Master Power Cord Connector Types for Optimal B2B Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for power cord connector types
Power cord connectors are a fundamental component in the global supply chain, impacting everything from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing these critical components, understanding the various types of power cord connectors becomes essential. With different standards such as NEMA, IEC, and CEE prevalent across regions, selecting the right connector can ensure compatibility, safety, and efficiency in your operations.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad types of power cord connectors, their materials, and manufacturing quality control practices. It also offers insights into supplier networks, cost considerations, and market trends, tailored for buyers from diverse regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you can make informed sourcing decisions that align with your business needs and regulatory requirements.
Furthermore, this guide addresses frequently asked questions that arise during the sourcing process, empowering you with the knowledge to negotiate effectively and select reliable suppliers. Whether you are in the UK, Vietnam, or elsewhere, understanding power cord connector types is not just about compliance—it’s about enhancing your supply chain resilience and operational efficiency. Equip yourself with the insights needed to thrive in today’s competitive global market.
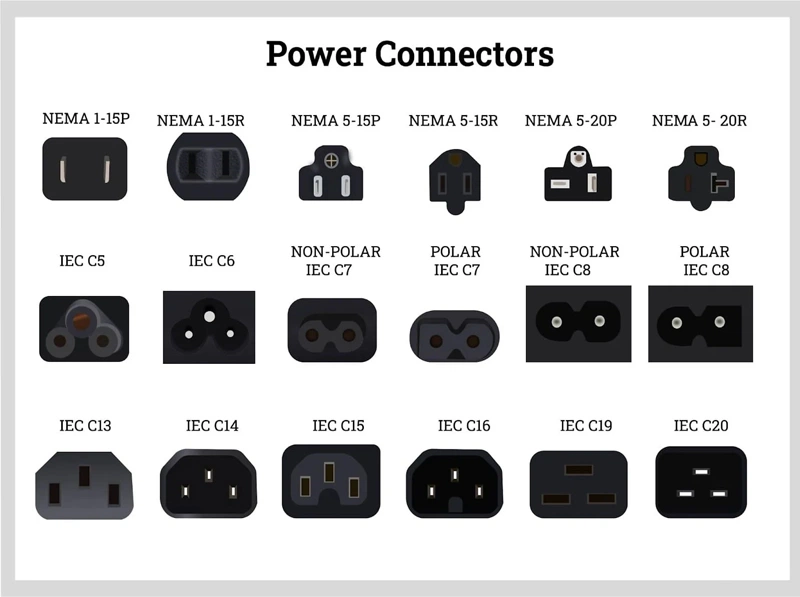
Understanding power cord connector types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEMA | Standardized US connectors with a variety of configurations. | Commercial and industrial equipment, appliances, and generators. | Pros: Wide availability, robust standards. Cons: Limited international compatibility. |
| IEC | International standards with a focus on safety and versatility. | Data centers, computing equipment, and consumer electronics. | Pros: Globally recognized, flexible use across devices. Cons: Requires adapters for non-IEC devices. |
| CEE | Heavy-duty connectors designed for high power applications. | Industrial machinery, construction sites, and events. | Pros: High durability, weather-resistant options. Cons: Bulkier, may require specific installation expertise. |
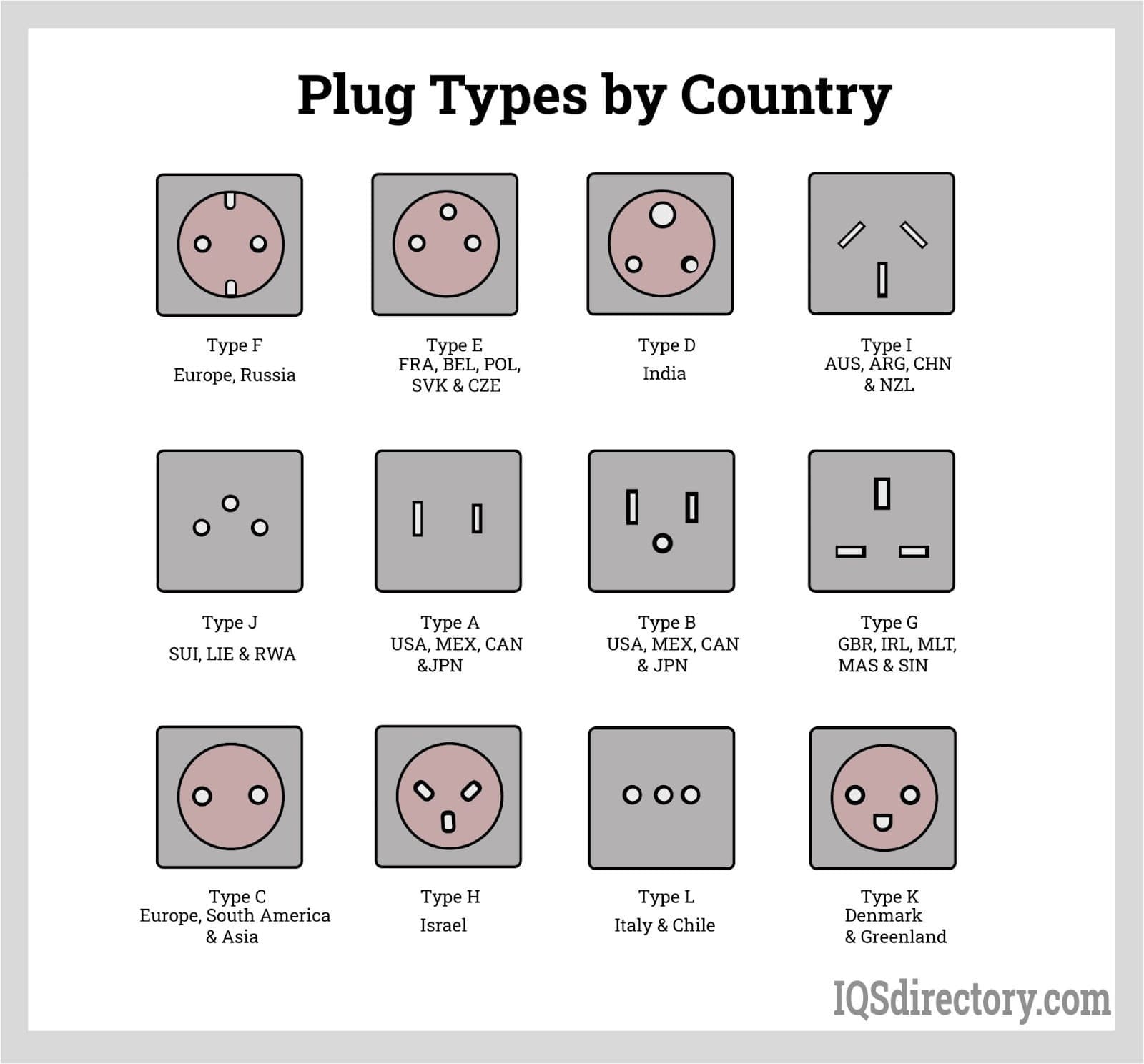
| Schuko | European standard with grounding for enhanced safety. | Household appliances, power tools, and office equipment. | Pros: Strong grounding, widely used in Europe. Cons: Not compatible with non-European devices. |
| BS 1363 | UK standard with integrated safety features and fused plugs. | Domestic appliances, office equipment, and consumer electronics. | Pros: Enhanced safety, prevents overloads. Cons: May not be suitable for high-power applications without specific ratings. |
NEMA Connectors
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) connectors are widely used in the United States and are characterized by their standardized configurations. They are found in various applications, including commercial and industrial settings, often powering equipment like generators and large appliances. For B2B buyers, the primary consideration is the compatibility with existing equipment. While they are readily available in the US market, their limited international compatibility may pose challenges for businesses operating globally.
IEC Connectors
IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) connectors are recognized for their safety and versatility, making them a popular choice in data centers and computing environments. These connectors allow for a flexible connection to various devices, accommodating different voltage and current ratings. B2B buyers should consider the global recognition of IEC connectors, which facilitates international trade. However, they may require adapters when interfacing with non-IEC devices, which can add complexity to purchasing decisions.
CEE Connectors
CEE (International Commission on Rules for the Approval of Electrical Equipment) connectors are designed for heavy-duty applications, making them ideal for industrial machinery and construction sites. Their robust construction often includes weather-resistant features, ensuring reliability in challenging environments. For B2B buyers, the durability and high power ratings are significant advantages, though the bulkiness of these connectors may necessitate specialized installation expertise.
Schuko Connectors
Schuko connectors are a standard in many European countries and feature grounding for enhanced safety. Commonly used for household appliances and power tools, they provide a secure connection and are favored for their reliability. B2B buyers should note that while Schuko connectors offer strong grounding capabilities, they may not be compatible with non-European devices, which could limit their use in international operations.
BS 1363 Connectors
BS 1363 connectors are the standard in the UK, known for their integrated safety features, including fused plugs that prevent overloads. They are widely used in domestic appliances and office equipment. For B2B buyers, the enhanced safety measures are a key advantage, especially in environments where equipment reliability is crucial. However, BS 1363 connectors may not be suitable for high-power applications without adhering to specific ratings, which should be considered during procurement.
Related Video: All Power Supply Cable Types EXPLAINED
Key Industrial Applications of power cord connector types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Power Cord Connector Types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Use of IEC connectors for machinery and equipment | Ensures reliable power supply, reducing downtime and maintenance costs | Compliance with local electrical standards and certifications |
| Healthcare | NEMA connectors in medical devices | Guarantees safety and efficiency in patient care and diagnostics | High-quality materials to withstand sterilization and frequent use |
| Telecommunications | CEE connectors for data centers and server farms | Supports high power demands and ensures system reliability | Compatibility with international power standards and robustness |
| Construction | Power cord connectors for heavy machinery and tools | Enhances operational efficiency and safety on job sites | Durability and resistance to environmental conditions |
| Consumer Electronics | Power cord connectors for home appliances | Facilitates user convenience and product reliability | Adherence to regional voltage and plug standards |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, IEC connectors are commonly used to connect machinery and equipment to power sources. These connectors provide a reliable and consistent power supply, which is crucial for maintaining production schedules and minimizing downtime. For international buyers, it is essential to ensure that the IEC connectors meet local electrical standards and certifications, as non-compliance can lead to operational disruptions and safety hazards.
Healthcare
In healthcare, NEMA connectors are integral to the operation of medical devices. These connectors ensure that devices such as imaging equipment and monitoring systems receive a stable power supply, which is vital for patient care and accurate diagnostics. Buyers in the healthcare sector should prioritize connectors made from high-quality materials that can withstand sterilization processes and frequent handling, ensuring both safety and reliability in critical environments.
Telecommunications
The telecommunications industry relies heavily on CEE connectors, especially in data centers and server farms where high power demands are commonplace. These connectors not only support robust power requirements but also enhance system reliability, which is crucial for uninterrupted service. B2B buyers should consider compatibility with international power standards and the robustness of connectors to withstand the rigors of continuous operation in demanding environments.
Construction
Power cord connectors play a vital role in the construction industry, particularly for heavy machinery and tools. These connectors enhance operational efficiency and safety on job sites by providing a reliable power source. Buyers should focus on sourcing connectors that are durable and resistant to harsh environmental conditions, as construction sites often expose equipment to dust, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Consumer Electronics
In the consumer electronics sector, power cord connectors are essential for home appliances. They facilitate user convenience and contribute to product reliability, ensuring that devices function as intended. International buyers must ensure that the power cord connectors adhere to regional voltage and plug standards to avoid compatibility issues and enhance consumer satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for power cord connector types
When selecting materials for power cord connectors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in power cord connectors: Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU), and Metal Alloys. Each material presents unique properties and considerations that can influence the decision-making process.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE)
Key Properties: TPEs are known for their flexibility and resilience. They can withstand a wide temperature range, typically from -40°C to 100°C, and have excellent resistance to abrasion and UV light.
Pros & Cons: TPE connectors are durable and provide a good grip, making them suitable for frequent handling. However, they can be more expensive than traditional materials, and their manufacturing process may be complex, which can lead to higher production costs.
Impact on Application: TPE is compatible with various media, including oils and chemicals, making it ideal for industrial applications. However, buyers should ensure that the specific TPE used meets the required standards for their application.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America may need to consider local sourcing options to mitigate costs.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties: PVC is a widely used material due to its excellent electrical insulation properties and resistance to moisture and chemicals. It has a temperature rating of up to 60°C.
Pros & Cons: PVC is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. However, its rigidity can limit flexibility, and it may not perform well under extreme temperatures.
Impact on Application: PVC is suitable for general-purpose applications but may not be ideal for environments with high temperatures or exposure to certain chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: PVC connectors must comply with local regulations regarding flame retardancy and environmental impact. Buyers in Europe, for example, should be aware of REACH regulations.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
Key Properties: TPU offers a combination of flexibility, toughness, and chemical resistance. It can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: TPU connectors are highly durable and resistant to abrasion, making them suitable for harsh environments. However, they can be more expensive than PVC and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: TPU is ideal for applications requiring high flexibility and resistance to wear, such as in automotive and industrial settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that TPU materials meet international standards for safety and performance, especially in regions with stringent regulations.
Metal Alloys
Key Properties: Metal alloys, such as aluminum or brass, provide excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: Metal connectors are highly durable and suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, they are typically more expensive and may require additional coatings to prevent corrosion.
Impact on Application: Metal connectors are ideal for high-power applications, but their weight and cost can be limiting factors in some designs.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with industry standards is critical, especially in sectors like aerospace and automotive. Buyers should also consider the availability of metal alloys in their local markets.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for power cord connector types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) | Industrial applications requiring flexibility | Excellent flexibility and UV resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | General-purpose connectors | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited flexibility under extreme temps | Low |
| Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) | Automotive and industrial applications | High durability and chemical resistance | More expensive and specialized processes | High |
| Metal Alloys | Heavy-duty power applications | Excellent conductivity and strength | Higher cost and potential corrosion | High |
By understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of these materials, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for power cord connector types
Manufacturing Processes for Power Cord Connector Types
The manufacturing of power cord connectors involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets quality and performance expectations. Understanding these processes is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly in international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing power cord connectors is the preparation of raw materials. Common materials include:
- Copper: Used for conductors due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Plastic: Typically thermoplastics, which are molded to create housings and insulators.
- Rubber: Often used for additional insulation and flexibility.
During this stage, materials are sourced from reputable suppliers. Buyers should inquire about the origin of materials to ensure compliance with international standards and regulations.
2. Forming
Forming is the process where raw materials are shaped into the components of the connector. This stage can involve several techniques:
- Injection Molding: Primarily used for plastic components, this technique allows for precise shaping and scalability.
- Stamping: Used for metal parts, such as connectors and pins, where sheets of metal are stamped into the desired shape.
- Extrusion: Often used for cables, where heated material is forced through a die to create long sections of material.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers who utilize advanced forming technologies, as these often lead to better precision and lower defect rates.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, they are assembled to create the final power cord connector. This involves:
- Soldering or Crimping: Connecting wires to terminals, which requires precision to ensure good electrical contact.
- Housing Assembly: Fitting the plastic or rubber housing over the assembled components to provide protection and insulation.
Automated assembly lines are common in modern manufacturing, leading to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. Buyers should verify the assembly methods employed by suppliers to ensure they align with their quality expectations.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the appearance and functionality of the connectors. This may include:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as plating or coating to improve corrosion resistance.
- Labeling: Ensuring that connectors are appropriately marked with specifications and compliance labels.
Buyers should look for suppliers that adhere to finishing standards that prevent wear and tear in diverse environments, particularly in regions with varying climates.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in ensuring that power cord connectors are safe, reliable, and compliant with international standards. The QA process typically includes several key components:
International and Industry-Specific Standards
- ISO 9001: This international standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- UL Certification: Particularly important for connectors used in North America, ensuring they meet safety standards.
B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with certifications that align with their target markets.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors processes during manufacturing to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts a thorough inspection of the finished product before shipping.
Establishing clear expectations regarding QC checkpoints can help buyers mitigate risks associated with defective products.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are vital for verifying product integrity. Common tests include:
- Electrical Testing: Ensures connectors can handle specified voltage and current levels without failure.
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses durability under stress, including pull tests and flex tests.
- Environmental Testing: Evaluates performance under extreme conditions, such as temperature and humidity variations.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on testing methods and results from potential suppliers to ensure compliance with their quality standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can reveal their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should consider third-party audit firms to ensure objectivity.
-
Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their QC processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC records. These reports can help buyers assess the reliability of the supplier’s quality management system.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspection Services: Utilizing independent inspection services before shipment can provide additional assurance of product quality and compliance with specifications.
-
Understand Regional Certifications: Buyers from different regions should be aware of local certifications that may impact product acceptance in their markets, such as SABS in South Africa or INMETRO in Brazil.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance mechanisms for power cord connectors are intricate but essential for ensuring safety and reliability. B2B buyers must engage thoroughly with suppliers, understanding their manufacturing techniques, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards. By doing so, they can secure high-quality products that meet their operational needs and enhance their market competitiveness.
Related Video: Cell Production | Battery Manufacturing Automation
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for power cord connector types Sourcing
In sourcing power cord connectors, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis outlines the primary cost components, pricing influencers, and actionable tips for buyers to optimize their procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as copper for conductors and plastics for insulation, significantly impacts pricing. Fluctuations in commodity prices can lead to changes in overall costs. Buyers should consider sourcing materials from stable suppliers to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can influence the final price of connectors. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing; however, this may come with trade-offs in quality. Evaluating labor standards and practices is essential.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with factory operations, utilities, and indirect labor. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for specific connector types can be substantial. For custom designs or specifications, these costs should be factored into the total cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes is vital. Higher QC standards often lead to increased costs but can prevent costly returns and replacements.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing costs must be considered. International shipping can introduce additional costs, especially with fluctuating fuel prices and customs tariffs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their expenses and ensure business viability. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid in negotiation.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities often leads to lower per-unit prices. Buyers should evaluate their needs to determine optimal order sizes.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom connectors may incur additional costs due to unique tooling and design requirements. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential price increases.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can significantly affect costs. High-quality materials may be more expensive but could offer better performance and longevity.
-
Quality/Certifications: Connectors that meet international safety and quality standards may command higher prices. However, investing in certified products can enhance buyer credibility and reduce risks.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they can also provide assurance of product reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is critical. Incoterms dictate responsibilities between buyers and sellers, impacting overall costs. Buyers should clarify terms to avoid unexpected expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume commitments and long-term partnerships to negotiate better pricing. Suppliers may be more flexible with pricing for reliable, repeat customers.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze total costs, including logistics and import duties, to identify the most cost-effective sourcing strategies. Consider local suppliers for reduced shipping costs.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate connectors based on TCO, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over their lifespan. Investing in higher-quality connectors may result in lower overall costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, regional market conditions, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Conduct thorough market research to understand regional pricing trends.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, and it’s advisable to seek current quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
By understanding these dynamics, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing power cord connectors, ensuring both cost-effectiveness and product quality.
Spotlight on Potential power cord connector types Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘power cord connector types’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for power cord connector types
In the realm of power cord connectors, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also ensures compliance with international standards and operational efficiency.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of material used in the manufacturing of connectors, such as copper, aluminum, or thermoplastics.
– Importance: Material grade affects conductivity, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. High-grade materials can enhance the lifespan of connectors, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. -
Current Rating (Amperage)
– Definition: The maximum amount of electric current a connector can safely carry without overheating.
– Importance: Selecting a connector with the appropriate current rating is vital to prevent electrical failures or hazards. This is particularly crucial in industrial settings where high power demands are common. -
Voltage Rating
– Definition: The maximum voltage that a connector can handle.
– Importance: Ensuring that connectors are rated for the correct voltage levels is essential to maintain safety and prevent equipment damage. This is especially relevant for international buyers dealing with varying voltage standards. -
Temperature Range
– Definition: The operating temperature limits within which a connector can function effectively.
– Importance: Connectors used in extreme environments must withstand high or low temperatures without degrading. Understanding this property ensures reliability in diverse climates, particularly in regions like Africa and South America. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable variation in dimensions and electrical properties of connectors.
– Importance: High tolerance levels ensure that connectors fit well and perform as intended, reducing the likelihood of connection failures. This is crucial in applications requiring precision, such as telecommunications and medical devices.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Ingress Protection (IP) Rating
– Definition: A classification that indicates the degree of protection a connector has against dust and water.
– Importance: An appropriate IP rating is essential for connectors used in outdoor or harsh environments. Buyers must consider this to ensure longevity and reliability in their applications.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Explanation: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers negotiate better pricing and ensure the quality of components sourced from trusted manufacturers. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Explanation: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget, especially in regions where storage space is limited or cash flow is constrained. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Explanation: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ process enables buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they get the best value for their investment. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Explanation: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for buyers to understand shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications in cross-border trade. -
Lead Time
– Explanation: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the goods.
– Relevance: Knowing the lead time helps buyers manage project timelines and avoid delays in production or installation.
- Certification
– Explanation: Documentation that verifies a product meets specific standards or regulations.
– Relevance: Certifications can assure buyers of product quality and compliance with safety regulations, which is particularly important when dealing with international suppliers.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the right power cord connectors for their operational needs. This knowledge fosters better supplier relationships and supports successful international trade operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the power cord connector types Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The power cord connector types market is witnessing significant transformation, driven by several global factors. Increased demand for electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, and smart home devices is reshaping the landscape. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this presents an opportunity to source innovative and high-quality connector solutions that meet evolving technology standards.
Emerging trends include the shift towards standardized connectors, such as NEMA in North America and IEC in Europe, which facilitate compatibility across devices and reduce installation complexities. Additionally, the integration of smart technology in connectors—allowing for real-time monitoring and control—enhances functionality and user experience. The market is also seeing an uptick in demand for connectors that support higher voltages and currents, driven by advancements in power delivery systems.
B2B buyers should be aware of the growing importance of local sourcing strategies. As supply chain disruptions continue to affect global trade, partnering with regional manufacturers can mitigate risks and provide more responsive service. Establishing connections with suppliers who understand local regulations and market needs is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in this dynamic landscape.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral concern; it is a core requirement for B2B buyers in the power cord connector sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, calls for a shift towards more sustainable practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint, utilizing eco-friendly materials, and implementing efficient manufacturing techniques.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should ensure that their supply chains adhere to fair labor practices and comply with international standards. This includes verifying that materials used in power cord connectors are sourced responsibly and that suppliers possess relevant certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances). By aligning with suppliers who share these values, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Furthermore, exploring ‘green’ certifications and materials—such as biodegradable plastics or recycled metals—can lead to innovative product offerings that meet the demands of a growing market for sustainable solutions.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of power cord connectors can be traced back to the early 20th century when the first standardized connectors were introduced. Initially, these connectors were designed for basic electrical appliances. As technology advanced, the need for more sophisticated and versatile connectors emerged, leading to the development of various types, including NEMA, IEC, and CEE.
The push for higher safety standards and efficiency led to the adoption of international standards, which facilitated global trade and interoperability. In recent years, the rise of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles has further driven innovation, resulting in connectors that can handle increased power loads and provide enhanced functionality. This historical context is essential for B2B buyers as it highlights the importance of choosing connectors that not only meet current requirements but are also adaptable for future technological advancements.
In summary, navigating the power cord connector types sector requires an understanding of market dynamics, sustainability practices, and historical evolution to make informed sourcing decisions that align with both business goals and environmental responsibilities.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of power cord connector types
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for power cord connectors?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, certifications, and compliance with international standards such as IEC or NEMA. Check for reviews and testimonials from other clients, particularly those in your region. Request samples to evaluate product quality. Also, ensure the supplier can meet your specific needs in terms of customization and technical support. -
Can power cord connectors be customized for my specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options. You can specify connector types, cable lengths, and material specifications. It is essential to communicate your requirements clearly during initial discussions. Be sure to ask about lead times for custom orders and any additional costs involved in the customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for power cord connectors?
MOQs can vary significantly between suppliers and types of connectors. Some suppliers may require a minimum of 100 units, while others may accommodate smaller orders. It is crucial to confirm these details upfront to avoid unexpected costs and delays in your procurement process. If your order is smaller than the MOQ, inquire about options for combining orders or sourcing from other suppliers. -
How long does it usually take to receive power cord connectors after placing an order?
Lead times depend on various factors, including order size, customization requirements, and the supplier’s location. Typically, standard orders may take 2-4 weeks, while custom orders could extend to 6-8 weeks or longer. Always confirm lead times during negotiation and consider any potential delays that may arise from international shipping or customs clearance. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing power cord connectors internationally?
Payment terms vary by supplier and region, but common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. It is advisable to negotiate terms that protect both parties, such as partial payments upfront and the balance upon delivery. Be cautious with suppliers who demand full payment in advance, especially if they lack a proven track record. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in power cord connectors?
Ensure that suppliers have robust quality assurance protocols in place. This includes certifications like ISO 9001 and compliance with safety standards relevant to your market. Request documentation of quality control tests conducted on the connectors. Additionally, consider conducting third-party inspections before shipment to ensure product quality meets your specifications. -
How should I approach logistics and shipping for power cord connectors?
Work with suppliers who have experience in international shipping and can provide options for freight forwarding. Understand the costs involved, including duties and taxes, and choose a shipping method that balances speed and cost-effectiveness. Consider working with a logistics partner familiar with customs procedures in your region to minimize delays. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with international suppliers?
To handle disputes effectively, maintain clear and documented communication throughout the transaction. Establish a contract outlining expectations, responsibilities, and procedures for addressing issues. If a dispute arises, begin with direct discussions to seek resolution. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as outlined in your contract, as these can be more effective than litigation in international contexts.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for power cord connector types
In conclusion, the landscape of power cord connector types is characterized by a diverse array of options tailored to meet the unique needs of various industries. NEMA, IEC, and CEE standards are pivotal for ensuring compatibility and safety across different regions, particularly for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding these standards not only facilitates compliance but also enhances the reliability of electrical systems.
Strategic sourcing plays a crucial role in optimizing procurement processes. By leveraging global suppliers, businesses can secure high-quality components at competitive prices, ultimately improving their bottom line. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research to identify reputable manufacturers and suppliers who adhere to international standards.
Looking ahead, the demand for innovative and efficient power solutions is expected to rise, driven by advancements in technology and sustainability initiatives. B2B buyers should proactively engage with suppliers who are committed to innovation and can provide tailored solutions to meet specific operational needs. Embrace the opportunities presented by the evolving market and make informed sourcing decisions to ensure a competitive edge in your industry.