Master the 7 Essential Types of Conveyor Belt for Optimal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for types of conveyor belt
Navigating the complexities of the global market for conveyor belts is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency. Conveyor belts are not merely mechanical components; they are integral to optimizing material handling processes across diverse industries, including manufacturing, food processing, logistics, and pharmaceuticals. As businesses strive for automation and increased productivity, understanding the various types of conveyor belts available becomes critical.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of conveyor belts, examining their applications, materials, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and supplier landscapes. From flat belt conveyors to modular systems, each type offers unique advantages tailored to specific operational needs. Furthermore, the guide provides insights into cost structures and market dynamics, enabling buyers to make informed financial decisions.
International buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe will find actionable insights that empower them to navigate the sourcing process effectively. By understanding the nuances of different conveyor belt types and their corresponding applications, buyers can align their purchasing strategies with operational goals, ultimately driving productivity and reducing costs. This guide serves as a vital resource for making strategic sourcing decisions, ensuring that businesses remain competitive in an increasingly globalized marketplace.
Understanding types of conveyor belt Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt Conveyor | Continuous flat belt over pulleys; versatile and simple design | Assembly lines, packaging, sorting | Pros: Easy installation, low maintenance costs; Cons: Limited incline capability. |
| Modular Belt Conveyor | Interlocking plastic segments; flexible and hygienic | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Pros: Easy to clean, customizable; Cons: Higher initial cost compared to flat belts. |
| Cleated Belt Conveyor | Belt with raised barriers; prevents material slippage | Inclined transport of bulk materials | Pros: Effective on steep inclines; Cons: Requires careful design to avoid blockages. |
| Roller Bed Conveyor | Uses rollers for support; reduces friction | Heavy load transport, warehousing | Pros: Suitable for long distances; Cons: Higher upfront investment and maintenance. |
| Curved Belt Conveyor | Curved frame allows for directional changes | Complex plant layouts, product sorting | Pros: Space-efficient design; Cons: May require specific installation considerations. |
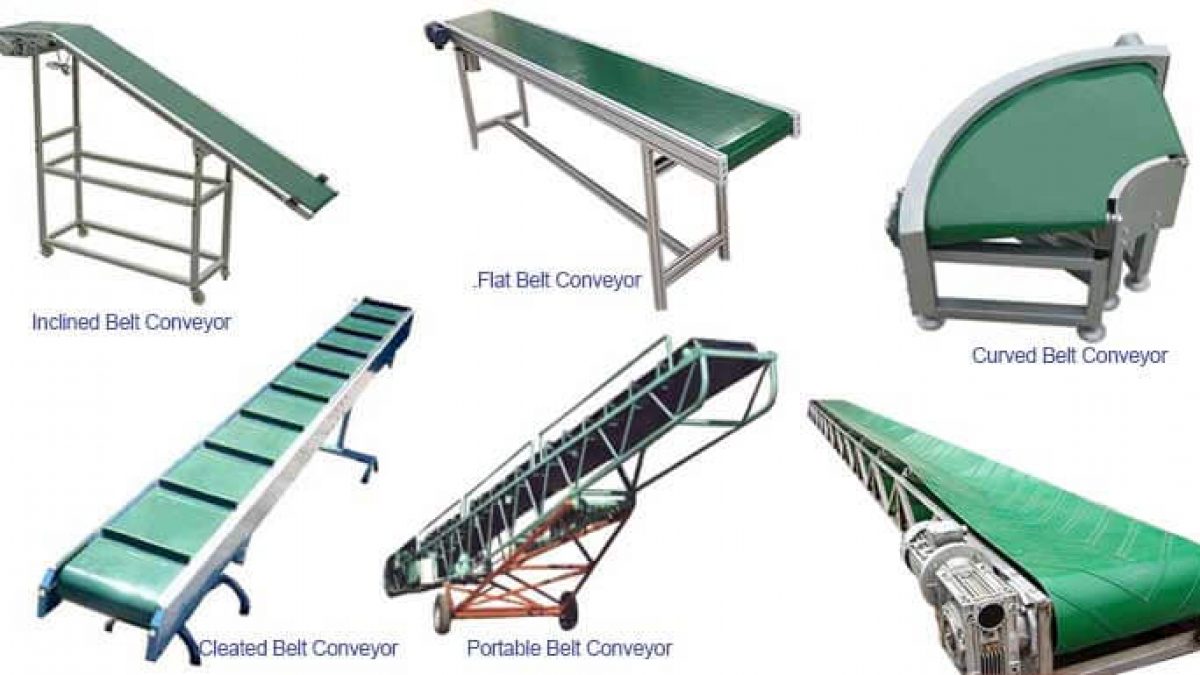
Flat Belt Conveyor
Flat belt conveyors are the most prevalent type in various industries. Their simple construction allows for the transport of a wide range of materials over short to medium distances, making them ideal for assembly lines and packaging processes. When considering a flat belt conveyor, buyers should evaluate the specific load requirements and the potential need for incline capabilities, as these conveyors perform best in horizontal settings.
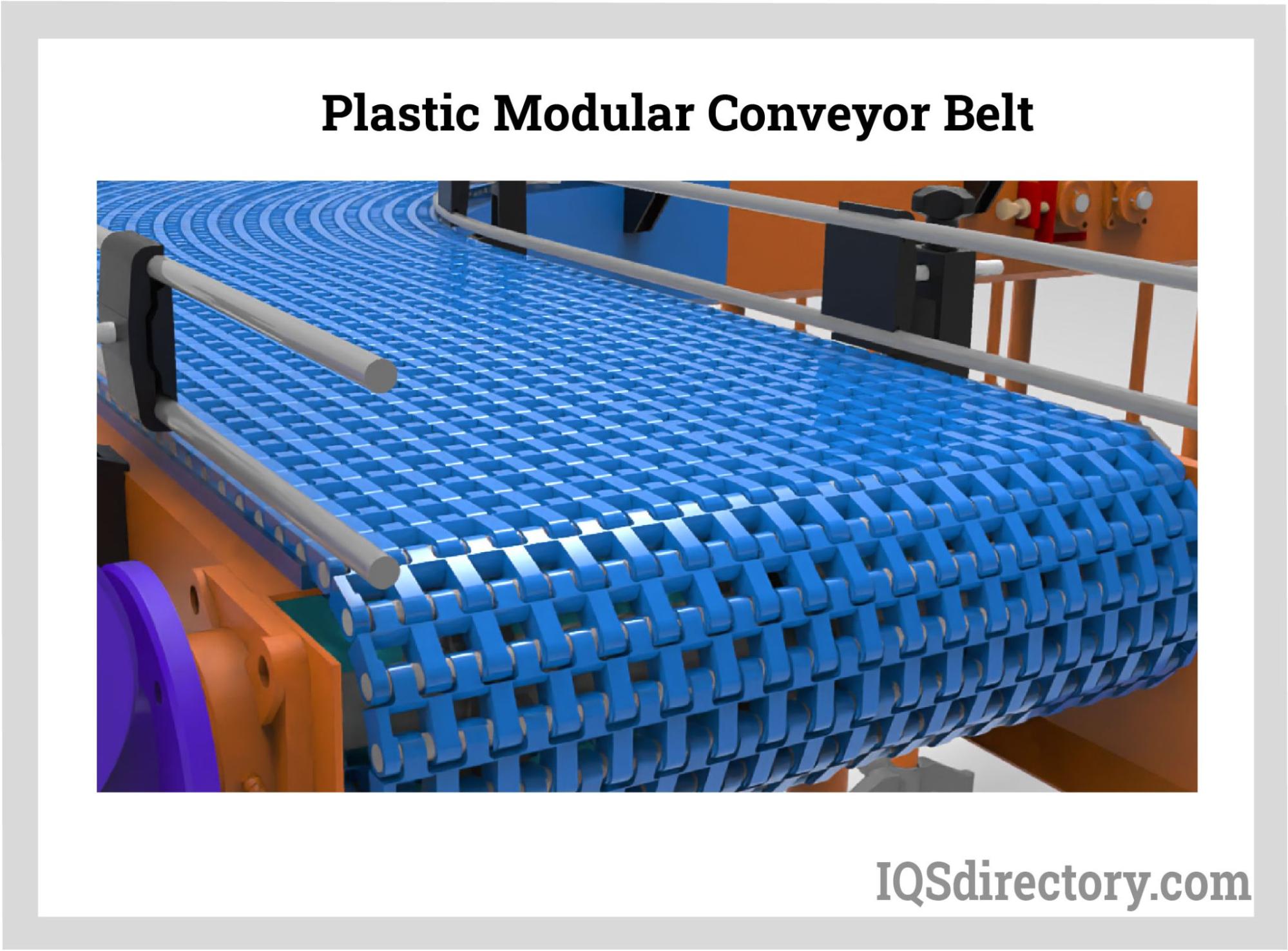
Modular Belt Conveyor
Modular belt conveyors consist of interlocking plastic segments that provide flexibility and durability. They are particularly well-suited for industries requiring high hygiene standards, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals. The key purchasing considerations include the need for easy cleaning and adaptability for future layout changes. While they may have a higher upfront cost, their long-term reliability and low maintenance needs can justify the investment.
Cleated Belt Conveyor
Cleated belt conveyors feature raised barriers that prevent materials from sliding back, making them ideal for transporting bulk materials at inclined angles. These conveyors are especially useful in industries such as mining and agriculture. Buyers should consider the specific incline angles and material types to ensure optimal performance. While they provide excellent control over material flow, careful design is crucial to prevent blockages and ensure smooth operation.
Roller Bed Conveyor
Roller bed conveyors utilize rollers to support the belt, significantly reducing friction and allowing for the transportation of heavier loads over longer distances. They are widely used in warehousing and distribution centers. When purchasing, buyers should assess the load capacity and the layout of their facility, as these conveyors are most effective in straight paths. Although they require a higher initial investment and ongoing maintenance, their efficiency in moving heavy materials can lead to cost savings over time.
Curved Belt Conveyor
Curved belt conveyors are designed to navigate around corners and obstacles, making them essential for complex plant layouts. They help maintain a continuous flow of materials without the need for multiple conveyor systems. Buyers should focus on the radius of curvature and the potential for material spillage, as these factors can affect performance. While they offer significant space-saving advantages, installation may require specialized expertise to ensure proper alignment and functionality.
Related Video: Belt conveyor | Tutorial | Types | Applications | Grades | Splicing | Joining | Steel cord | Safety
Key Industrial Applications of types of conveyor belt
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of types of conveyor belt | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Transporting packaged goods through assembly lines | Increases efficiency, reduces manual handling, and ensures hygiene standards | Compliance with food safety regulations and ease of cleaning |
| Automotive Manufacturing | Moving components along assembly lines | Streamlines production, minimizes downtime, and enhances safety | Customization for load specifications and operational layout |
| Mining and Bulk Material | Conveying ores and minerals from extraction sites | Reduces labor costs and improves safety in hazardous environments | Durability and resistance to harsh conditions are crucial |
| Pharmaceuticals | Handling raw materials and finished products | Ensures strict hygiene and minimizes contamination risks | Materials must meet regulatory standards for safety and compliance |
| E-commerce and Logistics | Sorting and transporting goods in warehouses | Enhances order fulfillment speed and accuracy | Flexibility in design to accommodate various product sizes |
Food Processing
In the food processing sector, conveyor belts are vital for transporting packaged goods through assembly lines. They help maintain hygiene standards while significantly reducing manual handling, which can lead to contamination. International buyers must ensure that the conveyor systems comply with local food safety regulations, particularly in regions like Europe and North America. Additionally, ease of cleaning is crucial, so sourcing options that offer smooth surfaces and resistant materials are preferred.
Automotive Manufacturing
Conveyor belts are extensively used in automotive manufacturing to move components along assembly lines. This application streamlines production, minimizes downtime, and enhances worker safety by automating material handling. Buyers in this sector should consider customization options for load specifications and operational layouts to fit their specific production needs. Additionally, sourcing durable belts that can handle heavy loads and operate reliably under continuous use is essential.
Mining and Bulk Material
In the mining and bulk material industry, conveyor belts are employed to convey ores and minerals from extraction sites to processing facilities. This application reduces labor costs and improves safety in hazardous environments by minimizing the need for manual transport. International buyers should focus on sourcing durable conveyor systems that can withstand harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures and abrasive materials. Additionally, the ability to customize the conveyor layout to fit specific site conditions is a vital consideration.
Pharmaceuticals
Conveyor belts play a critical role in handling raw materials and finished products within the pharmaceutical industry. They ensure strict hygiene standards and minimize contamination risks, which are paramount in this highly regulated sector. Buyers must ensure that the materials used in the conveyor systems meet stringent regulatory standards for safety and compliance, especially in regions with rigorous health regulations. Furthermore, sourcing options that allow for easy maintenance and cleaning are essential for maintaining operational efficiency.
E-commerce and Logistics
In the e-commerce and logistics sectors, conveyor belts are crucial for sorting and transporting goods within warehouses. They enhance order fulfillment speed and accuracy, which are critical for meeting customer expectations in today’s fast-paced market. Buyers should consider sourcing flexible conveyor designs that can accommodate various product sizes and shapes, allowing for efficient sorting and transport. Additionally, the ability to integrate these systems with existing warehouse management systems can further optimize operations.
Related Video: Types of Conveyor Belts Explained | Uses, Advantages & Applications in Industries
Strategic Material Selection Guide for types of conveyor belt
When selecting conveyor belt materials, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in conveyor belts, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber conveyor belts are known for their excellent elasticity, abrasion resistance, and ability to operate in a wide temperature range (typically -40°C to 100°C). They also offer good chemical resistance, depending on the specific type of rubber used.
Pros & Cons:
Rubber belts are highly durable and can handle heavy loads, making them suitable for various industrial applications. However, they can be more expensive than other materials and may require more complex manufacturing processes. Additionally, rubber can degrade under UV exposure, which is a consideration in outdoor applications.
Impact on Application:
Rubber belts are ideal for transporting bulk materials like coal, grains, and aggregates, making them popular in mining and construction industries.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for material specifications. In regions with high UV exposure, selecting rubber with UV-resistant additives is advisable.
2. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Key Properties:
PVC conveyor belts are lightweight, flexible, and have a good resistance to oils and chemicals. They can operate effectively in temperatures ranging from -10°C to 60°C.
Pros & Cons:
PVC belts are cost-effective and easy to clean, making them suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications. However, they may not be as durable as rubber belts and can be prone to wear in high-load situations.
Impact on Application:
These belts are commonly used in packaging, food processing, and light-duty applications where hygiene is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA or EU regulations) is essential for buyers in the food industry. Additionally, understanding the specific chemical compatibility of PVC with the materials being transported is crucial.
3. Polyurethane
Key Properties:
Polyurethane belts exhibit excellent abrasion resistance, flexibility, and can operate in a temperature range of -30°C to 80°C. They also provide good resistance to oils and greases.
Pros & Cons:
These belts are highly durable and suitable for heavy-duty applications. However, they are generally more expensive than PVC and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Polyurethane belts are often used in industries requiring high durability, such as automotive and packaging, where they can handle heavy loads and sharp edges.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that polyurethane belts meet relevant industrial standards and consider the specific operational environment, especially in regions with extreme temperatures.
4. Steel
Key Properties:
Steel conveyor belts are known for their high strength and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and heavy loads. They can handle temperatures up to 1000°C, making them suitable for specialized applications.
Pros & Cons:
Steel belts are incredibly durable and can transport heavy materials over long distances. However, they are typically more expensive and can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application:
These belts are ideal for heavy-duty applications such as metal stamping, glass manufacturing, and in environments where heat resistance is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider corrosion resistance treatments, especially in humid or corrosive environments, and ensure compliance with international safety standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for types of conveyor belt | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rubber | Bulk material handling (mining, construction) | Excellent durability and elasticity | Higher cost, UV degradation risk | High |
| PVC | Food processing, packaging | Cost-effective and easy to clean | Less durable under heavy loads | Medium |
| Polyurethane | Automotive, packaging | High abrasion resistance | More expensive, complex mfg | High |
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications (metal stamping) | Extremely durable and strong | Corrosion risk, high cost | High |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for conveyor belts, aiding international B2B buyers in making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for types of conveyor belt
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance (QA) protocols for conveyor belts are critical for ensuring that these systems meet the operational demands of various industries. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can facilitate informed purchasing decisions and enhance supplier relationships.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of conveyor belts typically involves several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing conveyor belts is sourcing and preparing raw materials. Common materials include rubber, PVC, polyurethane, and fabric. Each material is selected based on the conveyor’s intended application, such as food handling, heavy industrial use, or general transport.
- Material Selection: Buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, such as temperature resistance, chemical exposure, and load capacity.
- Pre-processing: Raw materials undergo processes like cutting, mixing, and compounding to achieve the desired properties, including flexibility and strength.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they are formed into the desired shape. This can involve several techniques:
- Molding: Rubber and plastic materials are molded into the shape of the conveyor belt. This method ensures uniformity and consistency in thickness and material distribution.
- Extrusion: For specific profiles, materials may be extruded, allowing for continuous production of belts with varying widths and thicknesses.
- Weaving: In some cases, fabric belts are woven to achieve flexibility and strength, particularly for modular belts.
3. Assembly
In this stage, the formed materials are assembled into a complete conveyor system.
- Joining Techniques: Conveyor belts can be joined using mechanical fasteners, adhesives, or by vulcanization, depending on the material and intended use.
- Integration with Components: This includes the installation of pulleys, rollers, and other components that are necessary for the conveyor system to function effectively.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes that enhance the conveyor belt’s performance and durability.
- Surface Treatments: These may include coating the belt with materials that improve wear resistance or enhance grip.
- Quality Checks: Before the belts are packaged, they undergo rigorous checks to ensure they meet specified standards.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of conveyor belts is crucial for ensuring reliability and safety. Various international and industry-specific standards govern these processes.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers must demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- ISO 14001: For companies focused on environmental management, this standard ensures that manufacturing processes are sustainable and comply with environmental regulations.
Industry-Specific Standards
- CE Marking: Required in Europe, this certification indicates that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures that materials and construction methods are suitable for the demanding environments they will face.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integral throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints established:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are performed to monitor processes and ensure that they remain within acceptable limits.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the conveyor belts are completed, a final inspection is conducted to assess overall quality, performance, and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
To validate the quality of conveyor belts, various testing methods are employed:
- Tensile Strength Testing: Determines the maximum load the belt can handle before failure.
- Abrasion Resistance Testing: Assesses the belt’s durability against wear and tear.
- Fatigue Testing: Evaluates the belt’s performance under repetitive stress conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance documentation, including test results and compliance certifications, can help buyers assess a supplier’s reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspectors to evaluate the manufacturing facilities and processes can provide an unbiased assessment of quality standards.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances when sourcing conveyor belts:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulatory requirements, necessitating a thorough understanding of local laws and standards.
- Cultural Differences: Communication styles and business practices vary by region, which can impact negotiations and expectations regarding quality and delivery.
- Supply Chain Logistics: Understanding the logistics involved in transporting conveyor belts, including potential delays at customs, is crucial for timely project execution.
By thoroughly understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements. This knowledge not only enhances procurement strategies but also fosters stronger partnerships with suppliers across the globe.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for types of conveyor belt Sourcing
When sourcing conveyor belts, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis focuses on the key cost components and price influencers that affect sourcing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver is the type of materials used in conveyor belt manufacturing. High-quality materials, such as rubber or specialized plastics, can significantly increase costs. Buyers should consider the performance specifications required for their applications, as more durable materials can lead to lower maintenance costs over time.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass both direct and indirect labor associated with manufacturing. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s crucial to assess the quality and expertise of the workforce, especially for custom solutions that require skilled labor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead costs, which may be passed on to buyers in the form of lower prices.
-
Tooling: Custom conveyor belts often require specialized tooling for production. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, and suppliers may include these costs in the pricing. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs to understand their impact on overall pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures product reliability but adds to costs. Suppliers with certified quality management systems may charge a premium, reflecting their commitment to quality and consistency.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and logistics efficiency. Buyers should factor in shipping costs, including duties and tariffs, especially when importing from overseas suppliers.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and generate profit. This margin can vary based on competition, supplier reputation, and market conditions.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger volumes often results in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQ) to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom conveyor belts tailored to specific applications can significantly affect pricing. The more customized the solution, the higher the cost. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) influences both the cost and the perceived value of the conveyor belts. Higher quality certifications may justify a higher price due to the assurance of compliance and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge a premium, but they also offer greater assurance in terms of product quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international buyers as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Choosing the right Incoterm can significantly affect the total cost of ownership.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to secure favorable terms. Leverage volume purchases to negotiate better pricing or additional services.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider long-term factors such as maintenance, durability, and potential downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and regional pricing differences. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage in negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices and costs mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary significantly based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential types of conveyor belt Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘types of conveyor belt’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for types of conveyor belt
When selecting conveyor belts for industrial applications, understanding the technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are essential specifications and common terms that will aid international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Critical Technical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Conveyor belts are made from various materials, including rubber, PVC, and polyurethane. The grade of material affects durability, flexibility, and resistance to wear and tear. For instance, food-grade materials are necessary in food processing to comply with health regulations.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right material grade ensures the conveyor belt meets operational demands and regulatory requirements, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs. -
Belt Width
– This specification refers to the width of the conveyor belt and is critical for determining the volume of material that can be transported at one time. Standard widths range from a few inches to several feet.
– B2B Importance: Choosing the appropriate belt width helps optimize space and improves efficiency in material handling, directly impacting productivity levels. -
Belt Thickness
– Thickness impacts the belt’s strength and load capacity. Thicker belts can carry heavier loads but may be less flexible. A balance must be struck based on the type of materials being transported.
– B2B Importance: Understanding thickness requirements is vital for ensuring that the conveyor can handle specific loads without risk of damage or failure. -
Tension Rating
– This indicates the maximum tension that a conveyor belt can withstand without breaking. It is influenced by the belt construction and material used.
– B2B Importance: Proper tension ratings prevent belt slippage and ensure smooth operation, reducing operational costs and enhancing safety. -
Temperature Resistance
– Conveyor belts may be exposed to various temperatures depending on the application. Temperature resistance indicates the belt’s ability to maintain integrity under heat or cold.
– B2B Importance: Ensuring the belt can handle the specific temperature range of the application minimizes the risk of premature wear or failure, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Surface Profile
– This refers to the texture or pattern on the belt’s surface, which can include flat, textured, or cleated designs. The choice of surface profile is crucial for material handling, especially for incline or decline applications.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the correct surface profile ensures secure material transport and minimizes the risk of slippage, especially in steep or complex layouts.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of conveyor belts, OEMs supply belts that meet specific equipment requirements.
– Relevance: Working with OEMs ensures compatibility and reliability in the machinery where the belts will be used. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning.
– Relevance: Buyers must assess whether the MOQ aligns with their production needs to avoid excess inventory costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products. This process is crucial for comparing costs and ensuring competitive pricing.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ helps buyers secure the best pricing and terms, which is vital for maintaining budgetary constraints. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in shipping goods.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is essential for international B2B transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. -
Lead Time
– This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product. Lead times can vary based on supplier capabilities and the complexity of the order.
– Relevance: Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their operations and inventory management effectively. -
Warranty
– A warranty is a guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the quality and longevity of the product. It typically covers defects and may include service terms.
– Relevance: A clear warranty policy provides assurance to buyers regarding the reliability of the conveyor belts, influencing purchasing decisions.
By grasping these technical specifications and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make better-informed decisions, ensuring that their conveyor belt selections align with their operational needs and industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the types of conveyor belt Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global conveyor belt market is experiencing significant growth driven by industrial automation and the increasing demand for efficient material handling solutions. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, businesses are adopting advanced technologies such as IoT and AI to enhance conveyor systems’ performance. The integration of smart technologies allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Emerging trends include the customization of conveyor systems to cater to specific industry needs. For instance, modular and flexible conveyor belts are gaining traction in the food and pharmaceutical industries due to their ease of cleaning and adaptability to various layouts. Additionally, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in sourcing decisions, with buyers increasingly looking for suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and practices.
B2B buyers are also witnessing a shift towards automated solutions that streamline logistics and warehousing processes. The rise of e-commerce, particularly in South America, has led to higher demand for conveyor systems that can handle diverse product types and sizes. As businesses seek to optimize their supply chains, understanding these market dynamics and trends is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability in the conveyor belt sector is becoming a non-negotiable aspect of procurement strategies. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in industries like mining and food processing, necessitates a focus on ethical sourcing and sustainable materials. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint through the use of recycled materials and energy-efficient production methods.
Certifications such as ISO 14001, which pertains to effective environmental management systems, are becoming vital for suppliers aiming to establish credibility in the market. Buyers should seek out conveyor belt manufacturers that adhere to these standards and utilize environmentally friendly materials, such as biodegradable or recyclable components.
Moreover, ethical supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and transparency are gaining importance. By partnering with suppliers committed to sustainability and ethical practices, businesses not only enhance their corporate social responsibility but also appeal to a growing consumer base that values environmental stewardship.
Brief Evolution/History
The conveyor belt system has evolved dramatically since its inception in the late 18th century. Originally developed for transporting goods in mining operations, the technology has undergone continuous innovation, adapting to the needs of various industries. The introduction of motorized systems in the early 20th century revolutionized material handling, increasing efficiency and reducing manual labor.
In recent decades, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of specialized conveyor belts that cater to specific applications, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. Today, the focus is on integrating smart technologies and sustainable practices, reflecting the changing priorities of global industries and B2B buyers. Understanding this evolution provides valuable context for making informed decisions in the current marketplace.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of types of conveyor belt
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for conveyor belts?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a solid reputation and proven experience in the conveyor belt industry. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request references from previous clients and conduct site visits if feasible. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or ThomasNet to find verified suppliers. It’s also beneficial to join industry-specific forums or groups to gain insights and reviews from other buyers, particularly those in your region. -
What customization options are available for conveyor belts?
Many suppliers offer customization options to suit specific operational needs. Common modifications include belt width, material type, and design features such as cleats or sidewalls. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly, including the type of materials being handled and the operational environment. Some suppliers may also provide design assistance to help optimize your conveyor belt system for efficiency and safety.
-
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the conveyor belt design. Generally, MOQs range from 50 to 100 units for standard models, while custom designs may have higher thresholds. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the supplier’s production capacity and your location. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing conveyor belts?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include a deposit (30-50%) upon order confirmation and the balance due before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or payment upon delivery, particularly for larger orders or established business relationships. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and financial strategies, and ensure you understand the implications of each payment method. -
What quality assurance measures should be in place?
Quality assurance is vital when sourcing conveyor belts. Ensure that the supplier conducts regular inspections throughout the production process, including material quality checks and final product testing. Request documentation of these processes, including certificates of conformity and test results. If applicable, inquire about warranty policies and after-sales support to ensure you have recourse in case of defects or performance issues. -
How do logistics and shipping impact my conveyor belt purchase?
Logistics play a critical role in the overall cost and efficiency of your conveyor belt purchase. Consider the shipping methods available, as air freight is faster but more expensive than sea freight. Factor in customs regulations and potential duties, especially when importing from different regions. Work closely with your supplier to coordinate shipping schedules and ensure that you have all necessary documentation to prevent delays at customs. -
What should I do in case of disputes with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. Document all correspondence and agreements to support your case. If resolution fails, consider mediation or arbitration, which can be faster and less costly than legal action. Familiarize yourself with the supplier’s terms of service and any applicable international trade laws that may govern the contract. Engaging a legal expert experienced in international trade disputes may also be beneficial. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for when sourcing conveyor belts?
Yes, several certifications can indicate a supplier’s commitment to quality and safety standards. Look for ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and specific industry certifications such as FDA approval for food-grade belts or ATEX for explosive environments. These certifications can provide assurance that the supplier adheres to recognized standards, which is crucial for maintaining operational safety and compliance in your industry.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for types of conveyor belt
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing and logistics, understanding the diverse types of conveyor belts is critical for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. Each conveyor type, from flat belts to modular systems, offers unique advantages tailored to specific material handling needs. Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in selecting the right conveyor system, enabling businesses to align their equipment choices with operational goals while ensuring compliance with industry standards.
International B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should prioritize suppliers who offer customizable solutions that can adapt to their unique market requirements. When sourcing conveyor systems, consider factors such as load capacity, material compatibility, and maintenance ease. Collaborating with manufacturers that understand regional challenges can provide a competitive edge in maximizing productivity.
As industries continue to innovate, the demand for specialized conveyor solutions will grow. Now is the time to invest in the right technology to future-proof your operations. Engage with trusted suppliers, explore the latest advancements, and harness the power of efficient conveyor systems to propel your business forward.