Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Heat Sink Supplier
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heat sink supplier
In an era where thermal management is critical to the performance and longevity of electronic systems, the role of a reliable heat sink supplier cannot be overstated. Across various industries—including telecommunications, automotive, and consumer electronics—heat sinks are essential for dissipating excess heat, ensuring operational efficiency, and preventing equipment failure. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, identifying the right supplier is a strategic priority that directly impacts competitiveness.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This comprehensive guide serves as a vital resource for navigating the complexities of the heat sink market. It covers a wide array of topics, including the different types of heat sinks available, essential material selection criteria, advanced manufacturing and quality control practices, and profiles of reputable global suppliers. Additionally, it provides detailed cost analyses and insights into market trends that affect pricing and availability.
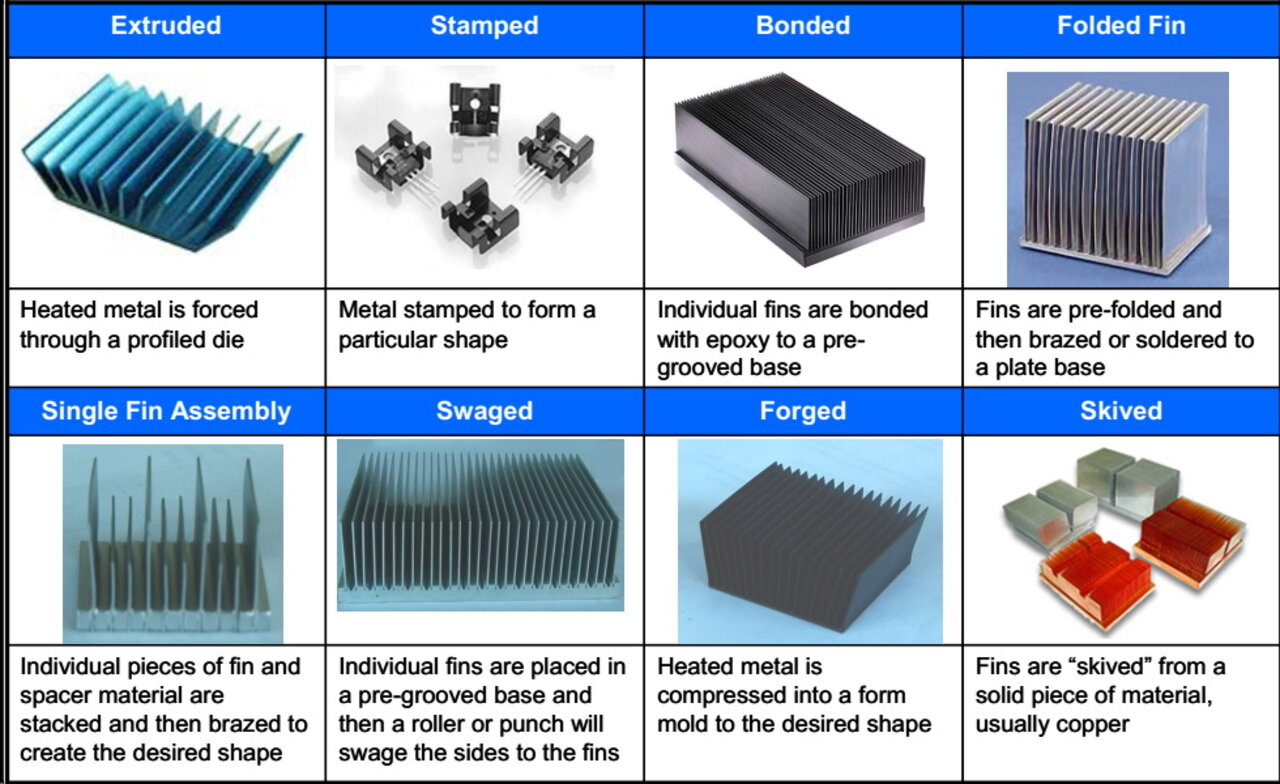
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By equipping procurement professionals and engineering leads with the knowledge they need, this guide empowers informed sourcing decisions. From understanding the nuances of various heat sink designs to evaluating supplier capabilities, readers will find actionable insights that enhance their procurement strategies and contribute to the success of their thermal management systems. Whether you’re looking to establish a new supply chain or refine existing partnerships, the information presented here is designed to support your objectives and drive business growth.
Understanding heat sink supplier Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skived Copper Heat Sink | Solid copper with thin, high-density fins; no soldering required | High-performance servers, telecom | Pros: Excellent thermal efficiency; Cons: Higher cost and tooling requirements |
| Stamped Copper Heat Sink | Formed from copper sheets; cost-effective for mass production | Consumer electronics, LED lighting | Pros: Affordable for large volumes; Cons: Limited design complexity and thermal performance |
| Finned/Bonded Copper Heat Sink | Assembled design with bonded fins for enhanced surface area | Power electronics, inverters | Pros: Customizable; Cons: Heavier and complex assembly may increase costs |
| Heat Pipe Embedded Copper Heat Sink | Integrated heat pipes for superior heat transfer | Data centers, graphics cards | Pros: Effective for compact designs; Cons: Higher manufacturing complexity and cost |
| CNC Machined Copper Heat Sink | Fully machined from copper blocks; high precision | Specialized electronics, R&D | Pros: Fully customizable; Cons: Highest cost and longer lead times |
Skived Copper Heat Sink
Skived copper heat sinks are crafted by slicing thin fins directly from a solid copper block, providing a highly efficient thermal path. They are particularly suitable for applications in high-performance servers and telecom equipment where space is limited and continuous operation is critical. B2B buyers should be prepared for higher initial costs and tooling investments, but the long-term thermal efficiency can justify the expense in demanding environments.
Stamped Copper Heat Sink
These heat sinks are produced by stamping copper sheets into desired shapes, making them a cost-effective solution for high-volume applications, such as consumer electronics and LED lighting. While they offer a favorable balance of cost and performance, buyers should note their limitations in terms of design complexity and thermal efficiency. This type is ideal for OEMs looking for scalable solutions without requiring intricate thermal management.
Finned/Bonded Copper Heat Sink
Finned or bonded copper heat sinks feature a base with mechanically or thermally affixed fins, which significantly increase the surface area for heat dissipation. This design is well-suited for power electronics and industrial applications where heat generation is substantial. Buyers should consider the customizability of these heat sinks, though the increased weight and complexity in assembly may raise logistical costs, particularly in regions with limited infrastructure.
Heat Pipe Embedded Copper Heat Sink
This type incorporates embedded heat pipes that facilitate rapid heat transfer away from concentrated sources, making it ideal for data centers and high-performance graphics cards. While the performance benefits are notable, the complexity and cost of manufacturing these heat sinks can be a hurdle for budget-conscious buyers. Companies dealing with compact or thermally-challenged applications will find significant value in this design.
CNC Machined Copper Heat Sink
CNC machined copper heat sinks allow for full customization in terms of geometry and thermal performance, making them suitable for specialized electronics and research and development projects. The precision achieved through CNC machining can meet specific thermal resistance requirements. However, buyers should be aware that this option typically comes with the highest costs and longer lead times, which may impact project timelines.
Related Video: SE 12 : All SDLC Models Revision | Software Engineering Full Course
Key Industrial Applications of heat sink supplier
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Heat Sink Supplier | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Cooling for high-performance computing systems | Enhances reliability and extends lifespan of critical components | Need for high thermal conductivity and customization options |
| Telecommunications | Heat management in telecom equipment | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs | Consideration of environmental factors and regional standards |
| Automotive | Thermal management in electric vehicle battery systems | Improves efficiency and safety of battery operation | Focus on lightweight materials and robust design |
| Medical Devices | Cooling solutions for imaging and diagnostic equipment | Ensures precision and reliability in sensitive applications | Compliance with health regulations and quality certifications |
| Industrial Machinery | Heat dissipation in manufacturing equipment | Increases operational efficiency and reduces failure rates | Evaluation of manufacturing processes and lead times |
Electronics
In the electronics sector, heat sinks are critical for cooling high-performance computing systems, such as servers and GPUs. These systems generate significant heat, which can lead to performance degradation or failure if not managed effectively. Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should prioritize suppliers that offer high thermal conductivity materials and customization options to meet specific design requirements. Additionally, the capacity for rapid prototyping and scalable production is essential for keeping up with fast-paced technological advancements.
Telecommunications
Telecom equipment, such as base stations and routers, requires effective heat management to maintain operational efficiency. Heat sinks help dissipate heat generated by electronic components, reducing the risk of overheating, which can lead to service interruptions. International buyers, particularly from the Middle East and Europe, should consider suppliers that understand local environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature extremes, which can impact thermal performance. Ensuring compliance with regional standards is also crucial for long-term reliability.
Automotive
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), thermal management in battery systems has become increasingly important. Heat sinks are used to regulate the temperature of battery packs, ensuring optimal performance and safety. B2B buyers in Europe and South America should focus on sourcing lightweight yet durable materials that can withstand the rigors of automotive applications. Suppliers must also demonstrate expertise in designing heat sinks that fit within compact spaces while maintaining efficiency, as these factors are vital for the evolving automotive landscape.
Medical Devices
In medical devices, particularly imaging and diagnostic equipment, maintaining a stable operating temperature is crucial for accuracy and reliability. Heat sinks are employed to manage the heat produced by high-intensity components, ensuring consistent performance. Buyers, especially in Africa and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers who comply with stringent health regulations and possess relevant quality certifications. The ability to provide thermal testing and engineering support will also enhance the procurement process for these critical applications.
Industrial Machinery
In industrial settings, heat sinks are essential for dissipating heat in manufacturing equipment, such as CNC machines and robotics. Effective thermal management contributes to increased operational efficiency and reduced risk of equipment failure. International buyers from regions like Europe and South America should evaluate suppliers based on their manufacturing processes and lead times, as timely delivery of high-quality components can significantly impact production schedules. Customization capabilities to suit specific machinery requirements are also an important consideration in the sourcing process.
Related Video: Plate Heat Exchanger Applications and working principle hvac heat transfer
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heat sink supplier
When selecting materials for heat sinks, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in heat sink manufacturing: aluminum, copper, graphite, and composites. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can affect procurement decisions, especially in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent thermal conductivity (approximately 205 W/mK), and is resistant to corrosion due to the formation of a protective oxide layer. It typically withstands temperatures up to 150°C, making it suitable for many electronic applications.
Pros & Cons: Aluminum heat sinks are cost-effective and easier to manufacture, allowing for complex shapes through extrusion. However, they have lower thermal conductivity compared to copper, which can limit their effectiveness in high-performance applications. Their lightweight nature makes them ideal for portable devices, but they may require additional surface treatments to enhance performance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with most electronic media and is commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive components, and LED lighting. Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for outdoor applications, particularly in humid or coastal environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with regional standards such as ASTM and DIN. Additionally, the availability of aluminum in local markets can vary, impacting lead times and costs.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper boasts superior thermal conductivity (approximately 400 W/mK) and excellent heat dissipation capabilities. It can handle higher temperatures, typically up to 200°C, and is highly resistant to thermal fatigue.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its thermal performance, making it ideal for high-power applications like data centers and industrial machinery. However, copper is heavier and more expensive than aluminum, which can increase shipping costs and complicate manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: Copper heat sinks are particularly effective in applications requiring rapid heat transfer, such as high-performance computing and medical devices. Their ability to maintain performance under extreme conditions makes them suitable for critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must account for the higher cost and potential supply chain complexities associated with copper. Compliance with standards like JIS and local regulations is essential, particularly in markets with stringent material sourcing guidelines.
Graphite
Key Properties: Graphite is known for its excellent thermal conductivity (around 150-200 W/mK) and lightweight nature. It can operate effectively at high temperatures (up to 300°C) and is chemically stable.
Pros & Cons: Graphite heat sinks can be molded into complex shapes, offering design flexibility. However, they are generally less durable than metals and can be more expensive due to specialized manufacturing processes. Their brittleness can also pose challenges during handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Graphite is suitable for applications involving high temperatures and where weight is a critical factor, such as aerospace and specialized electronics. Its thermal properties make it beneficial in environments where traditional metals may fail.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the availability of graphite materials and the need for specialized suppliers. Compliance with international standards is crucial, especially in sectors like aerospace and defense.
Composites
Key Properties: Composite materials, often a combination of metals and polymers, offer tailored thermal properties and can be designed for specific applications. Their thermal conductivity can vary widely based on the composition.
Pros & Cons: Composites can provide a balance between weight, strength, and thermal performance. However, they can be more complex to manufacture and may not offer the same thermal efficiency as metals. The variability in properties can also complicate sourcing decisions.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in automotive and aerospace applications where weight savings are critical. They can also be designed to resist specific environmental conditions, making them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the manufacturing capabilities of suppliers and their ability to meet specific performance criteria. Understanding local regulations regarding composite materials is essential, especially in regions with stringent environmental standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for heat sink supplier | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Consumer electronics, automotive | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower thermal conductivity | Low |
| Copper | Data centers, high-performance computing | Superior thermal performance | Higher cost and weight | High |
| Graphite | Aerospace, high-temperature electronics | Excellent thermal stability | Brittle and more expensive | Medium |
| Composites | Automotive, specialized applications | Tailored properties and lightweight | Complex manufacturing | Medium to High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in heat sink production, highlighting the critical factors that B2B buyers should consider when sourcing heat sinks for their applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heat sink supplier
Manufacturing Processes for Heat Sink Suppliers
For international B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes of heat sinks is crucial to ensure that the products meet specific performance and reliability standards. The process typically involves several key stages, each with its own techniques and technologies.
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of heat sinks is material preparation. Copper and aluminum are the most common materials due to their excellent thermal conductivity. Suppliers often begin by sourcing high-purity raw materials, which are then cut into manageable sizes for further processing.
- Alloy Selection: Different alloys may be selected based on the intended application. For instance, aluminum 6063 is frequently chosen for its balance of strength and weight.
- Surface Treatment: Before forming, materials may undergo treatments such as anodizing or plating to enhance corrosion resistance and surface finish.
Forming Techniques
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo various forming techniques to create the desired shapes and profiles.
- Extrusion: This is a prevalent method where materials are forced through a die to create specific cross-sectional shapes. This technique is suitable for producing uniform profiles and can be used for both aluminum and copper heat sinks.
- Stamping: For lower-cost applications, copper sheets can be stamped into shape. This method is efficient for mass production but may limit design complexity.
- CNC Machining: For custom requirements, CNC machining is employed. This allows for precise geometries and complex designs, which are essential for specialized applications.
Assembly Processes
In cases where heat sinks consist of multiple components, assembly processes come into play.
- Bonding: Fins may be bonded to a base using thermal adhesives or soldering techniques. This is common in finned or bonded heat sinks where maximized surface area is essential.
- Integration: Advanced designs may include embedded heat pipes, which require careful integration during assembly to ensure optimal thermal performance.
Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the aesthetics and functional properties of heat sinks.
- Anodizing: This electrochemical process increases corrosion resistance and can provide a variety of color finishes.
- Polishing: For applications that require a high level of thermal efficiency, polishing can reduce surface roughness, improving thermal contact.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of heat sink manufacturing, ensuring that products meet industry standards and customer specifications. For B2B buyers, understanding QA practices can help in selecting reliable suppliers.
International Standards
Several international standards are relevant in the heat sink manufacturing industry:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must comply with health, safety, and environmental protection standards, which is verified through CE marking.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated into various stages of the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps catch defects early. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) are often employed.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the heat sinks are manufactured, they undergo final inspections to confirm that they meet design specifications and performance criteria.
Common Testing Methods
To verify the performance and durability of heat sinks, several testing methods are commonly used:
- Thermal Resistance Testing: This evaluates how effectively a heat sink dissipates heat, which is critical for performance in electronic applications.
- Mechanical Testing: These tests assess the structural integrity and durability of heat sinks, ensuring they can withstand operational stresses.
- Environmental Testing: Heat sinks may undergo exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity to evaluate their performance in real-world conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, quality control practices, and adherence to standards directly.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports, including testing results and compliance certifications, provides insights into the supplier’s reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can help validate the quality claims of suppliers, ensuring unbiased assessments.
Considerations for International Buyers
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, there are specific nuances to consider:
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local regulations and standards that may differ from international ones. For example, certain countries may require specific certifications not covered by ISO.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Understand the implications of shipping and logistics on quality. Temperature fluctuations during transport can affect the performance of heat sinks, particularly those with sensitive materials.
- Cultural and Communication Factors: Building strong relationships with suppliers is essential, especially in regions where business practices may differ. Clear communication regarding quality expectations can mitigate misunderstandings.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in heat sink production, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and standards. This knowledge not only helps in selecting the right suppliers but also ensures that the thermal management solutions they procure will deliver reliable performance in their applications.
Related Video: How Things Are Made | An Animated Introduction to Manufacturing Processes
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heat sink supplier Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of heat sink suppliers is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will provide insights into the various cost components, price influencers, and strategic tips to optimize procurement processes.
Cost Components
The total cost of acquiring heat sinks can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Copper, for instance, offers superior thermal conductivity but is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum. Prices fluctuate based on market demand and availability, necessitating ongoing market monitoring.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and supplier. In countries with higher labor costs, such as many in Europe, the total production cost may be elevated. Conversely, suppliers in regions with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing but may compromise on quality or lead times.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operations, utilities, and general administrative expenses. Efficient suppliers often manage these costs effectively, passing savings on to their customers.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific heat sink designs can be a substantial initial investment. Buyers should be prepared for higher upfront costs when opting for specialized designs, particularly for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes adds to the cost but is essential for maintaining performance standards. Suppliers with robust QC systems may charge more, but they reduce the risk of defects that could lead to costly failures.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs are influenced by distance, shipping method, and Incoterms. International buyers must factor in customs duties, tariffs, and transportation fees when evaluating total costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely. Understanding a supplier’s pricing structure can help buyers gauge the competitiveness of their offers.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of heat sinks:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders typically benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their needs to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized heat sinks tailored to specific applications often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against potential cost increases.
-
Material Choices: The type and quality of materials used directly impact the price. Buyers should assess whether premium materials are necessary for their application or if cost-effective alternatives suffice.
-
Quality and Certifications: Suppliers that comply with international quality standards and certifications can command higher prices. However, these certifications often ensure reliability, which is critical for mission-critical applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial health of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers may offer more stability but can charge higher rates.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed terms of shipment and responsibility can greatly affect total costs. Buyers should negotiate favorable Incoterms that minimize their financial exposure.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the cost landscape effectively, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for larger orders. Highlighting long-term partnerships can motivate suppliers to offer better rates.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, maintenance, and potential downtime costs. Sometimes, a higher initial investment in quality can lead to significant long-term savings.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Understand currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. Buyers in Africa or South America, for instance, should be aware of exchange rates when sourcing from Europe or Asia.
-
Market Research: Continuous monitoring of market trends, material costs, and supplier performance helps in making informed purchasing decisions. Utilize local market insights to negotiate better prices.
Disclaimer
The prices and strategies discussed are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence when engaging with suppliers.
Spotlight on Potential heat sink supplier Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘heat sink supplier’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heat sink supplier
When sourcing heat sinks, understanding the essential technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for making informed procurement decisions. This section outlines key specifications and common trade terms relevant to B2B buyers, particularly from diverse regions including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the specific type of material used in the heat sink, commonly copper or aluminum. Each material has distinct thermal conductivity and mechanical properties.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right material grade impacts thermal efficiency, weight, and cost. Copper offers superior thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance applications, while aluminum is lighter and often more cost-effective for general use. -
Thermal Resistance
– Definition: A measurement of the heat sink’s ability to dissipate heat, typically expressed in degrees Celsius per watt (°C/W).
– B2B Importance: Lower thermal resistance indicates better heat dissipation, crucial for preventing overheating in electronics. Buyers should align thermal resistance values with their specific application requirements to ensure optimal performance. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from specified dimensions during manufacturing, often expressed as a range (e.g., ±0.1 mm).
– B2B Importance: High precision in tolerances ensures that heat sinks fit seamlessly into the intended assemblies, which is vital for maintaining thermal management efficiency. Tighter tolerances can lead to higher production costs but may be necessary for critical applications. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: The treatment applied to the heat sink’s surface, which can include anodizing, plating, or polishing.
– B2B Importance: Surface finishes can enhance thermal performance, improve corrosion resistance, and affect aesthetic qualities. For example, anodized finishes increase durability and thermal efficiency, which is particularly beneficial in harsh environments. -
Fin Design and Density
– Definition: Refers to the shape, arrangement, and number of fins on the heat sink, which are critical for maximizing surface area.
– B2B Importance: A well-designed fin structure improves airflow and heat dissipation. Buyers should consider the application’s thermal requirements to determine the optimal fin design for their needs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships is vital for B2B buyers looking to integrate heat sinks into their products, as it affects supply chain dynamics and product compatibility. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Buyers must be aware of MOQs to ensure they can meet purchasing requirements without overcommitting financially. This is particularly important for startups or smaller companies with limited budgets. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other terms for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Submitting an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms effectively. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International Commercial Terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, insurance, and cost allocation, which can significantly impact overall project budgets. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered.
– Relevance: Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that production schedules are met. Buyers should inquire about lead times during the RFQ process to avoid delays.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies for heat sinks, ensuring they select the best suppliers and products for their unique operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the heat sink supplier Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global heat sink market is witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for efficient thermal management solutions. Key sectors such as electronics, automotive, and renewable energy are propelling this growth, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing high-performance heat sinks that meet stringent specifications for thermal efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Emerging trends in sourcing include the rise of customization and modular designs. Suppliers are offering tailored solutions that cater to specific applications, allowing buyers to optimize performance while managing costs. Additionally, digital procurement tools and AI-driven supply chain management are enhancing the purchasing process, enabling buyers to make informed decisions based on real-time data.
Market dynamics are influenced by fluctuating raw material prices, particularly copper and aluminum, which are essential for heat sink manufacturing. Buyers need to stay informed about supply chain disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, which can affect availability and pricing. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on energy efficiency is pushing manufacturers to innovate, leading to the development of advanced heat sink designs that utilize innovative materials and technologies, such as heat pipes and phase change materials.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the sourcing of heat sinks. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on eco-friendly practices. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that adhere to sustainable manufacturing principles, which can include the use of recycled materials and low-impact production techniques.
In addition to material choices, the importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency in their sourcing practices and who comply with international labor standards. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical operations.
Moreover, the integration of green materials into heat sink design, such as aluminum alloys with reduced environmental footprints, is gaining traction. Suppliers who invest in sustainable practices not only contribute to environmental stewardship but also enhance their brand reputation, making them more attractive partners for conscientious B2B buyers.
Brief Evolution/History
The heat sink industry has evolved significantly over the last few decades. Initially dominated by simple designs primarily using aluminum, advancements in manufacturing technologies have allowed for the introduction of more complex structures, such as bonded and heat pipe integrated heat sinks. These innovations have expanded the applications of heat sinks in high-performance computing, telecommunications, and renewable energy sectors.
As technology continues to advance, the demand for increasingly efficient thermal management solutions has led to the development of sophisticated materials and designs. This evolution reflects the industry’s responsiveness to the growing need for energy-efficient and sustainable solutions in various sectors, ensuring that heat sinks remain a critical component in modern electronic systems.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heat sink supplier
-
What criteria should I use to vet potential heat sink suppliers?
When vetting heat sink suppliers, focus on several key criteria: industry experience, technical expertise, and production capabilities. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 to ensure quality management practices. Evaluate their portfolio for previous projects that align with your needs, and seek references from other clients in your region. Additionally, assess their responsiveness to inquiries and their ability to provide customized solutions, which is critical for meeting specific thermal management requirements. -
Can I customize heat sink designs to fit my specific applications?
Yes, many heat sink suppliers offer customization options to meet unique application requirements. This can include variations in size, shape, material, and surface treatments. When engaging with suppliers, communicate your specific thermal resistance needs, airflow considerations, and any constraints related to your product design. Ensure the supplier has the necessary engineering capabilities, such as thermal analysis and CFD simulations, to support the customization process effectively. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for heat sinks?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for heat sinks can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the design. Typically, MOQs can range from 100 to 1,000 units for standard designs, while custom designs may require higher volumes. Lead times also differ, with standard products often available in 4-6 weeks, while custom solutions may take 8-12 weeks or more. It’s advisable to discuss these factors upfront to align your production schedules and avoid delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing heat sinks internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include partial upfront payments (30-50%) with the balance due upon delivery or after inspection. Letters of credit are also a secure option for international transactions. Ensure you clarify payment methods accepted (e.g., bank transfers, PayPal) and any additional costs, such as tariffs or shipping fees. Establishing clear payment terms can help prevent disputes and foster a smoother transaction process. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications from my heat sink supplier?
To ensure quality, request documentation of the supplier’s quality management system and relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or RoHS compliance. Inquire about their quality control processes, including material inspections, performance testing, and production audits. It may also be beneficial to request samples for evaluation before placing a large order, allowing you to assess the quality and performance of the heat sinks firsthand. -
What logistical considerations should I be aware of when sourcing heat sinks?
Logistics play a crucial role in international sourcing. Consider the supplier’s location relative to your operations, as this impacts shipping costs and delivery times. Assess the supplier’s experience with international shipping, including customs clearance and handling of tariffs. Additionally, discuss packaging methods to prevent damage during transit, and clarify who is responsible for shipping costs and insurance to avoid unexpected expenses. -
How should I handle disputes with a heat sink supplier?
Dispute resolution should start with clear communication. If issues arise, engage in a direct conversation with the supplier to discuss your concerns and seek a resolution. Document all correspondence and agreements to ensure clarity. If the dispute escalates, refer to the contract for terms regarding conflict resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Establishing a mutual understanding and maintaining a professional relationship can often lead to satisfactory outcomes. -
What are the trends in the heat sink market that I should be aware of?
Current trends in the heat sink market include an increasing focus on energy efficiency and sustainability, leading to the adoption of advanced materials like aluminum and composite structures. The rise of high-performance computing and data centers is driving demand for innovative thermal solutions, such as heat pipe technology and customized designs. Additionally, suppliers are enhancing their offerings with thermal simulations and CFD analysis to optimize performance. Staying informed about these trends can help you make strategic sourcing decisions that align with industry advancements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heat sink supplier
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of heat sinks is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance their thermal management systems. By understanding the diverse types of copper heat sinks available—ranging from skived and stamped to heat pipe embedded designs—buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs. Key considerations such as supplier quality, customization capabilities, and comprehensive technical support are fundamental in selecting a reliable partner.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe navigate this complex landscape, embracing a strategic sourcing approach will not only optimize thermal performance but also drive cost efficiencies and supply chain resilience. The emphasis on quality assurance and adherence to regional standards cannot be overstated, as these factors significantly influence product reliability and operational success.
Moving forward, it is imperative for B2B buyers to actively engage with suppliers, leveraging their expertise to explore innovative solutions and foster long-term partnerships. As the market evolves, staying informed about emerging trends and technologies will empower businesses to maintain a competitive edge. Take action today by evaluating your current sourcing strategies and identifying opportunities for improvement in your heat sink procurement process.