Master Vertical Conveyor Belt Sourcing: Essential Insights
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for vertical conveyor belt
Vertical conveyor belts are essential components in modern industrial operations, enabling the efficient transportation of goods in a vertical orientation. This capability not only optimizes space but also enhances workflow productivity, making vertical conveyors a critical investment for businesses across various sectors, including manufacturing, food processing, and logistics. As international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance their operational efficiency, understanding the intricacies of vertical conveyor belt systems becomes paramount.
This guide offers a comprehensive overview of vertical conveyor belts, addressing key factors such as types, materials, and manufacturing quality control. We will explore the diverse options available in the market, ranging from standard models to customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs. Buyers will gain insights into supplier selection, cost considerations, and market trends, equipping them with the knowledge to make informed purchasing decisions.
Furthermore, this resource addresses common FAQs that arise during the procurement process, ensuring that potential buyers are well-prepared to engage with suppliers. By leveraging the information presented in this guide, businesses can confidently navigate the global market for vertical conveyor belts, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and competitiveness in an increasingly complex landscape.
Understanding vertical conveyor belt Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bucket Elevator | Vertical lifting using buckets attached to a belt or chain. | Grain handling, mining, food processing | Pros: High capacity, minimal footprint. Cons: Limited to bulk materials, potential for spillage. |
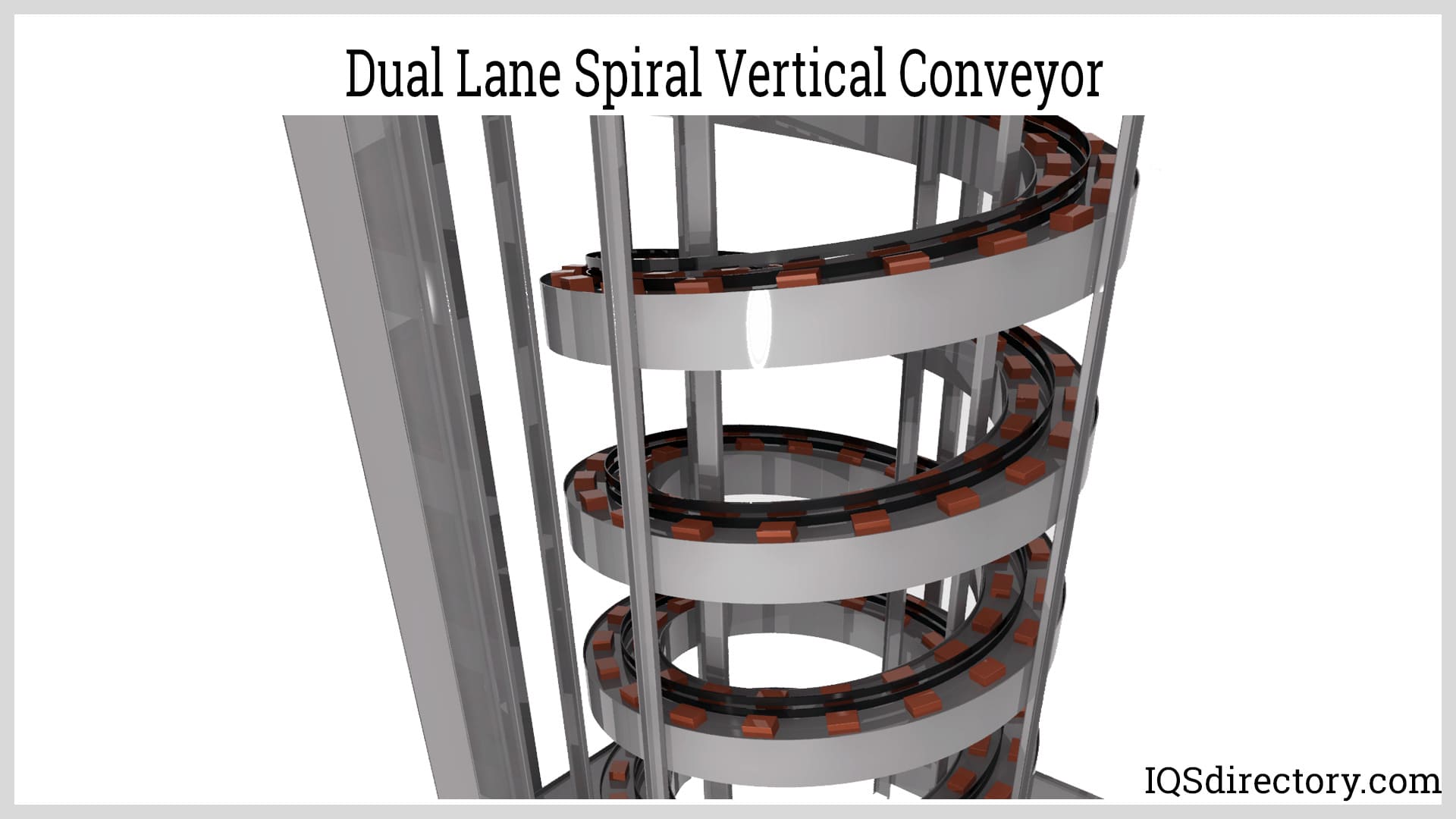
| Spiral Conveyor | Continuous spiral design, allowing for compact vertical transport. | Food processing, packaging, retail | Pros: Space-efficient, versatile. Cons: Higher initial costs, maintenance complexity. |
| Vertical Reciprocating Conveyor (VRC) | Uses a platform that moves vertically between levels. | Warehousing, manufacturing | Pros: Efficient for heavy loads, easy access. Cons: Slower compared to other options, requires safety measures. |
| Incline Belt Conveyor | Operates at an angle, often adjustable for varying heights. | Assembly lines, distribution centers | Pros: Flexible height adjustments, suitable for various materials. Cons: Limited to moderate height gains. |
| Modular Belt Conveyor | Composed of interlocking plastic segments, adaptable design. | Food industry, packaging | Pros: Easy maintenance, customizable. Cons: May require frequent replacement of segments, higher costs. |
Bucket Elevator
Bucket elevators are designed for vertical lifting of bulk materials using buckets attached to a belt or chain. They are highly efficient for transporting grains, ores, and other bulk materials, making them a staple in industries such as agriculture and mining. When considering a bucket elevator, buyers should evaluate capacity requirements, material compatibility, and installation space. While they offer a minimal footprint and high capacity, they may not be suitable for all materials due to spillage concerns.
Spiral Conveyor
Spiral conveyors feature a continuous spiral design that allows for compact vertical transport. They are particularly useful in food processing and packaging industries, where space efficiency is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific application, as spiral conveyors can handle a variety of products, including packaged goods. Their initial investment may be higher, and maintenance can be complex, but the versatility and space-saving design can justify the costs in many scenarios.
Vertical Reciprocating Conveyor (VRC)
Vertical reciprocating conveyors (VRCs) utilize a platform that moves vertically between different levels, making them ideal for warehousing and manufacturing applications. These systems are especially beneficial for transporting heavy loads and providing easy access to multiple levels. Buyers should consider the load capacity and safety features when selecting a VRC, as they require compliance with safety regulations. While they are efficient, they may operate slower than other conveyor types and necessitate additional safety measures.
Incline Belt Conveyor
Incline belt conveyors operate at an angle, allowing materials to be transported vertically or at a slight incline. They are commonly used in assembly lines and distribution centers, where flexibility in height adjustment is needed. Buyers should assess the height requirements and the types of materials being transported. While incline conveyors offer adaptability, they are typically limited to moderate height gains and may not be suitable for very steep inclines.
Modular Belt Conveyor
Modular belt conveyors are made of interlocking plastic segments, allowing for a flexible and adaptable design. They are widely used in the food industry and packaging applications due to their easy maintenance and customization options. When purchasing a modular belt conveyor, buyers should consider the specific application requirements and frequency of use. Although they offer significant advantages in terms of maintenance and adaptability, the costs and potential need for frequent segment replacements should also be factored into the decision-making process.
Related Video: Dorner AquaPruf VBT (Vertical Belt Technology)
Key Industrial Applications of vertical conveyor belt
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Vertical Conveyor Belt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food & Beverage | Transporting packaged goods between production lines | Increases efficiency and reduces manual handling errors | Compliance with food safety standards; sanitation features |
| Pharmaceuticals | Vertical transport of vials and medications | Enhances product integrity and minimizes contamination | Material compatibility with pharmaceuticals; precise control mechanisms |
| Manufacturing | Moving components between assembly stations | Streamlines operations and maximizes floor space usage | Load capacity; customization options for specific parts |
| Logistics & Warehousing | Sorting and stacking items in distribution centers | Improves order accuracy and reduces labor costs | Integration with existing systems; scalability for future growth |
| Automotive | Elevating parts for assembly lines | Increases throughput and reduces bottlenecks | Durability under heavy loads; maintenance support |
Food & Beverage
In the food and beverage sector, vertical conveyor belts are employed to transport packaged goods efficiently between different production lines. This system minimizes the risk of manual handling errors, thereby improving overall efficiency. For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, it’s crucial to ensure that the conveyor systems comply with local food safety standards and include features that facilitate easy sanitation to meet hygiene regulations.
Pharmaceuticals
Vertical conveyors are vital in the pharmaceutical industry for transporting vials and medications safely. They help maintain product integrity and minimize contamination risks during the transport process. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing conveyors that are compatible with pharmaceutical materials and offer precise control mechanisms to ensure accurate handling, which is essential for compliance with stringent regulatory standards.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, vertical conveyor belts facilitate the movement of components between various assembly stations. This not only streamlines operations but also maximizes the use of available floor space, which is particularly beneficial for manufacturers in densely populated areas in Europe and Asia. When sourcing these systems, businesses should consider the load capacity and the customization options available to meet specific production needs.
Logistics & Warehousing
Vertical conveyors are increasingly used in logistics and warehousing to sort and stack items efficiently in distribution centers. This application significantly enhances order accuracy and reduces labor costs, which is especially important in competitive markets across Africa and South America. Buyers should evaluate how well these systems can integrate with existing warehouse management systems and their scalability to accommodate future growth.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Automotive
In the automotive industry, vertical conveyor belts are utilized to elevate parts for assembly lines, thus increasing throughput and reducing bottlenecks in production. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Europe, it is essential to source durable conveyor systems that can withstand heavy loads and offer ongoing maintenance support, ensuring operational reliability and longevity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for vertical conveyor belt
When selecting materials for vertical conveyor belts, it is essential to consider various factors that can impact performance, durability, and overall operational efficiency. Here, we analyze four common materials used in vertical conveyor belts, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber conveyor belts offer excellent flexibility and can withstand a wide range of temperatures. They exhibit good abrasion resistance and are suitable for handling bulk materials. However, their performance can degrade under extreme temperatures or exposure to certain chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber is durable and provides good grip, making it ideal for inclined applications. Its cost is relatively low compared to other materials. However, rubber belts may require more frequent replacements due to wear and tear, especially in high-load applications.
Impact on Application:
Rubber is compatible with a variety of media, including aggregates and packaged goods. However, it may not be suitable for applications involving sharp or abrasive materials, which can lead to premature failure.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding material safety and environmental impact. Familiarity with standards such as ASTM D378 and DIN 22102 can aid in selection.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel belts are known for their high strength and corrosion resistance. They can operate effectively in extreme temperatures and are compatible with a variety of cleaning agents, making them suitable for hygienic applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is unmatched, providing a long service life even in harsh environments. However, the initial manufacturing cost is high, and the belts can be heavier, which may require more robust supporting structures.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is ideal for food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical handling due to its hygienic properties. It is also suitable for applications involving corrosive substances.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with health and safety regulations is crucial, particularly in food-related industries. Buyers should be aware of standards such as JIS G4305 and EN 10088 for stainless steel grades.
3. Plastic (Polymer)
Key Properties:
Plastic conveyor belts are lightweight and flexible, making them easy to install and maintain. They exhibit good chemical resistance and can be engineered for specific applications, including modular designs for easy replacement.
Pros & Cons:
Plastic belts are cost-effective and can be customized for various applications. However, they may not be as durable as metal options and can be susceptible to damage from high temperatures or heavy loads.
Impact on Application:
These belts are suitable for light to medium-duty applications, including packaging and assembly lines. They can handle a range of materials but may not be ideal for heavy bulk handling.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should check for compliance with industry standards such as FDA regulations for food contact materials. Awareness of local certifications can help in selecting the right product.
4. Fabric (Textile)
Key Properties:
Fabric belts are flexible and can be designed to handle various materials. They typically have good tensile strength and can be coated for enhanced durability and slip resistance.
Pros & Cons:
Fabric belts are generally lower in cost and can be produced in various widths and lengths. However, they may have a shorter lifespan compared to metal or rubber belts, especially in abrasive environments.
Impact on Application:
These belts are suitable for conveying packaged goods and lighter bulk materials. They can be used in environments where flexibility and adaptability are required.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the environmental impact of fabric materials and ensure compliance with relevant standards, such as ISO 14800 for textile conveyor belts.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for vertical conveyor belt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Bulk material handling | Good flexibility and grip | Shorter lifespan in high-load use | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | High strength and corrosion resistance | High initial cost | High |
| Plastic (Polymer) | Packaging, assembly lines | Lightweight and customizable | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Fabric (Textile) | Conveying packaged goods | Cost-effective and flexible | Shorter lifespan in abrasive environments | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for B2B buyers looking to optimize their vertical conveyor belt systems, ensuring they choose the most suitable material for their specific applications and operational needs.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for vertical conveyor belt
Manufacturing Processes for Vertical Conveyor Belts
Manufacturing vertical conveyor belts involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the required specifications and quality standards. Understanding these processes can help international B2B buyers select suppliers that align with their operational needs.
Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with material selection, which is vital for the performance and durability of the conveyor belts. Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and rubber, each chosen based on the application requirements such as weight capacity, environmental resistance, and flexibility.
After material selection, the materials undergo cutting and shaping to create the desired belt dimensions. This stage may involve advanced techniques such as laser cutting or die cutting to achieve precise measurements.
Forming
In the forming stage, the prepped materials are manipulated into the correct shape. This may involve:
- Bending and Welding: For metal belts, bending processes shape the metal into the required configurations. Welding techniques, such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, are utilized to join different sections, ensuring strength and stability.
- Molding: For plastic belts, molding processes are employed to create desired profiles and features, such as grooves or cleats, which enhance material handling capabilities.
Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled into a complete conveyor system. This stage involves:
- Integration of Components: The belt is combined with pulleys, frames, and drive systems. Each component must fit together seamlessly to ensure optimal performance.
- Adjustment and Testing: After assembly, initial adjustments are made to the system to ensure proper alignment and functionality. This might include checking belt tension and tracking.
Finishing
The final stage involves applying finishing touches to enhance durability and performance. This can include:
- Coating: Applying protective coatings to prevent corrosion and wear, especially for belts operating in harsh environments.
- Quality Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components meet design specifications and industry standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of vertical conveyor belts, as it directly impacts performance and reliability. Understanding the QA processes can help B2B buyers assess potential suppliers.
International Standards
Most manufacturers adhere to recognized international standards to ensure quality. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: A certification that indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards is essential for ensuring product reliability and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated at various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this initial stage, raw materials are inspected for quality and conformity to specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, continuous monitoring is conducted to detect and address any deviations from quality standards in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the conveyor belts are fully assembled, they undergo comprehensive testing to verify that they meet all specified requirements before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods utilized in the QA process include:
- Load Testing: Assessing the belt’s ability to handle specified weights under operational conditions.
- Fatigue Testing: Evaluating the belt’s durability and performance under repetitive stress.
- Environmental Testing: Simulating various environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity) to ensure the belt operates effectively in diverse settings.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take proactive steps to verify the quality control measures of potential suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate manufacturing processes, equipment, and adherence to quality standards firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports and documentation can provide insights into the supplier’s QA processes, testing results, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s manufacturing and quality control practices.
Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, specific nuances must be considered:
- Cultural and Regulatory Differences: Understanding local regulations and cultural practices related to manufacturing and quality can impact supplier selection. Buyers should be aware of the specific compliance requirements in their regions.
- Communication: Establishing clear communication channels is essential to address any quality concerns or requirements effectively. Language barriers can pose challenges; thus, utilizing multilingual teams or translators may be necessary.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Ensure that the supplier has robust logistics and supply chain processes to maintain quality during transportation and storage. This is especially important in regions where infrastructure may pose challenges.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in the production of vertical conveyor belts, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when selecting suppliers that meet their operational and quality standards.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for vertical conveyor belt Sourcing
When sourcing vertical conveyor belts, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. The price of vertical conveyor belts can vary significantly based on several components and influencing factors. This analysis breaks down the key cost components and price influencers to aid buyers in making informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary raw materials used in vertical conveyor belts include metals (such as stainless steel), plastics, and rubber. The choice of material significantly impacts both the durability and cost of the belt. For instance, stainless steel belts are typically more expensive but offer superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the location of the manufacturer and the complexity of the belt design. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality control processes, which can add to the overall cost. In regions like Africa and South America, labor costs may be lower compared to Europe, potentially influencing sourcing decisions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Manufacturers with advanced technologies may have higher overhead costs but can also offer better precision and quality.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling is essential for producing specialized belts. The cost of tooling can be significant, especially for customized solutions, and is often amortized over the production run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are critical to ensure the reliability and safety of conveyor belts. Investing in quality control systems can increase upfront costs but can lead to lower failure rates and maintenance costs over time.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance from the supplier, weight of the materials, and chosen Incoterms. For international buyers, understanding these logistics costs is vital for calculating the total landed cost of the belts.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin that can range from 10% to 30% depending on the competitive landscape and the uniqueness of the product.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to significant discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing when placing bulk orders.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customization can significantly affect pricing. Buyers need to clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of quality certifications (like ISO or FDA) can influence the price. Buyers should consider the long-term benefits of investing in higher quality belts that meet industry standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can also affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality and service may charge a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms selected for the transaction is crucial as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs and risks.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and be prepared to negotiate terms. Highlighting long-term relationships can lead to better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs. A lower initial purchase price might not always lead to better cost efficiency.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and import duties that can affect the final price. Building relationships with local suppliers can also mitigate some of these risks.
Disclaimer
Prices for vertical conveyor belts can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The information provided in this analysis is indicative and should be verified with suppliers for accurate pricing tailored to specific needs and conditions.
Spotlight on Potential vertical conveyor belt Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘vertical conveyor belt’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for vertical conveyor belt
Key Technical Properties of Vertical Conveyor Belts
When considering the procurement of vertical conveyor belts, it’s essential to understand their critical technical specifications. These properties not only influence the performance and durability of the conveyor system but also impact the overall operational efficiency of your business.
-
Material Grade
The material grade of the belt affects its strength, flexibility, and resistance to wear. Common materials include stainless steel, plastic, and rubber, each offering different benefits. For instance, stainless steel belts are ideal for high-temperature applications, while rubber belts provide excellent grip for inclined surfaces. Selecting the appropriate material is crucial for meeting specific industry requirements and ensuring longevity. -
Belt Width and Length
The width and length of the conveyor belt determine its capacity and the types of materials it can handle. Wider belts can transport larger loads but may require more power to operate. It’s important to assess your material handling needs to choose a belt that optimally balances capacity and energy consumption, ultimately affecting your operational costs. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from the specified dimensions of the conveyor belt. This specification is critical for ensuring the belt fits properly within the conveyor system and operates smoothly. Tighter tolerances are essential for applications requiring precise positioning and alignment, such as in automated manufacturing processes. -
Weight Capacity
The weight capacity of the vertical conveyor belt must align with the heaviest loads it will transport. Exceeding the specified weight capacity can lead to premature wear, increased maintenance costs, or even system failure. It’s vital to conduct a thorough analysis of the materials being handled to avoid costly downtimes and repairs. -
Operating Temperature Range
Each material type has an optimal operating temperature range. Understanding this range is crucial, particularly in industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, where extreme temperatures may be encountered. Selecting a belt that can withstand the expected temperature variations ensures consistent performance and compliance with industry standards. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of the belt influences its friction properties and material handling capabilities. A textured surface can enhance grip, making it suitable for inclined applications, while a smooth finish is beneficial for horizontal transport of fragile items. Evaluating the surface finish based on your specific application will enhance operational efficiency and product safety.
Common Trade Terminology
Understanding industry-specific jargon is equally important for effective communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some essential terms you should know:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that are marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of vertical conveyors, sourcing from OEMs ensures that you receive quality components that meet industry standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory levels and negotiate better terms, especially when dealing with international suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products. It outlines the buyer’s requirements and is crucial for comparing costs and terms from different vendors. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping, covering aspects like delivery, risk, and costs. Familiarity with these terms helps in understanding shipment logistics and reducing potential disputes. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period from placing an order to receiving the goods. Understanding lead times is essential for planning and maintaining production schedules, particularly in industries with tight deadlines. -
Tensile Strength
This term describes the maximum amount of tensile (stretching) stress that a material can withstand before failure. High tensile strength is critical for vertical conveyor belts that need to support heavy loads without stretching or breaking.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their vertical conveyor belt systems are efficient, reliable, and suited to their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the vertical conveyor belt Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The vertical conveyor belt sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by an increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions across various industries. Key global drivers include the rise of automation, particularly in manufacturing and logistics, and the need for space-saving solutions in urban environments. As businesses look to optimize their operations, vertical conveyor systems are increasingly being integrated into production lines to enhance throughput and reduce labor costs.
Emerging B2B technology trends are shaping the sourcing landscape for vertical conveyor belts. Innovations such as IoT-enabled monitoring systems and AI-driven analytics are allowing companies to improve operational efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. This shift towards smart automation not only optimizes performance but also minimizes downtime, which is crucial for international buyers seeking reliable suppliers.
In terms of sourcing trends, there is a noticeable shift towards local suppliers in Africa, South America, and the Middle East, driven by a desire to reduce lead times and shipping costs. European buyers are increasingly favoring suppliers with strong sustainability credentials, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental impacts. This convergence of market dynamics underscores the necessity for B2B buyers to stay informed about regional trends and technological advancements to make strategic sourcing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the vertical conveyor belt sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted a shift towards greener practices. Buyers are increasingly demanding products made from sustainable materials and those that utilize energy-efficient technologies in their operations.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as stakeholders are becoming more conscious of the supply chain’s social and environmental implications. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to ethical labor practices and demonstrate transparency in their sourcing methods. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
The adoption of recyclable and eco-friendly materials in vertical conveyor belts is also gaining traction. For instance, using metal or composite materials that are recyclable contributes to a circular economy approach. By aligning with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the increasing regulatory demands for sustainable practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The vertical conveyor belt has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Originally designed for basic material handling tasks, advancements in technology have transformed these systems into sophisticated solutions integral to modern manufacturing and logistics. The introduction of automated systems and the integration of sensors have made vertical conveyors more efficient and capable of handling a wider range of materials.
As industries continue to embrace automation and smart technologies, the future of vertical conveyor belts looks promising. The ongoing evolution will likely focus on enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability, aligning with global trends toward greener manufacturing processes. International B2B buyers should be aware of these historical advancements to better understand the capabilities and potential of vertical conveyor systems in their operations.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of vertical conveyor belt
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of vertical conveyor belts?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience in the industry, quality certifications, and customer reviews. It’s crucial to confirm their manufacturing capabilities, including the technology and materials they use. Additionally, inquire about their after-sales support and warranty policies. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who have a proven track record in your specific region, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, can provide insights into local regulations and market needs. -
Can vertical conveyor belts be customized for specific applications?
Yes, vertical conveyor belts can be tailored to meet specific operational requirements. Customization options include belt material, size, load capacity, and speed. When discussing customization with suppliers, provide detailed information about your application, including the type of materials being handled and the desired throughput. This will help ensure that the solution fits your operational needs and enhances efficiency. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for vertical conveyor belts?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the complexity and customization of the belts. Lead times typically range from a few weeks to several months, influenced by factors such as manufacturing capacity and material availability. To avoid disruptions, it’s advisable to confirm these details upfront and plan your procurement schedule accordingly. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of vertical conveyor belts?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common options include partial upfront payments, payment upon delivery, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). Ensure you understand the payment structure before finalizing contracts. Additionally, consider using secure payment methods and confirm any potential fees related to international transactions to avoid unexpected costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should provide quality assurance (QA) certifications such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific standards. Request documentation that outlines their QA processes, including material inspections, testing protocols, and compliance with safety regulations. Regular audits and certifications can help ensure that the vertical conveyor belts meet both your specifications and international quality standards. -
How do I manage logistics when importing vertical conveyor belts?
When importing vertical conveyor belts, consider working with a logistics partner experienced in international shipping. Ensure that all necessary documentation, such as import/export licenses, customs declarations, and shipping insurance, is in place. Discuss with your supplier about packaging requirements to prevent damage during transit. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local regulations to avoid potential delays at customs. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
To effectively manage disputes, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements and interactions. Should a conflict arise, start with a direct conversation to address the issue. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Maintaining a professional relationship and understanding cultural nuances can also facilitate smoother negotiations. -
What certifications should I look for in vertical conveyor belts?
Certifications to consider include ISO standards, CE marking for compliance with European safety regulations, and specific industry certifications relevant to your sector (e.g., food safety certifications for food processing applications). These certifications indicate adherence to quality and safety standards, ensuring that the belts are suitable for your operational environment and comply with local regulations. Always request documentation to verify these certifications before proceeding with a purchase.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for vertical conveyor belt
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of vertical conveyor belts presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers across diverse markets, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the unique requirements of their operations, businesses can select conveyor systems that optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating suppliers based on their ability to provide customized solutions, the significance of material selection for durability and performance, and the need for thorough maintenance plans to ensure long-term reliability.
As the global demand for automation and material handling continues to rise, investing in high-quality vertical conveyor systems will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge. Buyers are encouraged to engage with manufacturers who offer robust customer support and innovative technologies, as these partnerships can lead to tailored solutions that meet specific operational challenges.
Looking ahead, the evolution of conveyor technology, including advancements in automation and integration with Industry 4.0, will further enhance the value proposition of vertical conveyors. Now is the time for international B2B buyers to leverage these trends and position themselves for future growth by making informed, strategic sourcing decisions.