Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing List Bolt Manufacturers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for list bolt manufacturers head markings
Navigating the global market for bolt manufacturers requires a keen understanding of head markings, which serve as a critical identifier of a bolt’s grade, material, and tensile strength. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these markings are essential for ensuring the reliability and safety of their projects. With a diverse range of materials and specifications available, knowing how to interpret these markings can significantly impact purchasing decisions and project outcomes.
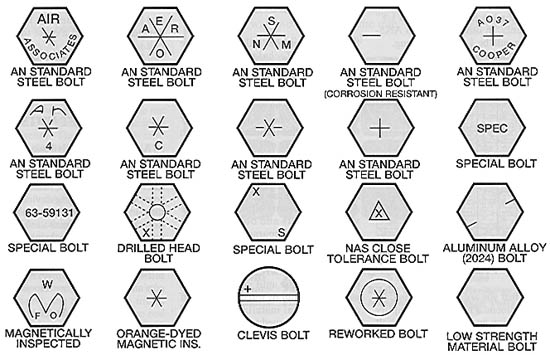
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This comprehensive guide delves into the various aspects of bolt head markings, including types, materials, manufacturing standards, and quality control measures. Buyers will benefit from insights into leading suppliers, associated costs, and emerging market trends, empowering them to make informed sourcing decisions. By understanding the nuances of bolt head markings, businesses can enhance their procurement strategies, minimize risks, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Additionally, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, providing clarity on common concerns and misconceptions in the bolt procurement process. With this resource, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of the global fastener market with confidence, ensuring they select the right products for their specific applications and operational needs.
Understanding list bolt manufacturers head markings Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grade Markings | Numeric or alphanumeric codes indicating strength and material | Construction, Manufacturing | Pros: Clear strength indicators. Cons: Misinterpretation can lead to failures. |
| Manufacturer’s Logo | Unique logo or initials of the manufacturer | Automotive, Aerospace, Heavy Industry | Pros: Ensures traceability and quality assurance. Cons: May not indicate strength. |
| Material Designation | Symbols indicating material type (e.g., A325, A490) | Structural, Civil Engineering | Pros: Helps in selecting appropriate materials. Cons: Requires knowledge of material properties. |
| Specialty Markings | Unique identifiers for high-performance or custom bolts | Oil & Gas, Marine, Defense | Pros: Tailored for specific applications. Cons: Limited availability and higher costs. |
| Finish Markings | Indicators of surface treatments (e.g., zinc, black oxide) | Marine, Automotive, Construction | Pros: Enhances corrosion resistance. Cons: May require additional maintenance. |
Grade Markings
Grade markings are crucial for identifying the strength and material properties of bolts. These markings often consist of numeric or alphanumeric codes that indicate the bolt’s tensile strength and yield strength. In B2B applications, particularly in construction and manufacturing, understanding these grades is essential for ensuring that the correct bolts are used for specific load-bearing tasks. Buyers should be aware that misinterpreting these markings can lead to structural failures, so investing in training or resources to accurately read these codes is advisable.
Manufacturer’s Logo
The presence of a manufacturer’s logo or initials on a bolt serves as a mark of authenticity and quality assurance. This is especially important in industries like automotive and aerospace, where safety is paramount. For B2B buyers, selecting bolts from reputable manufacturers can reduce the risk of product failure. However, it is essential to note that while a logo signifies a trusted source, it does not inherently provide information about the bolt’s strength, which must be verified through additional markings.
Material Designation
Material designation markings, such as A325 or A490, provide vital information about the composition of the bolt. These symbols are particularly important in structural and civil engineering applications, where specific material properties are required to meet safety standards. B2B buyers should prioritize understanding these designations to ensure they select bolts that meet the necessary specifications for their projects. However, it requires a certain level of expertise to interpret these designations effectively.
Specialty Markings
Specialty markings are used for high-performance or custom bolts designed for specific applications, such as those used in the oil and gas industry or defense sectors. These markings can indicate enhanced features such as heat treatment or specific coatings. While these bolts offer tailored solutions for demanding environments, they may come at a higher cost and may not be as readily available as standard options. Buyers should assess whether the benefits of these specialty bolts align with their project requirements.
Finish Markings
Finish markings indicate the type of surface treatment applied to the bolt, such as zinc plating or black oxide finishes. These treatments enhance the bolt’s resistance to corrosion and wear, making them suitable for use in marine and automotive applications. For B2B buyers, choosing bolts with appropriate finish markings can significantly extend the lifespan of their products. However, it’s essential to consider that certain finishes may require additional maintenance or care over time, impacting overall project costs.
Related Video: Bolt head markings—what do the letters and symbols mean? | FAQ
Key Industrial Applications of list bolt manufacturers head markings
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of list bolt manufacturers head markings | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Use in structural frameworks and building assemblies | Ensures safety and compliance with construction standards | Confirm compliance with local and international standards; verify manufacturer certifications |
| Automotive | Fastening components in vehicles | Enhances durability and reliability of vehicle assembly | Assess the tensile strength and corrosion resistance; ensure compatibility with OEM specifications |
| Oil and Gas | Use in pipeline and rig assembly | Increases operational safety and efficiency | Evaluate resistance to extreme conditions and environmental factors; check for industry-specific certifications |
| Renewable Energy | Securing solar panels and wind turbine components | Supports sustainable energy initiatives and reliability | Look for suppliers with experience in renewable applications; verify performance under varying environmental conditions |
| Aerospace | Fastening parts in aircraft and spacecraft | Critical for safety and performance in flight | Ensure adherence to stringent aerospace standards; prioritize traceability of materials and components |
In the construction industry, bolt head markings play a vital role in identifying the grade and strength of bolts used in structural frameworks and building assemblies. These markings ensure that the materials meet safety standards and regulatory requirements, which is crucial in preventing structural failures. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers who can provide documentation of compliance with local and international building codes.
In the automotive sector, bolts with specific head markings are essential for fastening various components, from engines to body panels. The markings indicate the strength and material properties, which directly impact vehicle safety and performance. B2B buyers must assess the tensile strength and corrosion resistance of these bolts to ensure they align with OEM specifications, particularly in markets where vehicle durability is critical.
The oil and gas industry relies heavily on bolts for assembling pipelines and rigs. Head markings help identify bolts that can withstand harsh conditions, such as high pressure and corrosive environments. This is particularly important for international buyers who operate in diverse climates across the Middle East and Africa. Evaluating the resistance of these fasteners to extreme conditions is crucial for maintaining safety and operational efficiency.
In the renewable energy sector, bolt head markings are used to secure solar panels and wind turbine components. These applications require fasteners that not only meet structural integrity standards but also perform reliably in various environmental conditions. Buyers should seek suppliers experienced in renewable applications and verify that the products can withstand factors like wind load and temperature fluctuations.
Lastly, in the aerospace industry, bolt head markings are critical for fastening parts in aircraft and spacecraft, where safety is paramount. The markings indicate compliance with rigorous aerospace standards, ensuring that components can endure the stresses of flight. B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers who can provide traceability for materials and adherence to industry-specific certifications, which is essential in maintaining the integrity of aerospace applications.
Related Video: Bolt head markings what do they mean?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for list bolt manufacturers head markings
When selecting materials for bolt head markings, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of commonly used materials. This knowledge will facilitate informed decisions that align with application requirements and regional standards.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high tensile strength and hardness, making it suitable for high-load applications. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle moderate pressure levels.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, which makes it a popular choice among manufacturers. However, it has limited corrosion resistance unless treated or coated, which can increase manufacturing complexity. This limitation makes it less suitable for applications in corrosive environments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel bolts are commonly used in construction and automotive applications where strength is paramount. However, buyers must consider the environment in which these bolts will operate, as exposure to moisture can lead to rust and degradation.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933. Additionally, they may need to consider protective coatings to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in humid climates.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 1500°F (815°C). Its mechanical properties make it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor or marine applications. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel, which could impact budget constraints for some projects.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolts are often used in chemical processing, food production, and marine environments. Their compatibility with various media makes them versatile for different applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards like ASTM A193 or JIS B1180. The preference for stainless steel in these regions is driven by regulatory requirements for corrosion resistance in specific industries.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel is engineered to provide enhanced properties such as increased strength and toughness. It can withstand higher temperatures and pressures compared to standard carbon steel.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steel is its superior performance in demanding applications, making it suitable for heavy machinery and structural components. However, it is more expensive and requires careful handling during manufacturing due to its complex composition.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel bolts are commonly used in the aerospace and automotive industries, where high strength-to-weight ratios are essential. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them ideal for critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions with stringent safety standards, such as Europe, must ensure that alloy steel bolts meet specific certifications like ISO 898-1. Understanding the local market’s acceptance of alloy steel can also influence purchasing decisions.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its lightweight and high strength, with excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in saline environments. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 1200°F (649°C).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of titanium is its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for aerospace and marine applications. However, titanium is significantly more expensive than other materials and can be challenging to machine.
Impact on Application: Titanium bolts are increasingly used in high-performance applications, including aerospace and medical devices, where weight and corrosion resistance are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East and Europe may find titanium bolts appealing due to their performance in harsh environments. However, they must consider the higher costs and ensure compliance with standards like ASTM F136.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for list bolt manufacturers head markings | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Construction, automotive | Cost-effective | Limited corrosion resistance | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing, food production, marine environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost compared to carbon steel | Medium |
| Alloy Steel | Aerospace, automotive | Superior strength and toughness | More expensive, complex manufacturing | High |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical devices | Lightweight, high strength | Very high cost, difficult to machine | High |
This guide serves as a valuable resource for international buyers looking to make informed decisions regarding bolt head marking materials, ensuring compatibility with their specific applications and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for list bolt manufacturers head markings
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for bolt manufacturers, particularly regarding head markings, is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section will provide an in-depth look at these processes, focusing on key manufacturing stages, quality control measures, relevant standards, and how buyers can verify supplier practices.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of bolts involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the necessary specifications and quality standards. Below are the primary stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in bolt manufacturing is selecting the appropriate materials, typically high-strength carbon steel or alloy steel. The material undergoes various treatments, such as heat treatment, to enhance its mechanical properties. This stage may also involve cutting the raw materials into specific lengths, which are then inspected for any defects.
2. Forming
In the forming stage, the prepared material is shaped into the desired bolt profile. This is usually done through processes like:
– Forging: Hot or cold forging techniques are commonly used to create the bolt’s head and shank. This method improves the material’s strength and ensures precise dimensions.
– Machining: After forging, bolts may require machining to achieve tighter tolerances and specific features, such as threads and head markings.
– Cold Heading: This is a specialized process where the bolt is formed at room temperature, enhancing its tensile strength and reducing waste.
3. Assembly
For bolts that require additional components, such as nuts or washers, the assembly process includes fitting these parts together. This stage often involves automated systems to ensure efficiency and precision.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves several treatments to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. Common techniques include:
– Coating: Applying zinc plating, powder coating, or other finishes to protect against environmental factors.
– Heat Treatment: Further heat treatment may be applied to achieve specific hardness levels, critical for high-strength applications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in bolt manufacturing is vital for ensuring product reliability and safety. The following outlines typical practices and international standards relevant to bolt head markings:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines quality management systems and emphasizes continuous improvement, ensuring that manufacturers meet customer requirements and regulatory compliance.
- CE Marking: For products sold within the European Union, CE marking indicates compliance with safety standards.
- API Standards: In industries like oil and gas, compliance with API (American Petroleum Institute) standards ensures that the bolts can withstand harsh operating conditions.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically divided into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial inspection checks the raw materials for defects before they enter production.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular inspections are conducted to ensure compliance with specifications. This includes monitoring dimensions, head markings, and material properties.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): After production, finished bolts undergo rigorous testing to verify that they meet all requirements, including strength tests and visual inspections for marking accuracy.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to validate the quality of bolts:
– Tensile Testing: Measures the maximum load the bolt can withstand before failure.
– Hardness Testing: Assesses the hardness of the material, ensuring it meets specified standards.
– Visual Inspection: Checks for proper head markings, dimensions, and surface defects.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential. Here are actionable steps to ensure supplier quality:
Conducting Supplier Audits
- On-site Audits: Regularly visiting manufacturing facilities allows buyers to observe processes firsthand, assess compliance with standards, and review quality control records.
- Third-party Audits: Engaging independent auditors can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s practices and adherence to international standards.
Requesting Quality Reports
Buyers should request and review quality control reports, including:
– Inspection Reports: Documentation of IQC, IPQC, and FQC results.
– Test Certificates: Evidence of testing methods and results, particularly for critical applications.
Understanding Certification Nuances
Different regions may have varying certification requirements. It’s vital for buyers to understand:
– Local Regulations: Familiarity with regulations in their specific market can help ensure compliance and product acceptance.
– Certification Bodies: Recognizing reputable certification bodies can aid in assessing the credibility of supplier claims.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for bolt manufacturers, especially regarding head markings, is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant quality standards, and effective verification methods, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers who meet their specific needs. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also fosters long-term business relationships built on trust and quality.
Related Video: Business English Vocabulary : VV 47 – Manufacturing & Production Process (1) | English Vocabulary
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for list bolt manufacturers head markings Sourcing
When sourcing bolt manufacturers and their head markings, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will cover the key cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable buyer tips tailored to markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in bolt manufacturing is the raw material used, typically carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel. Prices can fluctuate based on market demand, availability, and geopolitical factors. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally when possible to reduce costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers may offer more competitive pricing. However, the expertise and skill level of the workforce can impact product quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to production facilities, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, making it a crucial area for buyers to investigate when evaluating potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: The cost of molds and machinery used in production is significant, especially for custom or specialized bolts. Buyers should inquire about tooling costs as they may be amortized over larger orders, potentially leading to lower unit prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is vital, particularly for high-stress applications. QC processes add to the overall cost but are essential for compliance with international standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust QC protocols to mitigate risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the destination, volume of the order, and chosen Incoterms. Buyers should evaluate shipping options and consider consolidating shipments to achieve cost efficiencies.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically apply a markup based on their cost structure and the market position. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers negotiate better pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders generally attract better pricing. Buyers should assess their needs and consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can lead to higher costs due to additional tooling and production complexities. Clear communication of requirements can minimize misunderstandings and related costs.
-
Materials: The choice of material directly affects pricing. High-grade materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ASTM, ISO) may come at a premium but offer long-term value through durability.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certified products often carry higher prices but provide assurance of quality and compliance. Buyers should balance their quality requirements with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher prices but can provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms impacts logistics costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms is crucial for budgeting and risk management.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better terms. Be prepared to discuss pricing openly and ask for breakdowns to understand where costs arise.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), not just the upfront price. Consider factors such as durability, maintenance, and the potential costs of failures or replacements.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to labor and material costs. For instance, sourcing from manufacturers in Brazil or Kenya may offer cost advantages compared to European suppliers, depending on the product specifications.
-
Local Partnerships: Establish relationships with local distributors or agents who understand the market dynamics and can provide insights into competitive pricing and quality.
Buyers should keep in mind that prices can vary based on numerous factors, and it is advisable to conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to ensure the best sourcing decisions are made.
Spotlight on Potential list bolt manufacturers head markings Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘list bolt manufacturers head markings’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for list bolt manufacturers head markings
Key Technical Properties for Bolt Manufacturers Head Markings
Understanding the technical specifications related to bolt head markings is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are some essential properties to consider:
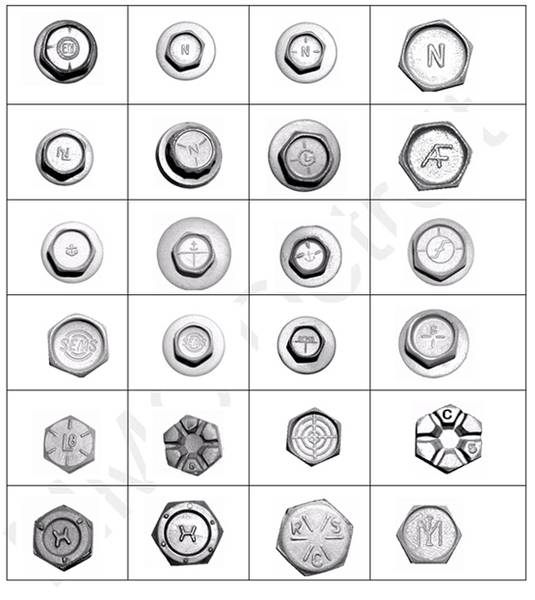
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade: This indicates the strength and type of material used in the bolt. Common grades include Grade 2, Grade 5, and Grade 8, with higher numbers representing stronger materials. Choosing the correct grade is vital for ensuring the structural integrity of your application, especially in high-stress environments.
-
Tensile Strength: This property defines the maximum load a bolt can withstand while being pulled apart without breaking. It is typically measured in pounds per square inch (PSI). Understanding tensile strength helps buyers select bolts that can handle the specific demands of their projects, thereby preventing failures that could lead to costly downtimes.
-
Yield Strength: Yield strength refers to the maximum stress that can be applied to a bolt without causing permanent deformation. This is particularly important in applications where precise alignment and fit are critical. Selecting bolts with appropriate yield strength is essential for maintaining safety and performance standards.
-
Thread Pitch: This specification describes the distance between threads on a bolt. It is typically measured in millimeters for metric bolts or threads per inch (TPI) for imperial bolts. Correct thread pitch is important for ensuring compatibility with corresponding nuts and fittings, which can affect assembly efficiency.
-
Corrosion Resistance: This property indicates how well a bolt can withstand environmental factors such as moisture and chemicals without deteriorating. Coatings like zinc plating or the use of stainless steel can enhance corrosion resistance. For buyers in humid or chemically aggressive environments, selecting bolts with suitable corrosion resistance is crucial to prolonging service life.
-
Tolerance: This defines the allowable deviation in measurements of the bolt, including diameter and length. Tighter tolerances often lead to better performance and fit, which is essential for applications requiring precision. Buyers should be aware of tolerance specifications to ensure that the bolts will fit seamlessly into their assemblies.
Common Trade Terms in Bolt Manufacturing
Familiarity with industry terminology can facilitate smoother transactions and better negotiation outcomes. Here are some essential trade terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce components that are then used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality components.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This specifies the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budget planning and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses or startups.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for a specific quantity of products. Using RFQs can help buyers compare options and negotiate better deals.
-
Incoterms: These are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in global trade. Familiarity with Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and delivery obligations, ensuring smoother logistics.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the time it takes from placing an order to receiving it. Understanding lead times is essential for planning project timelines and ensuring that materials are available when needed.
-
Certification: This indicates that a bolt meets specific industry standards, such as ISO or ASTM. Certification can assure buyers of the quality and safety of their purchased products, making it a critical consideration in procurement decisions.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right bolts for their applications while navigating the complexities of international trade effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the list bolt manufacturers head markings Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for bolt manufacturers, particularly in the head markings sector, is experiencing significant growth driven by infrastructure development, automotive production, and the construction industry. Emerging economies in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly investing in infrastructure projects, leading to a heightened demand for high-strength bolts with proper identification markings. Notably, countries like Kenya and Brazil are ramping up their construction initiatives, creating lucrative opportunities for suppliers.
Key trends shaping the B2B landscape include the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as automation and digitalization, which enhance production efficiency and quality control. Manufacturers are increasingly utilizing Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, to monitor production processes and ensure compliance with international standards for bolt strength and safety. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on traceability in the supply chain, compelling manufacturers to invest in sophisticated marking techniques that not only comply with regulatory requirements but also facilitate easier identification for quality assurance.
Furthermore, the shift towards sustainable sourcing practices is influencing purchasing decisions. International buyers are prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate commitment to ethical sourcing and transparency in their supply chains. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in regions where environmental regulations are becoming more stringent, prompting manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly materials and processes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the procurement process for bolt manufacturers. The environmental impact of production processes, including resource extraction and energy consumption, is under increasing scrutiny. International buyers are now more inclined to partner with manufacturers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste.
Ethical sourcing is also gaining traction, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, where social responsibility is becoming a priority. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that adhere to ethical labor practices and fair trade principles. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certification are becoming essential criteria for selecting suppliers.
Moreover, the demand for “green” certifications and materials is on the rise. Manufacturers that can provide evidence of sustainable practices and eco-friendly products are more likely to attract international buyers. This trend not only enhances brand reputation but also aligns with the global shift towards a circular economy, where products are designed with their lifecycle in mind, promoting reuse and recycling.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of bolt head markings has been driven by advancements in manufacturing processes and the need for standardization. Initially, markings were primarily used for identification purposes; however, as industries expanded and regulations tightened, the focus shifted towards ensuring safety and compliance with specific strength requirements.
In the mid-20th century, standardization organizations began to establish guidelines for bolt head markings, leading to a more systematic approach in identifying grades and materials. Today, manufacturers must comply with international standards, such as ASTM and ISO, which dictate not only the markings themselves but also the testing and quality assurance processes that underpin their production. This evolution has resulted in a more transparent and reliable market, ultimately benefiting B2B buyers by providing clearer information on the products they procure.
Related Video: Bolt Head Markings: What do they mean? | Fasteners 101
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of list bolt manufacturers head markings
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of bolt manufacturers with specific head markings?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their reputation and experience in the industry. Check for certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicate quality management practices. It’s essential to request references or case studies from previous clients, particularly those in your region. Additionally, assess their capacity to meet your volume needs and any specific customizations you may require. Communication responsiveness and willingness to engage in technical discussions about head markings and grades are also critical indicators of a reliable supplier. -
Can I customize bolt head markings according to my specifications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for bolt head markings to meet specific client needs. Discuss your requirements upfront, including any unique identification codes or logo placements. Be aware that customization may affect lead times and costs. It’s advisable to obtain written confirmation of the customization capabilities and any associated fees. Always request samples or prototypes to ensure the final product aligns with your expectations before placing a bulk order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for bulk bolt purchases?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier and can range from a few hundred to several thousand units. Factors influencing MOQs include the type of bolt, customization requests, and the supplier’s production capacity. Lead times generally range from 2 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s location. To avoid delays, communicate your timeline requirements clearly and consider suppliers who have a history of meeting delivery schedules. -
What payment terms are commonly offered when sourcing bolts internationally?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the transaction. Common terms include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. International transactions often involve letters of credit or escrow services to protect both parties. Always clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., wire transfers, PayPal) and any additional fees associated with international transactions. Establishing clear payment terms in the contract can mitigate future disputes. -
How can I ensure the quality of bolts meets industry standards?
To ensure quality, request certifications for the bolts, such as ASTM, ISO, or other relevant standards specific to your industry. Implement a quality assurance process that includes pre-shipment inspections or third-party audits. It’s advisable to establish a relationship with suppliers that provide transparent documentation of their quality control measures. Regularly review the performance of the bolts in your applications to ensure they meet your specifications and standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing bolts from international suppliers?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and delivery times. Evaluate whether the supplier offers door-to-door delivery or if you need to arrange shipping separately. Be aware of customs regulations in your country, as they can impact delivery timelines and costs. It’s also beneficial to understand the supplier’s return policy and how they handle defective products, as these factors can affect your overall logistics planning. -
What steps should I take if I encounter disputes with a supplier regarding bolt specifications or delivery?
In the event of a dispute, initiate communication with the supplier to discuss the issue clearly and calmly. Refer to the contract or purchase order for specific terms related to specifications and delivery timelines. If the issue remains unresolved, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Document all communications and agreements related to the dispute for future reference. If necessary, seek legal advice to understand your rights and options for resolution. -
Are there specific certifications or quality assurance measures that international buyers should look for in bolt manufacturers?
Yes, international buyers should look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and specific product standards like ASTM or SAE. These certifications indicate that the manufacturer adheres to recognized quality and safety protocols. Additionally, inquire about their testing procedures for materials and finished products, as well as any third-party audits they undergo. Understanding these measures can provide assurance that the bolts will perform reliably in your applications.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for list bolt manufacturers head markings
The importance of strategic sourcing in the procurement of bolts, particularly those with specific head markings, cannot be overstated. Understanding the implications of bolt head markings—which indicate strength, material properties, and manufacturer identification—empowers international buyers to select appropriate fasteners that meet their operational requirements. This knowledge is crucial for ensuring safety, compliance with local standards, and optimizing supply chain efficiency.
Key takeaways for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe include:
- Prioritize Quality: Choose manufacturers that provide clear, standardized head markings to ensure product reliability and traceability.
- Engage with Suppliers: Building relationships with reputable bolt manufacturers can provide insights into the latest industry standards and innovations.
- Stay Informed: Regularly update your knowledge on bolt specifications and market trends to make informed purchasing decisions.
As the global market continues to evolve, the demand for high-quality, marked fasteners will grow. International buyers are encouraged to leverage strategic sourcing practices to enhance their procurement processes. By proactively engaging with suppliers and understanding the nuances of bolt head markings, businesses can position themselves for success in a competitive landscape.