Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Airplane Cables
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for airplane cables
Navigating the complex landscape of the global market for airplane cables is critical for international B2B buyers looking to ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of their aviation operations. Airplane cables, known for their high tensile strength and flexibility, are indispensable components in various applications ranging from flight control systems to heavy lifting during aircraft assembly. Their unique characteristics not only meet stringent aviation standards but also serve a diverse range of industries including marine, construction, and military sectors.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types and materials of airplane cables, highlighting the advantages of stainless steel versus galvanized options. It also addresses manufacturing and quality control standards, ensuring that buyers understand the importance of sourcing compliant products. A detailed overview of suppliers across different regions, including insights into cost factors and market trends, empowers buyers to make informed decisions tailored to their specific needs.
Furthermore, the guide tackles frequently asked questions, providing clarity on critical issues that can impact sourcing strategies. For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—such as those in Poland and Argentina—this resource serves as an essential tool for optimizing procurement processes, enhancing operational efficiency, and maintaining competitive advantage in the aviation sector. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can navigate the global market for airplane cables with confidence and precision.
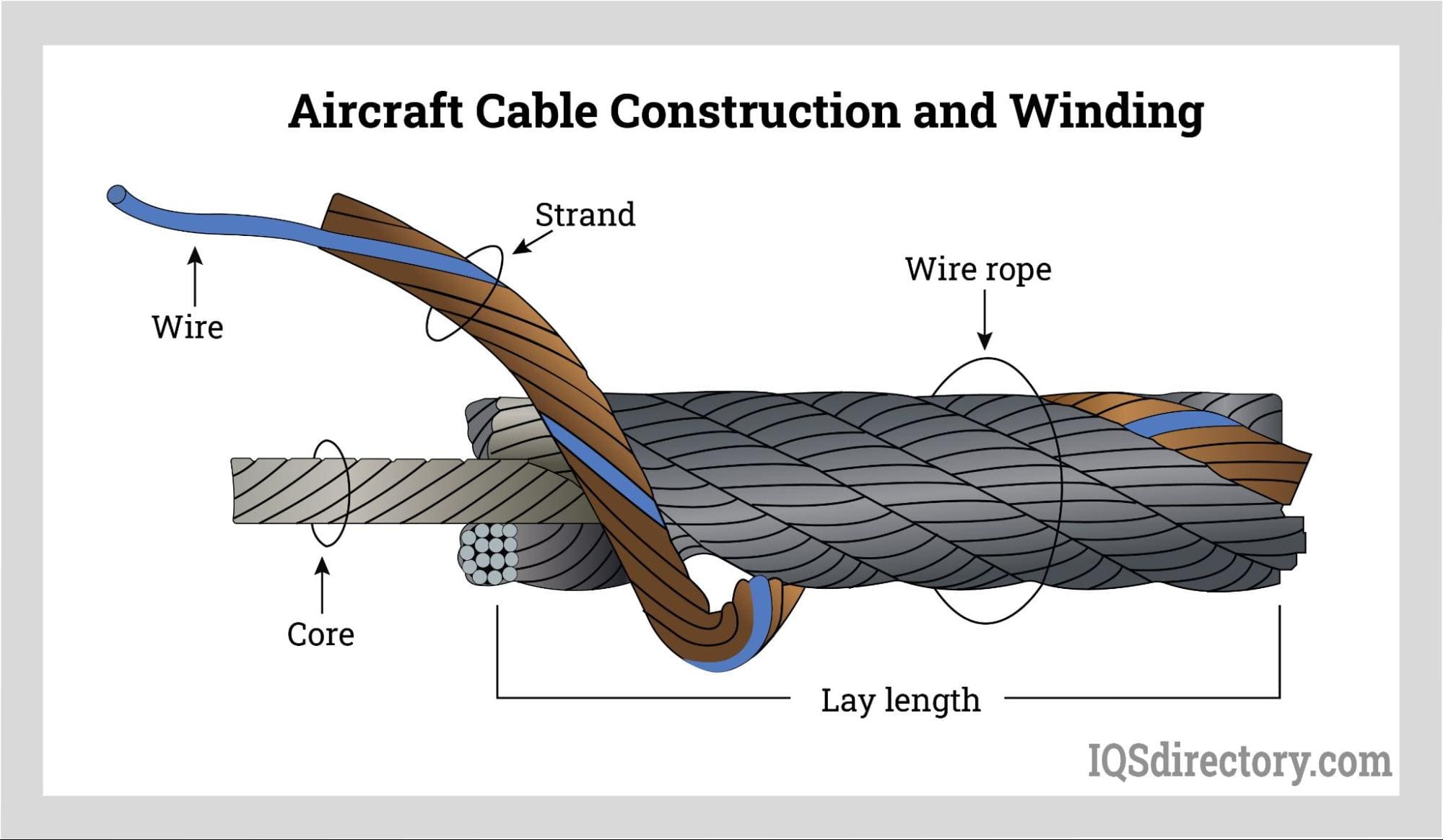
Understanding airplane cables Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Cables | High corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, non-magnetic | Flight control systems, marine applications, rigging | Pros: Durable, low maintenance. Cons: Higher cost than galvanized cables. |
| Galvanized Cables | Cost-effective, zinc-coated for corrosion resistance | Agricultural use, construction, general lifting | Pros: Economical, readily available. Cons: Limited corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel. |
| 7×7 Construction Cables | Flexible with moderate load capacity | Aircraft controls, safety cables | Pros: Good flexibility, compact size. Cons: Less load capacity than 7×19 cables. |
| 7×19 Construction Cables | Enhanced flexibility and higher load capacity | Heavy-duty applications, military, aerospace | Pros: Superior load-bearing capacity. Cons: Bulkier than 7×7 cables. |
| Custom Configured Cables | Tailored specifications for unique applications | Specialized aerospace, military, and industrial uses | Pros: Meets specific needs. Cons: Potentially higher lead times and costs. |
Stainless Steel Cables
Stainless steel aircraft cables are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, making them suitable for demanding environments. They are commonly used in flight control systems and marine applications, where exposure to moisture and saltwater is prevalent. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific alloy (such as 316 for marine use) and the required tensile strength for their application, as well as the long-term cost benefits of reduced maintenance.
Galvanized Cables
Galvanized aircraft cables are coated with zinc to enhance corrosion resistance, offering a cost-effective solution for various applications, particularly in agriculture and construction. Their strength makes them suitable for general lifting and utility rigging. Buyers should weigh the benefits of lower costs against the potential for reduced longevity in highly corrosive environments, ensuring that the choice aligns with their operational needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7×7 Construction Cables
The 7×7 construction cables consist of seven strands of seven wires, providing a balance of flexibility and load capacity. These cables are ideal for applications such as aircraft controls and safety cables, where maneuverability is crucial. B2B buyers should assess the specific flexibility requirements and load ratings to ensure compatibility with their equipment, as these cables may not handle as much weight as heavier constructions.
7×19 Construction Cables
Offering increased flexibility and load capacity, 7×19 construction cables consist of seven strands of nineteen wires, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications, including military and aerospace uses. Their superior load-bearing capabilities make them a preferred choice for critical applications. Buyers should consider the size and weight constraints of their projects, as well as the specific regulatory standards that may apply.
Custom Configured Cables
Custom configured cables are tailored to meet unique specifications for specialized applications in aerospace, military, and industrial sectors. These cables can be designed for specific load requirements, diameters, and material compositions. B2B buyers should evaluate the lead times and costs associated with custom orders, ensuring that the investment aligns with their operational goals and that the specifications meet the necessary safety and performance standards.
Related Video: What are Transformer Models and how do they work?
Key Industrial Applications of airplane cables
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Airplane Cables | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Flight Control Systems | Enhanced safety and precision in aircraft operation | Compliance with FAA and military standards; supplier certifications |
| Marine | Lifeline and Safety Systems | Improved safety for crew and passengers | Corrosion resistance; availability in marine-grade materials |
| Construction | Lifting and Rigging Equipment | Efficient lifting of heavy materials | Load capacity specifications; flexibility in tight spaces |
| Agriculture | Irrigation and Crop Management Systems | Increased efficiency in water management | Durability against environmental stressors; cost-effectiveness |
| Defense & Military | Arresting Gear for Aircraft | Safe deceleration of aircraft in high-stakes scenarios | High tensile strength; compliance with military specifications |
Aerospace: Flight Control Systems
In the aerospace sector, airplane cables are integral to flight control systems, facilitating the precise movement of control surfaces such as ailerons, elevators, and rudders. These cables must meet stringent safety and performance standards, ensuring reliability during flight. For international buyers, particularly those in Europe and the Middle East, sourcing cables that comply with FAA and military standards is crucial. Additionally, understanding the specific tensile strength requirements and ensuring the supplier has the necessary certifications can mitigate risks associated with aircraft safety.
Marine: Lifeline and Safety Systems
Airplane cables are widely used in marine applications as lifelines and safety systems to protect crew members and passengers. Their high corrosion resistance, particularly in 316 stainless steel variants, makes them suitable for coastal and marine environments. Buyers from South America and Africa should prioritize suppliers that provide cables specifically designed for marine use, ensuring they can withstand harsh conditions. Assessing the durability and maintenance requirements of these cables can lead to long-term safety and reduced replacement costs.
Construction: Lifting and Rigging Equipment
In construction, airplane cables are employed for lifting and rigging heavy materials, providing a reliable solution for construction sites. Their flexibility and compact design allow for efficient routing through tight spaces, which is essential in urban environments. B2B buyers in Europe, especially in Poland, should consider the load capacity specifications and the cable’s ability to endure repeated stress. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who offer detailed product specifications can enhance project efficiency and safety.
Agriculture: Irrigation and Crop Management Systems
Airplane cables find applications in agricultural irrigation systems, where they assist in managing water flow and supporting irrigation equipment. Their durability against environmental stressors ensures longevity, making them a cost-effective solution for farmers in South America and Africa. Buyers should focus on sourcing cables that offer resistance to corrosion and wear, as well as those that can handle the specific demands of agricultural environments. Evaluating the cost versus the expected lifespan can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Defense & Military: Arresting Gear for Aircraft
In military applications, airplane cables serve as arresting gear for aircraft, providing a critical function in safely decelerating planes on short landing strips or aircraft carriers. The cables must possess high tensile strength and fatigue resistance to endure extreme conditions. For international buyers, particularly from the Middle East, ensuring compliance with military specifications is essential. It is also important to engage with suppliers who have a proven track record in military contracts, as this can influence the reliability and safety of the equipment.
Related Video: Rigging Flight Control Cables
Strategic Material Selection Guide for airplane cables
When selecting materials for airplane cables, it’s essential to consider properties that influence performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in airplane cables, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel cables, particularly those made from 316 and 304 alloys, offer excellent corrosion resistance, high tensile strength, and flexibility. They can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding aviation environments.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is highly durable and requires minimal maintenance, which is advantageous for long-term use. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which may increase overall project costs. The manufacturing process can also be complex, requiring specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
These cables are ideal for critical applications such as flight control systems and safety cables, where reliability is paramount. Their corrosion resistance makes them suitable for marine environments or areas exposed to harsh chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and MIL specifications. Additionally, understanding local sourcing capabilities for stainless steel can help mitigate costs.
Galvanized Steel
Key Properties:
Galvanized steel cables are made from carbon steel that has been coated with zinc to enhance corrosion resistance. They provide good tensile strength and are available in various diameters.
Pros & Cons:
These cables are cost-effective and readily available, making them a popular choice for general industrial applications. However, they are less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel, which may limit their use in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
Galvanized cables are suitable for applications such as winch systems and general rigging. While they perform well under normal conditions, they may not be ideal for environments with high humidity or exposure to saltwater.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from South America and Africa should be aware of local standards and certifications for galvanized steel. Understanding the environmental conditions where the cables will be used is crucial for ensuring longevity and performance.
Nylon-Coated Steel
Key Properties:
Nylon-coated steel cables combine the strength of steel with a protective nylon layer that enhances corrosion resistance and reduces wear. This coating also provides additional flexibility.
Pros & Cons:
The nylon coating offers excellent protection against abrasion and environmental factors, making these cables suitable for outdoor applications. However, the coating can wear off over time, potentially exposing the steel beneath to corrosion.
Impact on Application:
These cables are often used in applications requiring a combination of strength and flexibility, such as in control systems and safety mechanisms. The nylon layer also reduces noise and vibration, which can be beneficial in certain aircraft systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
When sourcing nylon-coated cables, buyers should verify compliance with relevant standards, especially in regions with stringent aviation regulations. Understanding the expected lifespan of the coating can aid in maintenance planning.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite cables utilize a combination of materials, such as carbon fiber and polymers, to achieve lightweight and high-strength properties. They are designed to withstand high stress and environmental impacts.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of composite cables is their lightweight nature, which can contribute to overall fuel efficiency in aircraft. However, they tend to be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
These cables are particularly useful in modern aircraft designs where weight reduction is critical. They can be used in a variety of applications, including structural components and control systems.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should be aware of the evolving standards for composite materials in aviation. Understanding the supply chain for these specialized materials is also crucial for timely procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for airplane cables | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Flight control systems | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Galvanized Steel | General rigging and winch systems | Cost-effective and readily available | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Nylon-Coated Steel | Control systems and safety cables | Enhanced abrasion resistance | Coating can wear off | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Structural components in aircraft | Lightweight and high strength | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
This comprehensive material selection guide provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights into the various types of airplane cables, enabling informed decisions based on specific application requirements and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for airplane cables
Airplane cables are integral components in aviation, demanding a high level of precision and quality assurance throughout their manufacturing process. This section provides a detailed overview of the typical manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality control measures that are essential for B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of airplane cables involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure the final product meets stringent safety and performance standards.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Most airplane cables are made from high-strength steel or stainless steel, often classified under grades such as 302, 304, or 316.
- Wire Sourcing: Suppliers must ensure that the wires meet specific tensile strength and corrosion resistance requirements. Buyers should verify that raw materials are sourced from reputable suppliers that adhere to international standards.
- Pre-treatment: The wires undergo cleaning and surface treatment processes, such as pickling, to remove impurities and enhance adhesion for coatings.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming the wires into strands.
- Stranding: Wires are twisted together to form strands, typically in configurations such as 7×7 or 7×19. This process is crucial for achieving the desired flexibility and load-bearing capacity.
- Coating: Depending on the application, the cables may receive protective coatings, such as galvanization or nylon coating, to improve corrosion resistance and durability.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves combining the strands to create the final cable structure.
- Cabling: The individual strands are further twisted together to form the complete cable. Precision in this step is vital to ensure uniformity and strength.
- End Fittings: Depending on the application, end fittings such as swages or loops may be added. These fittings must be securely attached to maintain integrity under load.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves a series of finishing processes to ensure the cable is ready for use.
- Inspection: Each cable undergoes a thorough inspection to identify any defects. This is often performed using visual checks and automated systems.
- Packaging: Cables are then packaged for transport, ensuring they are protected from environmental factors that could cause damage during shipping.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for airplane cables, ensuring that they meet international safety and performance standards.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the relevant international and industry-specific standards applicable to airplane cables:
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures that manufacturers maintain consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For cables used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to API specifications is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to ensure adherence to standards:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the finished products, including dimensional checks and strength tests.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality of airplane cables:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the maximum load the cable can withstand before failure.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses the cable’s performance under repeated loading conditions.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Evaluates the cable’s ability to withstand environmental exposure, particularly important for cables used in marine or harsh conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols.
- Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing results, compliance with standards, and any deviations from expected performance.
- Third-party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspectors to evaluate the supplier’s facilities and processes. This provides an unbiased assessment of their capabilities.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be mindful of specific quality control nuances:
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers understand and comply with both local and international regulations governing aviation products.
- Cultural Considerations: Be aware of cultural differences that may affect manufacturing practices and communication regarding quality standards.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Understand how global supply chain issues may impact the availability of quality materials and adherence to timelines.
In conclusion, the manufacturing and quality assurance processes for airplane cables are complex but critical for ensuring safety and reliability in aviation applications. By understanding these processes and implementing thorough verification measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions and foster successful partnerships with suppliers.
Related Video: Boeing & Airbus Factory✈️2025 Production line and Assembly – Manufacturing process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for airplane cables Sourcing
Airplane cables, essential components in the aviation industry, come with a multifaceted cost structure that B2B buyers must understand to ensure optimal sourcing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver for airplane cables is the raw materials used. High-strength steel, stainless steel (304 and 316), and galvanized steel are common materials, each affecting price based on market fluctuations. Stainless steel typically commands a higher price due to its superior corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs involve both the workforce needed for manufacturing and any specialized skills required for assembly and quality assurance. Regions with lower labor costs can provide more competitive pricing, making it essential for international buyers to consider sourcing from such locations.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and factory operations. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, impacting overall pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling, which includes molds and dies for cable production, can be significant. However, this cost is often amortized over large production runs, making it crucial to assess the volume of the order.
-
Quality Control (QC): Given the critical safety applications of airplane cables, rigorous QC processes are necessary. This includes testing for tensile strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance, contributing to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., FAA, ASTM) also add to expenses but are essential for compliance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Logistics: Shipping costs vary significantly based on distance, mode of transport, and volume. International buyers must consider these costs, especially if they are importing from regions like Asia or North America.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the supplier’s position in the market and their perceived value proposition.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of airplane cables:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications, such as unique diameters or materials, can increase costs. Standardized products tend to be more economical.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher-quality cables with recognized certifications will be priced at a premium. Buyers should balance the need for quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is crucial for assessing total costs. Different terms can significantly affect the final price based on who bears the shipping risk and costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume purchasing to negotiate better terms. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable pricing and terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, replacement, and operational costs over the product’s lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances: For international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, currency fluctuations and import duties can significantly impact pricing. It’s prudent to factor in these variables during negotiations.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct market research to understand the typical pricing structures and available suppliers in your region. Benchmarking against competitors can provide insights into fair pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices for airplane cables can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors and market conditions. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before making sourcing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential airplane cables Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘airplane cables’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for airplane cables
Aircraft cables, also referred to as airplane cables, are integral components in aviation and various industrial applications. Understanding their technical properties and the associated trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. Below is a concise overview of essential specifications and common industry terms that every buyer should know.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of the cable material based on its composition and mechanical properties. Common grades include 302, 304, and 316 stainless steel, as well as galvanized carbon steel.
– B2B Importance: Material grade affects corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and suitability for specific environments. For example, 316 stainless steel is ideal for marine applications due to its superior saltwater resistance, making it a preferred choice for buyers in coastal regions. -
Construction Type
– Definition: The arrangement of wires in the cable, typically represented as 7×7 or 7×19 configurations, indicating the number of strands and wires per strand.
– B2B Importance: The construction type influences flexibility and load-bearing capacity. Buyers must select the appropriate configuration to ensure optimal performance in their specific application, such as flight controls or lifting mechanisms. -
Diameter
– Definition: The thickness of the cable, usually measured in inches or millimeters, with common sizes ranging from 3/64″ to 3/8″.
– B2B Importance: The diameter directly correlates with the cable’s strength and application. Buyers need to assess the load requirements of their projects to determine the necessary diameter, ensuring safety and functionality. -
Breaking Strength
– Definition: The maximum load that a cable can withstand before failure, typically expressed in pounds or kilograms.
– B2B Importance: Understanding breaking strength is crucial for safety and compliance with regulatory standards. B2B buyers must ensure that the selected cable can handle the anticipated loads in their applications without risk of failure. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from specified dimensions, which can affect the cable’s fit and performance in mechanical systems.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance levels are vital for ensuring that cables fit properly within pulleys or other mechanisms. Buyers should specify tolerance requirements to prevent operational issues.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers from regions with limited demand must negotiate terms that suit their purchasing capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent by buyers to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare offers from multiple suppliers, facilitating better negotiation and decision-making. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risk, and costs associated with international purchases, particularly relevant for buyers in Africa and South America. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should consider lead times when sourcing airplane cables to avoid delays in operations.
By grasping these specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing airplane cables, ensuring safety, compliance, and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the airplane cables Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The airplane cables sector is witnessing significant transformation driven by various global factors, including technological advancements, increasing demand for lightweight materials, and the push for enhanced safety standards. Key trends impacting international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, include the integration of digital technologies in sourcing and manufacturing processes. Innovations such as automation in production and the use of data analytics for supply chain optimization are becoming prevalent, allowing companies to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Moreover, there is a growing emphasis on the use of high-performance materials, such as advanced composites and specialty coatings, which enhance the durability and corrosion resistance of airplane cables. This trend is particularly relevant for regions with harsh environmental conditions, such as coastal areas in South America and the Middle East, where corrosion resistance is crucial. Buyers should also be aware of the regulatory landscape, as compliance with international safety standards, such as those set by the FAA and EASA, is essential for maintaining market access.
Finally, the increasing focus on sustainability is reshaping sourcing strategies. B2B buyers are now prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including reduced carbon footprints and ethical labor practices. This shift not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also meets the growing consumer demand for responsible sourcing.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability in the airplane cables sector extends beyond mere compliance; it encompasses a holistic approach that addresses environmental impacts throughout the product lifecycle. The production of airplane cables often involves processes that can be resource-intensive and polluting. Therefore, B2B buyers must evaluate suppliers based on their environmental practices, including waste management, water usage, and energy consumption.
Ethical sourcing is increasingly vital, especially as global supply chains become more complex. Buyers should seek suppliers who are transparent about their sourcing practices and who adhere to fair labor standards. This not only mitigates reputational risks but also fosters long-term relationships built on trust and responsibility.
Additionally, the adoption of “green” certifications and materials is gaining traction. Look for suppliers offering cables made from recycled materials or those that have certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management. These credentials can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and can help buyers make informed decisions that align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of airplane cables can be traced back to the early days of aviation, where the need for reliable and lightweight components was paramount. Initially, these cables were simple wire ropes used primarily for control surfaces. Over the decades, advancements in metallurgy and engineering have led to the creation of specialized cables designed to withstand the rigorous demands of aviation, including high tensile strength and fatigue resistance.
With the advent of modern aviation, the specifications for airplane cables have evolved significantly, incorporating materials such as stainless steel and advanced composites. This evolution has been driven by the need for greater safety, efficiency, and performance in aircraft operations. As the aviation industry continues to innovate, the airplane cables sector is expected to further adapt, focusing on sustainability and technological integration, making it an exciting area for international B2B buyers to explore.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of airplane cables
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of airplane cables?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with industry certifications such as FAA or MIL-DTL-83420 compliance. Check their experience in the aviation sector and their track record with international clients. Request references and assess their production capabilities, including quality control processes. Additionally, ensure they have a reliable supply chain and can provide documentation for traceability and quality assurance. Conducting a site visit, if feasible, can also give insights into their operations. -
Can I customize airplane cables to fit my specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for airplane cables. You can specify dimensions, materials (such as stainless steel or galvanized), and construction types (like 7×7 or 7×19). It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly and confirm that the supplier can meet applicable safety standards. Be prepared to provide details on your application to help the supplier recommend the best cable configuration for your needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for airplane cables?
MOQs for airplane cables can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 meters, depending on the customization required. Lead times can also fluctuate based on production schedules and material availability, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss these factors during initial negotiations to align expectations and avoid delays. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing airplane cables internationally?
Common payment terms include wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal, depending on the supplier’s policy and your relationship with them. For large orders, suppliers may require a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due before shipment. Always clarify the payment schedule and any conditions for payment to prevent disputes. Utilizing escrow services for significant transactions can provide an added layer of security. -
How can I ensure the quality of the airplane cables I am purchasing?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test reports from the supplier, confirming compliance with international standards like ASTM and MIL. Conduct third-party inspections during production and before shipment. Establish clear quality assurance criteria in your contract, including tolerances, material specifications, and testing protocols. Regularly reviewing supplier performance can also help maintain consistent quality. -
What certifications should airplane cables have for international trade?
Key certifications include FAA standards for aviation components, MIL-DTL-83420 for military applications, and ASTM standards for material specifications. Depending on your market, other certifications may be necessary, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Always verify that the supplier can provide documentation for these certifications, as they are critical for compliance and safety in international trade. -
What are the logistics considerations when importing airplane cables?
Logistics considerations include shipping methods (air freight vs. sea freight), customs regulations, and import duties specific to your country. Ensure your supplier is familiar with international shipping requirements and can provide necessary documentation such as bills of lading and customs declarations. Collaborating with a reliable logistics partner can help streamline the import process and mitigate potential delays or issues at customs. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers of airplane cables?
Effective dispute resolution starts with clear communication and a well-defined contract outlining terms and conditions. In the event of a dispute, document all correspondence and agreements. If direct negotiation fails, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods, as these can be less costly and time-consuming than litigation. Familiarize yourself with international trade laws that may apply to your situation, as they can influence the resolution process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for airplane cables
In summary, strategic sourcing of airplane cables is crucial for ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of aviation operations. International B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers that meet stringent industry standards and offer a range of materials, such as stainless steel and galvanized options, to suit diverse applications. Key considerations include tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and flexibility, which are essential for performance in critical aviation environments.
As the global aviation industry continues to evolve, the demand for high-quality airplane cables will only increase. Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should leverage this opportunity by establishing strong relationships with reliable manufacturers. By doing so, they can ensure a consistent supply of high-performance cables that meet the unique requirements of their operations.
Looking ahead, the focus should be on innovation and sustainability in sourcing practices. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize environmentally friendly manufacturing processes and materials will not only enhance operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable aviation industry. Now is the time to take action—evaluate your current sourcing strategies and align them with the future of aviation to secure a competitive advantage.