Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Size Reduction Equipment
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
In the fast-evolving pharmaceutical industry, the significance of size reduction cannot be overstated. This critical process transforms raw materials into fine powders, enhancing drug bioavailability, improving dissolution rates, and ultimately ensuring therapeutic effectiveness. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of size reduction equipment is essential for sourcing high-quality machinery that meets stringent manufacturing standards.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of size reduction equipment, including cutting, compression, impact, and attrition mills. It explores the materials used in the process, the manufacturing and quality control measures that ensure optimal performance, and the key suppliers who dominate the market landscape. Additionally, it addresses cost considerations and provides insights into market trends that can influence purchasing decisions.
By empowering B2B buyers with actionable insights and detailed information, this guide serves as a valuable resource for making informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are looking to enhance your production capabilities or improve product consistency, understanding the intricacies of size reduction equipment will enable you to navigate the global market effectively. With a focus on practical applications and strategic insights, this guide is designed to support your quest for excellence in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Understanding size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hammer Mill | Utilizes high-speed rotating hammers for impact. | Grinding of grains, powders, and granules. | Pros: Efficient for large volumes; Cons: Can generate heat, affecting sensitive materials. |
| Ball Mill | Employs balls to grind materials through impact. | Fine grinding of powders and pigments. | Pros: Produces very fine particles; Cons: High energy consumption. |
| Roller Mill | Uses cylindrical rollers to crush materials. | Producing flour, powdered drugs, and granules. | Pros: Uniform particle size; Cons: Limited to softer materials. |
| Cutting Mill | Features sharp blades for slicing materials. | Processing fibrous and tough materials. | Pros: Effective for tough materials; Cons: Slower compared to other methods. |
| Fluid Energy Mill | Utilizes high-velocity air to reduce particle size. | Creating fine powders for pharmaceuticals. | Pros: Produces ultra-fine powders; Cons: Equipment can be complex and costly. |
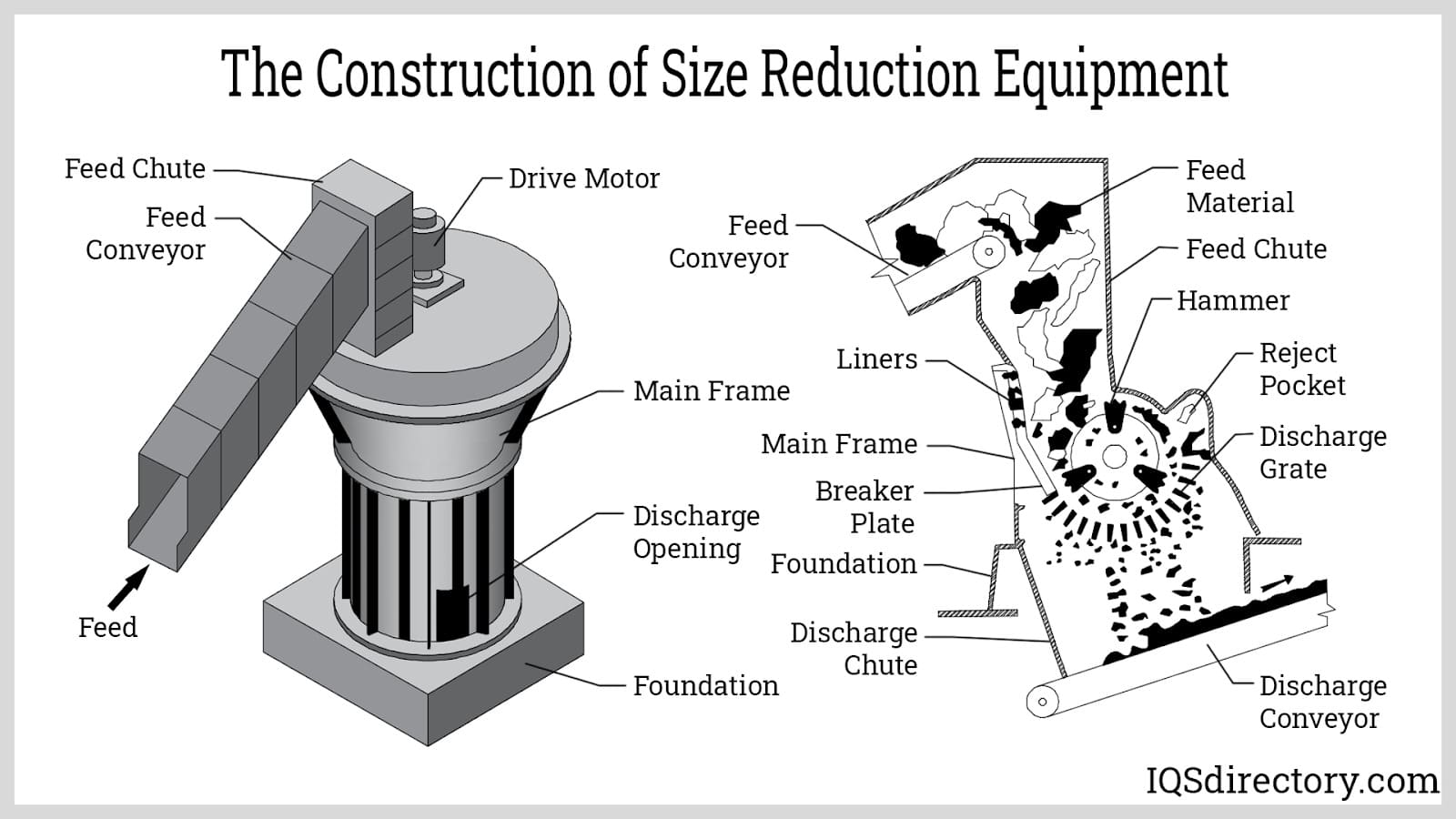
Hammer Mill
Hammer mills are renowned for their ability to process large volumes of materials efficiently. They operate by using high-speed rotating hammers to impact the material, effectively reducing it to smaller particles. This equipment is particularly suitable for grinding grains, powders, and granules, making it ideal for pharmaceutical applications where bulk processing is required. Buyers should consider the heat generated during operation, as this can affect the stability of sensitive materials.
Ball Mill
Ball mills are versatile devices that utilize balls to grind materials through impact and attrition. They are particularly effective for fine grinding and are commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry for producing very fine powders and pigments. Their ability to achieve a high degree of fineness makes them suitable for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). However, buyers should be aware of the high energy consumption associated with ball mills, which can impact operational costs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Roller Mill
Roller mills employ cylindrical rollers to crush and grind materials, making them a popular choice for producing flour and powdered drugs. They are known for providing a uniform particle size, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. However, roller mills are generally limited to softer materials, so buyers must assess the hardness of the materials they plan to process before investing.
Cutting Mill
Cutting mills are equipped with sharp blades designed to slice and shear materials, making them particularly effective for processing fibrous and tough substances. This type of equipment is beneficial for the pharmaceutical industry when dealing with materials that resist traditional grinding methods. While cutting mills are slower than other reduction methods, their ability to handle challenging materials can justify their use. Buyers should evaluate the throughput requirements of their operations when considering this equipment.
Fluid Energy Mill
Fluid energy mills utilize high-velocity air to create a fluidized bed of particles, which collide and break apart, resulting in ultra-fine powders. This technology is particularly advantageous for creating fine powders required in various pharmaceutical formulations. While fluid energy mills can produce exceptional particle sizes, their complexity and associated costs may be a barrier for some buyers. It’s essential for B2B purchasers to weigh the benefits of ultra-fine powders against the investment and operational complexities involved.
Related Video: Size Reduction by different milling machines and their principles
Key Industrial Applications of size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical Manufacturing | Fine grinding of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Enhances bioavailability and efficacy of medications | Equipment must ensure high purity and minimal contamination |
| Nutraceuticals | Size reduction for vitamins and dietary supplements | Improves absorption rates and product consistency | Need for compliance with health regulations and standards |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care | Milling of powdered ingredients for creams and lotions | Ensures smooth texture and effective delivery of active ingredients | Equipment must handle various material properties and moisture content |
| Biopharmaceuticals | Particle size optimization for biologics | Facilitates better drug delivery and stability | Consideration of temperature control and material compatibility |
| Research and Development | Preparation of fine powders for formulation testing | Aids in accurate dosing and formulation development | Flexibility in equipment for various materials and formulations |
In the pharmaceutical manufacturing sector, size reduction equipment is crucial for grinding active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) into fine powders. This process enhances the bioavailability of drugs, ensuring they are absorbed more effectively by the body. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing equipment that guarantees high purity and minimal contamination is essential to comply with stringent regulatory standards.
In the nutraceuticals industry, size reduction is utilized for vitamins and dietary supplements to improve their absorption rates. By breaking down particles into smaller sizes, manufacturers can ensure consistent product quality and efficacy. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who adhere to health regulations and provide equipment capable of maintaining the nutritional integrity of the products.
The cosmetics and personal care industry benefits from size reduction through the milling of powdered ingredients for creams and lotions. This process ensures a smooth texture and effective delivery of active ingredients, which is critical for consumer satisfaction. Buyers must consider equipment that can handle varying material properties and moisture content to achieve desired product characteristics.
In the field of biopharmaceuticals, size reduction plays a vital role in optimizing particle size for biologic drugs. This ensures better drug delivery and stability, which is particularly important for complex formulations. Buyers should focus on equipment that offers precise temperature control and compatibility with different materials to maintain the integrity of sensitive compounds.
Lastly, in research and development, size reduction equipment is employed to prepare fine powders for formulation testing. This is essential for accurate dosing and the development of new formulations. Buyers should seek flexible equipment capable of processing various materials and formulations, allowing for innovation and experimentation in drug development.
Related Video: Size Reduction | Mechanism | Laws | Factors Affecting Size Reduction | Pharmaceutical Engineering
Strategic Material Selection Guide for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
When selecting materials for size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry, it is essential to consider the unique properties of each material, their advantages and disadvantages, and how they align with specific application requirements. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in size reduction equipment, focusing on their relevance to B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. The most commonly used grades in pharmaceuticals are 304 and 316, with 316 offering superior resistance to chlorides and other corrosive agents.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is durable and easy to clean, making it suitable for applications requiring strict hygiene standards. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive substances, making it ideal for various pharmaceutical formulations. Its non-reactive nature ensures that the integrity of the drug is maintained during size reduction.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for material quality. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding material safety and hygiene is crucial, especially in regions like the UAE and Egypt, where strict compliance is enforced.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties:
Carbon steel is characterized by its high tensile strength and hardness. However, it has lower corrosion resistance compared to stainless steel, making it less suitable for applications involving aggressive chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious buyers. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can lead to increased maintenance costs and potential contamination of pharmaceutical products.
Impact on Application:
Carbon steel is best suited for size reduction processes involving non-corrosive materials. Its strength allows for effective size reduction, but buyers must consider the potential for material degradation over time.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments should be cautious when selecting carbon steel. Compliance with local standards and ensuring proper protective coatings can mitigate some of the risks associated with this material.
Ceramic Materials
Key Properties:
Ceramic materials are known for their hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. They are often used in applications where contamination must be minimized.
Pros & Cons:
Ceramics provide excellent durability and can be used with abrasive materials without significant wear. However, they are brittle and can fracture under impact, which may limit their application in certain size reduction processes.
Impact on Application:
Ceramics are ideal for applications requiring high purity and minimal contamination, such as in the production of fine powders for pharmaceuticals. Their chemical inertness ensures that they do not react with the materials being processed.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the fragility of ceramic materials and ensure that their equipment is designed to handle potential impacts. Additionally, adherence to international quality standards is vital to ensure product safety and efficacy.
Polymeric Materials
Key Properties:
Polymeric materials, such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene, offer good chemical resistance and flexibility. They can be designed to withstand specific temperatures and pressures depending on the formulation.
Pros & Cons:
Polymeric materials are lightweight and cost-effective, making them an attractive option for many applications. However, they may not withstand high temperatures as effectively as metals or ceramics, which can limit their use in certain processes.
Impact on Application:
These materials are often used in applications where chemical compatibility is crucial. They can be effective for size reduction processes involving less abrasive materials, but their lower durability may require more frequent replacements.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate local regulations regarding the use of polymers in pharmaceutical applications, especially in regions with stringent safety standards. Ensuring compliance with relevant certifications can enhance marketability and acceptance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Used in high-hygiene applications for various pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | Suitable for non-corrosive materials in size reduction | Cost-effective | Susceptible to rust and contamination | Low |
| Ceramic Materials | Ideal for high purity applications and fine powders | Excellent durability and wear resistance | Brittle and prone to fracture | Medium |
| Polymeric Materials | Used for chemical compatibility in less abrasive processes | Lightweight and cost-effective | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, facilitating informed decisions when selecting size reduction equipment materials in the pharmaceutical industry.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
Manufacturing Processes for Size Reduction Equipment in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The manufacturing of size reduction equipment is a critical component in the pharmaceutical industry, where precision and reliability are paramount. The process typically involves several stages, including material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing equipment.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– The first step involves selecting high-quality materials, often stainless steel or specialized alloys, to ensure durability and resistance to corrosion.
– Materials are subjected to rigorous testing to confirm their compliance with industry standards.
– After selection, materials undergo cutting and shaping to prepare them for forming. -
Forming
– This stage includes various techniques such as machining, casting, or forging to create the basic components of the equipment.
– Precision machining is vital, as it allows for the creation of intricate parts that will fit together seamlessly.
– Advanced technologies, such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, are often employed to enhance precision and repeatability. -
Assembly
– After forming, components are assembled into the final equipment. This may involve welding, bolting, or using adhesives.
– During assembly, special attention is paid to the alignment and fit of parts, as these factors influence the equipment’s performance and longevity.
– Automated assembly lines can improve efficiency and reduce human error, ensuring consistent quality. -
Finishing
– The finishing process includes surface treatment to enhance durability and prevent contamination. Common treatments include passivation, anodizing, or coating.
– Equipment is then subjected to cleaning processes to eliminate any residues from manufacturing.
– Finally, equipment may undergo painting or labeling to comply with branding and regulatory requirements.
Key Techniques in Manufacturing
- Precision Machining: Essential for creating parts that must fit together with minimal tolerance.
- Welding and Bonding: Techniques that ensure structural integrity and reduce the risk of leaks or failures.
- Surface Treatments: Important for enhancing resistance to wear and chemical exposure, critical in pharmaceutical applications.
Quality Assurance in Size Reduction Equipment
Quality assurance (QA) is crucial in the manufacturing of size reduction equipment, especially in the pharmaceutical industry where product efficacy and safety are non-negotiable. B2B buyers should be well-versed in international standards and industry-specific regulations to evaluate potential suppliers effectively.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance indicates that a supplier has established a consistent approach to quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: For equipment used in the production of active pharmaceutical ingredients, adherence to API guidelines is essential to ensure quality and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This involves inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified standards before they enter the manufacturing process. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Throughout the manufacturing stages, various checks are performed to monitor processes and ensure that equipment is being produced correctly.
– This may include dimensional checks and functional testing to identify any deviations from specifications early in the process. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Once manufacturing is complete, a comprehensive evaluation of the equipment is performed to confirm it meets all specifications and standards.
– This may involve performance testing under simulated operational conditions.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to measure critical dimensions of components.
- Functional Testing: Ensuring that the equipment operates as intended, often under real-world conditions.
- Material Testing: Analyzing the properties of materials used to ensure they meet required standards for strength and durability.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of potential suppliers. Here are several actionable strategies:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities to assess their compliance with quality standards.
- Request Reports: Ask for documented evidence of quality control processes, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the equipment before purchase.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is vital. Buyers should consider:
- Regional Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements. For example, the UAE has specific standards for medical devices that may differ from those in Europe or Africa.
- Import Standards: Ensure that the equipment meets the import regulations of the destination country to avoid delays and compliance issues.
- Supplier Reputation: Assess the supplier’s reputation in the market, including reviews and feedback from other international buyers. This can provide insight into their reliability and adherence to quality standards.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing size reduction equipment for the pharmaceutical industry. This understanding not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also ensures that the equipment procured meets the stringent standards necessary for effective pharmaceutical production.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry Sourcing
Analyzing the cost structure and pricing for size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry is essential for international B2B buyers. Understanding the various components that contribute to costs and the factors influencing pricing can empower buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in manufacturing size reduction equipment is the materials used. High-quality steels, specialized alloys, and advanced composites enhance durability and performance, impacting the overall cost. Buyers should consider the trade-off between upfront costs and long-term operational reliability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for both production and assembly of size reduction equipment. Labor costs can vary significantly by region, with countries in Europe and the Middle East often facing higher wage rates compared to those in Africa and South America. Understanding local labor market conditions can help buyers anticipate these costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can help reduce overhead costs. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s production capabilities to assess potential savings.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized equipment, increasing initial costs. However, this investment often leads to enhanced production efficiency and product quality, providing long-term value. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of custom tooling based on their specific production needs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are vital in the pharmaceutical industry to ensure compliance with safety and efficacy standards. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the equipment and the certifications required. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who maintain high QC standards to mitigate risks.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can significantly affect the total price, especially for international transactions. Factors such as shipping distance, mode of transport, and customs duties should be considered. Buyers should explore Incoterms to understand their responsibilities regarding transportation and risk.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market positioning and competition. It’s beneficial for buyers to understand the market landscape and negotiate accordingly to achieve favorable pricing.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of size reduction equipment:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases typically lead to lower unit prices. Buyers should assess their production needs and negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their operational capacity.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom features or specifications can drive up costs. Buyers should determine which features are essential versus those that may be unnecessary to avoid overspending.
-
Materials and Quality: The quality and type of materials used can significantly affect pricing. Premium materials may lead to higher initial costs but can offer better performance and longevity.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and service offerings (such as after-sales support) can impact pricing. Buyers should conduct thorough due diligence to select reliable partners.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of different Incoterms is crucial for managing costs related to shipping, insurance, and risk. Buyers should select terms that provide clarity on responsibilities and costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to significant cost savings. Buyers should come prepared with market data and be clear about their budget constraints.
-
Cost Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. A lower initial purchase price may not always equate to a better deal if long-term costs are higher.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and local market dynamics that could affect pricing. Leveraging local expertise can help navigate these complexities.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and may vary based on current market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific equipment requirements. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology associated with size reduction equipment is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below is a comprehensive overview tailored for international B2B buyers.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the quality and type of materials used in the construction of size reduction equipment, typically stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant alloys.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure longevity, hygiene, and resistance to wear and tear, which is vital in pharmaceutical manufacturing where cleanliness and durability are paramount. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension of the equipment, impacting the precision of size reduction.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are essential for achieving consistent particle sizes, which directly influence drug bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness. This is critical for regulatory compliance and product quality. -
Energy Consumption
– Definition: This property measures the amount of energy the equipment requires to operate effectively during the size reduction process.
– Importance: Understanding energy consumption helps in estimating operational costs. Efficient machines reduce energy costs while maintaining performance, appealing to budget-conscious buyers. -
Production Capacity
– Definition: This specification refers to the amount of material that the equipment can process in a given time frame, typically measured in kilograms per hour (kg/h).
– Importance: Knowing the production capacity is vital for scaling operations and meeting market demand. Buyers must align equipment capacity with their production goals to avoid bottlenecks. -
Particle Size Distribution
– Definition: This property describes the range and frequency of particle sizes produced by the equipment, often specified in microns.
– Importance: A consistent particle size distribution is crucial for ensuring uniformity in pharmaceutical formulations, impacting the release and absorption rates of drugs.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM partnerships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and assess the quality and compatibility of replacement parts for maintenance. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: This term refers to the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their inventory and budget effectively. Suppliers with high MOQs may require a larger upfront investment, which could be a barrier for smaller firms. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit price and terms for specific products.
– Importance: Issuing RFQs allows buyers to compare pricing, terms, and conditions from different suppliers, ensuring they receive competitive offers that align with their budget and quality standards. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for buyers engaged in cross-border trade, as they clarify costs, risks, and responsibilities during shipping, ensuring smooth logistics. -
Lead Time
– Definition: This term refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is essential for planning production schedules and managing inventory levels. Longer lead times can affect product availability and market responsiveness.
By familiarizing themselves with these specifications and terminology, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring compliance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry is witnessing significant growth, driven by several key factors. One of the primary drivers is the increasing demand for high-quality pharmaceuticals that require precise particle size for enhanced bioavailability and absorption. The rise in chronic diseases across regions such as Africa and South America is propelling the need for efficient drug formulations, thus boosting the demand for advanced size reduction technologies.
Emerging trends include the adoption of automation and digital technologies, which enhance efficiency and reduce operational costs. Equipment manufacturers are integrating Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, allowing real-time monitoring and data analytics to optimize production processes. Additionally, the shift towards continuous manufacturing processes is shaping the landscape, favoring equipment that supports scalability and flexibility in production.
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Europe, understanding local regulations and compliance standards is crucial. The pharmaceutical sector is heavily regulated, and equipment must meet stringent quality and safety benchmarks. Buyers should also consider regional market dynamics, such as the availability of skilled labor and infrastructure, which can impact sourcing decisions. Collaborating with local suppliers can provide insights into these dynamics, facilitating smoother procurement processes.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a focal point for B2B buyers in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly concerning the sourcing of size reduction equipment. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and equipment operation cannot be overlooked, as regulations tighten globally. Buyers are increasingly seeking equipment that minimizes energy consumption and waste generation. This includes technologies that utilize less energy for size reduction and offer longer operational lifespans, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint.
Ethical sourcing practices are equally important, as stakeholders demand transparency in supply chains. Equipment manufacturers are encouraged to adopt ethical supply chain practices that ensure fair labor conditions and responsible sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the use of ‘green’ materials in the manufacturing of size reduction equipment is gaining traction. Buyers should actively seek suppliers who utilize environmentally friendly materials and processes, thereby contributing to a more sustainable pharmaceutical production landscape.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry has been marked by technological advancements and increasing complexity in drug formulations. Initially, traditional methods such as mortar and pestle were employed, but as the demand for precision grew, more sophisticated machinery emerged. The introduction of impact mills and ball mills revolutionized the process, allowing for finer particle sizes and improved efficiency.
Over the past few decades, the focus has shifted towards automation and digitization. Modern equipment not only meets the stringent requirements of pharmaceutical production but also integrates features that enhance productivity and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. This evolution reflects the industry’s commitment to improving drug efficacy while addressing sustainability and ethical sourcing challenges.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for size reduction equipment?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the pharmaceutical sector, reputation, and compliance with international quality standards. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 and relevant pharmaceutical certifications (e.g., cGMP). Request references and case studies from previous clients to assess their reliability. Evaluate their technical support and after-sales service, as these are crucial for maintaining equipment efficiency. Additionally, consider suppliers’ ability to provide customized solutions tailored to your specific production needs. -
Can size reduction equipment be customized to meet specific production requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for size reduction equipment. Customization can include adjustments in the design, material specifications, and size of the equipment to align with your production processes. When discussing customization, be clear about your requirements, such as particle size distribution, throughput capacity, and operational conditions. Collaborating closely with suppliers during the design phase can lead to more efficient solutions and better alignment with your operational needs. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead time for size reduction equipment?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the equipment. Generally, established suppliers may have a MOQ ranging from one unit for standard machines to multiple units for customized solutions. Lead times can also vary, typically ranging from 4 to 16 weeks depending on the equipment’s complexity and customization level. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront with suppliers to align production schedules and avoid potential delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing size reduction equipment?
Payment terms can differ between suppliers, often influenced by the transaction’s size and complexity. Common arrangements include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%), with the balance due upon shipment or installation. Some suppliers may offer financing options or extended payment terms for larger orders. Always clarify payment terms in the contract, ensuring they are aligned with your financial capabilities and cash flow management strategies. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for the equipment I purchase?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed documentation of the supplier’s certifications, including ISO standards and compliance with FDA or EMA regulations, depending on your market. Ask for validation protocols and testing reports that demonstrate the equipment meets specified performance criteria. It’s also beneficial to inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes and whether they conduct regular audits to maintain compliance with international standards, ensuring the equipment’s reliability and safety. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing size reduction equipment?
Logistics are critical when importing size reduction equipment. Consider factors such as shipping methods, customs clearance, and transportation costs. Ensure that your supplier has experience in international shipping and can provide necessary documentation, including bills of lading and customs invoices. Additionally, assess local regulations regarding equipment importation in your country and collaborate with a reliable freight forwarder to streamline the shipping process and mitigate potential delays. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers effectively?
To handle disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels with your supplier from the outset. Ensure that all agreements, including delivery timelines, quality standards, and payment terms, are documented in a contract. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it through direct negotiation, providing evidence and documentation to support your position. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods, and familiarize yourself with legal frameworks applicable in your jurisdiction to protect your interests. -
What are the best practices for maintaining size reduction equipment to ensure longevity and performance?
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of size reduction equipment. Implement a scheduled maintenance plan that includes routine inspections, cleaning, and calibration. Train your staff on proper operating procedures to minimize wear and tear. Keep detailed maintenance logs to track performance and identify any issues early. Additionally, collaborate with the supplier for maintenance support, including access to spare parts and technical assistance, ensuring your equipment remains in optimal working condition.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for size reduction equipment for pharmaceutical industry
The strategic sourcing of size reduction equipment in the pharmaceutical industry is essential for enhancing drug effectiveness and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. By investing in high-quality, innovative machinery, international B2B buyers can significantly improve their production processes, increase drug bioavailability, and maintain consistency across batches. Key factors to consider include the equipment’s ability to handle diverse material properties, energy efficiency, and contamination risks.
As markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for advanced size reduction solutions is on the rise. Buyers are encouraged to evaluate suppliers not just on cost but also on technological capabilities, support services, and their commitment to sustainability. Engaging in strategic partnerships can facilitate access to cutting-edge technologies and expertise, ultimately driving competitive advantage.
Looking ahead, the pharmaceutical landscape will increasingly require agility and innovation. By prioritizing strategic sourcing initiatives today, organizations can position themselves for success in meeting the growing demands of tomorrow’s healthcare markets. Take action now to explore the best options for size reduction equipment, ensuring that your operations are equipped to deliver quality products efficiently and effectively.