Master Tumbling Machining: Your Essential Guide to Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for tumbling machining
In the competitive landscape of global manufacturing, tumbling machining stands out as a vital process for achieving superior surface finishes and enhancing the durability of metal components. This mass finishing technique, which utilizes abrasive media and mechanical action, is essential across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical devices. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of tumbling machining can significantly impact procurement strategies and operational efficiency.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of tumbling machining, covering various types of equipment and media, the selection of materials, and the intricacies of manufacturing and quality control processes. We will also explore the landscape of suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends to equip you with the knowledge necessary for making informed sourcing decisions.
By addressing common FAQs and providing actionable insights, this guide empowers you to navigate the complexities of tumbling machining confidently. Whether you are sourcing for a new project or seeking to optimize existing processes, understanding the capabilities and applications of tumbling machining will enhance your competitive edge. Engage with this resource to unlock the potential of your manufacturing operations and ensure the highest quality in your products.
Understanding tumbling machining Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barrel Tumblers | Hexagonal or octagonal containers, low RPM (20-45), gentle action | Heavy metal parts, stone polishing | Pros: Cost-effective, suitable for large batches. Cons: Slower cycle times, less aggressive. |
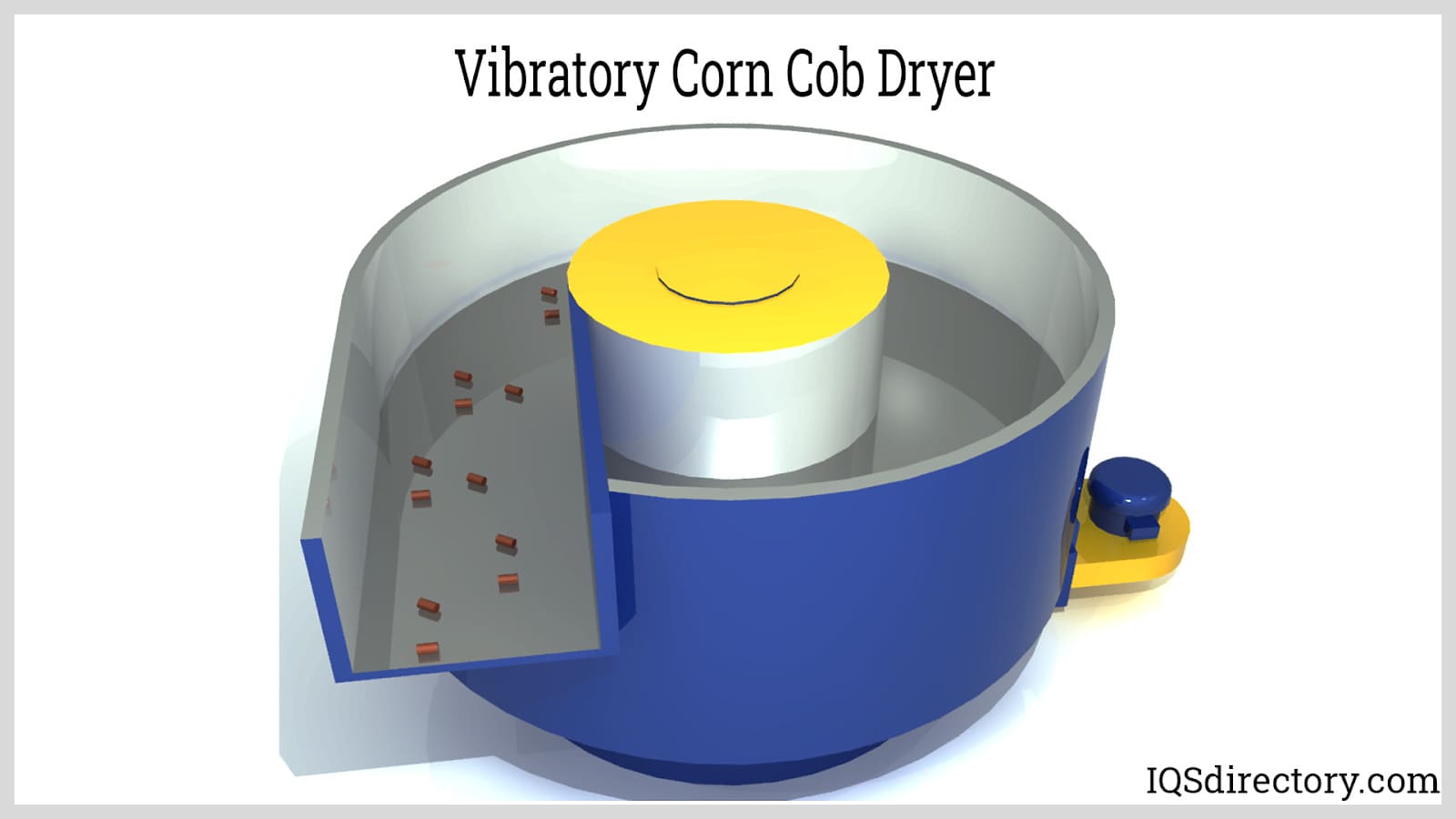
| Vibratory Tumbling Machines | Eccentric weights create oscillation, 1200-3600 vibrations/min | Precision components, complex parts | Pros: High efficiency, gentle on parts. Cons: Higher upfront cost, may require specific media. |
| High-Energy Centrifugal Systems | Turret spinning, intense finishing action, high G-forces | Tough materials (titanium, hardened steel) | Pros: Extremely fast cycle times, aggressive burr removal. Cons: Higher investment, more complex operation. |
| Dry Tumbling Systems | No water used, relies on abrasive media alone | Delicate or intricate parts | Pros: Ideal for sensitive components, consistent finishes. Cons: Limited to certain materials, may require more monitoring. |
| Wet Tumbling Systems | Utilizes water and compounds, reduces friction | General metal finishing, deburring | Pros: Effective cleaning, reduces wear on components. Cons: Requires more maintenance, potential for wastewater management issues. |
Barrel Tumblers
Barrel tumblers are traditional rotary systems that utilize hexagonal or octagonal containers to achieve a uniform finish on heavy metal parts. They operate at lower speeds (20-45 RPM) and are effective for large batches, making them a cost-effective choice for businesses looking to polish or deburr substantial quantities. However, their slower cycle times and less aggressive nature may not suit all applications, particularly where rapid processing is essential.
Vibratory Tumbling Machines
Vibratory tumblers generate an oscillating motion through eccentric weights, resulting in a three-dimensional motion profile. This type of machine operates at higher speeds (1200-3600 vibrations per minute), making it ideal for precision components and complex geometries. While vibratory tumblers offer high efficiency and a gentle finishing action that protects delicate parts, they typically come with a higher initial investment and may necessitate the use of specific media for optimal results.
High-Energy Centrifugal Systems
High-energy centrifugal systems are designed for aggressive finishing, utilizing turret spinning to create high G-forces that significantly reduce processing times. These systems are particularly effective for tough materials such as titanium and hardened steel, delivering rapid burr removal and a high-quality finish. However, the complexity of operation and higher upfront costs may deter some buyers, particularly those with lower volume needs.
Dry Tumbling Systems
Dry tumbling systems operate without water, relying solely on abrasive media to finish parts. They are particularly suitable for delicate or intricate components, providing consistent finishes while minimizing the risk of damage. Despite their advantages, dry tumblers are limited to certain materials and require careful monitoring to ensure the effectiveness of the finishing process.
Wet Tumbling Systems
Wet tumbling systems incorporate water and abrasive compounds to reduce friction during the finishing process. This method is widely used for general metal finishing and deburring, as it effectively cleans parts while minimizing wear. However, wet tumbling requires more maintenance and presents potential challenges in wastewater management, which buyers should consider when evaluating their options.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of tumbling machining
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of tumbling machining | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Deburring and polishing of engine components | Enhanced part performance and durability | Availability of specialized media for various metals |
| Aerospace | Surface finishing of turbine blades | Improved aerodynamics and fuel efficiency | Compliance with strict industry standards and certifications |
| Medical Devices | Finishing of surgical instruments and implants | Enhanced safety and biocompatibility | Source from suppliers with ISO certifications |
| Jewelry Manufacturing | Polishing of precious metal components | Superior aesthetic appeal and market competitiveness | Access to fine abrasives and environmentally friendly options |
| Electronics | Deburring and surface preparation of connectors | Improved electrical conductivity and reliability | Consistency in media quality and process control |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, tumbling machining is primarily utilized for deburring and polishing engine components such as pistons, crankshafts, and valves. This process enhances the performance and durability of parts by removing sharp edges and surface imperfections. For international buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, sourcing reliable tumbling equipment that can handle diverse metal compositions is crucial. Additionally, understanding the local regulations regarding emissions and waste management during the tumbling process is essential for compliance.
Aerospace Sector
Tumbling machining plays a vital role in the aerospace industry, especially for finishing turbine blades. This application not only improves the surface quality but also enhances aerodynamics and fuel efficiency, which are critical for aircraft performance. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent aerospace standards, such as AS9100, to guarantee the quality and safety of finished components. Furthermore, sourcing high-density ceramic media can provide better results for tough materials like titanium.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, tumbling machining is crucial for finishing surgical instruments and implants. The process helps achieve a smooth surface finish that is essential for safety and biocompatibility. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions with growing medical sectors like Egypt, should prioritize suppliers with ISO certifications to ensure that the tumbling process meets health and safety standards. Additionally, sourcing environmentally friendly media can enhance the sustainability profile of their manufacturing operations.
Jewelry Manufacturing
For jewelry manufacturers, tumbling machining is employed for polishing precious metal components, enhancing their aesthetic appeal. This process is essential for creating high-quality finishes that attract customers in competitive markets. B2B buyers from South America and Europe should focus on suppliers that offer fine abrasives and environmentally friendly options to meet consumer demand for sustainable practices. Understanding the nuances of different tumbling media can also help achieve the desired finish without damaging delicate pieces.
Electronics Industry
In the electronics sector, tumbling machining is used for deburring and surface preparation of connectors and other components. This application improves electrical conductivity and overall reliability, which are critical for electronic devices. Buyers, especially in Africa and the Middle East, should consider sourcing consistent media quality and ensuring effective process control to maintain production efficiency. Establishing partnerships with reputable suppliers who understand the specific needs of the electronics industry can lead to better outcomes and reduced operational risks.
Related Video: Tumbling Brass – A Basic Overview for Beginners New to Reloading
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tumbling machining
Analysis of Common Materials for Tumbling Machining
1. Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is known for its high bulk density and excellent wear resistance. It can withstand considerable pressure during the tumbling process, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel media is its ability to produce a shiny finish while significantly reducing finishing times. However, it is prone to rusting if not properly maintained, which can lead to contamination of the workpieces.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is particularly effective for burnishing and polishing metals, enhancing their surface hardness and wear resistance. It is compatible with various tumbling machines, but users must ensure proper maintenance to avoid corrosion.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local regulations regarding the use of steel media, especially in industries with strict compliance standards. Familiarity with ASTM standards can aid in selecting the right product.
2. High-Density Ceramics
Key Properties: High-density ceramic media is characterized by its durability and resistance to fracture, making it suitable for aggressive cutting applications. It operates effectively under high temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of high-density ceramics is their ability to provide a superior polish and reduced processing times. However, they can be more expensive than other media types, which may affect budget considerations for some manufacturers.
Impact on Application: This material excels in applications requiring intricate finishing and is particularly effective for harder metals. Its compatibility with various tumbling systems enhances its versatility in different manufacturing settings.
Considerations for International Buyers: European buyers should consider compliance with DIN standards when selecting ceramic media. Additionally, the availability of high-density ceramics may vary by region, impacting supply chain logistics.
3. Plastic Media
Key Properties: Plastic media is lightweight and flexible, making it ideal for delicate components. It is resistant to corrosion and can operate effectively in wet or dry tumbling processes.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic media is its ability to cushion components during tumbling, reducing the risk of damage. However, it may not provide the same level of polish as metal or ceramic media, which could be a limitation for certain applications.
Impact on Application: Plastic media is particularly well-suited for soft metals and plastic components, ensuring consistent finishes without the risk of scratching. Its compatibility with various tumbling processes makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in the Middle East should consider local preferences for non-corrosive materials, especially in humid environments. Understanding JIS standards can also guide the selection of suitable plastic media.
4. Wood Media
Key Properties: Wood media, often used in dry tumbling processes, is lightweight and provides a cushioning effect. It is biodegradable and environmentally friendly, making it an attractive option for sustainable manufacturing.
Pros & Cons: The advantage of wood media lies in its ability to achieve mirror-like finishes on metal components while being gentle enough for delicate parts. However, it may not be suitable for high-volume applications due to its slower processing speed.
Impact on Application: Wood media is ideal for applications requiring a soft touch, such as polishing jewelry or delicate metal parts. Its use can enhance the aesthetic appeal of the finished product without compromising integrity.
Considerations for International Buyers: In regions like Argentina, where environmental regulations are increasingly strict, wood media may align well with sustainability goals. Buyers should ensure that the wood is sourced responsibly to comply with local regulations.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for tumbling machining | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Steel | Burnishing and polishing metals | Produces shiny finishes quickly | Prone to rusting if not maintained | Medium |
| High-Density Ceramics | Intricate finishing of hard metals | Superior polish and reduced processing times | Higher cost compared to other media types | High |
| Plastic Media | Finishing soft metals and plastics | Cushions components, reducing damage risk | May not achieve as high a polish | Low |
| Wood Media | Polishing delicate metal components | Achieves mirror-like finishes | Slower processing speed for high volumes | Low |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tumbling machining
Manufacturing Processes in Tumbling Machining
Understanding the manufacturing processes involved in tumbling machining is essential for B2B buyers looking to ensure quality and efficiency in production. This section delves into the typical stages of manufacturing, key techniques employed, and the importance of quality assurance (QA) throughout the process.
Main Stages of Tumbling Machining
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: The first step involves selecting appropriate materials, which can range from metals like titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum to plastics. The choice of material affects the tumbling process and the type of media used.
– Pre-Treatment: Components may undergo pre-treatment processes such as cleaning to remove any contaminants that could affect the tumbling results. -
Forming
– Initial Shaping: Parts are often shaped through machining processes like turning or milling before tumbling. This initial shaping is crucial for achieving desired dimensions and surface characteristics.
– Deburring: If the components have sharp edges or burrs from machining, they may undergo initial deburring to facilitate smoother tumbling. -
Assembly
– Batch Preparation: Parts are grouped together based on size and material for efficient tumbling. This grouping ensures uniformity in the finishing process.
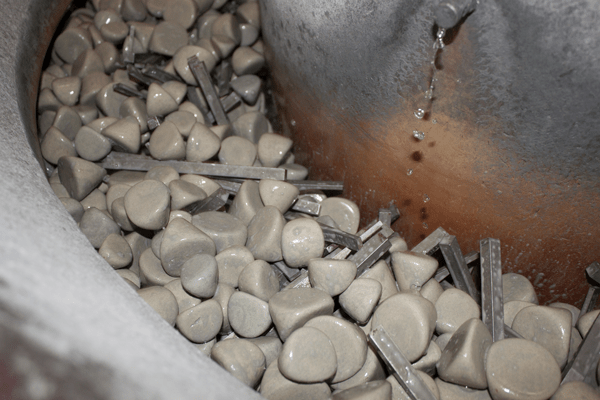
– Media Selection: Choosing the right tumbling media (ceramics, steel shot, or plastics) is critical for achieving the desired finish and wear resistance. The media must complement the material of the parts being tumbled. -
Finishing
– Tumbling Process: The assembled components and media are placed in a tumbling machine. This machine may operate using rotary, vibratory, or centrifugal systems, each offering different advantages in terms of efficiency and finish quality.
– Cycle Time and Conditions: The duration of the tumbling process varies based on the desired finish and the materials involved. Parameters such as rotational speed, media type, and the presence of lubricants or abrasives are adjusted to optimize results.
Key Techniques in Tumbling Machining
- Wet vs. Dry Tumbling: Depending on the application, tumbling can be done wet (with water and compounds) or dry. Wet tumbling often results in better finishes and reduced friction, while dry tumbling is suitable for delicate components.
- Media Types: The choice of media significantly influences the outcome. Hard media (like steel shot) is used for aggressive polishing, while softer media (like hardwood) is suitable for delicate parts requiring gentler treatment.
- Advanced Technologies: Modern tumbling machines incorporate technology such as computer-based control for precise parameter adjustments, allowing for consistent quality across batches.
Quality Assurance in Tumbling Machining
Quality assurance is paramount in tumbling machining to ensure that the finished products meet international standards and customer expectations. The following outlines the relevant standards, checkpoints, and testing methods.
International Standards and Certifications
- ISO 9001: This is the most widely recognized quality management standard, ensuring that organizations meet customer and regulatory requirements while demonstrating continuous improvement.
- Industry-Specific Standards: Depending on the application, other certifications such as CE (for European markets) and API (for the petroleum industry) may be relevant. These certifications ensure compliance with specific industry regulations.
QC Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Materials are inspected upon arrival to verify specifications and quality before production begins. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During the tumbling process, regular checks are performed to monitor parameters such as cycle time, media wear, and part quality. Any deviations are addressed immediately to prevent defects. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Once tumbling is complete, finished parts undergo thorough inspection, which may include visual checks, dimensional verification, and surface quality assessments.
Common Testing Methods
- Visual Inspection: A basic but effective method to identify surface defects and overall finish quality.
- Dimensional Measurement: Tools such as calipers and micrometers are used to ensure that parts meet specified tolerances.
- Surface Roughness Testing: Specialized equipment measures the roughness of surfaces to confirm that they meet the required standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control is crucial. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their quality management systems and adherence to international standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for documentation of their QC processes, including inspection reports and certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to verify the quality of products before shipment. This adds an extra layer of assurance.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality assurance and certification that may vary across regions:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and quality expectations is essential for establishing effective partnerships.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers must ensure that suppliers comply with both local and international regulations, which may differ significantly.
- Language Barriers: Effective communication regarding quality standards and expectations is vital. Consider employing bilingual staff or translators when negotiating with suppliers.
By focusing on the manufacturing processes and quality assurance strategies outlined above, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing tumbling machining services, ultimately ensuring high-quality outcomes and operational efficiency.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tumbling machining Sourcing
Cost Structure of Tumbling Machining
Understanding the cost structure of tumbling machining is essential for international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. The costs can be broken down into several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of abrasive media, compounds, and any additional consumables significantly impacts costs. For instance, high-density ceramics or carbon steel media may have a higher upfront cost but can lead to better finishes and reduced cycle times, ultimately lowering the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the region and skill level required. In countries with lower labor costs, such as certain nations in Africa and South America, buyers might find more cost-effective solutions. However, skilled labor is necessary for quality assurance and machine operation.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can vary widely based on the supplier’s operational efficiency and geographic location.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling and setup costs can add to the initial investment, especially for specialized parts. Buyers should consider suppliers that can offer flexibility in tooling to minimize costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict QC measures ensures high-quality outputs but can add to overall costs. Buyers should assess whether the supplier’s QC processes align with their quality standards and whether these costs are justified.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs, particularly for international buyers, can significantly affect pricing. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in determining who bears these costs, so understanding them is vital.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on the supplier’s market position, reputation, and the complexity of the services offered.
Price Influencers in Tumbling Machining
Several factors can influence the pricing of tumbling machining services:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger order quantities often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to leverage volume discounts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses associated with redesigns or additional processing.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the price but also the durability and performance of the finished product. Selecting the right media and compounds can optimize performance and reduce long-term costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers offering higher-quality finishes or industry certifications may charge a premium. Buyers must weigh the benefits of these certifications against their budget and quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and relationship history can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices but can offer reliability and consistency.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) dictate responsibility for costs and risks, impacting the overall pricing structure.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
To maximize cost-efficiency when sourcing tumbling machining services, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, payment terms, and MOQs. Building a solid relationship can lead to better pricing and terms.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond initial costs, consider long-term factors such as maintenance, operational efficiency, and the expected lifespan of the finished components. A higher initial investment might yield lower TCO.
-
Research Local Suppliers: Especially for buyers in Africa and South America, local suppliers can offer reduced logistics costs and better understanding of regional material preferences.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware of seasonal fluctuations, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical factors that may affect pricing. Keeping abreast of these factors can help in timing purchases more effectively.
-
Request Samples: Before committing to large orders, request samples to evaluate quality. This can prevent costly mistakes and ensure that the supplier meets your specifications.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific buyer requirements. Always conduct thorough due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential tumbling machining Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘tumbling machining’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tumbling machining
When engaging in tumbling machining, understanding the critical technical properties and common trade terminology is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines key specifications and industry jargon that are particularly relevant for international B2B buyers.
Essential Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of the raw materials used in manufacturing parts, such as steel, aluminum, or titanium.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade is crucial for achieving desired performance characteristics, such as strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. Buyers should ensure that the material meets industry standards specific to their applications, particularly in sectors like aerospace or automotive. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance indicates the allowable variation in dimensions of the machined parts.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are essential for components that must fit precisely within assemblies. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers communicate their needs effectively and ensures compatibility with existing systems. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish refers to the texture and smoothness of a part’s surface after the tumbling process.
– B2B Importance: Different applications require varying surface finishes; for example, medical devices may need ultra-smooth finishes to prevent bacteria accumulation. Buyers must specify the desired finish to meet regulatory standards and performance requirements. -
Cycle Time
– Definition: Cycle time is the total time taken to complete the tumbling process, from start to finish.
– B2B Importance: Shorter cycle times can significantly enhance productivity and reduce costs. Buyers should inquire about expected cycle times to optimize production schedules and meet delivery deadlines. -
Media Type
– Definition: Media type refers to the abrasive materials used during the tumbling process, such as ceramic, plastic, or steel.
– B2B Importance: The choice of media affects the effectiveness and quality of the finishing process. Different media types are suited for various materials and desired outcomes, so buyers must select the right type to achieve optimal results. -
Process Parameters
– Definition: Process parameters include factors such as speed, temperature, and lubrication that influence the tumbling process.
– B2B Importance: Understanding these parameters allows buyers to optimize the tumbling process for efficiency and quality. Proper tuning can lead to significant cost savings and improved product quality.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Buyers often source tumbling services from OEMs to ensure quality and compatibility with their products. Knowing reputable OEMs is vital for establishing reliable supply chains. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQs helps buyers manage inventory and cash flow. It is essential for determining if a supplier meets the buyer’s purchasing needs without excessive stock accumulation. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specified goods or services.
– Importance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. It is a critical step in the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are standardized international trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risk management. This knowledge is essential for international transactions to avoid disputes. -
Batch Processing
– Definition: Batch processing refers to the simultaneous processing of multiple parts or components in one cycle.
– Importance: Understanding batch processing capabilities can help buyers maximize efficiency and reduce costs, particularly in high-volume production scenarios.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential properties and terminology, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of tumbling machining more effectively, ensuring they make informed and strategic purchasing decisions.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the tumbling machining Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The tumbling machining sector is witnessing robust growth driven by the increasing demand for precision-engineered components across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medical manufacturing. Key global drivers include advancements in technology that enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of tumbling processes. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding current and emerging sourcing trends is vital.
A notable trend is the shift towards automated and high-energy tumbling systems that significantly reduce cycle times while improving finish quality. Such equipment not only offers higher throughput but also minimizes labor costs, making it particularly attractive for manufacturers aiming for scalability. Additionally, the integration of IoT and AI in tumbling machinery is transforming process monitoring and optimization, allowing for real-time adjustments and data analytics that enhance productivity.
Buyers are also increasingly focused on sourcing equipment and services from suppliers that can demonstrate reliability and technological innovation. In markets such as Egypt and Argentina, where manufacturing capabilities are evolving, establishing partnerships with suppliers that prioritize modern technologies can provide a competitive edge. Furthermore, the emphasis on sustainability is prompting buyers to seek suppliers who utilize environmentally friendly practices and materials.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of business strategy in the tumbling machining sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including waste generation and energy consumption, has led many companies to adopt greener practices. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices is not only an ethical choice but also a strategic one, as it can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Ethical sourcing involves ensuring that suppliers comply with environmental regulations and labor standards. Buyers should look for certifications that indicate adherence to sustainable practices, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and other green certifications specific to materials used in tumbling processes. Sustainable materials, such as biodegradable media or recycled abrasives, are becoming more prevalent and can provide significant advantages in reducing waste and improving the overall sustainability profile of manufacturing operations.
Moreover, engaging in ethical supply chains fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers, contributing to a stable and reliable sourcing environment. This is particularly important for buyers in regions like the Middle East and Africa, where local regulations may increasingly demand compliance with sustainability standards.
Brief Evolution/History
The tumbling process has evolved significantly since its inception in early metalworking, where artisans utilized simple rotating drums for surface finishing. The 20th century saw the introduction of motorized barrel tumblers, which standardized the process for industrial applications. The development of vibratory tumblers in the 1950s further enhanced efficiency, allowing for faster and more consistent finishes.
Today, tumbling technology includes high-energy centrifugal systems that can achieve superior surface finishes in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. This evolution reflects the industry’s response to growing demands for precision, speed, and sustainability, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about technological advancements that can impact their sourcing strategies.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tumbling machining
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for tumbling machining?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the tumbling machining sector, particularly with the specific materials you require. Review their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management standards. Assess their production capabilities, including technology and equipment used, to ensure they can meet your specifications. Additionally, examine customer reviews and case studies that demonstrate their reliability and quality of service. Establishing clear communication and understanding their lead times can also mitigate potential issues. -
Can tumbling machining processes be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for tumbling machining processes. Customization can include selecting specific abrasive media, adjusting cycle times, and tailoring machine settings to achieve desired surface finishes. When discussing your needs with suppliers, provide detailed specifications about the materials and finishes required. Request samples or pilot runs to evaluate the quality of the finished product before committing to larger orders. This ensures that the supplier can meet your unique requirements effectively.
-
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for tumbling machining?
MOQs can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the machining process. Some suppliers may accommodate small batch orders, while others may require larger quantities to justify production costs. Lead times generally range from a few days to several weeks, influenced by factors such as order size, customization requirements, and the supplier’s current workload. It’s essential to discuss these aspects upfront to align expectations and avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What payment options are available for international orders in tumbling machining?
Payment options for international orders typically include bank transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal, among others. Discuss with your supplier which payment methods they accept and any associated fees. For larger orders, a letter of credit may provide more security for both parties. Additionally, consider negotiating payment terms that align with your cash flow, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the balance upon delivery. Be aware of currency fluctuations and associated risks when dealing with international transactions. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications from suppliers?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO standards. Inquire about their inspection methods, including any third-party audits they may undergo. It’s beneficial to establish a clear quality agreement that outlines the standards expected for your order. Some suppliers may offer certificates of conformity or material test reports, which can provide additional reassurance regarding the quality and specifications of the finished products. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing tumbling machined parts?
Logistics play a crucial role in the successful import of tumbling machined parts. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), which can affect costs and delivery times. Verify the supplier’s ability to handle logistics, including packaging and documentation for customs clearance. Additionally, assess the import regulations in your country to ensure compliance and avoid delays. Working with a reliable freight forwarder can streamline the process and help mitigate potential challenges associated with international shipping.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How can disputes with suppliers be effectively managed?
Disputes can arise from misunderstandings or quality issues, so it’s essential to have clear communication channels with your supplier. Establish a written agreement that includes terms of service, quality expectations, and dispute resolution procedures. If a dispute occurs, address it promptly by discussing the issue directly with the supplier to seek an amicable resolution. In cases where direct communication fails, consider mediation or arbitration as alternative methods to resolve conflicts without escalating to legal action. -
What are the implications of sourcing tumbling machining from different regions?
Sourcing tumbling machining from different regions can have various implications, including cost differences, quality standards, and lead times. For instance, suppliers from Europe may offer advanced technology and high-quality standards, but at a higher cost, while suppliers from Africa or South America may provide competitive pricing with varying quality levels. Consider logistical challenges and trade regulations that could impact delivery times and costs. Conduct thorough research on regional suppliers to find a balance between cost, quality, and reliability that meets your business needs.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tumbling machining
In conclusion, the tumbling machining process presents a myriad of opportunities for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging strategic sourcing, companies can optimize their supply chains, ensuring they acquire the most effective tumbling equipment and media tailored to their unique production needs. Buyers should consider the diverse options available, from traditional barrel tumblers to advanced high-energy systems, each offering specific advantages depending on the application and material type.
Key takeaways include:
- Understanding Equipment Types: Familiarize yourself with various tumbling machines and their capabilities to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Media Selection: Choose the appropriate media that enhances efficiency and finish quality, as this can significantly impact production outcomes.
- Process Optimization: Pay attention to critical parameters such as cycle time, media type, and chemical compounds to achieve superior results.
As global markets continue to evolve, embracing innovative tumbling solutions will be pivotal in maintaining a competitive edge. International buyers are encouraged to explore partnerships with reliable suppliers, ensuring they can meet the increasing demand for high-quality metal finishing. The future of tumbling machining is bright—seize the opportunity to enhance your operations today.