C. It is less resistant to corrosion than stainless steel but can be treated to improve its durability.
Pros & Cons: This material is cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for various applications. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its use in harsh environments unless properly coated.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is commonly used in automotive and industrial applications where strength is prioritized over corrosion resistance. It is suitable for dry environments or where protective coatings can be applied.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider the local climate and whether additional coatings or treatments are necessary to enhance corrosion resistance. Compliance with standards like ASTM A36 is also important.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. It has a lower melting point (around 900°C) and good electrical conductivity.
Pros & Cons: The aesthetic appeal and ease of machining make brass a preferred choice for decorative applications. However, it is softer than steel, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in applications requiring good corrosion resistance and conductivity, such as electrical connectors and decorative locks. Its use in marine environments is particularly advantageous due to its resistance to saltwater corrosion.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 for brass materials. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for marine applications can help in selecting the right grade.
Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties: Plastics, particularly high-performance polymers like nylon or polycarbonate, offer lightweight properties, good chemical resistance, and temperature ratings up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantages of plastic include low weight and resistance to corrosion. However, plastics can be less durable under high-stress conditions and may degrade over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: Plastic spring locks are often used in consumer products and applications where weight savings are critical. They are suitable for indoor use or environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is limited.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the selected plastic complies with relevant standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties. Additionally, understanding the environmental conditions the product will face is essential for material selection.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for spring lock mechanism | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical devices | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Steel | Automotive, industrial applications | Cost-effective, strong | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Brass | Electrical connectors, decorative locks | Aesthetic appeal, good machinability | Softer, limited high-stress use | Medium |
| Plastic (Polymer) | Consumer products, lightweight applications | Lightweight, chemical resistance | Less durable under stress | Low |
This comprehensive analysis of materials for spring lock mechanisms provides B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and compliance with international standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for spring lock mechanism
Manufacturing Processes for Spring Lock Mechanism
The manufacturing of spring lock mechanisms involves several intricate stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product meets the required specifications for functionality and durability. Below is a breakdown of the typical manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures pertinent to B2B buyers in international markets.
1. Material Preparation
Selection of Raw Materials
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection of appropriate raw materials. Common materials used for spring lock mechanisms include carbon steel, stainless steel, and sometimes specialized alloys, depending on the application. For buyers, understanding the grade and specifications of materials is essential, as these factors significantly influence the product’s performance and longevity.
Material Treatment
Once materials are selected, they often undergo treatments such as annealing or hardening to enhance their mechanical properties. These processes improve ductility, tensile strength, and resistance to wear and corrosion, essential for the durability of spring locks.
2. Forming
Techniques Used
The forming stage typically employs techniques such as stamping, forging, or CNC machining.
- Stamping is often used for high-volume production, allowing for precise shaping of metal sheets into specific geometries required for the spring lock.
- Forging improves the grain structure of the material, enhancing strength and resilience, which is particularly beneficial for high-stress applications.
- CNC Machining allows for intricate designs and tighter tolerances, providing flexibility for custom orders.
For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, understanding these techniques can help in assessing the capabilities and technological advancements of potential suppliers.
3. Assembly
Assembly Techniques
After forming, the components are assembled using methods such as riveting, welding, or the use of fasteners. Each method has its advantages, and the choice often depends on the design and required strength of the final product.
- Riveting is widely used for its reliability and ease of automation, suitable for mass production.
- Welding provides a permanent joint, essential for components that will face extreme conditions.
Importance of Precision
Ensuring precision during assembly is vital, as even minor misalignments can lead to functional failures. Buyers should inquire about the assembly techniques used by suppliers and the level of automation, as this impacts both quality and cost-efficiency.
4. Finishing
Surface Treatments
The finishing stage includes processes such as plating, coating, and polishing, aimed at enhancing aesthetic appeal and corrosion resistance. Common finishes include zinc plating, powder coating, and passivation for stainless steel components.
Quality of Finish
The quality of the finish can affect both the performance and longevity of the spring lock mechanism. Buyers should request specific details about finishing processes and their compliance with relevant industry standards, particularly when sourcing from diverse regions.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for spring lock mechanisms, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
1. International and Industry Standards
ISO 9001 Certification
ISO 9001 is a widely recognized standard for quality management systems. Suppliers with this certification have demonstrated their commitment to quality, which can be a significant factor for international buyers.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to ISO 9001, other certifications like CE marking for products sold within the European Economic Area, and API (American Petroleum Institute) specifications for products used in the oil and gas industry, may apply. Buyers should verify that their suppliers hold the necessary certifications relevant to their industry.
2. Quality Control Checkpoints
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This initial checkpoint involves inspecting materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust IQC processes to catch any defects early on.
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
During manufacturing, IPQC helps monitor processes and detect issues in real time. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) can be beneficial here.
Final Quality Control (FQC)
Before shipping, FQC involves thorough inspections and testing of the finished products to ensure they meet specifications. Common tests include mechanical performance tests, dimensional checks, and corrosion resistance assessments.
3. Common Testing Methods
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of materials.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses the durability of the spring lock under cyclic loading conditions.
- Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the resistance of materials to corrosion in various environments.
Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed reports of these tests to ensure compliance with expected quality standards.
4. Verifying Supplier Quality Control
Audits and Inspections
Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management practices. Buyers can arrange for third-party inspections to validate the quality control processes and ensure compliance with international standards.
Documentation and Reporting
Requesting detailed quality reports, including certificates of compliance and test results, can help buyers verify that products meet necessary specifications. This documentation is particularly crucial for international transactions, where standards may vary significantly across regions.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for spring lock mechanisms is essential for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets. By focusing on material quality, manufacturing techniques, and robust quality control systems, buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing these critical components. Engaging with suppliers that prioritize quality and compliance not only reduces risks but also enhances the reliability of the products they deliver.
Related Video: Factory IO – Production Line Project ( Programmed using Control IO and Tia Portal )
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for spring lock mechanism Sourcing
When sourcing spring lock mechanisms, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing influences is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will break down the cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips tailored to the needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in spring lock mechanisms include steel, brass, and plastics. Prices can fluctuate based on global commodity markets and local availability. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with lower raw material costs to optimize expenses.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. For instance, countries in Africa and South America may offer lower labor costs compared to Europe. However, it’s important to factor in the skill level required for assembly and quality assurance.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and other operational costs. Manufacturers in regions with high energy prices or stringent labor laws may have higher overhead, affecting the overall pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers should inquire about these costs upfront and consider their impact on the unit price, particularly for smaller orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is essential, and associated costs can vary based on the manufacturer’s QC processes. Higher quality certifications (like ISO standards) may increase costs but could enhance product reliability and reduce returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and freight insurance are critical components of the total cost. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) will dictate who bears these costs, significantly impacting pricing strategies.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can help in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should evaluate their needs against MOQ requirements to negotiate better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can increase costs. Clear communication of specifications can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with higher quality standards or certifications often come at a premium. However, they can lead to lower failure rates and warranty claims, enhancing long-term value.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capacity can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can significantly affect pricing. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties can help buyers make informed decisions.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing. Establishing a long-term relationship may lead to better terms over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Always assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential replacement costs. This approach ensures that you’re not just looking at the upfront price.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and international shipping costs. Working with suppliers who can provide stable pricing over long-term contracts may mitigate risks.
-
Local Market Insights: Buyers from regions such as Africa and South America should leverage local market knowledge to identify competitive suppliers. Networking and attending industry trade shows can provide valuable insights into pricing trends.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always seek multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before finalizing any sourcing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential spring lock mechanism Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘spring lock mechanism’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for spring lock mechanism
When considering the procurement of spring lock mechanisms, understanding their technical properties and the terminology used in the industry is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge can significantly influence decision-making, from sourcing to negotiations.
Key Technical Properties of Spring Lock Mechanisms
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type and quality of material used in manufacturing the spring lock mechanism, such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or brass.
– Importance: Material grade affects durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For buyers, selecting the right material ensures the lock will withstand environmental factors, especially in regions with harsh climates like parts of Africa or South America. -
Spring Force
– Definition: The amount of force exerted by the spring when it is compressed or extended.
– Importance: Knowing the spring force is crucial for applications requiring specific locking mechanisms. Buyers should ensure that the force meets their operational requirements, as insufficient force can lead to malfunction. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the manufacturing process.
– Importance: Tight tolerances ensure a precise fit and function, which is vital for the reliability of the lock mechanism. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can help assess quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
Finish Type
– Definition: The surface treatment applied to the lock, such as plating, powder coating, or anodizing.
– Importance: The finish not only affects aesthetic appeal but also enhances corrosion resistance and wear resistance. Buyers should evaluate finish types based on their specific use cases and environmental conditions.
- Locking Mechanism Type
– Definition: The specific design of the locking mechanism, such as pin tumbler, lever, or disc detainer.
– Importance: Different mechanisms offer varying levels of security and functionality. Understanding the types helps buyers choose locks that align with their security needs and operational requirements.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often deal with OEMs for custom parts. Knowing this term helps in sourcing reliable suppliers who can provide specific components tailored to their requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should confirm MOQs to avoid excess inventory and ensure they can meet demand without overcommitting. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and details for a specific product or service.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare multiple suppliers effectively. This process is vital for negotiating favorable terms and pricing, especially in competitive markets. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) related to international commercial law.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities and liabilities during the shipping process. This knowledge is essential for planning logistics and avoiding misunderstandings during cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when sourcing to ensure timely availability of locks.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that the spring lock mechanisms they procure meet their operational needs and quality standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the spring lock mechanism Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global spring lock mechanism market is experiencing significant growth, driven by rising demand in various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. International B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay informed about key market dynamics and emerging trends. Technological advancements are reshaping sourcing strategies, with automation and digital tools enhancing supply chain efficiency. For instance, implementing AI-driven demand forecasting can help businesses optimize inventory management and reduce lead times.
Moreover, sourcing trends indicate a shift towards local suppliers, particularly in light of recent disruptions in global supply chains. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that can demonstrate reliability and agility, which is particularly relevant for markets in Africa and South America where infrastructure may vary. The rise of e-commerce platforms tailored for B2B transactions is also noteworthy, enabling seamless connections between buyers and manufacturers. This trend allows for a broader selection of products and facilitates price comparisons, which is crucial for buyers looking to maximize value.
Finally, sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of sourcing decisions. Buyers are now seeking suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, which includes everything from energy-efficient manufacturing processes to responsible waste management. As the market evolves, B2B buyers must navigate these trends carefully to ensure they align with their strategic objectives and market demands.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is a critical concern for modern businesses, and the spring lock mechanism sector is no exception. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including resource depletion and pollution, is prompting buyers to seek suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing. This entails ensuring that raw materials are sourced responsibly and that manufacturing practices minimize ecological footprints.
Adopting green certifications and materials is becoming increasingly important. Buyers should look for suppliers who utilize recycled or eco-friendly materials in their spring lock mechanisms. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or ISO 50001 (Energy Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Furthermore, transparency in the supply chain is essential; buyers should inquire about the origin of materials and the supplier’s overall environmental policies.
Ethical sourcing not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also enhances brand reputation. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices are likely to attract more customers and foster loyalty, making it a strategic advantage in today’s market.
Brief Evolution/History
The spring lock mechanism has a rich history that reflects advancements in engineering and manufacturing. Initially developed for basic applications, these mechanisms have evolved to meet the increasing demands for safety and reliability in various industries. Over the years, innovations in materials science have enabled the production of stronger and more durable locks, which are crucial in sectors such as automotive and aerospace.
As the industry continues to evolve, the integration of smart technologies—such as electronic locking systems—has begun to reshape the landscape. This evolution not only highlights the importance of adaptability in manufacturing processes but also underlines the necessity for B2B buyers to stay updated on technological advancements and their implications for sourcing decisions. By understanding this history, buyers can better appreciate the capabilities of modern suppliers and the potential for future developments in the spring lock mechanism sector.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of spring lock mechanism
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of spring lock mechanisms?
When sourcing suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record in international trade. Check for certifications relevant to your industry, such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to read reviews and ratings. Consider requesting references from previous clients and conduct video calls to assess their manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, visiting the supplier’s facility can provide insights into their operations and quality control processes. -
What customization options are typically available for spring lock mechanisms?
Most suppliers offer customization based on your specific requirements, including dimensions, materials, and finishes. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and drawings to avoid misunderstandings. Ask about the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom products, as these may differ from standard offerings. It’s also prudent to inquire about lead times for custom orders, as they can significantly impact your production schedule. -
What are common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for spring lock mechanisms?
MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Typically, standard products may have lower MOQs, while custom orders could require larger quantities. Lead times generally range from a few weeks to several months, influenced by factors such as order complexity and the supplier’s production capacity. Always clarify these details upfront to align with your project timelines and inventory management strategies. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly by supplier and region. Common practices include upfront payments, deposits, and letters of credit. For large orders, negotiating partial payments based on milestones can mitigate risk. Always confirm the currency for transactions and be aware of any international banking fees. Utilizing secure payment platforms can also provide additional protection against fraud. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for?
Quality assurance is critical in manufacturing spring lock mechanisms. Look for suppliers with relevant certifications such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates adherence to quality management standards. Request documentation of quality control processes, including inspection reports and testing results. It may also be beneficial to conduct third-party audits or inspections to ensure compliance with your quality standards before finalizing orders. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing spring lock mechanisms?
When importing, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Work with a logistics provider experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. Ensure your supplier is familiar with export documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Additionally, factor in shipping times and costs, as these can significantly impact your overall budget and delivery schedules.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How can I resolve disputes with international suppliers?
Dispute resolution can be complex in international trade. To mitigate risks, include clear terms in your contracts regarding quality expectations, delivery timelines, and penalties for non-compliance. If disputes arise, attempt to resolve them through direct communication first. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration, which can be less costly than litigation. Always keep thorough documentation of communications and agreements to support your position. -
What are the best practices for maintaining communication with suppliers?
Effective communication is essential for successful international sourcing. Establish a regular schedule for updates and check-ins, utilizing tools like email, video calls, and project management software. Be clear and concise in your communication, and ensure that language barriers are addressed—consider employing bilingual staff or translation services if needed. Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance collaboration and responsiveness, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for spring lock mechanism
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing and product design, strategic sourcing of spring lock mechanisms is essential for international B2B buyers. By prioritizing quality, reliability, and supplier diversity, businesses can ensure optimal performance and longevity of their products. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage local suppliers where possible to reduce lead times and transportation costs, while also exploring global options for specialized needs.
Investing in strong supplier relationships fosters collaboration and innovation, enabling companies to adapt to market changes swiftly. It is crucial to conduct thorough market research to identify suppliers who not only meet technical specifications but also align with your company’s sustainability goals and ethical standards.
As we look ahead, the demand for advanced and customizable spring lock mechanisms will continue to grow. Embracing technological advancements and innovative materials will be key to staying competitive. B2B buyers are encouraged to actively engage in industry forums and trade shows to keep abreast of emerging trends and solutions. By taking these proactive steps, businesses can position themselves for success in an increasingly interconnected global market.