Mastering Shaft Coupling Types for Optimal B2B Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for shaft coupling types
In today’s interconnected global market, the significance of selecting the right shaft coupling types cannot be overstated. These mechanical devices are essential for ensuring the smooth transmission of power and torque between shafts, accommodating misalignments, and enhancing the longevity of machinery. For international B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Poland and Argentina—understanding the nuances of shaft couplings is pivotal in optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime.
This comprehensive guide delves into a wide array of shaft coupling types, detailing their specific applications, materials, and manufacturing processes. It also explores essential quality control measures and provides insights into sourcing reliable suppliers across the globe. Furthermore, buyers will gain access to information on pricing strategies and market trends, empowering them to make informed purchasing decisions.
By addressing frequently asked questions and presenting actionable insights, this guide equips B2B buyers with the tools necessary to navigate the complexities of the shaft coupling market. Whether you are enhancing an existing system or embarking on a new project, understanding the diverse options available will enable you to select the most suitable solutions tailored to your operational needs. Prepare to leverage this knowledge for strategic sourcing and to drive your business success in the global arena.
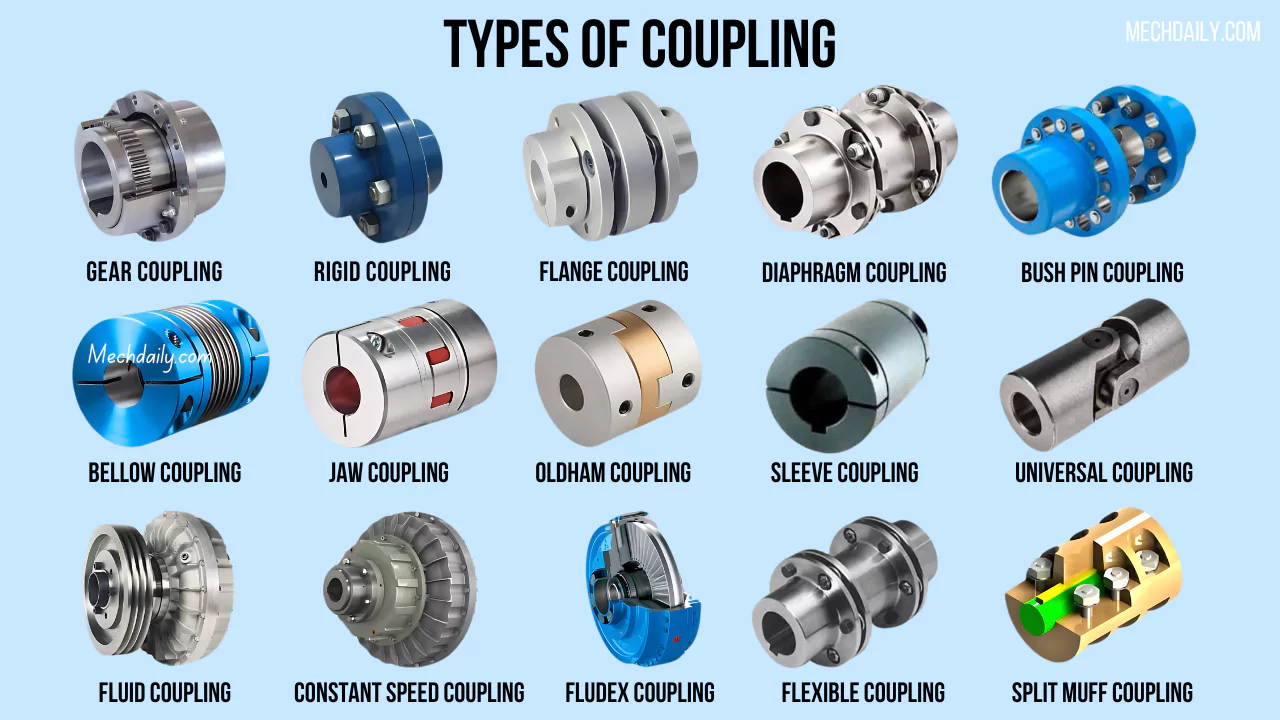
Understanding shaft coupling types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beam Couplings | Accepts small angular and parallel misalignments; zero-backlash designs available | Motion control applications | Pros: Lightweight, low cost. Cons: Limited torque capacity, not suitable for high power applications. |
| Bellows Couplings | High torsional stiffness; ideal for precision applications | Robotics, CNC machinery | Pros: Excellent for precise positioning. Cons: More expensive, limited misalignment tolerance. |
| Chain Couplings | Flexible design allowing significant misalignment; high power transmission | Heavy machinery, conveyor systems | Pros: Robust and durable, handles high torque. Cons: Requires regular maintenance, can be bulky. |
| Jaw Couplings | Composed of multi-jawed hubs; elastomeric spiders for vibration damping | Pumps, compressors, light machinery | Pros: Low backlash, easy to install. Cons: Limited angular misalignment capability. |
| Diaphragm Couplings | Flexible, with a thin membrane that accommodates misalignment | Aerospace, automotive applications | Pros: High torque capacity, excellent vibration dampening. Cons: Higher initial cost, complex installation. |
Beam Couplings
Beam couplings are characterized by their ability to handle small angular and parallel misalignments, typically up to 0.025 inches and 7 degrees, respectively. They are particularly suitable for motion control applications where precise positioning is crucial, such as in robotics and CNC machinery. When considering a beam coupling, buyers should evaluate the torque capacity, which is usually limited to less than 100 inch-lbs. Their lightweight construction and low cost make them an appealing option for many applications, but they may not be suitable for high-power transmissions.
Bellows Couplings
Bellows couplings are designed for high torsional stiffness, making them ideal for applications that require precise positioning, such as robotics and CNC machines. They consist of multiple metal convolutions that can tolerate some misalignment but are more rigid compared to beam couplings. B2B buyers should consider the application requirements for torsional stiffness and torque capacity, as these couplings are typically more expensive than others. Their advantages include excellent precision and durability, but they may not be the best choice for applications with significant misalignment.
Chain Couplings
Chain couplings are robust and flexible, allowing for significant angular and parallel misalignment. They are commonly used in heavy machinery and conveyor systems, where high power transmission is necessary. Buyers should note that while chain couplings can handle substantial torque loads, they require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Their durability and ability to accommodate misalignments make them a popular choice, but the bulkiness and maintenance requirements can be downsides for some applications.
Jaw Couplings
Jaw couplings consist of multi-jawed hubs that connect with elastomeric spiders to dampen vibrations and allow for slight misalignments. They are widely used in pumps, compressors, and light machinery. B2B buyers appreciate their low backlash and ease of installation, but they should also consider the limitations in angular misalignment, which can be less than 1 degree. Overall, jaw couplings provide a good balance of performance and cost-effectiveness for many applications.
Diaphragm Couplings
Diaphragm couplings utilize a flexible membrane to accommodate misalignment while transmitting torque. They are often found in aerospace and automotive applications due to their high torque capacity and excellent vibration dampening properties. Buyers should be aware that diaphragm couplings typically come with a higher initial cost and may require more complex installation processes. However, their ability to handle high loads and reduce vibrations makes them a valuable investment for critical applications.
Related Video: Coupling Selection Procedure | Complete Guide to Coupling Sizing Calculation | All Types of Coupling
Key Industrial Applications of shaft coupling types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of shaft coupling types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Power transmission in conveyor systems | Ensures efficient transfer of power, reducing downtime and maintenance costs | Consider torque capacity and misalignment tolerance for specific machinery |
| Oil & Gas | Coupling in drilling rigs and pumps | Enhances reliability and performance in harsh environments | Assess compatibility with high torque and vibration resistance |
| Automotive | Connection in electric vehicle motors | Supports precise torque transfer, improving energy efficiency | Evaluate weight, size, and material for optimal performance |
| Mining | Use in crushers and grinding equipment | Minimizes mechanical failures and operational disruptions | Focus on durability and resistance to heavy loads and harsh conditions |
| Renewable Energy | Integration in wind turbine gearboxes | Increases energy transfer efficiency, contributing to sustainability | Ensure couplings are rated for high torque and environmental conditions |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, shaft couplings are crucial for power transmission in conveyor systems. These couplings facilitate the efficient transfer of power between motors and conveyor belts, which is essential for maintaining production flow. They help reduce downtime due to mechanical failures and lower maintenance costs by accommodating minor misalignments. For buyers, it is important to consider the torque capacity and misalignment tolerance of the couplings to ensure compatibility with the specific machinery used in their operations.
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas industry, shaft couplings play a vital role in drilling rigs and pumps. They enhance the reliability and performance of equipment operating in harsh environments, where vibrations and torque fluctuations are common. Couplings that can withstand high torque and resist wear are essential for minimizing downtime and ensuring safety. Buyers should assess the compatibility of couplings with their existing systems, focusing on durability and performance under extreme conditions.
Automotive
The automotive industry increasingly relies on shaft couplings for electric vehicle motors, where precise torque transfer is critical for energy efficiency. These couplings help ensure smooth operation and optimal performance by connecting the motor to the drivetrain. For international buyers, evaluating the weight, size, and material of couplings is essential to meet specific design requirements and performance standards, especially as the industry moves towards more sustainable solutions.
Mining
In mining applications, shaft couplings are used in crushers and grinding equipment to minimize mechanical failures and operational disruptions. The heavy loads and harsh conditions in mining environments demand couplings that can handle significant stress while maintaining performance. Buyers should focus on the durability of the couplings and their ability to withstand heavy loads, ensuring they are suitable for the demanding nature of mining operations.
Renewable Energy
Shaft couplings are integral to the operation of wind turbine gearboxes, where they facilitate energy transfer from the rotor to the generator. By increasing energy transfer efficiency, these couplings contribute to the sustainability goals of renewable energy projects. Buyers should ensure that the couplings are rated for high torque and can withstand environmental conditions, which is critical for maintaining long-term performance and reliability in energy generation systems.
Related Video: Types of Shaft Coupling, Animation, Machine Design | Solidworks
Strategic Material Selection Guide for shaft coupling types
When selecting materials for shaft couplings, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and cost. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in shaft coupling types, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Steel
Key Properties: Steel couplings are known for their high strength and durability, with excellent temperature and pressure ratings. They can withstand harsh environments and have good fatigue resistance.
Pros & Cons: Steel is highly durable and can handle significant torque loads, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, it is susceptible to corrosion if not treated, which can lead to premature failure in humid or corrosive environments. Additionally, steel couplings can be heavier, which may not be ideal for all applications.
Impact on Application: Steel couplings are often used in industrial machinery and heavy equipment where strength is paramount. They are compatible with various media, including oil and water, but may require protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM or DIN for quality assurance. In regions with high humidity or corrosive conditions, selecting corrosion-resistant coatings or stainless steel options may be necessary.
2. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum couplings are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance. They typically have lower tensile strength compared to steel but can handle moderate torque loads effectively.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which reduces overall system weight and can improve energy efficiency. However, aluminum is less durable than steel and may not be suitable for high-torque applications. It is also more expensive than steel in some markets.
Impact on Application: Aluminum couplings are ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical, such as in aerospace and automotive industries. They are compatible with non-corrosive media but may not perform well in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost implications of aluminum versus steel, especially in regions where aluminum is less readily available. Compliance with industry standards is also essential, particularly in aerospace applications.
3. Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties: Plastic couplings, often made from materials like nylon or polyurethane, offer excellent corrosion resistance and are lightweight. They can handle moderate temperatures and pressures, but their mechanical strength is generally lower than metals.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of plastic couplings is their resistance to chemical corrosion, making them suitable for applications involving aggressive media. However, they may not handle high torque loads or extreme temperatures effectively, limiting their use in heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic couplings are commonly used in food processing, chemical handling, and other industries where corrosion resistance is vital. They are compatible with a wide range of media but should be evaluated for specific chemical compatibility.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers must assess the chemical compatibility of plastic materials with the media they will encounter. Additionally, they should verify that the materials meet relevant industry standards, especially in food and pharmaceutical applications.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite couplings combine materials like fiberglass or carbon fiber with resins, resulting in lightweight and high-strength products. They offer good resistance to corrosion and fatigue.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of composite materials is their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for applications where both properties are essential. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized techniques for installation.
Impact on Application: Composite couplings are often used in high-performance applications, such as aerospace and motorsports, where weight savings and strength are critical. They are compatible with various media but should be evaluated for specific environmental conditions.
Considerations for Buyers: International buyers should consider the availability of composite materials in their region and ensure compliance with relevant standards. The higher cost may be justified in applications where performance and weight are critical.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for shaft coupling types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial machinery | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace and automotive applications | Lightweight | Lower torque capacity than steel | High |
| Plastic (Polymer) | Food processing and chemical handling | Excellent corrosion resistance | Limited torque and temperature range | Medium |
| Composite Materials | High-performance aerospace and motorsport | Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding material selection for shaft couplings, considering their specific operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for shaft coupling types
Shaft couplings are essential mechanical components used to connect shafts and transmit torque while accommodating misalignment. Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section will provide an in-depth overview of the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality control measures relevant to shaft couplings.
Manufacturing Processes for Shaft Couplings
The manufacturing process of shaft couplings typically involves several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
The choice of material is fundamental in producing durable and effective couplings. Common materials include steel, aluminum, and various alloys, each chosen based on the application requirements such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
- Material Selection: Buyers should ensure that the materials used meet industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO) for the intended application.
- Cutting and Shaping: Materials are cut into blanks using techniques like laser cutting, water jet cutting, or machining.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the material into the desired coupling form.
- Techniques:
- Casting: Used for complex shapes, where molten metal is poured into molds.
- Forging: Involves shaping the metal through compressive forces, enhancing its strength.
- Machining: Precision tools are used to refine the shape and dimensions, ensuring tight tolerances.
3. Assembly
The assembly process varies based on the type of coupling being manufactured.
- Components: Different coupling designs (e.g., jaw, bellows, disc) may require assembly of multiple parts, such as hubs, elastomeric inserts, or bellows.
- Techniques:
- Welding: Commonly used for joining parts, especially in heavy-duty applications.
- Fastening: Bolts and screws may be used for easier disassembly and maintenance.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and performance of the couplings.
- Surface Treatments: Techniques such as anodizing, plating, or powder coating are applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
- Balancing: Dynamic balancing may be performed to reduce vibrations during operation.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality control (QC) is critical to ensure that shaft couplings meet performance standards and customer expectations. Key international and industry-specific standards include:
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard that outlines requirements for a quality management system.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for couplings used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they can withstand harsh conditions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective QC includes multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected for compliance with specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during production to ensure processes are followed and defects are minimized.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished products undergo rigorous testing and inspections to confirm they meet design specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to ensure the reliability and performance of shaft couplings:
- Dimensional Inspection: Verifying the physical dimensions against specifications using calipers and gauges.
- Load Testing: Assessing the coupling’s ability to withstand operational loads without failure.
- Vibration Testing: Ensuring the coupling operates smoothly without excessive vibration, which can lead to premature wear.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality assurance measures of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to evaluate the manufacturing processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Assurance Reports: Requesting documentation from suppliers that outlines their QC processes, including records of inspections and testing results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to assess the quality of the products before shipment, ensuring compliance with the agreed specifications.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances related to quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and international standards relevant to their markets.
- Cultural Differences: Understand that quality assurance practices may vary significantly by region. Establish clear communication regarding quality expectations.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Consider the impact of logistics on quality. Long shipping times may affect product integrity, so choosing suppliers with reliable shipping methods is crucial.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for shaft couplings is essential for B2B buyers seeking reliable suppliers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control practices, buyers can ensure they source high-quality components that meet their operational needs. Engaging in thorough supplier evaluations, including audits and compliance checks, will further mitigate risks and enhance supply chain reliability.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for shaft coupling types Sourcing
Understanding Cost Structure in Shaft Coupling Sourcing
When sourcing shaft couplings, B2B buyers must consider the multifaceted cost structure that influences pricing. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin. Each component plays a crucial role in determining the final price of the product.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly affects the cost. High-quality steel or specialized alloys will increase expenses, while standard materials may lower them. Buyers should assess the material requirements based on the application to balance performance and cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can impact pricing. In countries with lower wage rates, such as some South American and African nations, labor-intensive manufacturing processes may be more cost-effective, while Europe might see higher labor costs that reflect in the pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, equipment, and utilities. Efficient manufacturers will have lower overhead costs, which can result in more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The investment in specialized tooling can affect initial pricing. Custom couplings that require unique molds or machining processes will incur higher tooling costs, which may be spread over larger production runs to minimize impact.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that couplings meet industry standards and certifications adds to the cost but is essential for reliability and performance. Buyers should weigh the cost of QC against the potential costs of failure in the field.
-
Logistics: Transportation and handling costs can vary significantly based on the distance from the supplier and the shipping method chosen. Incoterms also play a role here, as they define the responsibilities and costs associated with shipping.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. Understanding the competitive landscape can help buyers negotiate better margins.
Key Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of shaft couplings:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should consider their purchasing strategy to optimize pricing.
-
Specs/Customization: Custom designs or specifications can increase costs. Buyers should determine if standard products meet their needs before opting for customization.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and certifications (like ISO standards) can justify premium pricing. Buyers must evaluate the trade-off between cost and quality based on their specific application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge higher prices due to their quality assurance processes and service levels.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial for cost management. Different Incoterms can shift costs and risks between buyer and seller, affecting the total cost of ownership.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
To maximize value when sourcing shaft couplings, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume commitments to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers are often willing to offer discounts for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. A slightly higher upfront cost may yield significant long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations can affect pricing for international buyers. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can help mitigate these risks.
-
Research and Comparison: Utilize platforms that allow for price comparisons and supplier evaluations. This can provide insights into market rates and assist in making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for shaft couplings can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The insights provided here are indicative and should be used as a guideline. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and engage with multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential shaft coupling types Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘shaft coupling types’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for shaft coupling types
When evaluating shaft couplings for industrial applications, understanding their essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are key specifications and industry terms that every B2B buyer should be familiar with.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the type of material used in the coupling, such as steel, aluminum, or plastic.
– Importance: Different materials provide varying levels of strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear. For instance, steel couplings are ideal for high-torque applications, while lightweight aluminum may be more suitable for motion control applications. -
Torque Rating
– Definition: The maximum amount of torque a coupling can handle without failure.
– Importance: Knowing the torque rating is essential to ensure that the coupling can transmit the required power without slipping or breaking, which can lead to costly downtime and repairs. -
Misalignment Tolerance
– Definition: The ability of a coupling to accommodate misalignment between shafts, typically expressed in terms of angular and parallel misalignment.
– Importance: High tolerance levels reduce the risk of mechanical failure and extend the lifespan of connected equipment. This is especially important in dynamic environments where slight misalignments may occur. -
Backlash
– Definition: The amount of free play or movement in a coupling before the output reacts to the input.
– Importance: Low or zero-backlash designs are critical in precision applications, such as robotics and CNC machinery, where accurate positioning is vital. -
Weight and Size
– Definition: The physical dimensions and weight of the coupling.
– Importance: Smaller, lighter couplings can be advantageous in applications with space constraints or where weight reduction is necessary for efficiency. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: The range of temperatures within which the coupling can operate effectively without degrading.
– Importance: Understanding this property helps in selecting couplings for specific environments, such as high-temperature industrial settings or cold storage facilities.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: B2B buyers often seek OEM parts for quality assurance and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and other details for specific products.
– Significance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, insurance responsibilities, and risk levels associated with the delivery of goods. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time it takes from placing an order until it is received.
– Significance: Knowing the lead time is crucial for planning production schedules and managing inventory, particularly in industries where downtime can be costly. -
Certification
– Definition: Official recognition that a product meets specific standards, such as ISO or ANSI.
– Significance: Certifications can provide buyers with confidence in the quality and reliability of couplings, which is particularly important in regulated industries.
By understanding these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when selecting shaft couplings, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and reducing risks.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the shaft coupling types Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global shaft coupling market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for efficient power transmission systems across various industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and energy. In particular, emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a surge in industrial activities, prompting the need for reliable coupling solutions. Technological advancements, including the integration of IoT and smart manufacturing practices, are reshaping sourcing trends. Buyers are increasingly favoring couplings that offer enhanced performance metrics, such as reduced vibration and improved torque transmission.
In terms of market dynamics, international B2B buyers must navigate a landscape characterized by fluctuating raw material costs and supply chain disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of resilient supply chains, compelling companies to diversify their sourcing strategies. Moreover, suppliers are investing in automation and digital platforms to streamline order processing and inventory management. For buyers, this means greater accessibility to product information and the ability to compare different coupling types more effectively.
Furthermore, the rise of e-commerce platforms is changing the sourcing landscape, enabling buyers from various regions to access a wider range of products. As the demand for customized solutions grows, suppliers are increasingly offering modular coupling designs that cater to specific application needs, allowing buyers to optimize their operations with tailored solutions.
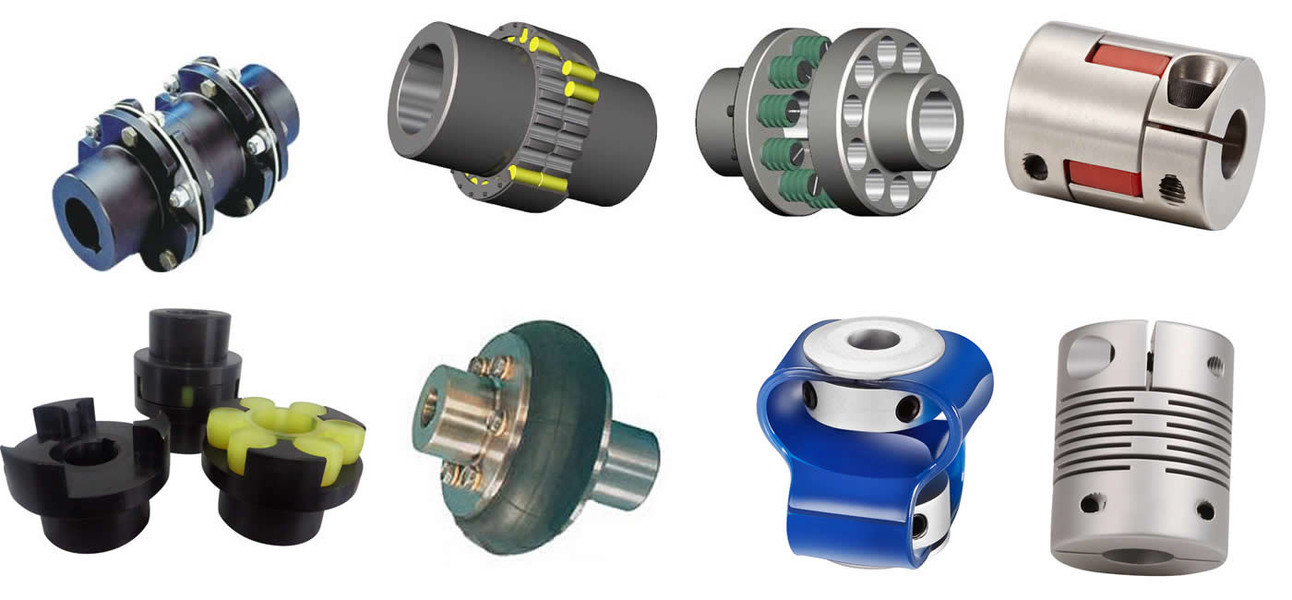

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a central concern for B2B buyers in the shaft coupling sector, reflecting a broader shift towards environmentally responsible practices. The production of shaft couplings can have a notable environmental impact, particularly due to the energy-intensive manufacturing processes and the use of non-recyclable materials. Therefore, international buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through the use of eco-friendly materials and processes.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Buyers should seek partnerships with manufacturers that adhere to ethical labor practices and possess relevant certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety. Additionally, the use of green certifications, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wooden components or recycled metals, can be a strong indicator of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, buyers not only reduce their ecological footprint but also enhance their brand reputation. This alignment can lead to improved customer loyalty and increased competitiveness in a market that increasingly values corporate responsibility.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of shaft couplings dates back to the early industrial revolution, where they were primarily used to connect steam engines to machinery. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of various coupling types tailored for specific applications, ranging from flexible couplings that accommodate misalignment to rigid couplings that provide maximum torque transfer.
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards enhancing coupling performance and sustainability. Innovations such as the use of composite materials and the integration of smart technologies have transformed the industry. Today, B2B buyers are not only looking for functional products but also for solutions that align with their operational efficiency and sustainability goals. This historical context underscores the importance of understanding the evolution of shaft couplings to make informed sourcing decisions in today’s dynamic market.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of shaft coupling types
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of shaft couplings?
When vetting suppliers, evaluate their industry experience, product range, and customer reviews. Check for certifications like ISO 9001, which indicate quality management standards. Additionally, consider their manufacturing capabilities, technological advancements, and compliance with international regulations. It’s also wise to request references from other clients to gauge reliability and service quality. -
Can I customize shaft couplings to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for shaft couplings. This can include modifications in size, materials, and design features to better suit your application. When discussing customization, ensure that you provide detailed specifications and ask for prototypes or samples. Confirm any additional costs and lead times associated with the customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for shaft couplings?
MOQs can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from 10 to 100 units, depending on the coupling type and complexity. Lead times also differ based on the supplier’s location, production capacity, and whether the product is standard or customized. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing shaft couplings internationally?
Payment terms can include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may request a deposit (often 30% to 50%) before production begins, especially for customized orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that provide security for both parties, and consider using escrow services for larger transactions to mitigate risks. -
How can I ensure the quality of shaft couplings before purchase?
To ensure quality, request product samples and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Ask suppliers for quality assurance certifications and testing reports. Consider establishing a Quality Assurance (QA) process that includes third-party inspections if necessary. This is particularly important when sourcing from regions with varying manufacturing standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing shaft couplings?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Discuss with your supplier about the best shipping options based on cost and urgency. Ensure they provide necessary documentation for customs, such as commercial invoices and certificates of origin, to avoid delays or unexpected charges during importation. -
How should disputes regarding shaft coupling orders be handled?
Establish clear terms in your contract regarding product specifications, delivery timelines, and quality expectations to prevent disputes. In case of disagreements, initiate communication with your supplier to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract, which can help maintain business relationships while addressing grievances. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing shaft couplings?
Look for certifications that reflect industry standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and specific product certifications relevant to your region. These certifications indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with safety regulations. Additionally, inquire about any industry-specific standards that may apply to your applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for shaft coupling types
In summary, the effective strategic sourcing of shaft couplings is crucial for international B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiency and reliability across various industries. Understanding the diverse types of shaft couplings—such as beam, bellows, chain, and jaw couplings—enables buyers to select the most suitable option for their specific applications, reducing the risk of misalignment and mechanical failures.
Moreover, leveraging strategic sourcing practices can lead to significant cost savings, improved supplier relationships, and access to innovative technologies. By carefully evaluating suppliers, assessing quality standards, and considering local market conditions, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can optimize their procurement strategies.
As we look to the future, embracing advancements in coupling technology and maintaining flexibility in sourcing strategies will be key. International B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and innovations while engaging with reliable suppliers who can meet their evolving needs. Investing in quality shaft couplings today not only ensures operational stability but also positions businesses for growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.