Master Sourcing Strategies for High-Quality Cable Aircraft
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cable aircraft
Navigating the complexities of the global market for aircraft cables is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and safety across diverse applications. Aircraft cables, known for their high tensile strength and flexibility, are pivotal not just in aviation but also in industries such as agriculture, construction, and marine services. Their unique properties make them indispensable for critical functions, including flight control systems and heavy lifting operations.
This comprehensive guide delves into the various types of aircraft cables, detailing the differences between stainless steel and galvanized options, and their specific applications. We will explore manufacturing standards and quality control measures that ensure safety and performance, essential for compliance in diverse markets. Additionally, the guide will provide insights into sourcing strategies, key suppliers, and cost considerations, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions.
With a focus on the needs of buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including regions like Turkey and Vietnam, this resource will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the aircraft cable landscape effectively. Whether you are involved in procurement, project management, or engineering, understanding the nuances of aircraft cables will enhance your ability to select the right products for your operations, ensuring reliability and excellence in performance.
Understanding cable aircraft Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Aircraft Cable | High corrosion resistance, flexible, durable | Aviation controls, marine applications, architectural rigging | Pros: Long lifespan, low maintenance; Cons: Higher initial cost. |
| Galvanized Aircraft Cable | Cost-effective, moderate corrosion resistance | General industrial, agricultural, construction | Pros: Economical, good strength; Cons: Limited longevity in harsh environments. |
| 7×7 Construction Cable | Seven strands of seven wires, excellent flexibility | Lifting, safety cables, rigging | Pros: Highly flexible, compact; Cons: Lower breaking strength than 7×19. |
| 7×19 Construction Cable | Seven strands of nineteen wires, superior load capacity | Heavy-duty applications, winching, tow cables | Pros: High tensile strength; Cons: Less flexible than 7×7 construction. |
| Custom Configured Cables | Tailored designs to meet specific needs | Specialized applications across various industries | Pros: Meets unique specifications; Cons: Longer lead times, potentially higher costs. |
Stainless Steel Aircraft Cable
Stainless steel aircraft cables are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for applications in aviation and marine environments. Typically constructed from 302, 304, or 316 stainless steel, these cables offer high tensile strength and flexibility. When purchasing, B2B buyers should consider the specific environmental conditions where the cables will be used, as well as the required load capacities. While they tend to have a higher upfront cost, their longevity and reduced maintenance needs can lead to significant savings over time.
Galvanized Aircraft Cable
Galvanized aircraft cables are a more economical option, coated with zinc to provide moderate corrosion resistance. They are widely used in general industrial applications, agriculture, and construction due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. Buyers should assess the environmental conditions, as galvanized cables may not perform as well in harsh or corrosive environments compared to stainless steel. The initial lower cost can be appealing, but it is essential to weigh this against potential long-term durability issues.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
7×7 Construction Cable
The 7×7 construction cable features seven strands of seven wires, offering excellent flexibility and compactness, making it suitable for applications requiring tight routing. Commonly used for lifting and rigging, it allows for easy manipulation in constrained spaces. B2B buyers should consider the specific load requirements and flexibility needs of their applications. While it provides good performance, it may not support as high a breaking strength as some other configurations, such as 7×19.
7×19 Construction Cable
7×19 construction cables consist of seven strands of nineteen wires, providing superior load-bearing capacity and tensile strength. This configuration is ideal for heavy-duty applications, including winching and tow cables. Buyers should focus on the specific strength requirements of their operations when selecting this type of cable. Although these cables are less flexible than their 7×7 counterparts, their robustness makes them a reliable choice for demanding environments.
Custom Configured Cables
Custom configured cables are designed to meet specific operational needs, allowing for tailored solutions across various industries. These cables can be constructed in different materials and configurations to suit unique applications, from specialized lifting to safety systems. B2B buyers should be prepared for potentially longer lead times and higher costs associated with custom orders. However, the ability to meet precise specifications can greatly enhance operational efficiency and safety, making them a worthwhile investment for specialized applications.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of cable aircraft
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cable aircraft | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Flight control systems and hoisting components | Ensures safety and reliability in aircraft operation | Compliance with FAA standards; rigorous testing certifications |
| Construction | Lifting and securing heavy materials | Increases efficiency in construction projects | Material selection (stainless vs. galvanized) for durability |
| Agriculture | Irrigation system support and maintenance | Enhances productivity in crop management | Resistance to environmental factors; tensile strength requirements |
| Marine | Rigging for boats and marine equipment | Provides safety and reliability in harsh environments | Corrosion resistance; compatibility with marine applications |
| Defense and Military | Control cables for military aircraft and vehicles | Critical for operational integrity and safety | Compliance with military specifications; high-performance standards |
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, aircraft cables are essential for flight control systems, where they facilitate the movement of a plane’s control surfaces. These cables must meet stringent safety standards set by the FAA and other aviation authorities, as any failure can lead to catastrophic results. Buyers in this sector must ensure that the cables they source are rigorously tested and certified to withstand extreme conditions, including temperature fluctuations and mechanical stress. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements for different aircraft types is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Construction
Within the construction industry, aircraft cables are often employed to lift and secure heavy materials during building projects. Their high tensile strength and lightweight design enable efficient handling of loads, reducing the risk of accidents and downtime. For international buyers, sourcing cables that meet local construction regulations and standards is essential. Moreover, choosing between stainless steel and galvanized options can impact long-term durability and maintenance costs, making it vital to assess the environmental conditions of the construction site.
Agriculture
In agriculture, aircraft cables play a critical role in supporting and maintaining irrigation systems. Their strength and flexibility allow for effective installation and operation in various terrains. By using aircraft cables, farmers can enhance their irrigation efficiency, leading to improved crop yields. Buyers must consider the cables’ resistance to corrosion and environmental factors, particularly in regions with high humidity or saline conditions. Additionally, selecting cables with appropriate tensile strength is vital to ensure they can withstand the weight of water and other loads.
Marine
Marine applications for aircraft cables include rigging for boats and other marine equipment, where safety and reliability are paramount. The ability of these cables to resist corrosion is particularly important in saltwater environments, making stainless steel options preferable for long-term use. International buyers must evaluate the specific marine conditions in their region, ensuring that the cables sourced can withstand exposure to harsh elements. Understanding the compatibility of different cable types with marine applications will enhance operational safety and performance.
Defense and Military
In defense and military sectors, aircraft cables are used for control mechanisms in military aircraft and vehicles, where operational integrity is crucial. These cables must adhere to strict military specifications and high-performance standards to ensure reliability under extreme conditions. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that can provide documentation of compliance with military standards, as well as the capability for custom solutions tailored to specific military applications. Understanding the rigorous testing and certification processes will help ensure the selected cables perform reliably in critical situations.
Related Video: Safe-T-Cable from DMC
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cable aircraft
When selecting materials for aircraft cables, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in aircraft cables, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations specific to international markets.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel aircraft cables, particularly those made from 316 and 302/304 alloys, offer exceptional corrosion resistance, making them ideal for harsh environments. They can withstand high temperatures and pressures, maintaining integrity under stress.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantages of stainless steel cables include their durability, low maintenance requirements, and long service life. However, they tend to be more expensive than other materials, which can affect budget considerations for international buyers. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as these cables require specific processes to ensure quality.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel cables are suitable for applications in marine environments, aerospace, and food processing, where cleanliness and resistance to rust are critical. They are compatible with various media, including water and chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with ASTM or MIL standards, particularly for military applications. In Europe, adherence to DIN standards is crucial. Buyers must also consider the availability of these materials in their local markets.
Galvanized Steel
Key Properties:
Galvanized steel cables are coated with zinc, providing a cost-effective solution with moderate corrosion resistance. They perform well in mild environments and can handle significant loads, making them versatile for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of galvanized cables is their affordability, which makes them attractive for budget-conscious projects. However, their corrosion resistance is inferior to stainless steel, limiting their use in highly corrosive environments. Manufacturing processes are relatively straightforward, contributing to lower costs.
Impact on Application:
These cables are commonly used in construction, agricultural applications, and general industrial settings. They are suitable for environments where exposure to moisture is limited.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in South America and Africa should verify compliance with local standards, as galvanized cables may not meet stringent requirements in certain industries. Understanding the local climate and potential exposure to corrosive elements is essential for selecting this material.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum cables are lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor. They can operate effectively at moderate temperatures and pressures.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of aluminum cables is their lightweight nature, which reduces overall aircraft weight and improves fuel efficiency. However, they have lower tensile strength compared to steel options, which may limit their use in high-load applications. Manufacturing aluminum cables can be more complex due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum cables are ideal for applications where weight savings are paramount, such as in aerospace components and lightweight rigging systems. They are compatible with non-corrosive media but may not perform well in extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, it is crucial to ensure that aluminum cables meet relevant standards such as JIS or ASTM. The availability of aluminum cables may vary by region, and buyers should assess local suppliers for compliance and quality assurance.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite cables, often made from a combination of materials, offer unique properties such as enhanced strength-to-weight ratios and improved fatigue resistance. They can be engineered to withstand specific environmental conditions.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of composite materials is their ability to be tailored for specific applications, providing both strength and flexibility. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which may deter some buyers.
Impact on Application:
Composite cables are suitable for high-performance applications in aerospace and military sectors, where both weight and strength are critical. They can be designed to be compatible with a wide range of media.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from emerging markets should be aware of the higher costs associated with composite materials and ensure that their suppliers adhere to international standards. Understanding the specific application requirements is vital to making informed purchasing decisions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for cable aircraft | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Marine, aerospace, food processing | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Construction, agriculture | Cost-effective | Limited corrosion resistance | Medium |
| Aluminum | Aerospace, lightweight rigging | Lightweight, improves fuel efficiency | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Composite Materials | High-performance aerospace | Tailored strength-to-weight ratios | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
This guide provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions when selecting the appropriate materials for aircraft cables based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cable aircraft
Manufacturing Processes for Aircraft Cables
The manufacturing of aircraft cables involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets stringent performance and safety standards. Understanding these processes is vital for B2B buyers who need to ensure they are sourcing high-quality cables for their applications.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing aircraft cables is selecting the appropriate materials. High-strength steel, stainless steel (typically grades 302, 304, and 316), and galvanized steel are common choices. The materials undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet specified mechanical properties and chemical compositions.
- Material Inspection: Incoming materials are subjected to Incoming Quality Control (IQC) checks, which include tensile strength tests and corrosion resistance assessments.
- Cutting: The raw materials are cut into specified lengths, ensuring minimal waste and optimal usage.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming the strands that will make up the cable. This involves several key techniques:
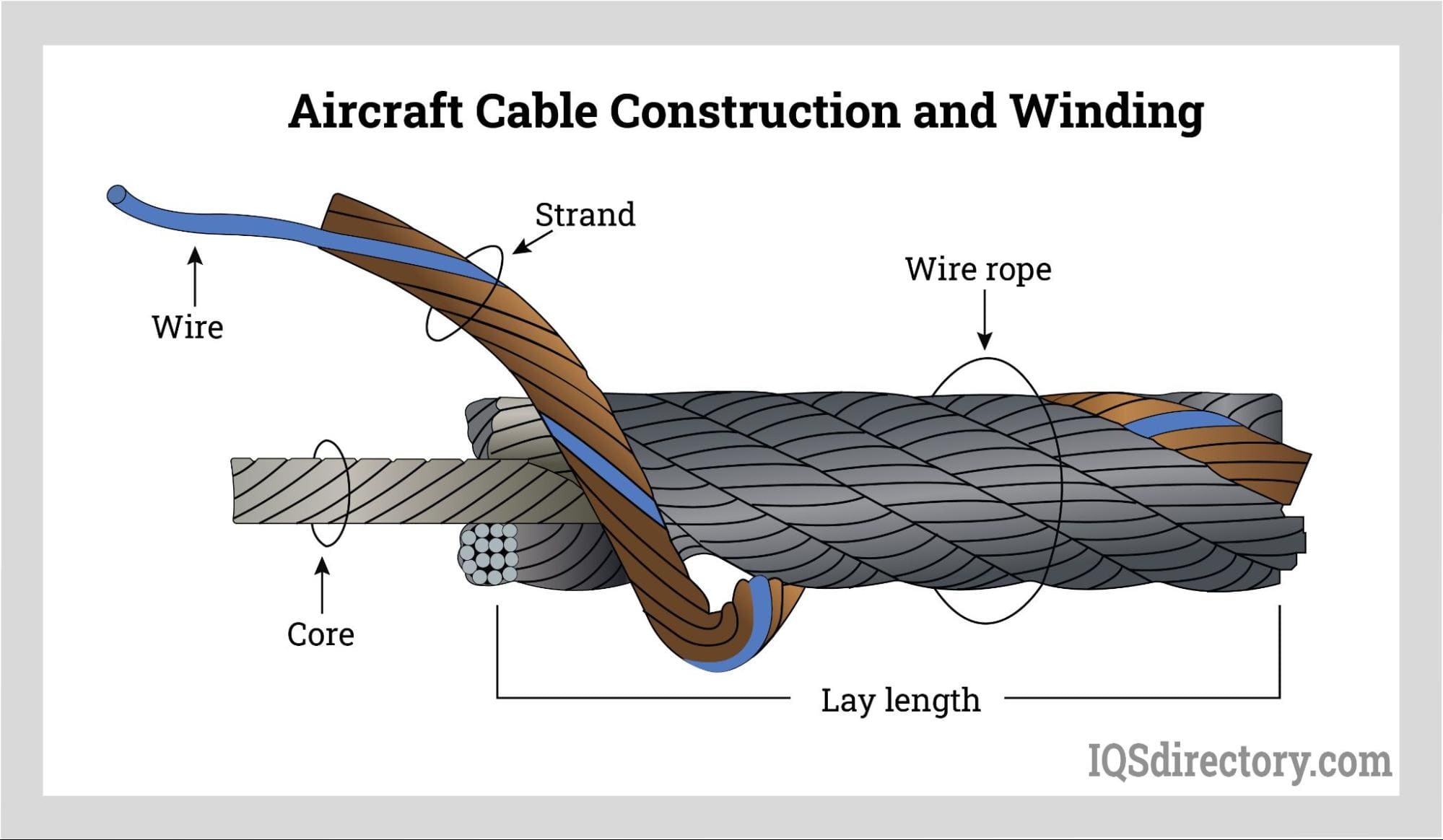
- Stranding: Individual wires are twisted together to create strands. The most common configurations are 7×7 and 7×19, which provide flexibility and strength. This process is critical, as the arrangement directly affects the cable’s load-bearing capacity and flexibility.
- Compacting: In some cases, strands are compacted to reduce the overall diameter while maintaining strength. This technique is particularly useful for applications requiring tight routing in confined spaces.
3. Assembly
After forming the strands, the next step is assembly, where the strands are combined into a single cable.
- Laying Up: The individual strands are laid together in a precise manner, often using automated machinery to ensure consistency.
- Tensioning: During this stage, the cable is tensioned to eliminate slack and ensure uniform strength distribution throughout the length of the cable.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing involves finishing processes that enhance the cable’s performance and durability.
- Coating: Cables may be coated with protective materials to enhance corrosion resistance. Stainless steel cables may receive passivation treatments, while galvanized cables are hot-dipped in zinc.
- Marking and Packaging: Each cable is marked with specifications such as diameter, material grade, and breaking strength before being packaged for shipment.
Quality Assurance in Aircraft Cable Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every cable produced meets international standards and customer specifications.
International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant international standards that govern the manufacturing of aircraft cables, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, ensuring consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- API (American Petroleum Institute): For cables used in oil and gas applications, compliance with API specifications is crucial.
- CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established throughout the manufacturing process to catch defects early and ensure compliance with standards:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspections of raw materials, focusing on mechanical properties and compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process, including strand formation and assembly, to ensure adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished cables, including tensile strength tests, fatigue resistance assessments, and corrosion resistance evaluations.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are commonly used to verify the quality and performance of aircraft cables:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the maximum load the cable can withstand before failure.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses the cable’s durability under repeated bending and loading conditions.
- Corrosion Testing: Evaluates the cable’s resistance to various corrosive environments, ensuring longevity in harsh conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers’ manufacturing facilities to ensure compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Requesting Reports: Ask for detailed QC reports that outline inspection results, testing outcomes, and compliance with international standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party inspectors to validate the quality of the products before they are shipped.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulations regarding cable specifications. Buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with local and international standards relevant to their market.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural nuances in business practices can facilitate better communication and expectations regarding quality assurance.
- Supply Chain Considerations: Buyers should consider the entire supply chain, from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, ensuring that quality standards are maintained at every stage.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for aircraft cables is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, finishing, and rigorous quality control, buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products that meet their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Related Video: Boeing & Airbus Factory✈️2025 Production line and Assembly – Manufacturing process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cable aircraft Sourcing
When sourcing aircraft cables, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. The cost of aircraft cables can be broken down into several key components:
Cost Components
-
Materials:
– The choice between stainless steel and galvanized steel significantly affects material costs. Stainless steel cables, while more expensive, offer superior corrosion resistance and longevity, making them ideal for harsh environments. Galvanized cables are more economical but may not provide the same durability. -
Labor:
– Labor costs can vary based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs may provide a competitive advantage, but it is crucial to ensure that quality standards are maintained. -
Manufacturing Overhead:
– This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead, which can be reflected in the pricing. -
Tooling:
– The need for specialized tools for cable production can add to costs. Custom orders may require additional investment in tooling, which can influence pricing. -
Quality Control (QC):
– Rigorous quality control processes are essential in ensuring safety and compliance with aviation standards. The costs associated with QC should be factored into the overall pricing of aircraft cables. -
Logistics:
– Shipping costs, including freight and customs duties, can vary significantly based on the origin and destination of the cables. This is particularly relevant for international buyers, who need to consider the total logistics expenses when calculating the final price. -
Margin:
– Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can vary based on market competition and supplier reputation.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of aircraft cables:
- Volume/MOQ:
-
Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization:
-
Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials:
-
As mentioned, the choice of materials will significantly impact pricing. Stainless steel is generally more expensive than galvanized options.
-
Quality/Certifications:
-
Products meeting higher quality standards or certifications (e.g., FAA, ASTM) may come at a premium. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications based on their application.
-
Supplier Factors:
-
Established suppliers with a reputation for quality may charge more. However, this often correlates with reliability and performance.
-
Incoterms:
- Understanding the Incoterms used in international shipping is crucial. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the total cost and responsibilities of buyers.
Buyer Tips
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies to enhance cost-efficiency:
- Negotiation:
-
Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially on larger orders. Leverage competition among suppliers to secure favorable pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
-
Evaluate the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance costs, lifespan, and potential downtime when choosing suppliers.
-
Pricing Nuances:
-
Be aware of regional pricing differences. Factors such as import tariffs, local market conditions, and exchange rates can affect overall costs.
-
Supplier Relationships:
- Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service levels. Regular communication and feedback can foster trust and collaboration.
Disclaimer
Prices for aircraft cables can fluctuate based on market conditions, material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure they receive competitive pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential cable aircraft Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘cable aircraft’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cable aircraft
Key Technical Properties of Aircraft Cables
Understanding the technical properties of aircraft cables is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right product for their applications. Here are some essential specifications:
-
Material Grade
Aircraft cables are typically made from stainless steel (grades 302, 304, and 316) or galvanized steel. The choice of material affects corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and overall durability. For instance, 316 stainless steel offers superior resistance to saltwater, making it ideal for marine applications. Buyers must assess the environment in which the cable will be used to choose the appropriate grade. -
Strand Configuration
Common configurations include 7×7 and 7×19, referring to the number of strands and wires per strand. The 7×19 configuration provides enhanced flexibility and fatigue resistance, making it suitable for applications involving repeated motion. Understanding strand configurations helps buyers evaluate the cable’s performance under various loading conditions. -
Breaking Strength
This specification indicates the maximum load the cable can withstand before failure. Breaking strengths can range significantly, often from hundreds to thousands of pounds, depending on diameter and material. Buyers should calculate the loads their cables will bear and select a breaking strength that offers a suitable safety margin. -
Diameter
Aircraft cables are available in diameters ranging from 3/64″ to 3/8″. The diameter impacts the cable’s flexibility, strength, and compatibility with hardware. A smaller diameter may be necessary for tight spaces, while larger diameters can support greater loads. Buyers should ensure that the selected diameter aligns with their operational requirements. -
Corrosion Resistance
This property determines how well a cable can withstand environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and salt. Stainless steel cables generally offer higher corrosion resistance compared to galvanized options. For international buyers operating in diverse climates, selecting the right corrosion-resistant material is vital to ensure longevity and reliability. -
Fatigue Resistance
This refers to a cable’s ability to endure repeated bending and stress without breaking. Cables with high fatigue resistance are essential for applications involving dynamic loads, such as flight controls. Buyers must consider this property when choosing cables for critical operations.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B marketplace. Here are some key terms:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces components or products that are used in another company’s end products. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers source high-quality cables that meet specific requirements.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This specifies the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers should be aware of MOQs to plan their purchasing and inventory management effectively, especially when sourcing from international suppliers. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products or services. It’s a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare options and negotiate terms. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers mitigate risks and clarify costs associated with their purchases. -
Lead Time
This refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Buyers must consider lead times when planning projects to avoid delays in operations. -
Certification Standards
These are regulatory benchmarks that products must meet to ensure safety and performance. Familiarity with certification standards (e.g., FAA, ASTM) is crucial for buyers to ensure compliance and reliability in their applications.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terminologies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure the most suitable aircraft cables for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the cable aircraft Sector
Global demand for aircraft cables is being driven by several interrelated factors, including advancements in aerospace technology, increased safety regulations, and the growth of various industries that utilize these cables beyond aviation. As international B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s crucial to understand the dynamics of this market. The aerospace sector is experiencing a resurgence due to the expansion of low-cost carriers and the rising demand for air travel. In parallel, industries such as agriculture, construction, and marine are increasingly incorporating aircraft cables due to their high tensile strength and versatility.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with digital platforms enhancing supplier visibility and simplifying procurement processes. B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics to optimize supply chains, predict market fluctuations, and assess supplier performance. Additionally, the trend towards just-in-time inventory practices is pushing manufacturers to adopt more flexible production methods, allowing for rapid response to changing demands. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for buyers operating in diverse markets, where conditions can shift dramatically.
In terms of market dynamics, geopolitical factors and trade regulations are influencing sourcing strategies. Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may face different regulatory requirements compared to those in Africa and South America. Understanding these nuances is essential for ensuring compliance and maintaining a competitive edge. As the market continues to evolve, staying informed about these trends will empower buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of manufacturing and sourcing aircraft cables is a growing concern for B2B buyers. The production process can generate significant waste and emissions, making it essential for companies to adopt sustainable practices. Ethical sourcing is becoming increasingly important as consumers and regulatory bodies demand transparency in supply chains. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications like ISO 14001 or those who utilize recycled materials in their products.
In the context of aircraft cables, utilizing stainless steel over galvanized options can enhance sustainability. Stainless steel cables, particularly those made from recycled materials, offer superior durability and longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers who adhere to green manufacturing processes can minimize the carbon footprint associated with production. As such, B2B buyers are encouraged to assess the sustainability credentials of their suppliers, ensuring that their procurement practices align with broader environmental goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The use of aircraft cables has evolved significantly since their inception. Initially designed for aviation applications, these cables have found utility across various sectors due to their unique properties, such as high tensile strength and flexibility. The development of advanced materials and manufacturing techniques has further enhanced the performance characteristics of aircraft cables, allowing them to meet stringent safety and regulatory standards across different industries. This evolution reflects a broader trend of innovation within the aerospace and manufacturing sectors, making aircraft cables a vital component in contemporary engineering and construction applications. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can provide insights into the reliability and versatility of aircraft cables, guiding informed purchasing decisions.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cable aircraft
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for aircraft cables?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, certifications, and quality control processes. Check if they comply with relevant standards such as FAA, ASTM, or MIL specifications. Request references from other clients, especially those in your region, to gauge their reliability and service quality. Additionally, assess their production capabilities to ensure they can meet your specific requirements, including custom cable solutions. Engaging in direct communication can also provide insights into their customer service and responsiveness. -
Can aircraft cables be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for aircraft cables to meet unique application needs. This may include variations in diameter, strand construction (e.g., 7×7 or 7×19), and material grade (stainless steel vs. galvanized). When seeking customization, communicate your specifications clearly to the supplier, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and intended use. Be prepared to discuss the trade-offs between cost and performance, as tailored solutions may involve higher lead times and minimum order quantities.
-
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for aircraft cables?
Minimum order quantities for aircraft cables can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Generally, MOQs can range from 100 meters to several kilometers for standard products. Lead times also vary, often between 2 to 6 weeks for standard orders, while custom orders may take longer due to additional manufacturing processes. Always clarify these details upfront with your supplier to align your project timelines and avoid potential delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing aircraft cables internationally?
Payment terms can vary by supplier and region, but common practices include advance payment, letter of credit, or net 30-60 days after delivery. For international transactions, consider using secure payment methods that protect both parties, such as escrow services or international bank transfers. Discuss and negotiate terms prior to placing your order to ensure clarity and prevent disputes. Understanding local customs and practices in your supplier’s country can also aid in establishing favorable payment terms. -
How can I ensure the quality of aircraft cables before purchase?
To ensure quality, request certifications and test reports from your supplier that verify compliance with industry standards. Look for documentation such as ISO certifications, material certifications, and test results demonstrating tensile strength and fatigue resistance. If possible, arrange for a pre-shipment inspection or consider third-party quality assurance services to evaluate the product before it arrives. Establishing a clear quality assurance process with your supplier is essential to minimize risks associated with faulty products. -
What certifications should I look for in aircraft cable suppliers?
Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 (Quality Management Systems), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and specific industry standards such as ASTM, FAA, and MIL-DTL. These certifications indicate that the supplier adheres to rigorous quality and safety standards. Additionally, inquire if they have certifications relevant to your specific region or industry, as these can affect regulatory compliance and product suitability for your applications. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aircraft cables?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of aircraft cables. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air, sea, or land), costs, and transit times based on your location. Ensure your supplier has experience with international shipping and understands customs regulations in your country. Discuss who will be responsible for import duties and taxes. Furthermore, consider using a freight forwarder to simplify the shipping process, especially for large or complex orders. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers effectively?
To resolve disputes effectively, maintain clear and open communication with your supplier from the outset. Document all agreements, specifications, and communications in writing to provide a clear reference. If a dispute arises, approach the situation calmly and professionally, seeking to understand the supplier’s perspective. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternative dispute resolution methods to avoid lengthy legal processes. Familiarize yourself with the supplier’s terms and conditions regarding disputes to ensure you are prepared to navigate any potential issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cable aircraft
The strategic sourcing of aircraft cables is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliable solutions in diverse applications, from aviation to agriculture. Understanding the distinct advantages of stainless steel versus galvanized cables allows buyers to make informed decisions that align with their specific operational needs. Key considerations include tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and application suitability, all of which impact the overall performance and longevity of the cables.
In today’s dynamic global market, a strategic sourcing approach not only ensures compliance with rigorous safety standards but also enhances operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize relationships with reputable manufacturers and suppliers to access high-quality products that meet their unique requirements.
As the demand for versatile and durable aircraft cables continues to grow, now is the time for international B2B buyers to leverage these insights. By investing in strategic sourcing, companies can position themselves competitively, ensuring they are well-equipped to meet future challenges and opportunities in their industries. Embrace the potential of aircraft cables and unlock new avenues for growth today.