Master the Types of O Ring Seals: Optimize Your Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of o ring seals
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing and industrial operations, the role of O-ring seals cannot be overstated. These seemingly simple components are integral to ensuring the reliability and efficiency of equipment across various sectors, including automotive, oil and gas, food processing, and pharmaceuticals. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the different types of O-ring seals available is crucial for maintaining operational integrity and minimizing costs.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, offering insights into the diverse types of O-ring seals and their specific applications. It delves into the intricacies of material selection, helping buyers match the right seal with their operational needs and environmental conditions. Furthermore, it covers essential aspects of manufacturing standards and quality control, ensuring that procurement decisions are based on reliable supplier certifications and inspection protocols.
Buyers will also find valuable information on supplier comparison across different regions, allowing for strategic sourcing decisions that align with local market dynamics. Key factors influencing cost drivers and market trends are explored, providing a clearer understanding of total cost of ownership. Lastly, the guide addresses common challenges through a dedicated FAQ section, empowering buyers to navigate potential pitfalls confidently.
By leveraging this knowledge, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that enhance operational resilience and drive long-term success in a competitive global marketplace.
Understanding types of o ring seals Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard O-Rings | Circular cross-section, elastomeric material, wide size range | Hydraulics, pneumatics, connectors | Cost-effective, versatile; may not suit aggressive environments |
| Quad Rings (X-Rings) | Four-lobed (X-shape) profile for enhanced sealing | Valves, pumps, rotary shafts | Superior sealing, reduces twisting; typically higher unit cost |
| PTFE (Teflon) Seals | Chemically inert, low friction, white/off-white appearance | Chemical processing, food & pharma industries | Outstanding chemical resistance; poor elasticity and higher cost |
| Metal O-Rings/Seals | Metal construction, high-pressure use | Oil & gas, aerospace, high-temperature areas | Extremely resilient; costly and less flexible |
| Encapsulated O-Rings | Elastomer core with seamless PTFE or FEP jacket | Aggressive chemicals, food contact | Combines flexibility with chemical resistance; complex sourcing |
Standard O-Rings
Standard O-rings are the backbone of sealing technology, characterized by their simple circular design and extensive compatibility with various fluids and gases. They are widely used in industries such as hydraulics, pneumatics, and water systems. When sourcing, buyers should focus on material compatibility (such as NBR or EPDM) and certifications to ensure reliability. While they are cost-effective and versatile, it is crucial to assess their suitability for specific environments, particularly those involving aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
Quad Rings (X-Rings)
Quad rings, or X-rings, feature a unique four-lobed design that enhances sealing capability by providing multiple contact points. This design minimizes twisting and rolling, making them ideal for dynamic applications such as pumps and valves. Although they come at a higher unit cost, their durability and superior sealing performance can lead to reduced total costs over time. Buyers should consider quad rings for applications where leakage prevention is critical, particularly in high-duty-cycle operations.
PTFE (Teflon) Seals
PTFE seals are renowned for their exceptional chemical resistance and ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making them essential in sectors like chemical processing and pharmaceuticals. Their low friction properties help minimize wear in aggressive environments. However, the poor elasticity of PTFE requires precise groove design during installation, which can complicate sourcing. Buyers must prioritize grade specifications and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, especially in food-grade applications, despite the higher initial investment.
Metal O-Rings/Seals
Metal O-rings and seals, typically made from materials like stainless steel or Inconel, are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications common in the oil & gas and aerospace industries. They offer remarkable mechanical strength and durability, making them suitable for extreme conditions. However, their higher cost and less flexibility can be limiting factors. Buyers should evaluate manufacturing tolerances and ensure that the selected metal seals meet the specific requirements of their applications, including compatibility with corrosive media.
Encapsulated O-Rings
Encapsulated O-rings consist of an elastomer core coated with a seamless layer of PTFE or FEP, offering the best of both worlds: flexibility and chemical resistance. These seals are particularly advantageous in applications involving aggressive chemicals or food contact. However, sourcing encapsulated O-rings can be more complex due to their specialized nature. Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including the need for compliance with safety standards, while also accounting for potential cost implications.
Related Video: O-Rings? O-Yeah! How to Select, Design, and Install O-Ring Seals
Key Industrial Applications of types of o ring seals
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of o ring seals | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Sealing in hydraulic systems for braking systems | Ensures safety and reliability in critical systems | Material compatibility, temperature tolerance, and certifications |
| Oil & Gas | Seals in drilling equipment and pipelines | Prevents leaks, ensuring operational efficiency and safety | High-pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and lead times |
| Food & Beverage | Sealing in processing equipment and packaging | Maintains hygiene and compliance with safety standards | FDA compliance, chemical resistance, and easy cleaning features |
| Pharmaceuticals | Seals in drug manufacturing and delivery systems | Ensures product integrity and regulatory compliance | Material certifications, sterility, and compatibility with various chemicals |
| Aerospace | Sealing in fuel systems and hydraulic components | Enhances performance and safety in demanding conditions | High-temperature resistance, lightweight materials, and rigorous testing standards |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, o-ring seals are critical for sealing hydraulic systems, particularly in braking systems. These seals prevent fluid leaks, ensuring the safety and reliability of the vehicle’s braking performance. Buyers should focus on materials that can withstand high pressures and varying temperatures, as well as ensure that the seals meet industry certifications. For international buyers, understanding local regulations regarding automotive components is essential to avoid compliance issues.
Oil & Gas Sector
O-rings play a vital role in the oil and gas industry, particularly in drilling equipment and pipelines. They are essential for preventing leaks that could lead to environmental hazards and operational inefficiencies. Buyers must consider high-pressure ratings and corrosion resistance when sourcing these seals. Additionally, lead times can be critical in this sector due to the often urgent nature of repairs and maintenance. Suppliers with a strong track record in oil and gas applications can provide added assurance.
Food & Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, o-ring seals are used in processing equipment and packaging to maintain hygiene and ensure compliance with safety standards. These seals must be made from FDA-compliant materials that can withstand cleaning chemicals and high temperatures. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing seals that offer both chemical resistance and ease of cleaning to minimize downtime. Understanding local food safety regulations is crucial for international buyers to ensure compliance in their markets.
Pharmaceuticals Sector
O-rings are indispensable in the pharmaceutical industry, where they are used in drug manufacturing and delivery systems. Their role is to ensure product integrity and meet stringent regulatory compliance standards. Buyers need to focus on sourcing materials that have the appropriate certifications for pharmaceutical applications, as well as those that maintain sterility and are compatible with various chemicals. International buyers must navigate differing regulatory environments to ensure compliance across borders.
Aerospace Industry
In aerospace applications, o-ring seals are utilized in fuel systems and hydraulic components, where they must perform reliably under extreme conditions. The materials used must exhibit high-temperature resistance and lightweight properties while adhering to rigorous testing standards. Buyers in this sector should seek suppliers with proven expertise in aerospace applications, as quality and reliability are paramount. Understanding the specific certifications required for aerospace components is essential for international procurement.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of o ring seals
When selecting O-ring seals for various applications, the choice of material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Here, we analyze four common materials used in O-ring seals, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Nitrile (Buna-N)
Key Properties: Nitrile O-rings are known for their excellent resistance to oils, fuels, and hydraulic fluids. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°F to 250°F (-40°C to 121°C) and have good mechanical strength.
Pros & Cons: Nitrile is cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for general-purpose applications. However, it is not suitable for exposure to ozone, sunlight, or high temperatures beyond its limits, which can lead to premature failure.
Impact on Application: Nitrile O-rings are ideal for automotive and industrial applications where oil and fuel resistance is essential. Their compatibility with a wide range of media makes them versatile, but buyers must ensure that the specific application does not expose them to conditions that exceed their limits.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM and ISO is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should also consider local sourcing options to minimize costs and lead times.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Key Properties: EPDM O-rings exhibit excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and weathering. They can handle temperatures from -40°F to 300°F (-40°C to 150°C) and maintain flexibility in extreme conditions.
Pros & Cons: The durability of EPDM makes it a preferred choice for outdoor applications and those exposed to harsh environmental conditions. However, it has limited compatibility with petroleum-based fluids, which can restrict its use in certain industries.
Impact on Application: EPDM is commonly used in automotive, HVAC, and plumbing applications where resistance to water and steam is necessary. Its unique properties make it suitable for outdoor use, but buyers must assess the chemical compatibility with specific media.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with local and international standards, particularly in Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations may apply. Understanding the specific application environment is essential for selecting the right material.
Fluoroelastomer (Viton)
Key Properties: Viton O-rings are known for their exceptional resistance to high temperatures (up to 400°F or 204°C) and a wide range of chemicals, including acids and solvents.
Pros & Cons: The high performance of Viton makes it suitable for demanding applications in the aerospace, automotive, and chemical processing industries. However, it comes at a higher cost than other elastomers and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Viton is ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures, ensuring reliability in critical systems. Buyers must consider the cost-benefit ratio, especially for applications where longevity and performance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions with strict chemical regulations, such as Europe, should ensure that Viton O-rings meet compliance standards. Additionally, understanding the supply chain for high-quality Viton can help mitigate risks associated with sourcing.
PTFE (Teflon)
Key Properties: PTFE O-rings are chemically inert and can withstand temperatures from -200°F to 500°F (-129°C to 260°C). They are ideal for applications requiring low friction and high chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: The outstanding chemical resistance of PTFE makes it suitable for food processing and pharmaceutical applications. However, its low elasticity can lead to installation challenges, and it is generally more expensive than elastomeric options.
Impact on Application: PTFE O-rings are often used in environments with aggressive chemicals or where cleanliness is critical. Buyers must ensure that the design accommodates the specific installation requirements of PTFE.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food and pharmaceutical standards is essential for buyers in the Middle East and Europe. Understanding local regulations and sourcing options can enhance the procurement process.
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of o ring seals | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrile (Buna-N) | Automotive and industrial applications | Excellent oil and fuel resistance | Not suitable for ozone or high temperatures | Low |
| EPDM | Outdoor and plumbing applications | Great resistance to heat and ozone | Limited compatibility with petroleum-based fluids | Medium |
| Fluoroelastomer (Viton) | Aerospace and chemical processing | Exceptional chemical and temperature resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Food processing and pharmaceuticals | Outstanding chemical inertness | Low elasticity and higher cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with critical insights into O-ring materials, enabling informed decisions that align with operational requirements and compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of o ring seals
In the competitive landscape of international B2B procurement, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for O-ring seals is crucial. This knowledge empowers buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to make informed sourcing decisions that ensure operational reliability and compliance with industry standards.
Manufacturing Processes for O-Ring Seals
The manufacturing of O-ring seals involves several key stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the quality and functionality of the seals.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. O-rings can be made from various elastomers such as Nitrile (Buna-N), Viton, EPDM, and PTFE. The choice of material depends on the specific application and environmental conditions.
- Compounding: Raw materials are mixed with additives to achieve desired properties like flexibility, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance. This process may include the use of fillers, plasticizers, and curing agents.
- Quality Control: Material properties are tested to ensure they meet the specifications before moving to the next stage.
2. Forming
The forming process shapes the compounded material into O-rings. This can be done using various techniques:
- Extrusion: The most common method where the material is forced through a die to create a long, continuous shape that is later cut into O-ring sizes.
- Molding: Used for complex shapes or larger O-rings, this process involves placing the material into molds and applying heat and pressure to cure the elastomer.
Each method has its advantages, with extrusion being more cost-effective for standard sizes and molding being preferred for custom or intricate designs.
3. Assembly
In some cases, O-rings may require assembly with other components, such as metal inserts for increased strength or encapsulation with PTFE. This step is crucial for ensuring the O-rings perform effectively in their intended applications.
- Bonding: For O-rings that need to be bonded with other materials, precise techniques must be employed to ensure a strong and reliable seal.
- Inspection: Each assembled unit undergoes a visual inspection to check for defects or inconsistencies.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the O-ring’s performance and prepare it for delivery. This includes:
- Surface Treatments: Processes like coating or polishing may be applied to improve chemical resistance or reduce friction.
- Packaging: Proper packaging is essential to prevent damage during transport and storage. O-rings are typically packaged in airtight containers to maintain their integrity.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of O-ring seals, particularly for international B2B buyers who must adhere to various standards and regulations. Effective quality control ensures the seals meet performance expectations and regulatory compliance.
International Standards
Several international standards govern the manufacturing and quality assurance of O-ring seals:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is essential for suppliers aiming to demonstrate consistent quality in their processes.
- ISO 16949: Specifically relevant for the automotive industry, this standard integrates the principles of ISO 9001 with specific automotive sector requirements.
- API Standards: For buyers in oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is critical, particularly for seals used in high-pressure environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
A robust quality control framework includes multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before use.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): O-rings are monitored during production to detect any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed O-rings undergo rigorous testing and inspection to verify their performance and compliance with specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of O-ring seals:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and elasticity of the material.
- Compression Set Testing: Evaluates the O-ring’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the material’s hardness, which can affect sealing performance.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers should implement strategies to verify the quality control practices of their suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers helps assess their adherence to quality standards and manufacturing processes.
- Quality Reports: Requesting comprehensive quality reports from suppliers can provide insights into their quality control measures and testing results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and product compliance.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing O-ring seals internationally, B2B buyers must consider specific nuances related to quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding and navigating the regulatory landscape in different regions (e.g., CE marking in Europe, ANVISA in Brazil) is critical for ensuring compliance.
- Cultural and Communication Differences: Effective communication is essential when dealing with suppliers from diverse cultural backgrounds. Clear specifications and expectations can help bridge gaps and reduce misunderstandings.
- Logistical Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the logistics involved in transporting O-rings, including potential delays and how they might impact quality during transit.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for O-ring seals, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of o ring seals Sourcing
Navigating the costs associated with sourcing O-ring seals involves understanding the multifaceted components that contribute to their pricing. This analysis will break down the key cost components and pricing influencers, providing actionable insights for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
- Materials
The choice of material significantly impacts the overall cost of O-ring seals. Common materials include Nitrile (Buna-N), EPDM, Viton, and PTFE. Each material comes with its own price point based on chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and application suitability. For instance, PTFE is generally more expensive due to its chemical inertness and durability.
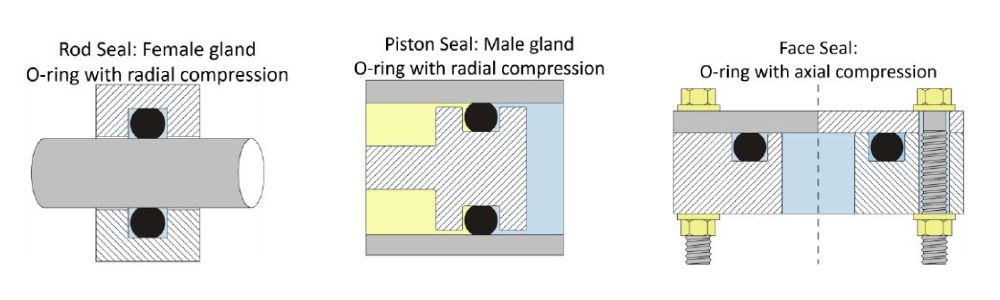
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Labor
Labor costs vary depending on the region and complexity of the manufacturing process. In regions with higher labor costs, such as Europe, the overall price of O-rings may be elevated. Conversely, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs can result in savings, but this must be weighed against potential quality issues. -
Manufacturing Overhead
This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory operations. Manufacturers with advanced technologies or stringent quality controls may have higher overhead, which can be reflected in the product price. -
Tooling
Custom tooling for specific O-ring dimensions or profiles can add significant costs, especially for low-volume orders. Buyers should consider the amortization of these costs over larger orders to maximize cost efficiency. -
Quality Control (QC)
Investing in quality assurance processes enhances product reliability but also contributes to the overall cost. Certifications (like ISO 9001) and compliance with industry standards can increase the price but are often essential for critical applications. -
Logistics
Transportation costs fluctuate based on distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. International buyers should account for these expenses when sourcing, as they can significantly affect the total landed cost of O-ring seals. -
Margin
Supplier margins vary based on market positioning and competitive landscape. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge a premium for their products, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
Bulk purchases typically lead to lower unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to secure better pricing, especially for high-demand applications. -
Specifications/Customization
Custom O-rings tailored for specific applications may incur additional costs. Buyers should ensure that the benefits of customization justify the extra expenditure. -
Material Selection
Choosing standard materials over specialty options can lead to significant savings. However, it’s crucial to balance cost with the performance requirements of the application. -
Quality and Certifications
Higher-quality O-rings with relevant certifications may command premium prices, but they often result in reduced failure rates and lower total cost of ownership (TCO). -
Supplier Factors
Evaluating supplier reliability, reputation, and service capabilities can influence pricing. Long-term partnerships may yield better pricing as trust and familiarity grow. -
Incoterms
Understanding and negotiating Incoterms can help manage logistics costs effectively. Terms such as FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can impact the overall pricing structure.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation
Always negotiate prices, especially for bulk orders. Leverage competitive offers from multiple suppliers to secure the best deal. -
Cost Efficiency
Conduct a thorough analysis of the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes initial purchase price, maintenance costs, and potential downtime. This holistic view helps in making informed purchasing decisions. -
Pricing Nuances
Be aware of regional market dynamics. Prices may vary significantly based on local supply and demand, tariffs, and import regulations, particularly in emerging markets like Africa and South America. -
Supplier Evaluation
Conduct due diligence on suppliers by checking references and reviewing their quality control processes. A reputable supplier can save money in the long run by reducing failures and associated costs.
By understanding these cost structures and pricing dynamics, international B2B buyers can make informed, strategic decisions when sourcing O-ring seals, ultimately optimizing their procurement processes for better operational efficiency.
Spotlight on Potential types of o ring seals Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘types of o ring seals’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of o ring seals
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with O-ring seals is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only helps in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures compatibility and reliability in various applications. Below are critical specifications and commonly used terms that every buyer should be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The specific type of elastomer or polymer used to manufacture the O-ring, such as Nitrile (Buna-N), EPDM, or Viton.
– B2B Importance: Material selection affects the O-ring’s resistance to chemicals, temperature, and wear. Understanding the material grade helps buyers match seals with their operational environments, ensuring longevity and reducing failure rates. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable variation in dimensions and shape of the O-ring, typically expressed in millimeters or inches.
– B2B Importance: Proper tolerances are crucial for sealing effectiveness. Inaccurate tolerances can lead to leaks or premature wear. Buyers must ensure that suppliers adhere to industry standards (like AS568) to guarantee compatibility with their applications. -
Durometer Hardness
– Definition: A measure of the material’s hardness, typically indicated on the Shore A scale.
– B2B Importance: Hardness affects the O-ring’s ability to compress and seal effectively. Buyers must consider the durometer rating to ensure the O-ring will perform optimally under specific pressure and temperature conditions. -
Temperature Range
– Definition: The range of temperatures within which the O-ring can operate effectively without losing performance.
– B2B Importance: Different applications encounter various temperature extremes. Buyers should select O-rings rated for their specific temperature requirements to avoid seal failure.
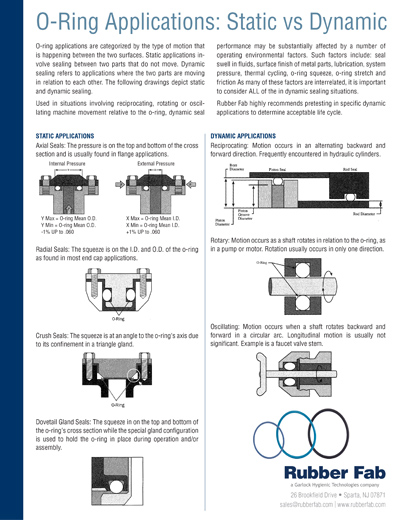
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Chemical Compatibility
– Definition: The ability of the O-ring material to withstand exposure to specific chemicals without degrading.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the wrong material can lead to rapid deterioration and system failure. Buyers should consult compatibility charts to ensure that the chosen O-ring can handle the chemicals it will encounter. -
Compression Set
– Definition: The permanent deformation of an O-ring after being compressed for a specific period at a given temperature.
– B2B Importance: A low compression set indicates that an O-ring will maintain its sealing properties over time. Buyers should prioritize materials with minimal compression set for applications requiring long-term reliability.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Explanation: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance for Buyers: Understanding OEM specifications ensures that the O-rings sourced meet the quality and performance standards required by original equipment. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Explanation: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance for Buyers: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory levels and costs, especially in regions with fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Explanation: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importance for Buyers: An RFQ allows buyers to compare prices, lead times, and terms from multiple suppliers, aiding in cost-effective sourcing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Explanation: A set of internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance for Buyers: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance with international trade regulations. -
Lead Time
– Explanation: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of goods.
– Importance for Buyers: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning and ensuring that production schedules are met without delays. -
Certification Standards
– Explanation: Industry-specific standards that ensure products meet safety and quality benchmarks (e.g., ISO, ASTM).
– Importance for Buyers: Verification of certification ensures that the O-rings comply with required regulations, reducing the risk of failures and legal issues in various industries.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the types of o ring seals Sector
Global drivers are shaping the market for o-ring seals, influenced by factors such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the demand for higher performance in diverse applications. The rise of automation and Industry 4.0 is propelling the need for reliable sealing solutions in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. Additionally, as industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for operational efficiency, there is a growing emphasis on minimizing downtime caused by seal failures. This is particularly relevant in regions where machinery maintenance can be costly and logistically challenging.
Emerging trends in sourcing o-rings include the adoption of digital procurement platforms, which enhance transparency and streamline supplier interactions. These platforms allow international buyers to access a broader range of suppliers and compare quality and pricing more effectively. Moreover, advancements in material science are leading to the development of high-performance elastomers that can withstand extreme conditions, further diversifying sourcing options. As buyers prioritize quality and compatibility, selecting suppliers with robust certifications and quality control processes becomes crucial to mitigate risks associated with substandard products.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As global awareness of environmental issues rises, sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the procurement of o-ring seals. Buyers are now more conscientious about the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. This shift necessitates a focus on ethical supply chains, where suppliers adhere to sustainable practices throughout the production process. For instance, sourcing materials from manufacturers that prioritize eco-friendly production methods can significantly reduce the overall carbon footprint associated with o-ring seals.
In addition to ethical sourcing, the demand for green certifications is on the rise. Buyers are encouraged to seek o-ring seals made from sustainable materials or those that meet recognized environmental standards, such as ISO 14001. Materials like bio-based elastomers or those with minimal chemical additives are becoming more popular, offering a viable alternative for environmentally conscious companies. By integrating sustainability into their procurement strategies, international buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also contribute to a more sustainable industrial landscape.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of o-ring seals can be traced back to the early 20th century when they were primarily used in hydraulic applications. Over the decades, advancements in material technology and manufacturing processes led to the widespread adoption of o-rings across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical. The introduction of synthetic elastomers in the mid-20th century expanded the applications of o-rings, allowing them to withstand higher temperatures and aggressive chemicals. As industries continue to evolve, the demand for specialized o-ring seals that meet stringent performance requirements is driving innovation and reshaping the sourcing landscape for international buyers.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of o ring seals
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of O-ring seals?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, production capabilities, and quality assurance processes. Request certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards pertinent to your application. Evaluate their financial stability, customer references, and previous project portfolios. It’s also wise to assess their ability to comply with local regulations and standards in your region, as this will impact your supply chain reliability. -
Can I customize O-ring seals for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for O-ring seals to meet specific application requirements. You can specify dimensions, material types, and even surface finishes. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and expected performance criteria. Be aware that customized solutions may have longer lead times and higher costs, so factor this into your procurement planning. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for O-ring seals?
MOQs can vary significantly by supplier and the type of O-ring you require. Standard O-rings might have lower MOQs, while custom designs often come with higher MOQs. Lead times also depend on the complexity of the order; standard products may ship within a week, while custom solutions could take several weeks to months. Always confirm these details with suppliers to align your production schedules accordingly. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing O-ring seals internationally?
Payment terms can differ by supplier and region. Common arrangements include advance payments, net 30, or even 60 days, depending on the buyer’s relationship with the supplier. For international transactions, consider using letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always discuss and agree on payment terms upfront to avoid disputes and ensure smooth transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for O-ring seals?
Request documentation of quality control measures from your suppliers, including details on their manufacturing processes and inspection protocols. Certifications such as ISO 9001, FDA approval (for food-grade applications), or specific industry-related certifications should be provided. Perform audits or request samples to validate their claims and ensure that their products meet your quality standards before placing large orders. -
What should I consider regarding logistics when importing O-ring seals?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of O-ring seals. Consider shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may apply to your imports. Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping to minimize delays. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides proper documentation, such as bills of lading and customs declarations, to facilitate smooth transit through customs. -
How can I resolve disputes with international suppliers?
Dispute resolution can be challenging in international trade. It’s essential to establish clear terms in your purchase agreements, including dispute resolution mechanisms. Consider arbitration clauses or mediation as preferred methods. Maintain open lines of communication with suppliers to address issues promptly. If disputes arise, documenting all communications and agreements will support your position in negotiations. -
What are the risks associated with sourcing O-ring seals from different regions?
Sourcing from various regions can introduce risks like supply chain disruptions, varying quality standards, and currency fluctuations. Each region may have its own set of regulations and compliance issues, which can complicate imports. To mitigate these risks, conduct thorough supplier assessments, diversify your supplier base, and establish robust contracts that address quality and delivery expectations. Regularly review geopolitical conditions that could affect your supply chain.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of o ring seals
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of O-ring seals is paramount for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and minimize costs. As highlighted, understanding the diverse types and materials of O-rings—such as standard O-rings, quad rings, PTFE seals, and metal O-rings—enables buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific industry requirements.
By prioritizing supplier reliability, material compatibility, and rigorous quality control, companies across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can significantly reduce the risk of component failure and the associated downtime costs. Engaging with suppliers who adhere to international standards and certifications ensures that the selected O-rings meet both performance and regulatory demands.
Looking ahead, it is crucial for buyers to stay informed about evolving material technologies and market dynamics that can influence pricing and availability. Embrace a proactive sourcing strategy by conducting regular reviews of your supply chain, exploring new supplier partnerships, and leveraging market intelligence to secure competitive advantages. By doing so, you will not only safeguard your operational integrity but also position your organization for sustainable growth in the global marketplace.