Master Sourcing Strategies for Spring Loaded Check Valves
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for spring loaded check valves
In today’s interconnected global market, spring loaded check valves play a pivotal role in ensuring the integrity and efficiency of fluid control systems across various industries. As silent guardians against backflow, these valves protect equipment from damage, enhance system performance, and maintain safety standards. Their importance is underscored in sectors such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, and water treatment, where even minor disruptions can lead to significant operational setbacks.
This comprehensive guide is designed specifically for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Nigeria and Thailand. It provides an in-depth exploration of spring loaded check valves, covering critical aspects such as types, materials, manufacturing and quality control standards, leading suppliers, and cost considerations. Additionally, the guide addresses frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns, empowering buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
By equipping stakeholders with valuable insights and actionable strategies, this guide not only simplifies the procurement process but also enhances the overall understanding of how spring loaded check valves can optimize operational efficiency and safety. Whether you are a seasoned buyer or new to the market, navigating the complexities of valve selection will become more manageable, ensuring that your projects run smoothly and cost-effectively.
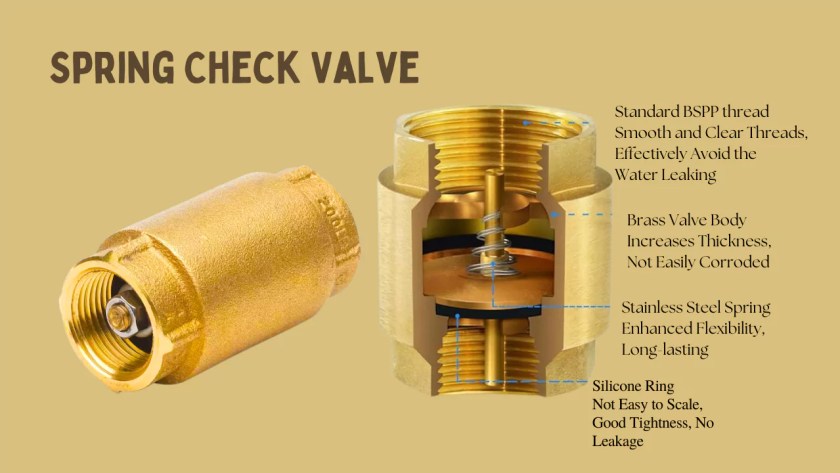
Understanding spring loaded check valves Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Spring Loaded Check Valve | Simple design, reliable one-way flow, spring-assisted closure | Water supply, HVAC systems | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to install; Cons: Limited to moderate pressure applications. |
| Dual Plate Check Valve | Compact design, lightweight, two plates for flow direction | Oil and gas, petrochemical industries | Pros: Reduced pressure drop, less space required; Cons: More complex and potentially higher cost. |
| Swing Check Valve | Disc pivots on a hinge, allows for large flow rates | Wastewater treatment, irrigation | Pros: High flow capacity, minimal maintenance; Cons: Bulky design may require larger installation space. |
| Piston Check Valve | Uses a piston mechanism for flow control | Hydraulic systems, heavy machinery | Pros: Handles high pressure and flow; Cons: More expensive and complex to maintain. |
| Spring Loaded Cartridge Check Valve | Integrated cartridge design, easy to replace | Industrial automation, fluid control | Pros: Simplified maintenance, versatile applications; Cons: Initial setup can be costly. |
Standard Spring Loaded Check Valve
Standard spring loaded check valves are characterized by their straightforward design, which features a spring mechanism that ensures the valve closes promptly when the flow direction reverses. These valves are widely used in water supply systems and HVAC applications due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. When purchasing, buyers should consider the valve’s pressure rating and whether it aligns with their specific application requirements, especially in terms of flow rates and operational conditions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Dual Plate Check Valve
The dual plate check valve is known for its compact and lightweight design, which includes two plates that open and close based on flow direction. This design minimizes pressure drop and is ideal for use in oil and gas or petrochemical industries, where space and efficiency are critical. Buyers should evaluate the valve’s material compatibility with their fluids and the installation space available, as these factors can influence performance and longevity.
Swing Check Valve
Swing check valves feature a disc that pivots on a hinge, allowing for large flow rates while preventing backflow. They are commonly used in wastewater treatment and irrigation systems. While they offer high flow capacity and low maintenance needs, their bulkier design requires more installation space. Buyers should assess the valve’s flow capacity and the specific installation requirements to ensure compatibility with their systems.
Piston Check Valve
Piston check valves utilize a piston mechanism to control flow, making them suitable for high-pressure applications in hydraulic systems and heavy machinery. They provide excellent flow control and reliability but come at a higher cost and complexity compared to other types. Buyers should consider the operational pressures and the potential need for specialized maintenance when choosing this valve type.
Spring Loaded Cartridge Check Valve
Spring loaded cartridge check valves feature an integrated cartridge design that simplifies maintenance, as the cartridge can be easily replaced without removing the entire valve. This versatility makes them suitable for various industrial applications, including fluid control and automation systems. While they may have higher initial costs, their ease of maintenance can lead to long-term savings. Buyers should evaluate compatibility with their system’s fluid characteristics and installation requirements to ensure optimal performance.
Related Video: Differences Between Swing Check Valves and Spring Check Valves
Key Industrial Applications of spring loaded check valves
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of spring loaded check valves | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Preventing backflow in pipelines | Protects equipment from damage and ensures safety. | Material compatibility with corrosive substances. |
| Water Treatment | Controlling flow in filtration systems | Enhances system efficiency and reduces maintenance costs. | Compliance with local regulations and standards. |
| Food & Beverage | Ensuring hygiene in processing systems | Maintains product integrity and prevents contamination. | Certification for food-grade materials. |
| HVAC Systems | Backflow prevention in cooling systems | Improves energy efficiency and system reliability. | Temperature and pressure ratings for specific applications. |
| Chemical Processing | Flow control in chemical transfer applications | Ensures safe handling of hazardous materials. | Resistance to chemicals and pressure ratings. |
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas sector, spring loaded check valves are crucial for preventing backflow in pipelines. This application safeguards pumps and other equipment from damage caused by reverse flow, which can lead to costly repairs and operational downtime. International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing valves made from materials that can withstand corrosive substances typically found in oil and gas operations.
Water Treatment
Spring loaded check valves are employed in water treatment facilities to control flow within filtration systems. By preventing backflow, these valves enhance the efficiency of the treatment process and minimize maintenance costs associated with equipment wear. Buyers in South America and Europe need to consider local regulations regarding water quality and ensure that the valves comply with these standards.
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, spring loaded check valves are essential for maintaining hygiene in processing systems. They help prevent contamination by ensuring that liquids flow in one direction, thereby safeguarding product integrity. Buyers should look for valves certified for food-grade materials, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations, especially in regions with strict food safety standards.
HVAC Systems
Within HVAC systems, spring loaded check valves are used to prevent backflow in cooling applications. This function is vital for improving energy efficiency and maintaining system reliability. International buyers should evaluate the temperature and pressure ratings of the valves to ensure they meet the specific requirements of their HVAC systems, particularly in diverse climates across Africa and Europe.
Chemical Processing
In chemical processing, spring loaded check valves play a key role in flow control during the transfer of hazardous materials. Their ability to prevent backflow is essential for ensuring safe operations and protecting personnel from potential exposure. Buyers in this sector must focus on sourcing valves that offer resistance to a wide range of chemicals and meet the necessary pressure ratings for their applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for spring loaded check valves
When selecting materials for spring-loaded check valves, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence performance, durability, and compatibility with specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the manufacturing of these valves: Stainless Steel, PVC, UPVC, and Brass. Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle pressures exceeding 150 psi, depending on the grade.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel makes it suitable for harsh environments, particularly in oil and gas applications. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact overall project costs. Manufacturing processes for stainless steel can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive fluids, making it ideal for applications in chemical processing and food industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. The higher initial cost may be justified by the longevity and reliability of the product, especially in demanding environments.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: PVC is lightweight and has good resistance to chemicals and corrosion. It is typically rated for temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and can handle pressures around 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: The cost-effectiveness of PVC makes it a popular choice for many applications. However, its temperature and pressure limitations restrict its use in high-stress environments. Additionally, PVC can become brittle over time when exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application: PVC is suitable for non-potable water systems and chemical transport, but it is not recommended for high-temperature applications or where extreme pressure is present.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider local regulations regarding the use of PVC in potable water systems. Compliance with standards such as JIS can also be necessary.
UPVC (Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties: UPVC offers similar benefits to PVC but with improved strength and thermal stability. It can operate at temperatures up to 140°F (60°C) and pressures of around 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: UPVC is more durable than standard PVC and is resistant to corrosion and chemicals. However, like PVC, it has limitations in high-temperature applications. The manufacturing process is generally simpler than that of metals, reducing production costs.
Impact on Application: UPVC is widely used in water treatment and drainage systems, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify that UPVC products meet local and international standards, especially in the Middle East, where harsh conditions may affect performance.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its good corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. It typically operates at temperatures up to 200°F (93°C) and pressures around 150 psi.
Pros & Cons: Brass is relatively easy to machine and offers good durability. However, it is more susceptible to dezincification in certain environments, which can compromise its integrity over time. The cost of brass is generally moderate compared to stainless steel.
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in plumbing and heating applications due to its thermal conductivity and strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the environmental regulations regarding brass, particularly in Europe, where restrictions on lead content are strict. Compliance with standards such as ASTM is crucial.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for spring loaded check valves | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Oil & gas, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| PVC | Non-potable water systems, chemical transport | Cost-effective, lightweight | Limited temperature/pressure rating | Low |
| UPVC | Water treatment, drainage systems | Durable, good chemical resistance | Similar limitations as PVC | Med |
| Brass | Plumbing, heating applications | Good mechanical properties | Susceptible to dezincification | Med |
This strategic material selection guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, aiding them in making informed decisions based on application requirements, cost considerations, and compliance with relevant standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for spring loaded check valves
Manufacturing Processes for Spring Loaded Check Valves
The manufacturing of spring loaded check valves is a meticulous process that ensures both functionality and reliability. Understanding the stages involved can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers. Here’s a breakdown of the typical manufacturing process:
Material Preparation
-
Material Selection: The choice of materials is critical, as it affects the valve’s performance under various conditions. Common materials include UPVC, stainless steel, and brass, each offering different advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, durability, and temperature tolerance.
-
Material Treatment: Prior to forming, materials may undergo treatments such as heat treatment or surface hardening to enhance their properties. For example, stainless steel may be passivated to improve corrosion resistance.
-
Cutting and Shaping: The raw materials are cut into precise dimensions using CNC machines or laser cutting technology. This ensures that each component will fit together correctly during assembly.
Forming
-
Molding and Casting: For plastic components, injection molding is commonly used. In contrast, metal parts may be produced through die casting or forging, depending on the required strength and tolerances.
-
Spring Manufacturing: The springs used in check valves are typically produced using coiling machines that create the correct tension and dimensions. Quality control at this stage is crucial, as the spring’s performance directly impacts the valve’s functionality.
-
Machining: Following the initial forming, components may require additional machining to achieve exact specifications. This includes operations like drilling, turning, and grinding.
Assembly
- Component Assembly: Each part of the check valve, including the body, spring, and seat, is meticulously assembled. This step often involves the use of jigs and fixtures to ensure proper alignment and fit.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Sealing: Gaskets or O-rings are installed to ensure a tight seal, preventing leaks. The choice of sealing materials should be compatible with the fluids the valve will encounter.
-
Final Adjustments: The assembly process may include final adjustments to the spring tension, ensuring that the check valve opens and closes correctly under specified conditions.
Finishing
-
Surface Treatment: After assembly, valves may undergo surface treatments such as anodizing or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
-
Marking and Labeling: Each valve is marked with essential information, including model number, size, and certifications, making it easier for buyers to identify compliant products.
-
Packaging: Finally, the valves are carefully packaged to prevent damage during transportation, often with protective materials to safeguard against impacts.
Quality Assurance Processes
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of manufacturing spring loaded check valves, ensuring that each product meets international and industry-specific standards. Here’s how it typically unfolds:
Relevant International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Suppliers who are ISO 9001 certified have demonstrated their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards for valves used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products can withstand the rigorous demands of these environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards. This includes checking for certifications and conducting material tests.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted at various stages to catch defects early. This includes monitoring machinery calibration and adherence to operational procedures.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the valves are assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing, including pressure testing, leak testing, and functional testing to ensure they perform as expected.
Common Testing Methods
-
Hydrostatic Testing: This method checks for leaks by subjecting the valve to high-pressure water.
-
Air Testing: Used to assess the valve’s ability to hold pressure, air testing is often quicker and can be used for smaller components.
-
Performance Testing: Valves are tested under simulated operational conditions to ensure they open and close correctly.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take several steps to verify a supplier’s quality control processes:
-
Audits: Conducting supplier audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality management systems, and adherence to standards.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting documentation, such as inspection reports and certificates of compliance, provides insight into the supplier’s quality assurance practices.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital:
-
Local Regulations: Buyers must be aware of local standards and regulations that may differ from international norms. Ensuring compliance with both sets of standards can mitigate risks.
-
Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and service. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication and understanding.
-
Supply Chain Logistics: Consider the logistics of transporting valves across borders, including potential delays due to customs inspections or documentation requirements. Proper planning can help ensure timely delivery.
In conclusion, a robust understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for spring loaded check valves can empower B2B buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they source products that meet their operational needs effectively and reliably.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for spring loaded check valves Sourcing
When sourcing spring-loaded check valves, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will break down the various components that contribute to the overall cost, identify key price influencers, and offer actionable tips for buyers to optimize their procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary material used in manufacturing spring-loaded check valves often includes stainless steel, brass, or plastic composites. The choice of material significantly impacts the cost, with stainless steel typically being the most expensive due to its durability and resistance to corrosion.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with higher labor costs, such as those in Europe, may result in higher prices, while manufacturers in regions like Southeast Asia may offer more competitive pricing due to lower labor expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to factory operations, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead costs, which in turn can lower the final price of the valves.
-
Tooling: The investment in specialized tooling for valve production can be substantial. Custom tooling increases initial costs but may lead to better quality and lower unit costs for large production runs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes is essential, especially for critical applications in industries like oil and gas. QC costs are often included in the manufacturing price but can vary based on the supplier’s standards and certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can significantly affect the total price, particularly for international shipments. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties play a vital role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. This margin can vary based on market competition, brand reputation, and the perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often leads to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can increase costs. It’s essential to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO or API) may lead to increased costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these factors based on their application needs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and service can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects the pricing structure, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and risk. Understanding these terms is crucial for accurate cost calculations.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for large orders. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts or better payment terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower upfront cost may not always result in long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international buyers may face additional costs such as tariffs, import duties, and currency fluctuations. Factor these into your budget when sourcing.
-
Supplier Evaluation: Research potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for reviews, references, and case studies to ensure they meet your quality and service expectations.
-
Long-Term Relationships: Cultivating long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service in the future. Regularly review supplier performance and maintain open lines of communication.
Disclaimer
Prices for spring-loaded check valves can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. Always request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and stay informed about market trends.
Spotlight on Potential spring loaded check valves Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘spring loaded check valves’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for spring loaded check valves
Key Technical Properties of Spring Loaded Check Valves
When sourcing spring loaded check valves, understanding their technical specifications is crucial for ensuring compatibility with your operational needs. Here are some essential properties:
-
Material Grade: The material used in manufacturing check valves, such as stainless steel, UPVC, or brass, impacts durability and resistance to corrosion and temperature fluctuations. For instance, stainless steel is preferred in harsh environments due to its strength and resistance to chemicals. Selecting the appropriate material can reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of the valve.
-
Pressure Rating: This specification indicates the maximum pressure the valve can withstand without failure. Common ratings include ANSI classes (150, 300, 600) or PN ratings (10, 16, 25). Understanding the pressure requirements of your system is essential to prevent leaks or catastrophic failures, which can lead to costly downtime.
-
Flow Rate: Measured in liters per minute (L/min) or gallons per minute (GPM), the flow rate indicates how much fluid can pass through the valve in a given time. It is vital to match this specification with your system’s requirements to ensure optimal performance and prevent bottlenecks.
-
Tolerance: This refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of the valve. Tight tolerances ensure better sealing and reduced risk of leaks. In applications where precision is critical, such as pharmaceuticals or food processing, understanding tolerance levels can be essential for compliance with industry standards.
-
Size and Connection Type: The dimensions of the valve, including its diameter and the type of connections (e.g., threaded, flanged), determine how well it fits into existing piping systems. Ensuring proper sizing and connection compatibility can prevent installation issues and additional costs.
-
Temperature Range: The operating temperature range defines the limits within which the valve can function effectively. Selecting a valve that can handle the temperatures of your specific application is critical for preventing premature failure or performance issues.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and enhance negotiation efficacy. Here are several key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help you identify reliable suppliers and ensure that components meet quality standards.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for international purchases where shipping costs can be significant.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and availability for specific products. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms can prevent misunderstandings and disputes in international transactions by clarifying who bears costs and risks during shipping.
-
Lead Time: This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management, particularly in industries with tight schedules.
-
Certification: Refers to the documentation that confirms compliance with specific industry standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM). Certifications can be critical for ensuring product quality and safety, especially in regulated industries.
By familiarizing yourself with these properties and terms, you can make informed decisions when sourcing spring loaded check valves, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the spring loaded check valves Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for spring-loaded check valves is witnessing significant growth, driven by the rising demand for efficient fluid control systems across various sectors, including oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing. B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly seeking innovative solutions that enhance operational efficiency and reliability. The integration of advanced technologies, such as IoT and automation, is becoming prevalent, allowing for real-time monitoring and optimization of valve performance.
Emerging trends include a shift towards lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials, such as UPVC and PVDF, which are favored for their durability and lower maintenance costs. Furthermore, the move towards sustainable practices is influencing sourcing decisions, with buyers prioritizing manufacturers that adhere to eco-friendly production methods. This aligns with a broader industry focus on reducing environmental footprints and improving energy efficiency.
Additionally, the competitive landscape is evolving, with new entrants and established players alike investing in R&D to innovate valve designs. This creates opportunities for international buyers to access a wider range of products tailored to specific applications, enhancing the overall value proposition of their procurement strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability has become a crucial consideration in the procurement of spring-loaded check valves. Buyers are increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions, prompting a demand for suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices. This includes the use of environmentally friendly materials and processes that minimize waste and reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical supply chains are also gaining prominence, as businesses recognize the importance of ensuring that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and materials that are recyclable or biodegradable are becoming benchmarks for evaluating suppliers.
Moreover, buyers are encouraged to seek out valves that are designed for longevity and efficiency, as these contribute to reduced resource consumption over time. By prioritizing sustainability in their sourcing decisions, international B2B buyers can not only fulfill regulatory requirements but also enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of spring-loaded check valves can be traced back to the early days of industrialization when the need for reliable fluid control mechanisms became apparent. Initially, these valves were rudimentary, focusing primarily on preventing backflow. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of more sophisticated designs that offer enhanced performance and durability.
The introduction of new materials, such as thermoplastics and advanced alloys, has enabled the production of check valves that withstand harsh operating conditions. As industries have evolved, so too have the applications for these valves, expanding into sectors like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and renewable energy. Today, spring-loaded check valves are integral components in a wide array of systems, underscoring their importance in ensuring safety and efficiency in fluid management across diverse industries.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of spring loaded check valves
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of spring loaded check valves?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, product quality certifications (e.g., ISO, API), and customer testimonials. It’s crucial to assess their production capabilities and quality control processes. Request samples to evaluate the product firsthand. Additionally, check for compliance with international standards relevant to your region, especially if you’re sourcing from different continents. Engaging with suppliers who have local representation can also facilitate communication and support. -
Can I customize spring loaded check valves to meet specific requirements?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for spring loaded check valves, including size, material, and pressure ratings. When requesting customization, provide detailed specifications and application requirements. Discuss lead times for custom orders, as these may vary significantly. It’s advisable to work with suppliers who have experience in your industry to ensure that the customized valves meet regulatory and operational standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for spring loaded check valves?
MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the type of valve. Standard products might have lower MOQs, while customized valves generally require larger orders. Lead times can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on production schedules and customization requirements. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid delays in your supply chain, especially if your project has strict timelines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from international suppliers?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers and regions. Common methods include letters of credit, upfront deposits, or payment upon delivery. Be aware of currency exchange rates and potential transaction fees. Establish clear payment terms in your contract to protect both parties, and consider using escrow services for large transactions to mitigate risk. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for?
Look for suppliers that adhere to recognized quality assurance standards like ISO 9001 or specific industry certifications (e.g., API for oil and gas). Request documentation of their quality control processes, including testing methods for the valves. An effective QA process should include routine inspections, performance testing, and traceability of materials used in production. This ensures the valves will perform reliably in your applications. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping effectively when sourcing internationally?
Work with suppliers who have experience with international shipping and can provide Incoterms that clarify responsibilities for shipping costs, risks, and insurance. Consider using freight forwarders for complex logistics needs, especially when shipping to or from regions with strict customs regulations. Establish a clear timeline for shipping and delivery to ensure that your project stays on schedule, and factor in potential delays due to customs clearance. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with my supplier?
First, try to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication. If that fails, refer to your contract for dispute resolution procedures, which may include mediation or arbitration. Keeping detailed records of all communications and agreements can be invaluable. It’s also wise to engage legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to navigate disputes effectively and protect your interests. -
Are there specific regulations I need to be aware of when importing check valves?
Yes, importing check valves may involve compliance with various regional regulations, including safety standards, environmental regulations, and import tariffs. Familiarize yourself with the import regulations of your country and any documentation required for customs clearance. Engaging with a customs broker can help ensure compliance and facilitate the import process, reducing the risk of delays or fines.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for spring loaded check valves
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of spring loaded check valves presents an invaluable opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality and reliability, businesses can mitigate risks associated with backflow and ensure operational efficiency. The importance of selecting the right valve cannot be overstated; it is essential to consider factors such as material composition, design suitability, and the specific application requirements.
Furthermore, engaging with reputable suppliers who offer a comprehensive range of products and expert guidance can lead to enhanced safety and efficiency within your operations. As industries evolve and demand for high-performance components rises, now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies.
Take action today: Evaluate your current suppliers, explore innovative solutions, and ensure your operations are supported by the best check valves available. This proactive approach will not only safeguard your investments but also position your business for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Your commitment to strategic sourcing today will pave the way for sustainable growth tomorrow.