Master Sourcing High-Quality Cold Headed Fasteners for Cost
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cold headed fasteners
Cold headed fasteners play a pivotal role in various industries, serving as essential components in everything from automotive to aerospace applications. Their unique manufacturing process not only enhances strength and precision but also significantly reduces material waste, making them a cost-effective choice for businesses worldwide. As global markets expand, understanding the intricacies of cold headed fasteners becomes crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of cold headed fasteners, including the different types available, materials used, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. Buyers will gain insights into sourcing reliable suppliers and understanding market trends, which are crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
With a focus on actionable information, this guide empowers businesses in regions like Brazil and Colombia to optimize their sourcing strategies, ensuring they procure high-quality fasteners that meet their specific needs. By navigating the complexities of the cold headed fastener market, buyers can enhance their operational efficiency and drive cost savings, ultimately supporting their growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Prepare to delve into a wealth of information designed to equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the global market effectively and make strategic sourcing choices that align with your business objectives.
Understanding cold headed fasteners Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bolts | Typically have a hexagonal head; available in various lengths and diameters. | Automotive, construction, machinery assembly | Pros: High strength, versatile. Cons: May require additional nuts or washers. |
| Nuts | Used in conjunction with bolts; available in various shapes (e.g., hex, square). | Machinery, automotive, furniture assembly | Pros: Essential for secure fastening. Cons: Potential for loosening over time. |
| Screws | Have a threaded shaft and various head styles; can be self-tapping. | Electronics, woodworking, metalworking | Pros: Easy to install, available in many sizes. Cons: Can strip if over-tightened. |
| Rivets | Permanent fastening solution; available in different materials and sizes. | Aerospace, automotive, construction | Pros: Strong, permanent join. Cons: Requires access to both sides of the assembly. |
| Pins | Include various types like dowel and cotter pins; often used for alignment or securing components. | Machinery, automotive, consumer products | Pros: Simple installation, low cost. Cons: Limited load-bearing capacity. |
Bolts
Cold headed bolts are characterized by their hexagonal heads and robust construction, making them ideal for high-strength applications. They are commonly used in automotive and construction sectors, where durability is essential. When purchasing bolts, buyers should consider the material type, coating options for corrosion resistance, and compatibility with nuts and washers. The ability to withstand high stress makes them a reliable choice, although their requirement for additional fastening components may add to assembly time.
Nuts
Nuts are essential components that work in tandem with bolts, providing a secure fastening solution. They come in various shapes, primarily hexagonal and square, and are used across diverse industries, including automotive and furniture assembly. Buyers should evaluate the nut’s material and thread compatibility with corresponding bolts to ensure a secure fit. While nuts are critical for maintaining joint integrity, they may loosen over time, necessitating periodic inspections and potential replacements.
Screws
Cold headed screws are versatile fasteners with a threaded shaft and various head styles, including flat, pan, and round. They are widely used in electronics, woodworking, and metalworking applications due to their ease of installation and availability in numerous sizes. Buyers should consider the screw’s material, thread type, and whether a self-tapping feature is needed for their specific application. Although they are simple to use, screws can strip if over-tightened, which may compromise the integrity of the assembly.
Rivets
Rivets offer a permanent fastening solution, making them ideal for applications in the aerospace and automotive industries where strong, lasting joins are required. They are available in various materials and sizes, allowing for flexibility in design. When purchasing rivets, buyers must ensure they have access to both sides of the assembly for installation, as rivets are typically set using a hammer or rivet gun. While they provide a strong bond, the permanence of rivets means that disassembly can be challenging if repairs are needed.
Pins
Cold headed pins, including dowel and cotter pins, are commonly used for alignment and securing components within machinery and automotive applications. Their simplicity and low cost make them an attractive option for many buyers. When selecting pins, it’s important to assess the load-bearing capacity and material, as these factors will influence their effectiveness in specific applications. While pins are easy to install, they may have limitations in terms of strength compared to other fastener types, which should be considered during the design phase.
Related Video: Multi-Stage Cold Heading – TR Product Manufacturing
Key Industrial Applications of cold headed fasteners
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Cold Headed Fasteners | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine assembly and chassis components | Increased strength and reduced weight of fasteners | Ensure compliance with international automotive standards |
| Aerospace | Aircraft structural components | Enhanced durability and reduced maintenance costs | Source from certified suppliers with aerospace experience |
| Electronics | Assembly of circuit boards | High precision and reliability in electronic devices | Look for fasteners with low electromagnetic interference |
| Construction | Structural framing and connections | Improved load-bearing capabilities and safety | Verify material certifications for environmental resistance |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine assembly | Lower operational costs and improved performance | Seek suppliers with experience in harsh environmental conditions |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, cold headed fasteners are extensively used in engine assemblies and chassis components. These fasteners provide superior strength-to-weight ratios, which is crucial for enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, ensuring that these fasteners meet rigorous automotive standards is essential. This includes adherence to specifications from organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE).
Aerospace
Cold headed fasteners are critical in the aerospace industry, particularly for aircraft structural components. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions while maintaining integrity makes them ideal for this sector. Buyers must prioritize sourcing from manufacturers that are certified to aerospace standards, such as AS9100. This ensures that the fasteners can handle the demanding requirements of flight, including weight constraints and durability over time, ultimately leading to reduced maintenance costs.
Electronics
In the electronics sector, cold headed fasteners are used in the assembly of circuit boards and other electronic devices. The precision and reliability of these fasteners are vital to ensure that devices function correctly over time. International buyers should focus on sourcing fasteners that minimize electromagnetic interference, as this can significantly impact electronic performance. Selecting suppliers with expertise in electronic applications can also help ensure that the fasteners meet specific industry standards.
Construction
Cold headed fasteners play a significant role in construction, particularly in structural framing and connections. These fasteners enhance load-bearing capabilities, which is crucial for the safety and stability of buildings. Buyers in this sector should verify that the materials used for these fasteners are certified for environmental resistance, particularly in regions prone to extreme weather. This will ensure long-term performance and safety of the structures being built.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, particularly in wind turbine assembly, cold headed fasteners are essential for ensuring structural integrity and efficiency. These fasteners help reduce operational costs by minimizing the need for frequent maintenance. Buyers should seek suppliers with experience in manufacturing fasteners that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, such as high winds and corrosive environments. This ensures that the fasteners will perform reliably throughout their intended lifespan.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cold headed fasteners
When selecting materials for cold headed fasteners, international B2B buyers must consider various factors, including the mechanical properties, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in the production of cold headed fasteners, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness. It performs well under high pressure and temperature conditions, making it suitable for a variety of applications. Its corrosion resistance can be enhanced with coatings.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel fasteners are durable and cost-effective, making them a popular choice. However, they can be susceptible to rust if not properly coated or treated, which limits their use in corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel fasteners are ideal for automotive and construction applications where strength is crucial. However, they may not be suitable for marine or chemical environments without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933 is essential. Buyers should also consider the availability of protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid regions.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel exhibits excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, especially in environments exposed to moisture and chemicals. It maintains its integrity at elevated temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel fasteners is their resistance to rust and corrosion, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they are generally more expensive than carbon steel and may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel fasteners are commonly used in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and marine industries due to their hygienic properties and resistance to corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A193 or ISO 3506. Additionally, understanding local market preferences for specific grades (e.g., 304 vs. 316) can influence procurement decisions.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance. It has good thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for specific applications.
Pros & Cons: Brass fasteners are aesthetically pleasing and resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for decorative applications. However, they are softer than steel, which may limit their use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Brass is often used in plumbing, electrical, and decorative applications where appearance and corrosion resistance are critical. Its lower strength may not be suitable for structural applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM B16 or JIS H3250 is vital. Buyers should also consider the environmental impact of brass, as it contains copper, which may be subject to specific regulations in certain regions.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good corrosion resistance. It has a lower tensile strength compared to steel but is highly malleable and can be easily formed into complex shapes.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of aluminum fasteners is their lightweight nature, making them ideal for applications where weight savings are crucial. However, they are less durable than steel and may not perform well under high-stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Aluminum fasteners are widely used in aerospace and automotive industries where weight reduction is essential. Their use in high-stress applications may require careful consideration of load-bearing capacities.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B211 or EN AW-6061. Understanding local preferences for aluminum grades can also influence purchasing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for cold headed fasteners | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Automotive, construction | High strength and cost-effective | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, marine | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical, decorative | Aesthetically pleasing, corrosion-resistant | Softer, limited high-stress use | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and malleable | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cold headed fasteners
Cold headed fasteners are increasingly favored in various industries due to their superior strength, lower production costs, and versatility. Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance (QA) protocols is essential for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section delves into the key manufacturing stages, quality control standards, and best practices for ensuring product reliability.
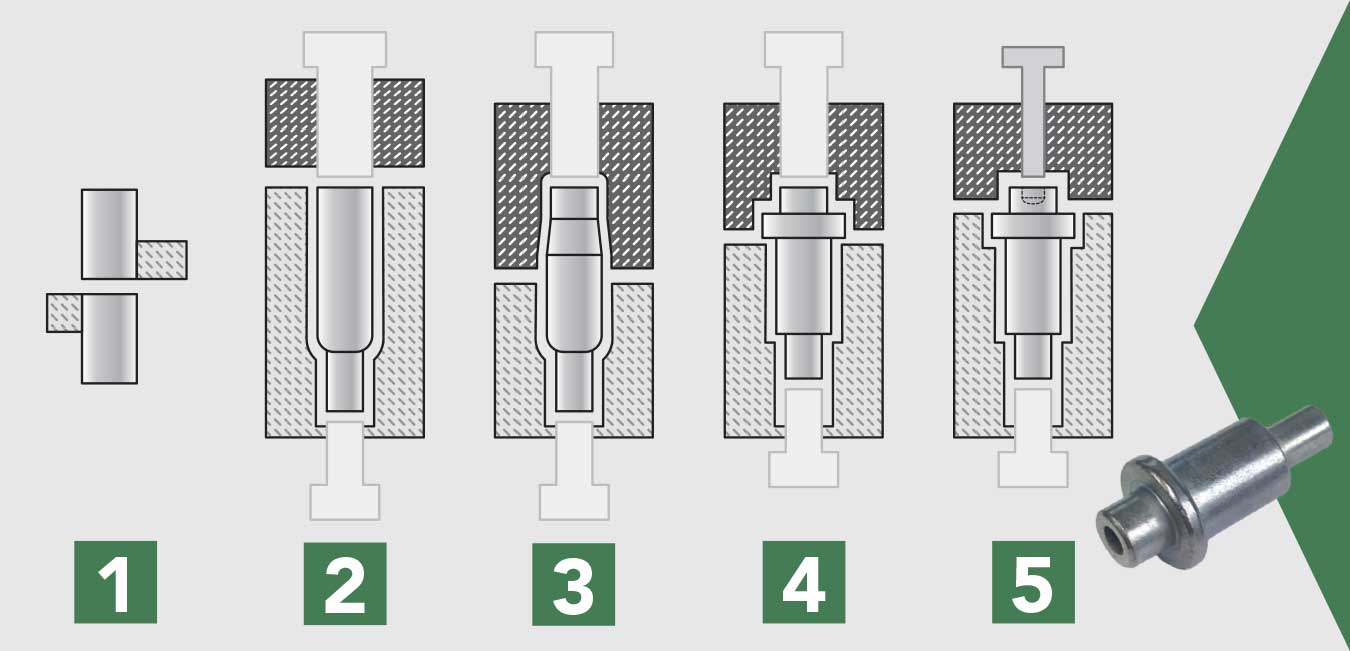
Manufacturing Process for Cold Headed Fasteners
The production of cold headed fasteners involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and performance.
1. Material Preparation
The process begins with the selection of appropriate raw materials, typically high-quality metal alloys such as carbon steel, brass, or stainless steel. The choice of material impacts the fastener’s strength, corrosion resistance, and overall performance.
- Material Inspection: Before use, incoming materials undergo rigorous inspection to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for impurities, dimensions, and mechanical properties.
- Blank Creation: Metal rods are cut into blanks of predetermined lengths, which will be fed into the cold heading machines. The size and shape of these blanks are crucial for achieving the desired final product.
2. Forming
The heart of the cold heading process is the actual forming stage, where the metal blanks are shaped into fasteners using high pressure.
- Cold Heading Machines: These machines utilize a die and punch system to deform the metal. The blank is placed in the die, and a punch applies pressure to shape it into the desired fastener configuration.
- Key Techniques:
- Multi-Stage Heading: For complex shapes, multiple forming operations may be employed. This technique allows for the production of intricate designs without the need for secondary machining.
- Near Net Shape (NNS) Production: This method reduces waste by creating parts that are close to their final dimensions, minimizing the need for further processing.
3. Assembly
In some cases, cold headed fasteners are part of multi-piece assemblies. Cold forming allows for the integration of multiple components into a single piece, streamlining the assembly process and reducing labor costs.
- Integration of Components: By forming multi-piece assemblies, manufacturers can eliminate welding and other joining processes, leading to a more efficient production line.
4. Finishing
After forming, cold headed fasteners may undergo various finishing processes to enhance their surface properties.
- Surface Treatments: Common treatments include plating, coating, and polishing to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Final Inspection: Each batch is subjected to a final inspection to ensure it meets the specified dimensions and quality standards.
Quality Assurance in Cold Headed Fasteners
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of cold headed fasteners, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following standards that govern the quality of cold headed fasteners:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), emphasizing customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental requirements.
- API Certification: Relevant for fasteners used in the oil and gas industry, API certification ensures products meet stringent industry-specific standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
The quality control process in cold headed fasteners typically includes several critical checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify any deviations from standards early on.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to verify that they meet all quality and dimensional requirements.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to ensure the integrity and performance of cold headed fasteners:
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile, shear, and hardness tests assess the material’s strength and durability.
- Dimensional Verification: Calipers and gauges are used to confirm that fasteners meet specified dimensions.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing help identify internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier compliance:
- Audits: Conduct on-site audits of potential suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols. This can include reviewing their certifications and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline testing results and compliance with standards. This documentation should cover both raw materials and finished products.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent third-party inspection services to assess the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance regarding product reliability.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing cold headed fasteners internationally, buyers should be aware of specific nuances:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding quality. Understanding these differences can help prevent compliance issues.
- Documentation Requirements: Ensure that all necessary documentation, including certificates of compliance and test reports, is provided. This is particularly important for buyers in regions like Europe, where regulatory compliance is strictly enforced.
- Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication regarding quality expectations and lead to improved compliance.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in cold headed fasteners, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and secure reliable, high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cold headed fasteners Sourcing
When sourcing cold headed fasteners, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and offers practical tips for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in cold headed fasteners is the raw material. Common materials include carbon steel, brass, aluminum, and stainless steel. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand and material availability, so it’s wise to monitor global commodity prices closely.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the workforce involved in the manufacturing process. Automated cold heading machines require fewer operators, which can lower labor costs. However, skilled labor is necessary for setup and quality control, impacting overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations such as utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes, like cold heading, tend to have lower overhead due to reduced energy consumption compared to hot forging.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs involve the initial investment in dies and machinery required for production. These costs are amortized over the production volume, making them a crucial factor in pricing, especially for custom or specialized fasteners.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the reliability and safety of fasteners requires rigorous QC processes. This may include testing for material properties, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish, which adds to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly affect the final price, particularly for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping mode, and customs duties must be accounted for.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. Understanding the supplier’s pricing strategy and market position can aid in negotiating better terms.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes generally lead to lower unit prices due to economies of scale. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can significantly impact the overall cost.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can drive up costs due to additional tooling and production complexities. Clearly defining your requirements can help suppliers provide accurate quotes.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice of material and the required quality certifications (like ISO or ASTM) can influence pricing. Premium materials or higher-quality standards will naturally incur higher costs.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, location, and production capabilities can affect pricing. Local suppliers may offer lower logistics costs, while established suppliers might charge more for their reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (like FOB, CIF) can impact the total cost. Buyers should clarify who bears the risk and costs during transit to avoid unexpected expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers. Open discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders or long-term contracts, can yield better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Always consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, replacement, and logistics costs. A slightly higher initial price may be justified by lower long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and taxes that can impact the final price. Building relationships with suppliers can also facilitate better pricing arrangements.
-
Quality Assurance: Insist on quality certifications and consider suppliers who offer robust warranty and return policies. This can save costs related to defective products.
-
Local Market Insight: Understanding the local market dynamics in regions such as Africa and South America can provide strategic advantages. Tailor your approach to align with regional practices and supplier capabilities.
Disclaimer
Prices for cold headed fasteners are indicative and can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable to obtain specific quotes from suppliers to ensure accurate budgeting.
Spotlight on Potential cold headed fasteners Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘cold headed fasteners’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cold headed fasteners
Cold headed fasteners are essential components in various manufacturing processes, and understanding their technical properties and associated trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only facilitates informed purchasing decisions but also enhances supplier communication, especially for businesses operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Technical Properties of Cold Headed Fasteners
-
Material Grade
The material grade of a cold headed fastener indicates its strength, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, brass, and aluminum. Selecting the appropriate material is vital for ensuring that the fastener can withstand the specific environmental and mechanical conditions it will encounter, thus minimizing the risk of failure. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the fastener’s size or shape. For cold headed fasteners, tighter tolerances often lead to better fit and function in assembly applications. Understanding tolerance requirements is essential for ensuring compatibility with other components and achieving the desired performance in your final product. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of a fastener affects its corrosion resistance, aesthetic appearance, and overall performance. Common surface finishes include zinc plating, passivation, and anodizing. Buyers must consider surface treatment options that align with their operational environments and product requirements, as these can significantly impact durability and maintenance. -
Head Styles
Cold headed fasteners come in various head styles (e.g., hex, round, flat) tailored to specific applications. The choice of head style impacts the fastener’s holding strength and ease of installation. Understanding the functional requirements of your project will help in selecting the right head style, which can influence the efficiency of assembly processes. -
Strength Class
Fasteners are often categorized by their strength class, which indicates their load-bearing capacity. This classification is particularly important in safety-critical applications where failure could have severe consequences. Buyers should evaluate the strength requirements based on the intended use of the fasteners to avoid under-specifying or over-specifying their purchases. -
Production Method
Recognizing the production method (e.g., cold heading vs. machining) helps buyers understand the benefits and limitations of the fasteners. Cold heading typically results in less waste and faster production times compared to machining. This insight can assist in aligning procurement strategies with manufacturing capabilities.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for ensuring that the fasteners meet the required specifications and quality standards for your products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Being aware of MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory effectively and negotiate better terms with suppliers, particularly when entering new markets or managing smaller-scale projects.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. Issuing an RFQ can streamline the procurement process and help buyers compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they secure the best possible deal. -
Incoterms
International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for managing logistics, shipping costs, and risk during the transportation of cold headed fasteners. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is vital for effective project planning and inventory management, especially in industries where production schedules are tight. -
Certification Standards
Certification standards (such as ISO, ASTM) indicate that the fasteners meet specific quality and safety criteria. Buyers should consider these certifications to ensure compliance with industry regulations and enhance the reliability of their supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their purchasing strategies, ensuring they procure the right cold headed fasteners that meet their operational needs and quality expectations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the cold headed fasteners Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The cold headed fasteners market is experiencing robust growth, driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for lightweight and durable materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction is propelling the adoption of cold headed fasteners. As manufacturers seek to enhance product performance while minimizing costs, the cold forming process proves advantageous due to its efficiency and reduced scrap rates.
Emerging technologies, such as Industry 4.0 and automation, are revolutionizing the sourcing and manufacturing processes in this sector. International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for procurement, enabling real-time access to supplier information and inventory levels. This shift towards e-commerce is particularly significant for buyers in regions like Africa and South America, where traditional supply chains may be less developed.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Additionally, sustainability is becoming a key purchasing criterion for B2B buyers. Companies are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate environmental responsibility and ethical practices. The integration of sustainable materials and production methods into the cold headed fasteners supply chain is not just a trend but a necessity for long-term competitiveness in the global market. Buyers should stay informed about these trends to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their operational goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In the cold headed fasteners sector, sustainability is increasingly crucial due to its environmental impact. Traditional manufacturing processes often generate significant waste and energy consumption. However, cold heading reduces material waste by minimizing scrap, which not only lowers costs but also lessens environmental footprints. By opting for suppliers who utilize eco-friendly practices, B2B buyers can contribute to a more sustainable supply chain.
Ethical sourcing is also paramount. Buyers should seek manufacturers that comply with international labor standards and demonstrate transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to ethical practices. Moreover, the use of recycled materials in manufacturing cold headed fasteners is gaining traction, aligning with global sustainability goals and enhancing brand reputation.
Investing in suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing not only fulfills corporate social responsibility (CSR) objectives but also attracts environmentally conscious customers, thereby creating a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Brief Evolution/History
The cold heading process has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially developed as a method to improve manufacturing efficiency, it has transformed into a vital technique for producing high-quality fasteners. The transition from traditional machining to cold forming technology has enabled manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances and complex geometries, making cold headed fasteners essential in various applications.
As industries have progressed, so has the technology behind cold heading. Innovations such as computer numerical control (CNC) and automation have further enhanced production capabilities, allowing for greater precision and speed. This evolution reflects the ongoing demand for high-performance fasteners and the necessity for manufacturers to adapt to changing market dynamics and consumer expectations. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that have shaped the cold headed fasteners industry today.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cold headed fasteners
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of cold headed fasteners?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience and reputation. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which demonstrates quality management systems. Assess their production capabilities, including technology and machinery used in the cold heading process. Request references or case studies from previous clients, particularly those in your region or industry. Additionally, consider their financial stability and ability to meet your volume requirements to ensure long-term reliability. -
Can I customize cold headed fasteners to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for cold headed fasteners. You can specify dimensions, materials, and coatings based on your application needs. Communicate your requirements clearly, including any technical drawings or specifications. Be aware that customized solutions may come with longer lead times and potential increases in minimum order quantities (MOQs), so plan accordingly. -
What are the typical lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQs) for cold headed fasteners?
Lead times vary by supplier and order complexity, but typically range from 2 to 6 weeks for standard products. For customized fasteners, expect longer lead times. MOQs can differ significantly; some suppliers may have a minimum of 1,000 units, while others might accommodate smaller orders. Discuss your needs with suppliers to find the best fit and clarify any implications for pricing and delivery. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by cold headed fastener suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common options include upfront payment, net 30, or net 60 terms. Some suppliers may offer discounts for early payment or larger orders. It’s essential to establish clear payment terms before placing an order to avoid misunderstandings. In international trade, consider using letters of credit for additional security, especially with new suppliers. -
How can I ensure the quality of cold headed fasteners I receive?
To ensure quality, request detailed documentation, including material certifications and inspection reports. Look for suppliers who implement stringent quality assurance processes, such as in-process inspections and final quality checks. Ask about their compliance with international quality standards. Conducting an audit or visiting the manufacturing facility can also provide insights into their quality control practices. -
What certifications should I look for in cold headed fastener suppliers?
Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management, and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Depending on your industry, you may also need specific certifications like RoHS or REACH for compliance with environmental regulations. Suppliers in the aerospace or automotive sectors may require additional certifications such as AS9100 or IATF 16949, respectively. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing cold headed fasteners internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and customs regulations in your country. Discuss logistics options with your supplier, including Incoterms that define the responsibilities for shipping and handling. Be aware of potential delays due to customs clearance and ensure you have the necessary documentation ready. Establishing a reliable logistics partner can help mitigate risks associated with international shipping. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers of cold headed fasteners?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing. If issues arise, first attempt to resolve them through direct communication. If a resolution isn’t achieved, consider mediation or arbitration as a next step, as these methods can be less confrontational and costly than litigation. Always ensure that your contracts include dispute resolution clauses to provide a structured approach to conflict resolution.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cold headed fasteners
Cold headed fasteners represent a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their procurement strategies. The advantages of this manufacturing process—including higher production rates, reduced scrap material, and enhanced strength—offer compelling reasons to consider cold heading over traditional methods. By leveraging these benefits, businesses can improve their bottom line while ensuring the reliability and performance of their fasteners.
Strategic sourcing in this domain is essential, as it enables buyers to align with reputable manufacturers who adhere to high-quality standards and innovative practices. Establishing strong partnerships can lead to reduced lead times, lower costs, and access to a diverse range of materials tailored to specific industry needs.
Looking ahead, as global demand for efficient and sustainable manufacturing grows, the cold headed fastener market is poised for expansion. Buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should proactively engage with suppliers to explore tailored solutions that meet their unique requirements. Invest in strategic sourcing today to secure a competitive advantage and ensure your supply chain remains robust and resilient in the face of evolving market dynamics.