Master Sourcing Infrared Heating Elements for Maximum
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for infrared heating elements
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial heating solutions, infrared heating elements stand out as a vital component for diverse applications, ranging from manufacturing to food processing. Their ability to deliver precise, efficient, and energy-saving heating makes them an attractive option for businesses looking to enhance productivity while reducing operational costs. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of this market is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of infrared heating elements. We will explore the various types and materials used, shedding light on their unique advantages and applications. Furthermore, we will discuss manufacturing processes and quality control standards, ensuring that buyers are equipped with the knowledge to select reliable suppliers.
Cost considerations are crucial for budget-conscious businesses, and our analysis will provide insights into pricing structures across different regions. Additionally, we will address common FAQs to clarify any uncertainties buyers may have.
By the end of this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered with actionable insights, enabling them to navigate the global market with confidence, optimize their sourcing strategies, and ultimately drive their business success through informed investment in infrared heating technology.
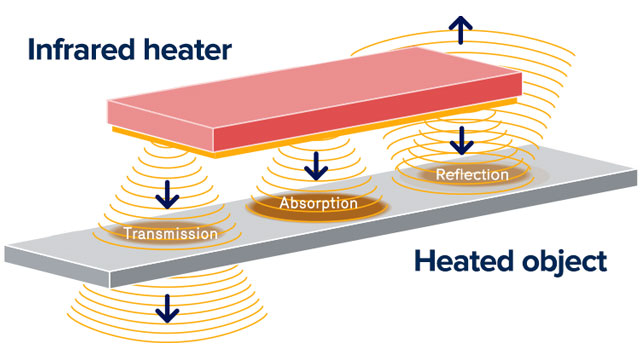
Understanding infrared heating elements Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz Infrared | Fast heating, high efficiency, compact design | Food service, industrial heating | Pros: Quick response time, high intensity. Cons: Fragile, can be costly. |
| Ceramic Infrared | Durable, even heat distribution | Manufacturing, drying processes | Pros: Long lifespan, stable temperature. Cons: Slower to heat up, bulkier design. |
| Metal Sheathed | Versatile, robust construction | HVAC systems, process heating | Pros: High durability, suitable for harsh conditions. Cons: Slower response, less efficient. |
| Carbon Infrared | Energy-efficient, low glare | Residential heating, spa facilities | Pros: Soft heat, energy savings. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
| Halogen Infrared | Instant heat, compact size | Retail displays, outdoor heating | Pros: Immediate warmth, lightweight. Cons: Short lifespan, can be less energy-efficient. |
Quartz Infrared Heating Elements
Quartz infrared heating elements are renowned for their rapid heating capabilities and high efficiency. They utilize quartz glass to produce infrared radiation, which can heat objects and surfaces directly without warming the air in between. This makes them ideal for applications in the food service industry, such as warming stations and conveyor ovens. When considering quartz infrared, B2B buyers should assess their operational environment, as these elements can be fragile and may require protective measures. Additionally, while they offer quick heating, the initial investment can be on the higher side.
Ceramic Infrared Heating Elements
Ceramic infrared heaters are characterized by their durability and ability to provide an even heat distribution. Made from ceramic materials, they are commonly used in manufacturing and drying processes where consistent temperature control is crucial. For B2B buyers, the longevity of ceramic infrared elements can lead to reduced replacement costs over time. However, they have a slower heat-up time compared to quartz elements, and their bulkier design may require more space in installations. Buyers should weigh the benefits of stability against the need for quicker heating solutions.
Metal Sheathed Infrared Heating Elements
Metal sheathed infrared heating elements are designed for versatility and robustness, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, including HVAC systems and process heating. Their construction allows them to withstand harsh conditions, which is an essential consideration for industries operating in extreme environments. While they are durable, B2B buyers should note that these elements typically have slower response times and may not be as energy-efficient as other options. Understanding the specific heating requirements of their processes will help buyers make informed decisions.
Carbon Infrared Heating Elements
Carbon infrared heating elements are known for their energy efficiency and low glare output. They emit a softer heat that is ideal for applications such as residential heating and spa facilities, where comfort is paramount. For international B2B buyers, the energy savings associated with carbon infrared can lead to significant cost reductions over time. However, the initial investment may be higher compared to other types, making it essential for buyers to evaluate their long-term operational costs against upfront expenses.
Halogen Infrared Heating Elements
Halogen infrared heating elements provide instant heat and are compact in size, making them suitable for applications like retail displays and outdoor heating solutions. They are particularly valued for their ability to deliver immediate warmth to spaces without delay. B2B buyers should consider the shorter lifespan of halogen elements, as well as their energy efficiency, which may not be as high as other types. For businesses that prioritize quick heating solutions, halogen infrared elements can be an effective choice, provided they are mindful of the potential need for more frequent replacements.
Key Industrial Applications of infrared heating elements
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Infrared Heating Elements | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Cooking, drying, and pasteurization of food | Enhanced cooking speed and improved food quality | Compliance with food safety standards; energy efficiency |
| Textile Manufacturing | Fabric drying and curing processes | Faster production cycles and reduced energy costs | Material compatibility; consistent heat distribution |
| Automotive Industry | Paint curing and surface treatment | Improved finish quality and reduced production time | Temperature control; durability of heating elements |
| Plastics and Composites | Preheating and curing of materials | Increased production efficiency and reduced waste | Resistance to chemical exposure; precision heating |
| Medical Equipment | Sterilization and heating of medical devices | Enhanced safety and effectiveness of medical products | Regulatory compliance; reliability and longevity |
Food Processing
Infrared heating elements are widely used in the food processing industry for cooking, drying, and pasteurization. Their ability to provide rapid heating ensures that food items are cooked evenly and quickly, addressing issues of inconsistent quality and lengthy processing times. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing infrared heaters that comply with local food safety regulations is crucial. Additionally, energy efficiency can significantly reduce operational costs, making it a key consideration.
Textile Manufacturing
In textile manufacturing, infrared heating elements play a vital role in fabric drying and curing processes. The use of infrared technology allows for quicker drying times compared to traditional methods, thus enhancing overall production cycles and reducing energy consumption. Buyers from Europe, especially Germany, should focus on sourcing heaters that offer consistent heat distribution to avoid fabric damage. Furthermore, the compatibility of heating elements with various fabric types is essential for maintaining product quality.
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector utilizes infrared heating elements for paint curing and surface treatment applications. Infrared technology accelerates the curing process, leading to improved finish quality and reduced production time. For B2B buyers in the Middle East, where the automotive market is growing, sourcing durable heating elements that can withstand high temperatures and offer precise temperature control is vital. This ensures that the final product meets high-quality standards while maximizing throughput.
Plastics and Composites
Infrared heating is integral to the preheating and curing of plastics and composite materials. This application leads to increased production efficiency and minimized material waste, addressing common challenges in the manufacturing process. Buyers from South America should prioritize sourcing infrared heaters that resist chemical exposure and provide precision heating, as these factors are critical in ensuring product integrity and operational reliability.
Medical Equipment
In the medical equipment sector, infrared heating elements are utilized for the sterilization and heating of various medical devices. This application is essential for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical products. International B2B buyers must consider regulatory compliance when sourcing heating elements, as adherence to health and safety standards is paramount. Reliability and longevity of the heating elements are also critical, as they directly impact the performance and safety of medical devices.
Related Video: Infrared heater efficiency — how much is radiated infrared?
Strategic Material Selection Guide for infrared heating elements
When selecting materials for infrared heating elements, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This knowledge will help in making informed decisions that align with specific application requirements, regional standards, and economic considerations. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in infrared heating elements: quartz, ceramic, metal, and carbon.
Quartz
Key Properties: Quartz is known for its excellent thermal stability and high-temperature resistance, typically rated up to 1,000°C. It has low thermal expansion, which minimizes the risk of cracking under thermal stress.
Pros & Cons: Quartz heating elements are durable and provide efficient heat transfer. However, they can be more fragile compared to other materials, making them susceptible to breakage during handling or installation. The manufacturing process can also be complex, impacting overall costs.
Impact on Application: Quartz is particularly suitable for applications requiring high temperatures and rapid heating, such as in food processing and industrial drying. Its transparency to infrared radiation allows for effective heat transfer to the target medium.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as DIN in Germany or ANSI in the USA. Additionally, the fragility of quartz may necessitate protective measures during shipping and installation, especially in regions with challenging logistics.
Ceramic
Key Properties: Ceramic materials exhibit excellent thermal insulation properties and can withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 1,200°C. They also offer good corrosion resistance, making them suitable for harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The durability and longevity of ceramic heating elements make them a popular choice. However, they can be heavier and more expensive than other materials. The manufacturing process can also require specialized techniques, which may lead to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are ideal for applications in high-temperature environments, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries, where heat retention is critical. Their ability to withstand corrosive media adds to their versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ISO and ASTM is essential. Buyers should also consider the logistical challenges of transporting heavier ceramic elements, especially in regions with less developed infrastructure.
Metal
Key Properties: Metals like stainless steel and aluminum are known for their strength and good thermal conductivity. They can typically operate at temperatures up to 800°C, depending on the alloy used.
Pros & Cons: Metal heating elements are robust and can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, making them versatile for different applications. However, they may corrode if not properly treated, and their thermal efficiency can be lower than that of ceramics or quartz.
Impact on Application: Metal elements are widely used in industrial heating applications, such as in ovens and furnaces, where durability and heat distribution are critical. Their compatibility with various environments makes them a go-to choice for many manufacturers.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the corrosion resistance of the metal used, especially in humid or corrosive environments typical in some regions. Compliance with local standards for materials and manufacturing practices is also necessary.
Carbon
Key Properties: Carbon-based materials, such as carbon fiber and graphite, offer excellent thermal conductivity and can withstand high temperatures, often exceeding 1,000°C. They have low thermal mass, allowing for rapid heating.
Pros & Cons: Carbon heating elements are lightweight and efficient, providing quick heat-up times. However, they can be more expensive and may require specific handling due to their sensitivity to mechanical stress.
Impact on Application: Carbon materials are particularly effective in applications where rapid heating is essential, such as in semiconductor manufacturing and specialized industrial processes.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific handling requirements for carbon materials to avoid damage. Compliance with international standards and regulations regarding the use of carbon materials is also critical.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for infrared heating elements | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quartz | Food processing, industrial drying | Excellent thermal stability | Fragile, complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Ceramic | Automotive, aerospace | High-temperature resistance | Heavier, more expensive | High |
| Metal | Ovens, furnaces | Robust and versatile | Potential for corrosion | Medium |
| Carbon | Semiconductor manufacturing | Quick heat-up times | Sensitive to mechanical stress | High |
This guide provides a foundational understanding of the materials used in infrared heating elements, enabling international B2B buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for infrared heating elements
Manufacturing Processes for Infrared Heating Elements
The production of infrared heating elements involves several critical stages, each requiring specialized techniques and materials. Understanding these processes helps B2B buyers make informed decisions when selecting suppliers.
Material Preparation
The first stage in the manufacturing process is material preparation. Infrared heating elements are typically made from materials such as silicon carbide, quartz, or ceramic. The choice of material influences not only the heating efficiency but also durability and application suitability.
- Selection of Raw Materials: Buyers should ensure that suppliers source high-quality raw materials, as this directly impacts the performance of the heating elements.
- Material Testing: Prior to production, raw materials undergo rigorous testing for purity and consistency. This may involve chemical analysis and physical property assessments.
Forming
After preparing the materials, the next step is forming. This involves shaping the raw materials into the desired configuration for heating elements.
- Techniques: Common methods include extrusion, molding, and machining. Each technique has its advantages; for instance, extrusion is suitable for producing long, uniform shapes, while molding can create complex geometries.
- Precision Engineering: For high-performance applications, precision is vital. Buyers should inquire about the tolerances and capabilities of the manufacturing equipment used by suppliers.
Assembly
Once the components are formed, they need to be assembled into final products. This stage is crucial for ensuring that the elements function correctly.
- Integration of Components: Infrared heating elements may consist of various components, such as electrical connections and protective casings. Each part must be assembled with care to avoid faults.
- Automation vs. Manual Assembly: Many manufacturers utilize automated assembly lines to enhance consistency and reduce human error. B2B buyers should assess whether suppliers employ automation and the extent to which it is implemented.
Finishing
The finishing stage involves applying treatments to enhance the performance and durability of infrared heating elements.
- Coating and Surface Treatments: This might include applying heat-resistant coatings or surface polishing to improve thermal efficiency and lifespan.
- Quality Checks: Finishing processes should include quality checks to ensure that the elements meet the required specifications. This is where quality assurance begins to integrate into the manufacturing process.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical aspect of the manufacturing process for infrared heating elements. It ensures that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
International Standards
To maintain high quality, manufacturers often adhere to recognized international standards. Buyers should look for these certifications when evaluating potential suppliers.
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is widely recognized across industries. Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate a commitment to continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For applications in industries like oil and gas, adherence to API standards can be critical.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) encompasses various checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process. These checkpoints help identify defects and ensure adherence to specifications.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This step involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility. Buyers should ensure suppliers have a robust IQC process to catch issues early.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed to monitor processes and identify deviations. This can involve sampling techniques and real-time monitoring.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the products are finished, a final inspection ensures they meet the necessary specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Different testing methods are employed to validate the performance and safety of infrared heating elements.
- Electrical Testing: This includes checking resistance, insulation, and power output to ensure elements operate within specified parameters.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluating the heating performance under various conditions helps to ascertain efficiency and reliability.
- Durability Testing: Elements may undergo stress tests to assess their longevity and performance under extreme conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insights into the manufacturing processes and QA practices. Buyers should assess the consistency of processes and the presence of necessary certifications.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their quality assurance protocols and testing results. This transparency is crucial for assessing their commitment to quality.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control measures and product reliability.
Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers
International buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, face unique challenges when it comes to supplier quality control.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must be aware of the regulatory requirements in their respective countries, as these can vary significantly. Understanding local compliance standards is essential when importing infrared heating elements.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Different regions may have varying standards and expectations regarding product quality. B2B buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to ensure alignment on quality benchmarks.
- Logistical Considerations: International shipping can introduce risks that impact product quality. Buyers should consider the handling and storage conditions during transit to mitigate potential damage.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for infrared heating elements is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, along with robust quality control measures, buyers can make informed decisions that ensure they source high-quality products. Implementing rigorous verification strategies and being mindful of international standards will further empower buyers to build strong relationships with reliable suppliers.
Related Video: The Production Planning Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for infrared heating elements Sourcing
In the sourcing of infrared heating elements, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in infrared heating elements is the raw materials used, such as ceramic, metal alloys, and specialized infrared emitting materials. The choice of materials affects not only the performance but also the durability and efficiency of the heating elements. Buyers should prioritize sourcing high-quality materials to ensure longevity and effectiveness.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on geographic location and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing; however, it is crucial to assess the skill level and expertise of the workforce, as this can impact the quality of the final product.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Overhead can fluctuate depending on the production scale and efficiency of the manufacturer. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s operational efficiencies to gain insights into potential cost savings.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Buyers looking for bespoke infrared heating elements should factor in these costs, as they can significantly affect the overall pricing. Volume orders can help amortize these costs over a larger number of units.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC measures ensures that the products meet specified standards. While this adds to the cost, it is a critical investment to mitigate the risk of defects and ensure compliance with international quality certifications.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling expenses can vary greatly based on the distance, mode of transport, and the chosen Incoterms. It is vital for buyers to consider these logistics costs in the total pricing structure, as they can impact the overall expenditure significantly.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the average margins in the infrared heating elements market can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Suppliers often set minimum order quantities (MOQs) that can affect pricing. Larger orders usually lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and consider consolidating orders where possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance criteria can lead to increased costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential price increase.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and certifications generally command higher prices. Buyers must balance cost against the expected performance and lifespan of the product.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge a premium, but this often correlates with better quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in terms of shipping costs, insurance, and risk. Choosing the right Incoterm can significantly affect the total landed cost of the goods.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing, especially regarding bulk orders. Leverage market knowledge to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, energy consumption, and replacement costs. This holistic view can guide better purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, European buyers may face different pricing structures compared to those in Africa or South America, influenced by local market dynamics and trade agreements.
Disclaimer
Prices for infrared heating elements can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and changes in material costs. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential infrared heating elements Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘infrared heating elements’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for infrared heating elements
Infrared heating elements are vital components in various industrial and commercial applications, from manufacturing processes to heating solutions in residential and commercial settings. Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology associated with these elements is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here’s a detailed overview of key specifications and terms that will facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Essential Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The material grade refers to the specific type of materials used in the construction of infrared heating elements, which often include ceramics, quartz, and metals.
– Importance: The choice of material influences the efficiency, durability, and thermal performance of the heating element. For example, quartz elements provide faster heating, while ceramic elements offer better insulation. Buyers should consider the operational environment when selecting the appropriate material grade. -
Watt Density
– Definition: Watt density is the amount of power (watts) per unit area (usually square inches or centimeters) that the heating element can emit.
– Importance: A higher watt density typically results in quicker heating times but can also lead to faster wear and tear. Understanding watt density helps buyers match the heating element to their specific application requirements, ensuring optimal performance without compromising longevity. -
Operating Temperature Range
– Definition: This specification indicates the minimum and maximum temperatures at which the infrared heating element can operate effectively.
– Importance: Different applications require varying temperature ranges. For instance, industrial applications may need elements that can withstand higher temperatures. Buyers must ensure that the selected heating element aligns with their operational needs to avoid premature failure. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions and performance of the heating element.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are essential in applications requiring precision. A clear understanding of tolerance levels can prevent issues related to misalignment or inefficiency, making it crucial for buyers to inquire about this specification when sourcing components. -
Life Span
– Definition: The life span indicates the expected operational duration of the heating element before it needs replacement.
– Importance: A longer life span translates to lower maintenance costs and reduced downtime. Buyers should evaluate the life span in conjunction with the element’s application to ensure cost-effectiveness over time.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is crucial for buyers looking for custom solutions or specific branding, ensuring compatibility and quality in their sourcing strategies. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and budget. It is particularly relevant for smaller businesses or those entering new markets, as it affects inventory management and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services.
– Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing and terms across multiple suppliers, fostering competitive bidding and potentially lowering costs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, used in international trade contracts.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, ensuring smoother transactions and reducing the risk of misunderstandings. -
Lead Time
– Definition: Lead time is the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is critical for planning and operational efficiency. Buyers need to account for lead times in their production schedules to avoid delays in project timelines.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the right infrared heating elements for their specific needs while optimizing their procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the infrared heating elements Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The infrared heating elements market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient heating solutions across various industries. Notably, sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, and food processing are adopting infrared technology due to its rapid heating capabilities and energy savings. In regions like Africa and South America, economic development and industrial expansion are contributing to a rise in demand for advanced heating solutions, while in Europe, stricter energy regulations are pushing businesses to seek greener alternatives.
Emerging technologies, such as smart heating systems integrated with IoT, are transforming the sourcing landscape. B2B buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who offer not just products, but comprehensive solutions that include automation and remote monitoring capabilities. Additionally, the shift towards e-commerce platforms for procurement is making it easier for international buyers to access a diverse range of suppliers and products, enhancing competition and pricing transparency.
Another key trend is the customization of infrared heating elements to meet specific industrial requirements. Buyers are encouraged to work closely with manufacturers to develop tailored solutions that optimize performance and efficiency for their unique applications. This collaborative approach can lead to long-term partnerships and improved supply chain resilience.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As environmental concerns gain prominence, sustainability in the infrared heating elements sector is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers. The production of infrared heating elements can have a significant environmental impact, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement sustainable practices in their manufacturing processes, such as using renewable energy sources and minimizing waste.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should seek suppliers that adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 50001 (Energy Management) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of infrared heating elements is gaining traction. Buyers should inquire about the materials used in manufacturing and whether they meet environmental standards. Opting for products that utilize recyclable or eco-friendly materials not only enhances the sustainability of operations but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of infrared heating elements can be traced back to the mid-20th century when they were first introduced as an efficient heating solution. Initially used in industrial applications, their versatility and energy efficiency led to wider adoption in residential and commercial sectors. Over the decades, advancements in technology have enhanced the performance and safety of infrared heating elements, making them a preferred choice for a variety of applications. Today, they are integral to numerous industries, reflecting a shift towards energy-efficient solutions that cater to both economic and environmental needs. As the market continues to evolve, international B2B buyers must stay informed about technological advancements and sustainability practices to remain competitive.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of infrared heating elements
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers of infrared heating elements?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize factors such as their industry experience, certifications (like ISO or CE), and client testimonials. Conduct background checks to assess their financial stability and production capabilities. Engage in discussions about their product range and customization options. Request samples to evaluate quality firsthand. Additionally, assess their communication responsiveness and willingness to collaborate on technical specifications, which can indicate their commitment to customer satisfaction. -
Can I customize infrared heating elements to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for infrared heating elements to suit specific applications. Discuss your requirements regarding size, shape, wattage, and mounting configurations with potential suppliers. Ensure they have the capability to produce prototypes before full-scale production. This process not only helps you obtain a product tailored to your needs but also builds a collaborative relationship with the supplier, which can be beneficial for future projects. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for infrared heating elements?
MOQs for infrared heating elements can vary significantly based on the supplier and product specifications, typically ranging from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times can also fluctuate depending on the supplier’s production capacity and the complexity of the order, usually spanning from 2 to 12 weeks. When negotiating, clarify these terms upfront to avoid any surprises. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier may lead to more flexible MOQs and expedited timelines in the future. -
What payment options are commonly available when purchasing infrared heating elements?
International B2B transactions often involve various payment methods, including bank transfers, letters of credit, or payment platforms like PayPal. Discuss payment terms with your supplier early in negotiations, including whether they require a deposit or full payment upfront. Consider using escrow services for large transactions to protect against fraud. Always ensure that the payment method chosen complies with local regulations and is secure for both parties involved. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for infrared heating elements?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes and relevant certifications from suppliers. This may include compliance with international standards such as ISO 9001 or specific industry certifications. Conduct regular audits of the supplier’s facility if feasible, or hire third-party inspection services to verify product quality before shipment. Establishing a clear agreement on quality expectations in your contract can also help mitigate risks associated with product defects. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing infrared heating elements internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger orders. Understand customs regulations in your country, as tariffs and duties can significantly impact total costs. Collaborate with logistics providers experienced in international shipping to ensure compliance and timely delivery. It’s also prudent to assess the supplier’s packaging methods to prevent damage during transit. -
What steps should I take if I encounter a dispute with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, begin by communicating directly with the supplier to discuss the issue and seek a resolution. Document all correspondence and agreements to maintain a clear record. If direct negotiations fail, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, which can be costly and time-consuming. Ensure that your contracts include clear dispute resolution clauses to guide the process. Maintaining a professional demeanor throughout can help preserve the business relationship. -
How can I stay informed about industry trends and technological advancements in infrared heating elements?
To stay updated, subscribe to industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in relevant webinars and workshops. Engage with industry associations and online forums where professionals share insights and experiences. Following key suppliers and thought leaders on social media can also provide valuable information about innovations and market shifts. Consider networking with other businesses in your sector to exchange knowledge and best practices related to infrared heating technology.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for infrared heating elements
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of infrared heating elements presents a multitude of opportunities for international B2B buyers. As industries increasingly prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability, understanding the nuances of infrared technology can significantly enhance procurement strategies. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating suppliers not only on price but also on their technological capabilities, compliance with international standards, and after-sales support.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, forging partnerships with reliable manufacturers can lead to long-term cost savings and improved operational efficiency. The growing trend towards automation and smart heating solutions further emphasizes the need for buyers to stay ahead of market innovations.
As we look to the future, it is imperative for businesses to adapt to evolving market demands and consumer preferences. Engage with suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and innovation. By leveraging strategic sourcing practices, you can ensure that your organization remains competitive and responsive in an ever-changing global landscape. Now is the time to explore new partnerships and harness the full potential of infrared heating technologies.