Master Sourcing Various Types of Bolts: A Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for various types of bolts
In today’s interconnected global economy, the selection of the right fasteners—particularly bolts—plays a crucial role in the success of industries ranging from construction to manufacturing. B2B buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate an intricate landscape of bolt types, each designed to meet specific mechanical demands and environmental conditions. With varying regulations, standards, and supplier capabilities, making informed choices is essential for operational efficiency and product integrity.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource for procurement professionals and engineering decision-makers, detailing the extensive variety of bolts available on the global market. It covers key bolt types, including hex head, carriage, and flange bolts, alongside their respective applications and advantages. Additionally, the guide delves into materials and coatings, highlighting the importance of corrosion resistance and tensile strength tailored to specific climates and industries.
Moreover, understanding manufacturing and quality control standards is vital for ensuring compliance and reliability in sourcing. Buyers will find effective supplier selection strategies and insights into global cost structures to optimize procurement processes. With market trends and frequently asked questions addressed, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to mitigate risks, enhance quality assurance, and secure a competitive edge in their sourcing decisions—facilitating smarter strategies across continents and industries.
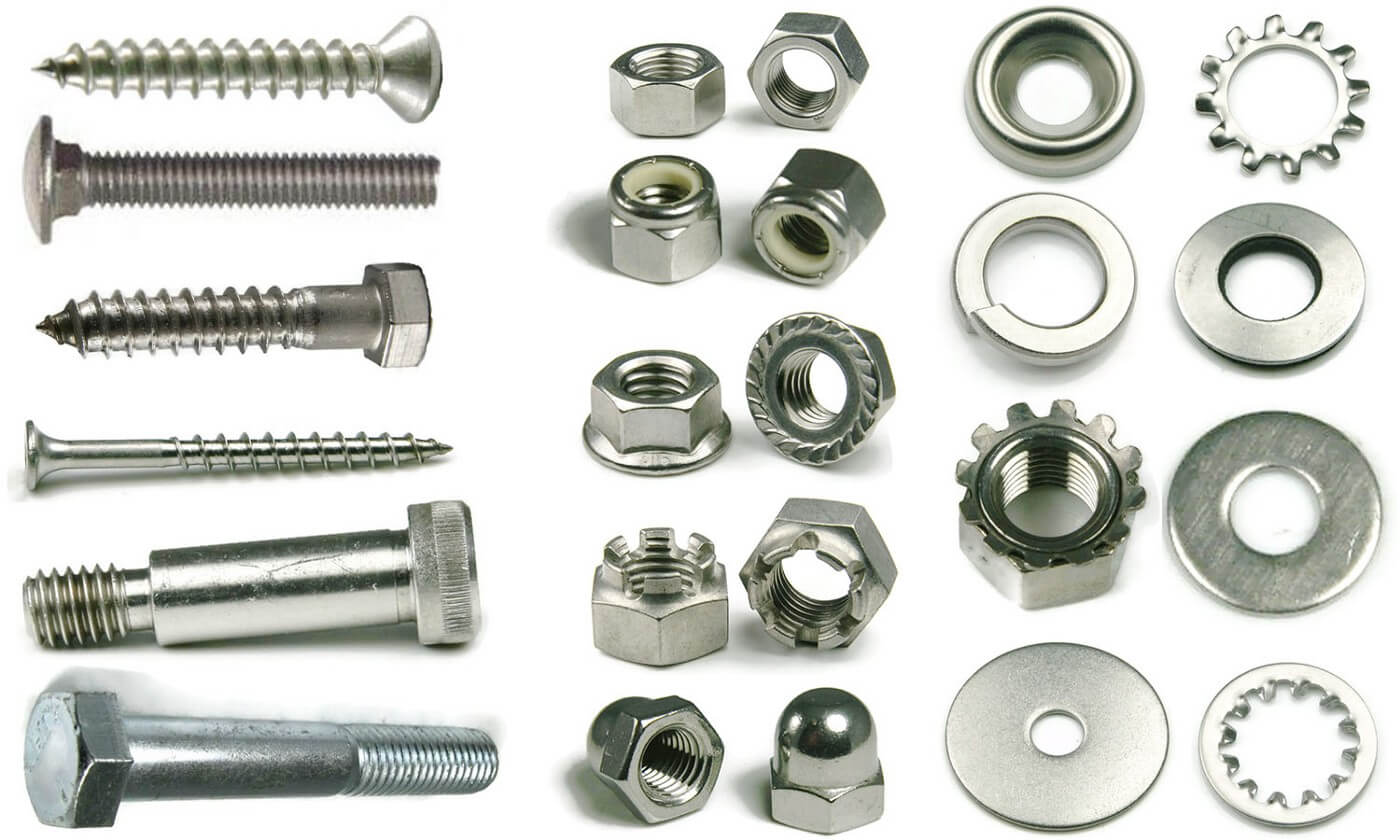
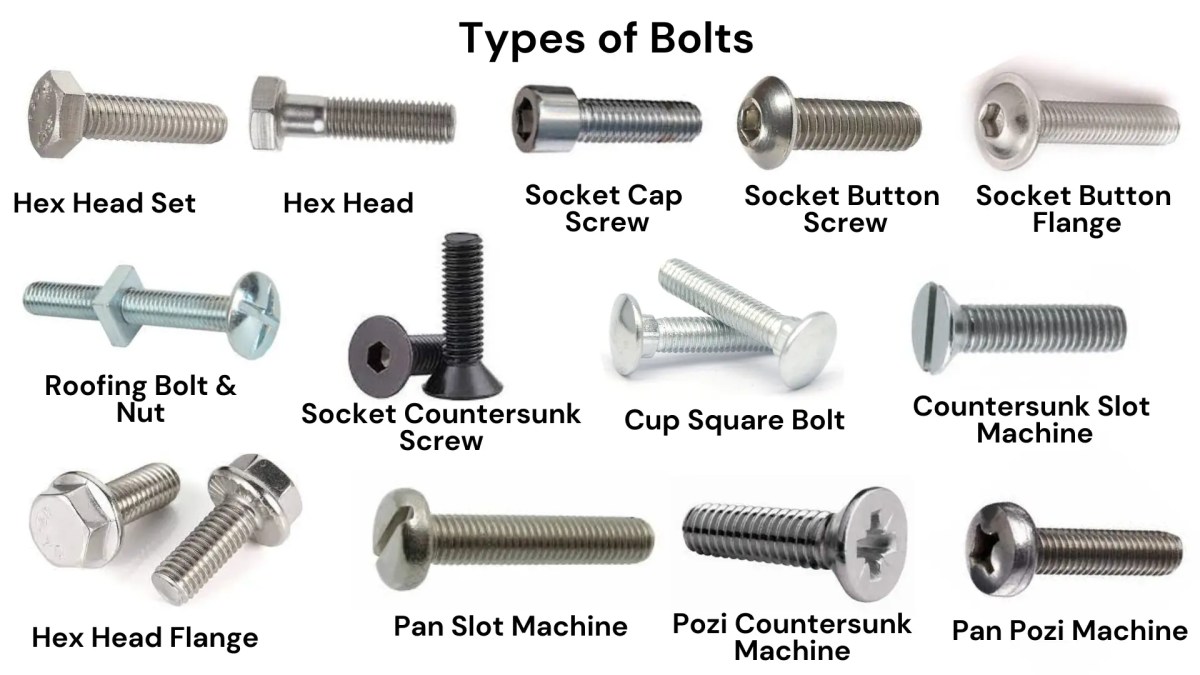
Understanding various types of bolts Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hex Head Bolt | Six-sided head; compatible with standard tools; various grades | Construction, automotive, machinery | Widely available; risk of overtightening |
| Carriage Bolt | Domed head with square neck; prevents rotation | Timber construction, furniture, railways | Tamper-resistant; limited to through-hole applications |
| Flange Bolt | Integrated flange acts as washer; distributes load evenly | Heavy equipment, automotive, pipelines | Reduces need for washers; bulkier design |
| Lock Nut | Features a locking mechanism; prevents loosening | Vibration-prone assemblies, heavy machinery | Enhances assembly security; may require more torque |
| Socket Head Cap Screw | Cylindrical head; requires an Allen wrench for installation | High-strength applications, machinery | High strength; compact design; specific tool required |
Hex Head Bolt
Characteristics: Hex head bolts are characterized by their six-sided heads, allowing for easy installation and removal with standard wrenches. They are available in various lengths, diameters, and grades, making them versatile for numerous applications.
Suitability: These bolts are ideal for construction, automotive, and machinery sectors, where high strength and reliability are paramount. Their widespread availability across global markets makes them a go-to choice for many B2B buyers.
B2B Considerations: When procuring hex head bolts, buyers should evaluate local supply chains for availability, preferred grades (metric or imperial), and compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, DIN). Ensuring compatibility with existing inventory is crucial for seamless project execution.
Carriage Bolt
Characteristics: Carriage bolts feature a smooth, domed head and a square neck that locks into softer materials, preventing rotation during tightening. This design makes them suitable for applications where tamper resistance is necessary.
Suitability: Commonly used in timber construction, furniture assembly, and public infrastructure, carriage bolts are ideal for wood-to-wood or wood-to-metal connections.
B2B Considerations: Buyers should confirm the shank length and protective coatings (such as zinc) to ensure durability in humid environments. When sourcing, consider bulk purchasing that includes matching nuts and compliance with local safety regulations.
Flange Bolt
Characteristics: Flange bolts come with an integrated flange that acts as a washer, distributing load evenly across the surface. This design minimizes damage to the connected materials and enhances joint integrity.
Suitability: These bolts are frequently used in heavy equipment manufacturing, automotive applications, and pipeline construction, where load distribution and vibration resistance are essential.
B2B Considerations: Buyers should assess the flange diameter and thickness in relation to load requirements. Specific flange designs may be mandated for projects in regions like Europe and the Middle East, necessitating careful verification with engineering specifications.
Lock Nut
Characteristics: Lock nuts are designed with a locking mechanism, such as a nylon insert or deformed threads, to prevent loosening due to vibration. This feature is crucial in dynamic environments.
Suitability: They are widely used in vibration-prone assemblies, heavy machinery, and transport applications where secure fastening is critical.
B2B Considerations: When sourcing lock nuts, buyers should consider the torque requirements for installation, as they may need more force than standard nuts. Ensuring compatibility with existing fasteners is also vital for effective assembly.
Socket Head Cap Screw
Characteristics: Socket head cap screws have a cylindrical head and require an Allen wrench for installation. They are often made from high-strength materials, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Suitability: These screws are commonly used in high-strength applications, including machinery and automotive sectors, where compact design and strength are required.
B2B Considerations: Buyers must ensure they have the appropriate tools for installation and consider the specific strength requirements of their applications. Custom manufacturing options may be necessary for unique specifications.
Related Video: Bolts Types, Usages and Applications
Key Industrial Applications of various types of bolts
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of various types of bolts | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Use of hex head bolts in structural steel frameworks | Provides strength and reliability in load-bearing structures | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards; assess availability of preferred grades and sizes. |
| Automotive | Flange bolts in vehicle assembly for chassis and body components | Enhances safety and durability of automotive structures | Verify compatibility with specific vehicle models; prioritize suppliers with automotive-grade certifications. |
| Manufacturing | Carriage bolts in machinery assembly for securing parts | Facilitates smooth operation and maintenance of machinery | Consider corrosion resistance for industrial environments; ensure bulk availability for large-scale projects. |
| Energy & Utilities | Lock nuts in pipeline installations to prevent loosening | Ensures operational safety and efficiency in energy transport | Evaluate environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, moisture) that may affect bolt performance; confirm compliance with safety regulations. |
| Furniture | Square head bolts in furniture assembly for aesthetics and strength | Supports product integrity and enhances design appeal | Assess wood compatibility and required finishes; seek suppliers who offer custom sizes for specific designs. |
Construction
In the construction sector, hex head bolts are integral to creating robust structural steel frameworks. They provide essential strength and reliability, ensuring that load-bearing structures can withstand environmental stresses. International buyers must ensure that the bolts comply with local building codes and standards, which can vary significantly across regions such as Africa and Europe. Additionally, assessing the availability of preferred grades and sizes is crucial to avoid delays in project timelines.
Automotive
Within the automotive industry, flange bolts are commonly used during the assembly of chassis and body components. Their design allows for an even distribution of load, enhancing the safety and durability of vehicles. For B2B buyers, it is vital to verify the compatibility of bolts with specific vehicle models, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. Prioritizing suppliers that hold automotive-grade certifications can ensure adherence to quality and safety standards.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, carriage bolts are often employed in machinery assembly to secure various parts effectively. Their design allows for easy installation while preventing rotation once tightened, which is crucial for the smooth operation and maintenance of machinery. Buyers should consider the corrosion resistance of bolts, particularly in industrial environments where moisture and chemicals may be present. Ensuring bulk availability from suppliers can also facilitate large-scale projects and reduce lead times.
Energy & Utilities
The energy and utilities sector frequently utilizes lock nuts in pipeline installations to prevent loosening due to vibrations. This application is critical for ensuring operational safety and efficiency in energy transport systems. Buyers should evaluate the environmental conditions, such as temperature fluctuations and moisture levels, which may affect bolt performance. Additionally, confirming compliance with safety regulations is essential to mitigate risks associated with pipeline integrity.
Furniture
In the furniture industry, square head bolts are used to enhance both aesthetics and strength in assembly. Their unique design allows for easy gripping and alignment, making them suitable for various wood types. For international B2B buyers, assessing wood compatibility and required finishes is crucial to ensure product integrity and appeal. Sourcing from suppliers who offer custom sizes can also provide an advantage in creating unique designs tailored to market demands.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for various types of bolts
When selecting bolts for various applications, the choice of material is critical to ensuring performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in bolt manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, limitations, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel bolts offer high tensile strength and are suitable for high-stress applications. They typically have a temperature rating up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle moderate pressure. However, they are prone to corrosion if not treated.
Pros & Cons: Carbon steel is relatively inexpensive and widely available, making it a popular choice for general construction and manufacturing. Its main disadvantage is susceptibility to rust, necessitating protective coatings like zinc plating or galvanization, which can increase costs and manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel bolts are ideal for use in dry environments or where they are protected from moisture. In humid climates, such as parts of Africa and South America, additional corrosion protection is essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A307 or DIN 933. Understanding local regulations regarding coatings and environmental impact is crucial, particularly in regions with stringent environmental laws.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel bolts exhibit excellent corrosion resistance due to the presence of chromium, making them suitable for harsh environments. They can withstand temperatures up to 1,500°F (815°C) and are generally stable under varying pressure conditions.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor and marine applications. However, stainless steel bolts are more expensive than carbon steel, and their manufacturing process can be complex, leading to higher costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel bolts are suitable for applications exposed to corrosive elements, such as saltwater or chemicals. This makes them a preferred choice in the Middle East and coastal regions of Europe and South America.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should look for compliance with standards such as ASTM A193 or ISO 3506. It’s important to consider the grade of stainless steel (e.g., 304 vs. 316) based on the specific environmental conditions of the application.
Alloy Steel
Key Properties: Alloy steel bolts are created by adding elements like nickel, chromium, or molybdenum to carbon steel, enhancing strength and toughness. They can handle high temperatures and pressures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of alloy steel is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for heavy machinery and structural applications. However, alloy steel can be more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing lead times.
Impact on Application: Alloy steel bolts are often used in automotive and aerospace applications, where performance and reliability are critical. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions makes them suitable for projects in diverse climates.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that alloy steel bolts meet relevant standards such as ASTM A325 or JIS B 1180. Understanding the specific alloy composition is essential for ensuring compatibility with project requirements.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass bolts are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and low friction properties. They can withstand temperatures up to 300°F (149°C) and are not suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of brass is its aesthetic appeal and resistance to tarnishing, making it suitable for decorative applications. However, brass is softer than steel, which can limit its use in high-stress environments.
Impact on Application: Brass bolts are often used in plumbing, electrical, and decorative applications where corrosion resistance is essential. They are particularly favored in humid environments, such as coastal regions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards such as ASTM B16 or ISO 4032. Understanding local preferences for materials in specific applications can guide sourcing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for various types of bolts | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | General construction, machinery assembly | High tensile strength | Prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, outdoor, and chemical applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Alloy Steel | Heavy machinery, automotive, aerospace | High strength-to-weight ratio | More expensive, complex mfg | Medium |
| Brass | Plumbing, electrical, decorative applications | Good corrosion resistance | Softer, limited high-stress use | Medium |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions when sourcing bolts for diverse applications across various regions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for various types of bolts
Manufacturing processes and quality assurance in the production of bolts are critical elements that can significantly influence the reliability and performance of fasteners in various applications. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can aid in making informed sourcing decisions and ensuring compliance with regional standards.
Manufacturing Processes for Various Types of Bolts
The manufacturing of bolts involves several key stages, each requiring precision and adherence to specific techniques to ensure high-quality outputs.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in bolt manufacturing is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel, chosen based on the required strength and corrosion resistance.
- Material Inspection: Before manufacturing begins, suppliers conduct an inspection of incoming materials to ensure they meet specified chemical and physical properties.
- Cutting and Heating: Raw materials are cut to size and may undergo heating processes to improve malleability, which facilitates subsequent forming operations.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the raw material into the desired bolt configuration.
- Cold Heading: This is a widely used technique where metal is deformed at room temperature. It allows for the rapid production of bolts with high strength and good surface finish.
- Thread Rolling: After forming the head, threads are added using thread rolling machines, which produce threads without cutting, preserving the material’s integrity and enhancing strength.
3. Assembly
While many bolts are manufactured as standalone components, some may require assembly with nuts or washers.
- Automated Assembly Lines: In high-volume production settings, automated systems are used to assemble nuts and bolts, ensuring consistent quality and reducing labor costs.
- Quality Checks During Assembly: Manufacturers often implement in-process inspections to verify that components fit together correctly and meet specified tolerances.
4. Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the bolt’s performance characteristics and aesthetic appeal.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as galvanizing, electroplating, or coating (e.g., with zinc or nylon) are applied to improve corrosion resistance and reduce friction.
- Heat Treatment: Some bolts undergo heat treatment to increase hardness or toughness, particularly for high-strength applications.
Quality Assurance in Bolt Manufacturing
Quality assurance is crucial in bolt manufacturing to ensure products meet international standards and customer specifications. Various quality control (QC) measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of relevant international standards such as:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system and is applicable to all organizations seeking to improve quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: In Europe, bolts used in construction and infrastructure must meet specific safety and performance criteria, often verified through CE marking.
- API Standards: For bolts used in the oil and gas industry, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential, ensuring products can withstand extreme conditions.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials before they enter the production process to ensure they conform to specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early, preventing costly rework.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Finished bolts undergo comprehensive testing, including dimensional checks, material property evaluations, and functional tests.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should familiarize themselves with common testing methods that manufacturers may employ, including:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of bolts to ensure they can withstand specified loads.
- Hardness Testing: Assesses the hardness of the bolt material, which correlates with strength and wear resistance.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Evaluates how well a bolt can withstand corrosive environments, critical for applications in humid or chemically aggressive settings.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
When sourcing bolts from international suppliers, B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control practices of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits can provide insights into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports can help assess a supplier’s compliance with international standards and internal quality benchmarks.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased evaluation of the manufacturing process and product quality, ensuring that the bolts meet specified requirements before shipment.
Regional Considerations for International Buyers
Understanding the nuances of sourcing bolts from different regions is vital for international buyers. Buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider:
- Local Regulations: Each region may have specific regulations regarding the import of fasteners, including safety and environmental standards.
- Cultural Differences: Building relationships with suppliers may vary significantly across regions, impacting negotiation and communication styles.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Consideration of logistics, including shipping times and costs, is essential, particularly when sourcing from distant suppliers.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies, international B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality bolts that meet their operational requirements and regulatory standards.
Related Video: The manufacturing process of hex nuts. mass production factory in korea.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for various types of bolts Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for various types of bolts is essential for international B2B buyers looking to maximize their procurement efficiency. Understanding the components that contribute to the overall cost can help buyers make informed decisions and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly influences the cost of bolts. Common materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, and specialized alloys. Prices fluctuate based on global commodity markets, with stainless steel generally commanding a higher price due to its corrosion resistance and durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and manufacturing practices. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing, but it’s essential to consider the trade-off with quality and reliability. Understanding the local labor market conditions can help buyers assess the feasibility of sourcing from specific regions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Manufacturers with efficient processes may pass on savings to buyers, making it crucial to evaluate the operational efficiency of potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling is a significant factor, especially for custom or specialized bolts. Tooling costs can be amortized over large production runs, making it advantageous for buyers to order in bulk to reduce per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure that the bolts meet industry standards and specifications. Suppliers that invest in quality assurance may charge higher prices, but this can lead to lower failure rates and reduced long-term costs for buyers.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, shipping method, and the volume of the order. Incoterms play a crucial role in determining who bears these costs, impacting the total landed cost of the bolts.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge whether a price is fair.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders typically result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs that align with their inventory needs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom bolts or those with specific certifications may incur additional charges. Buyers should clearly communicate their requirements to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Bolts that meet higher quality standards or industry-specific certifications (like ISO or ASTM) may be priced higher. However, investing in quality can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs in the long run.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of timely deliveries and quality products may charge a premium, which can be justified by the reduced risk.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is vital. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can shift costs and responsibilities between the buyer and seller, affecting overall expenditure.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage the insights from your cost analysis to negotiate better pricing. Be prepared to discuss volume commitments and payment terms that could benefit both parties.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. Consider factors like longevity, maintenance, and potential downtime caused by bolt failures.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For instance, sourcing from local suppliers in Africa or South America may reduce shipping costs but could lead to higher manufacturing costs. Always compare total landed costs to ensure the best deal.
Disclaimer
Prices for bolts can vary significantly based on fluctuating material costs, regional economic conditions, and supplier pricing strategies. This analysis provides a framework for understanding potential costs and should be used as a guideline rather than a definitive price list. Always conduct due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential various types of bolts Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘various types of bolts’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for various types of bolts
When sourcing bolts in the international B2B market, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here’s an overview of key specifications and common industry terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the type and quality of the material used to manufacture the bolt, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel.
– B2B Importance: Different grades offer varying strengths, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties. Buyers must align material grades with specific project requirements to ensure durability and performance, especially in challenging environments. -
Tensile Strength
– Definition: This is the maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that a bolt can withstand before failure.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the tensile strength helps buyers select bolts that can handle the forces in their application, reducing the risk of mechanical failure, which can lead to costly repairs and downtime. -
Thread Specification
– Definition: This includes the type (e.g., coarse or fine), size, and pitch of the threads on the bolt.
– B2B Importance: Proper thread specifications ensure compatibility with nuts and tapped holes. Misalignment can cause assembly issues, leading to increased labor costs and potential structural weaknesses.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Coating and Finish
– Definition: Coatings (such as zinc plating or galvanization) protect bolts from environmental factors like corrosion and wear.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate coating based on the application’s exposure to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures is essential for maintaining the integrity of fastened joints over time. -
Length and Diameter
– Definition: These dimensions define the size of the bolt, which influences its load-bearing capacity and suitability for specific applications.
– B2B Importance: Buyers must ensure that the selected length and diameter meet the requirements of the assembly to prevent overloading and ensure proper fit. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension of the bolt.
– B2B Importance: Understanding tolerances is critical for ensuring that bolts fit correctly in assemblies, especially in precision engineering applications where even minor discrepancies can lead to significant issues.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance for Buyers: Understanding OEM specifications is vital for ensuring that sourced bolts are compatible with existing equipment or systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance for Buyers: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their procurement strategy and manage inventory costs effectively, particularly in regions with fluctuating demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products.
– Importance for Buyers: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to gather competitive pricing and delivery options, facilitating better negotiation and sourcing decisions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of international rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Importance for Buyers: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost implications when sourcing bolts internationally. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time taken from the initiation of a process until its completion.
– Importance for Buyers: Understanding lead times is crucial for planning project timelines and ensuring that materials are available when needed, thus avoiding delays in production. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Standards that indicate the quality and safety of bolts, such as ISO, ASTM, or DIN.
– Importance for Buyers: Verification of certification ensures compliance with industry regulations and quality assurance, which is particularly critical in sectors like construction and automotive.
By mastering these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing bolts more effectively, leading to improved operational efficiency and reduced risk.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the various types of bolts Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for various types of bolts is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by several key factors. As industries worldwide strive for efficiency and reliability, the demand for high-quality fasteners is increasing. Notably, the construction, automotive, and aerospace sectors are significant consumers, with a growing emphasis on precision engineering and material strength. B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay abreast of these trends to optimize procurement strategies.
Emerging technologies, including automation in manufacturing and the rise of Industry 4.0, are reshaping sourcing practices. Digital platforms and marketplaces are enhancing visibility and accessibility, allowing buyers to compare suppliers, materials, and prices more effectively. Additionally, data analytics is playing a crucial role in forecasting demand and managing inventory, providing buyers with actionable insights that can lead to cost reductions and improved supply chain resilience.
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in sourcing decisions. Buyers are now more inclined to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate environmental responsibility, whether through the use of recycled materials or energy-efficient production processes. Understanding the local market dynamics, including regulatory changes and economic conditions, is vital for international B2B buyers seeking to navigate these trends effectively.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of the fastener industry cannot be overlooked, particularly as global attention shifts toward sustainability. B2B buyers are encouraged to adopt ethical sourcing practices by selecting suppliers that prioritize sustainable production methods. This includes using materials that are recyclable or derived from renewable sources, thereby reducing the carbon footprint associated with bolt manufacturing.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood-based fasteners are increasingly relevant. These certifications not only assure buyers of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability but also enhance their own brand reputation in a competitive market.
By fostering ethical supply chains, companies can mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations and consumer backlash. B2B buyers should actively engage with suppliers to understand their sustainability practices, ensuring that their sourcing strategies align with both market expectations and corporate social responsibility goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The development of bolts dates back thousands of years, evolving from rudimentary fastening methods to the sophisticated designs we see today. Initially crafted from wood, bolts transitioned to metal as industrialization progressed, allowing for increased strength and durability. The 19th century marked a significant turning point with the advent of standardized bolt sizes and grades, which facilitated mass production and international trade.
In contemporary times, the fastener industry has continued to innovate, incorporating advanced materials such as high-strength alloys and corrosion-resistant coatings. This evolution reflects the growing demands of modern industries for reliable and efficient fastening solutions. Understanding this historical context can provide B2B buyers with insights into product development trends and the importance of quality standards in their procurement processes.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of various types of bolts
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers for bolts?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, production capabilities, and quality management systems. Verify certifications such as ISO 9001 and industry-specific standards (e.g., ASTM, DIN). Request references from other B2B buyers, particularly those in your region, to gauge reliability. Additionally, evaluate their responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to provide samples. This diligence can mitigate risks associated with product quality and delivery timelines. -
Can I customize bolts for my specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for bolts, including thread patterns, lengths, materials, and coatings. Discuss your specific requirements with potential suppliers to understand their capabilities. Customization can enhance performance in unique applications, such as extreme temperatures or corrosion-prone environments. Always confirm minimum order quantities (MOQs) for custom products, as they may differ from standard offerings. -
What are the typical lead times for bulk orders of bolts?
Lead times for bulk orders can vary significantly based on the supplier’s location, production capacity, and the complexity of the order. Generally, standard products may have lead times ranging from 2 to 6 weeks, while custom orders can take longer—up to 12 weeks or more. It’s crucial to communicate your project timelines clearly and inquire about expedited options if necessary, especially for projects with tight deadlines. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing bolts internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and may include options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and risk tolerance. For larger orders, consider partial payments tied to milestones (e.g., deposit upon order confirmation, balance upon shipment). Always review the supplier’s payment policies and be cautious of any upfront costs that may be non-refundable. -
How can I ensure quality assurance for the bolts I purchase?
To ensure product quality, request a Certificate of Compliance (CoC) or material test reports from your supplier. Conducting third-party inspections prior to shipment can also help verify that the bolts meet your specifications. Establishing clear quality criteria in your purchase agreements, including dimensional tolerances and material properties, will help protect your interests. Regular audits of your suppliers can further enhance quality assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing bolts?
When importing bolts, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities. Ensure that all necessary documentation, including bills of lading and customs declarations, is in order to avoid delays. Additionally, plan for lead times by factoring in customs clearance and local transportation to your facility. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers over bolt quality or delivery?
To handle disputes effectively, maintain clear communication with your supplier and document all agreements and communications. If issues arise, refer to the terms outlined in your purchase order, including any warranty or return policies. Consider mediation or arbitration for resolution if direct communication fails. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations during disputes. -
What common certifications should I look for in bolt suppliers?
Look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Additionally, certifications related to specific industries (e.g., automotive, aerospace) can indicate a supplier’s capability to meet stringent requirements. Certifications like ASTM for material specifications or CE marking for European markets are also important. These certifications help ensure that the bolts you purchase meet safety and performance standards critical to your operations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for various types of bolts
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of bolts is paramount for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their procurement processes and enhance operational efficiency. Understanding the diverse types of bolts—ranging from hex head to lock nuts—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific industry needs and environmental conditions.
Key takeaways include the importance of assessing material specifications, coating options, and supplier reliability to ensure compliance with local and international standards. Engaging with suppliers who demonstrate a robust understanding of regional challenges—such as customs regulations and logistical complexities—can significantly mitigate risks associated with procurement.
As markets continue to evolve, staying ahead of trends in bolt technology and manufacturing practices will empower buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to secure a competitive edge. Now is the time to leverage this knowledge to refine your sourcing strategies and build resilient supply chains that can adapt to future demands. Take proactive steps today to ensure that your fastener choices contribute to the long-term success of your projects and operations.