Master the Essentials of Strand Wire Sourcing for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for strand wire
Strand wire is a vital component in various industries, playing a crucial role in electrical connectivity, structural applications, and mechanical systems. As international B2B buyers navigate the complexities of sourcing strand wire, understanding its significance and the intricacies of the supply chain becomes essential. This guide is designed to empower buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe by providing comprehensive insights into strand wire, including its types, materials, manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and cost considerations.
This resource delves into the nuances of strand wire production, covering critical topics such as the selection of raw materials like copper and aluminum, the manufacturing steps involved—from drawing to stranding—and the importance of quality testing. Additionally, the guide offers a thorough overview of the global market landscape, highlighting key suppliers and emerging trends that can influence purchasing decisions.
By equipping buyers with actionable information, this guide facilitates informed sourcing choices, enabling businesses to optimize their procurement strategies. Whether you’re in Colombia, Australia, or anywhere in between, understanding the global market for strand wire will enhance your ability to secure reliable and cost-effective solutions tailored to your specific needs. With the right knowledge at your fingertips, you can confidently navigate the market and forge successful partnerships that drive your business forward.
Understanding strand wire Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid Strand Wire | Composed of a single conductor, offers high conductivity | Electrical installations, power distribution | Pros: Lower resistance, high durability. Cons: Less flexible, difficult in dynamic applications. |
| Stranded Wire | Made of multiple thin wires twisted together, enhances flexibility | Automotive wiring, appliances, portable tools | Pros: Greater flexibility, easier to handle. Cons: Slightly higher resistance compared to solid wire. |
| Multi-Strand Wire | Features several layers of strands, providing additional strength | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Pros: High strength, excellent fatigue resistance. Cons: More complex manufacturing process may increase costs. |
| Braided Wire | Composed of braided strands for maximum flexibility and durability | Robotics, wearable technology, aerospace | Pros: Superior flexibility and resilience. Cons: May require specialized connectors and installation techniques. |
| PVC Insulated Wire | Coated with PVC for protection against environmental factors | General electrical wiring, construction | Pros: Cost-effective, good insulation properties. Cons: Limited temperature resistance compared to other insulations. |
Solid Strand Wire
Solid strand wire is characterized by its single conductor, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal resistance and maximum conductivity. This type is commonly used in permanent electrical installations and power distribution systems. When purchasing solid strand wire, buyers should consider the environment in which the wire will be installed, as it is less flexible and may not perform well in applications that require frequent movement or bending.
Stranded Wire
Stranded wire consists of multiple thin wires twisted together, providing enhanced flexibility. This makes it a popular choice for automotive wiring and appliances where movement is common. Buyers should assess the specific application needs, as stranded wire may exhibit slightly higher resistance than solid wire, but its ease of handling often outweighs this drawback in dynamic environments.
Multi-Strand Wire
Multi-strand wire incorporates several layers of strands, offering exceptional strength and fatigue resistance. This type is particularly suited for heavy machinery and industrial applications where high durability is essential. B2B buyers should evaluate the manufacturing process and overall cost, as the complexity of multi-strand wire can lead to increased pricing, but the benefits often justify the investment.
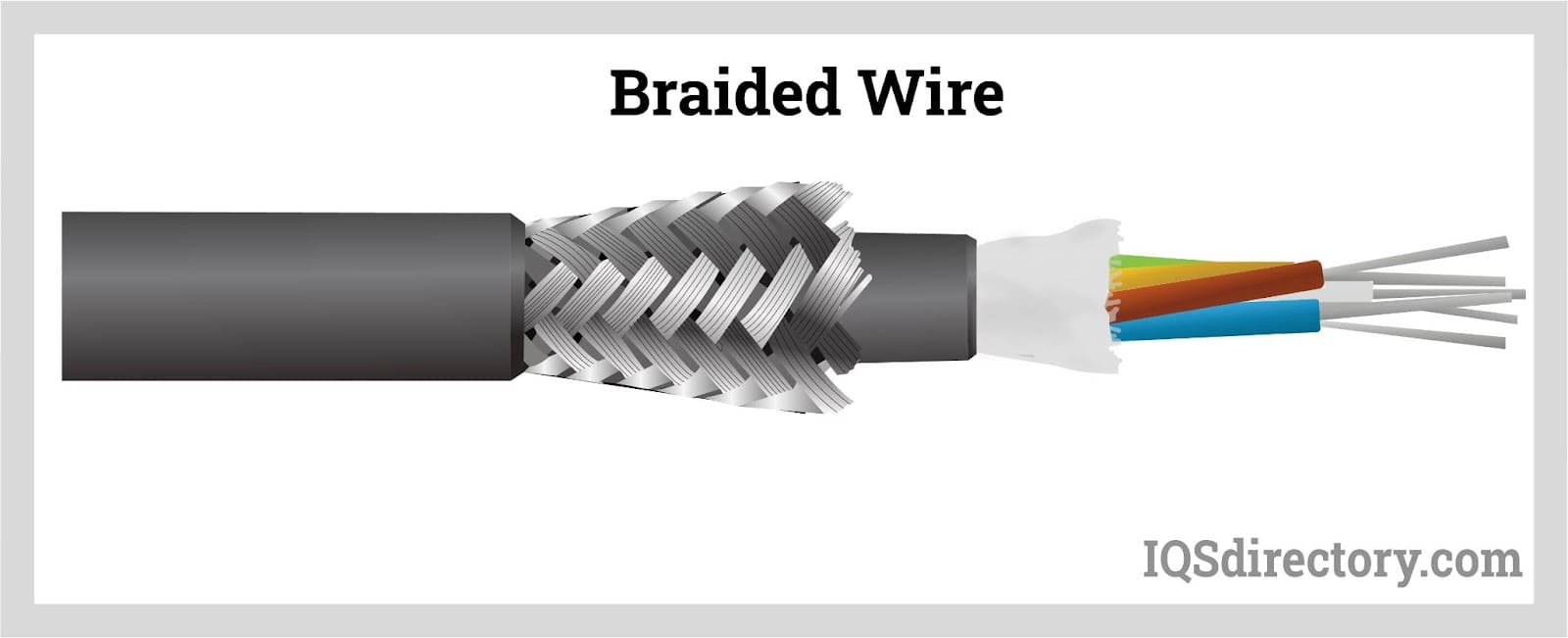
Braided Wire
Braided wire is formed by braiding multiple strands together, maximizing both flexibility and durability. It is commonly used in robotics, wearable technology, and aerospace applications where adaptability is crucial. Buyers should consider the specific connector requirements and installation techniques, as braided wire may necessitate specialized components, potentially affecting overall project costs.
PVC Insulated Wire
PVC insulated wire is coated with polyvinyl chloride, providing effective protection against various environmental factors. This type is widely used in general electrical wiring and construction projects due to its cost-effectiveness. When purchasing PVC insulated wire, buyers should be aware of its limitations in temperature resistance compared to other insulation materials, ensuring it meets the specific needs of their application.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of strand wire
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of strand wire | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Reinforcement in concrete structures | Enhances structural integrity and durability of buildings | Ensure compliance with local building codes and standards. |
| Telecommunications | Aerial and underground cabling | Reliable connectivity for data transmission and communication | Assess cable flexibility and resistance to environmental factors. |
| Automotive | Wiring harnesses in vehicles | Improved safety and performance of electrical systems | Focus on weight, temperature resistance, and corrosion protection. |
| Energy | Transmission lines for power distribution | Efficient and safe energy transfer over long distances | Evaluate conductor size, material, and insulation for specific needs. |
| Manufacturing | Machinery and equipment wiring | Ensures operational efficiency and safety in production | Consider the wire’s tensile strength and flexibility for specific applications. |
Construction
In the construction industry, strand wire is primarily used as reinforcement in concrete structures, such as bridges and high-rise buildings. By incorporating strand wire, builders enhance the tensile strength of concrete, which is inherently strong in compression but weak in tension. This application helps in preventing structural failures and extending the lifespan of buildings. International buyers should ensure that the strand wire meets local building codes and is sourced from reputable manufacturers to guarantee quality and compliance with safety standards.
Telecommunications
Strand wire plays a crucial role in the telecommunications sector, particularly in the installation of aerial and underground cabling systems. These cables are essential for providing reliable connectivity for data transmission and communication services. In regions with varying climates, buyers must assess the flexibility and environmental resistance of the strand wire to ensure optimal performance over time. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding telecommunications infrastructure can facilitate smoother project execution.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, strand wire is utilized in wiring harnesses that connect various electrical components in vehicles. This application is critical for enhancing the safety and performance of electrical systems, including lighting, ignition, and infotainment. Buyers should prioritize sourcing strand wire that is lightweight yet durable, with high-temperature resistance to withstand the automotive environment. Ensuring compliance with industry standards for automotive wiring can also prevent potential safety issues.
Energy
Strand wire is extensively used in the energy sector, particularly for power transmission lines. It facilitates the efficient and safe transfer of electricity over long distances, which is vital for connecting power generation facilities with consumers. Buyers in this sector must evaluate the size and material of the strand wire to ensure optimal conductivity and insulation properties. Additionally, understanding regional energy regulations and environmental considerations is essential for successful sourcing and installation.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, strand wire is integral to the wiring of machinery and equipment, ensuring operational efficiency and safety in production processes. This application helps minimize downtime caused by electrical failures and enhances the overall performance of manufacturing operations. Buyers should consider the tensile strength and flexibility of the strand wire to meet specific machinery requirements. Furthermore, sourcing from suppliers with a solid reputation for quality can significantly impact production reliability.
Related Video: Wire Drawing Process Step by Step: From Metal Rod to Wire
Strategic Material Selection Guide for strand wire
When selecting materials for strand wire, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that affect performance, cost, and suitability for specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in strand wire manufacturing: copper, aluminum, stainless steel, and fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP). Each material has unique properties, advantages, and limitations that influence their use in different industries.
Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is renowned for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and ductility. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 200°C) and has good corrosion resistance, especially when treated with protective coatings.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity makes it ideal for electrical applications, ensuring minimal energy loss. However, it is more expensive than alternatives like aluminum, which can increase overall project costs. Additionally, copper is heavier, making it less suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor.
Impact on Application:
Copper is widely used in power transmission and telecommunications due to its superior conductivity. It is compatible with various media, including water and gas, making it versatile across multiple sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B3 and DIN 48201. In regions like Europe, environmental regulations regarding copper extraction and recycling may also impact sourcing decisions.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has a lower thermal and electrical conductivity compared to copper. It can operate effectively in temperatures up to 80°C.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its cost-effectiveness and lightweight nature, making it suitable for overhead power lines and applications requiring mobility. However, its lower conductivity means that larger diameters are necessary to achieve the same performance as copper, which can complicate design and increase material use.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is commonly used in power distribution and transmission lines, especially in regions with high humidity or corrosive environments. Its resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for outdoor applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider standards such as ASTM B231 and JIS C 3102. In Africa and South America, the availability of aluminum may vary, influencing sourcing strategies.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers high tensile strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand extreme temperatures (up to 800°C). It is less conductive than copper and aluminum.
Pros & Cons:
Stainless steel is highly durable and suitable for harsh environments, making it ideal for industrial applications. However, its cost is significantly higher than both copper and aluminum, which can be a deterrent for large-scale projects.
Impact on Application:
This material is often used in marine, aerospace, and chemical processing industries due to its resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand high pressures.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with ASTM A313 and EN 10088 standards is crucial. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should also consider the implications of stringent environmental regulations on stainless steel sourcing.
Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP)
Key Properties:
FRP is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers, typically glass or carbon. It is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of FRP is its resistance to corrosion and chemical damage, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it lacks the electrical conductivity of metal options, limiting its use primarily to structural applications rather than electrical transmission.
Impact on Application:
FRP is increasingly used in applications such as telecommunications and construction, where lightweight and corrosion-resistant materials are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with ASTM D638 and ISO 527 standards. In regions like Africa and South America, the adoption of FRP may be limited due to higher initial costs and less familiarity with the material.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for strand wire | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Power transmission, telecommunications | Excellent electrical conductivity | High cost, heavier weight | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines, outdoor wiring | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower conductivity, larger diameter | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Marine, aerospace, chemical processing | High durability, corrosion-resistant | High cost, less conductive | High |
| Fiber-Reinforced Polymer | Telecommunications, structural applications | Corrosion-resistant, lightweight | Not conductive, limited electrical use | Medium |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for strand wire
The manufacturing of strand wire involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets stringent quality and performance standards. This section provides an in-depth overview of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices relevant to B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process for strand wire typically consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
Raw Material Selection
The first step involves the selection of high-quality materials, usually copper or aluminum, due to their excellent conductivity and reliability. The metals are sourced from reputable suppliers and are often subjected to initial quality checks to ensure they meet industry standards.
Wire Rod Production
Once the raw materials are selected, they are melted and cast into wire rods. This process may include casting and rolling to ensure uniform diameter and high tensile strength. The rods serve as the base material for subsequent wire drawing.
2. Forming
Wire Drawing
Wire rods are then cold-drawn through a series of progressively smaller dies. This step is crucial as it determines the wire’s final gauge, flexibility, and strength. Lubrication is applied to minimize friction and prevent breakage during this process.
Annealing
After drawing, the wire undergoes annealing—a heat treatment that softens the metal, enhancing its ductility. This is particularly important for copper wire, as it restores flexibility without compromising electrical properties.
3. Assembly
Stranding
In this stage, multiple wires are twisted together to create stranded wire. This method increases flexibility and resistance to breakage, making it suitable for dynamic applications. The choice between solid and stranded wire should be based on the application requirements.
4. Finishing
Insulation and Jacketing
The final step involves applying insulation materials such as PVC or XLPE to protect the wire from environmental factors and electrical hazards. This step is essential for ensuring the safety and longevity of the wire in various applications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of strand wire. It ensures that the product complies with international and industry-specific standards, thereby reducing risks for B2B buyers.
International Standards
ISO 9001
This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements. Compliance with ISO 9001 is a strong indicator of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality.
CE Marking
In Europe, CE marking indicates that the wire complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards. It is essential for B2B buyers in Europe to verify that suppliers have CE certification for their products.
API Standards
For buyers in sectors such as oil and gas, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards is crucial. These standards ensure that the wire meets specific performance criteria necessary for high-stress applications.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several checkpoints designed to catch defects early:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, periodic checks are conducted to monitor the quality of the wire at various stages, including drawing and annealing.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipping, the finished wire undergoes comprehensive testing to verify its electrical properties, strength, and compliance with standards.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the testing methods used to ensure quality:
- Electrical Conductivity Testing: Measures the wire’s ability to conduct electricity, which is crucial for performance.
- Tensile Strength Testing: Assesses the wire’s strength and flexibility, ensuring it can withstand operational stresses.
- Visual Inspection: Checks for physical defects such as surface irregularities or inconsistencies in insulation.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control practices of suppliers:
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their quality management systems and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, results, and compliance with standards can help assess a supplier’s reliability.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices, ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from different regions may encounter unique challenges when it comes to quality assurance:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and quality standards is essential for effective communication and collaboration.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, necessitating thorough research to ensure compliance.
- Logistical Considerations: Buyers should be aware of the potential impact of logistics on quality, such as how transportation methods may affect product integrity.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for strand wire is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on reputable suppliers, verifying quality control measures, and understanding international standards, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure the reliability of their wire products across various applications.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for strand wire Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of strand wire is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following analysis breaks down the cost components and price influencers, providing actionable insights for effective sourcing.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in strand wire production is the raw materials, typically copper or aluminum. The market prices for these metals fluctuate based on global supply and demand, geopolitical factors, and mining costs. Buyers should monitor commodity markets to understand potential price changes.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly across regions. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers can offer more competitive pricing. However, skilled labor is essential for quality production, so consider the balance between cost and expertise.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to factory operation, maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can help minimize overhead, which is vital for maintaining competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in machinery and tools for manufacturing strand wire can be substantial. These costs are often amortized over the production volume, making it essential to consider the minimum order quantities (MOQs) when negotiating prices.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of strand wire through rigorous testing and certification processes adds to the overall cost. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust QC measures to avoid future costs related to defective products.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary significantly based on the origin of the wire and the destination. Consideration of transportation methods, customs duties, and insurance is critical, especially for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market competition, supplier reputation, and the complexity of the order.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often attract discounts due to economies of scale. Negotiating lower prices per unit based on higher volumes can significantly reduce overall costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications for strand wire, such as diameter, insulation type, and tensile strength, can affect pricing. Customized solutions may incur additional costs, so it’s vital to clearly define requirements upfront.
-
Materials and Quality: The choice between standard and premium materials will influence price. Higher quality or certified materials typically command higher prices but can result in lower maintenance costs and increased lifespan.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier experience, reputation, and location can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a history of reliability may charge more, but they often provide better service and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The terms of sale can significantly impact costs. Understanding whether costs include shipping, insurance, and duties (FOB, CIF, etc.) is essential for calculating total expenses.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures and potential discounts based on volume or long-term contracts. Building strong relationships can lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate total cost of ownership rather than just upfront costs. This includes considering durability, maintenance, and potential failure rates of the wire.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, local regulations, and import tariffs that can affect the final price. Understanding the local market can provide leverage during negotiations.
-
Research: Thoroughly vet suppliers for their pricing models, production capabilities, and delivery timelines. Requesting quotes from multiple suppliers can help gauge market rates and identify the best value.
Disclaimer
Prices for strand wire can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers are advised to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they are making informed decisions.
Spotlight on Potential strand wire Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘strand wire’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for strand wire
Key Technical Properties of Strand Wire
Understanding the technical properties of strand wire is crucial for international B2B buyers, as these specifications directly impact performance and application suitability. Here are some essential properties:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of the wire based on its composition, typically copper or aluminum.
– Importance: Material grade affects conductivity, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. For instance, high-grade copper offers superior conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. Buyers should ensure the material aligns with project requirements to avoid costly failures. -
Stranding Configuration
– Definition: The arrangement of individual wires that make up the strand wire, which can be either solid or stranded.
– Importance: Stranded wire provides flexibility and is preferred in applications requiring movement, while solid wire is more rigid and ideal for permanent installations. Understanding the configuration helps buyers select the right type for specific applications. -
Diameter and Tolerance
– Definition: The nominal diameter of the wire and the permissible variation in size.
– Importance: Tolerance levels affect the wire’s electrical resistance and mechanical properties. Accurate diameter specifications ensure compatibility with connectors and other components, reducing the risk of electrical failures.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tensile Strength
– Definition: The maximum amount of tensile (pulling) stress that the wire can withstand before breaking.
– Importance: High tensile strength is essential in applications subjected to mechanical stress, such as overhead power lines. Buyers should assess tensile strength to ensure the wire can withstand environmental conditions and operational loads. -
Electrical Conductivity
– Definition: A measure of how easily electricity flows through the wire, typically expressed in siemens per meter (S/m).
– Importance: Higher conductivity results in lower energy losses during transmission, enhancing efficiency. Buyers must consider conductivity when selecting wire for electrical applications to optimize performance. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: The wire’s ability to resist deterioration from environmental factors, including moisture and chemicals.
– Importance: Corrosion can lead to significant performance degradation over time. Selecting wire with appropriate corrosion resistance is critical for applications in harsh environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Common Trade Terminology in the Strand Wire Industry
Familiarity with industry-specific jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are key terms that buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces components that are used in another company’s end product.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensures that the wire meets the necessary specifications for integration into larger systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers must negotiate favorable terms to avoid excess stock or increased costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ enables buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed decision-making and cost-effective purchasing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage shipping logistics and costs effectively, ensuring clarity in delivery terms and risk transfer. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Relevance: Awareness of lead times is critical for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should factor in lead times when making procurement decisions to avoid delays in project execution. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Compliance with specific standards (e.g., ISO, ASTM) that ensure product quality and safety.
– Relevance: Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to recognized certification standards, as this guarantees the wire’s reliability and performance in its intended application.
By understanding these properties and terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement strategies and project outcomes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the strand wire Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The strand wire market is witnessing significant evolution driven by technological advancements and global economic dynamics. Key drivers include the increasing demand for efficient electrical transmission solutions and the rise of renewable energy projects, particularly in Africa and South America. The shift towards urbanization and infrastructure development in emerging markets is propelling the need for high-quality strand wire products.
International B2B buyers are increasingly leveraging digital platforms for sourcing, which facilitates better supplier visibility and streamlined procurement processes. Innovations in manufacturing, such as automation and the use of AI for quality control, are enhancing product reliability and reducing lead times. Additionally, there’s a growing emphasis on customization, allowing buyers to specify unique requirements tailored to specific applications.
Another emerging trend is the shift towards lightweight materials, particularly in the automotive and aerospace sectors, where strand wire is essential for reducing overall vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in Europe, where stringent environmental regulations drive the need for sustainable solutions.
With geopolitical tensions affecting supply chains, buyers must remain vigilant about sourcing strategies, ensuring they have contingency plans to mitigate risks associated with fluctuating raw material prices and availability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone in the strand wire sector, with increasing pressure on manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly practices. The environmental impact of wire production, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, has led to a demand for greener manufacturing processes. International buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that utilize renewable energy sources and implement waste reduction strategies.
Ethical sourcing is another critical consideration. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparency throughout their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. Furthermore, the use of recycled materials in strand wire production is gaining traction, aligning with global efforts to reduce the carbon footprint of industrial operations.
Investing in suppliers that prioritize sustainability not only mitigates environmental risks but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust, which is increasingly vital in today’s market landscape.
Brief Evolution/History
The strand wire industry has evolved significantly over the past century, driven by advancements in metallurgy and manufacturing processes. Initially dominated by copper, the market has diversified to include aluminum and composite materials, enhancing the range of applications across various sectors. The introduction of technology in the late 20th century, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and automated production lines, has further refined the manufacturing process, leading to higher efficiency and reduced costs.
Today, the focus on sustainability and ethical sourcing marks a new chapter in the strand wire industry’s evolution, reflecting broader societal shifts towards environmental responsibility and corporate accountability. As international B2B buyers continue to navigate this dynamic landscape, understanding these historical trends can provide valuable insights into future market developments.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of strand wire
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers for strand wire?
When vetting suppliers for strand wire, prioritize their industry experience, certifications (such as ISO 9001), and references from previous clients. Assess their production capabilities and technology, ensuring they can meet your specifications. Evaluate their financial stability to avoid disruptions in supply. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and whether they perform regular inspections to maintain standards. This thorough vetting will help mitigate risks associated with unreliable suppliers. -
Can I customize strand wire specifications according to my needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for strand wire. You can specify dimensions, materials (like copper or aluminum), coating types, and stranding configurations. It’s essential to communicate your requirements clearly, including the intended application, as this will influence the design and material choices. Discussing customization early in the sourcing process can lead to better alignment between your needs and the supplier’s capabilities. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for strand wire?
Minimum order quantities for strand wire vary by supplier and can range from several hundred meters to several kilometers. Lead times typically depend on the complexity of the order, but standard timelines are usually between 4 to 12 weeks. For urgent needs, some suppliers may offer expedited production options, albeit at a higher cost. Always confirm MOQs and lead times before finalizing your order to ensure they align with your project timelines. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Reputable suppliers should have robust quality assurance (QA) measures in place, including material testing, dimensional checks, and performance assessments. Look for suppliers that provide certifications for their products, such as UL or CE marks, which indicate compliance with international safety standards. Request documentation of their QA processes and inquire about third-party testing to ensure the strand wire meets your specifications and industry standards. -
How do payment terms typically work in international transactions?
Payment terms in international transactions can vary widely. Common methods include letters of credit, advance payments, or payment upon delivery. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that protect both parties, especially in new supplier relationships. Many buyers prefer a letter of credit as it provides security. Always clarify payment methods and timelines before placing an order to avoid misunderstandings that could affect delivery and operations. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing strand wire?
When importing strand wire, consider shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs. Ensure that your supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance, including invoices and certificates of origin. Additionally, evaluate shipping timelines and choose a reliable logistics partner familiar with international shipping protocols. It’s wise to account for potential delays in transit and customs to avoid disruptions in your supply chain. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers effectively?
Dispute resolution with suppliers should begin with clear communication. Document all agreements and interactions to have a record if issues arise. Establish a formal dispute resolution process in your contracts, such as mediation or arbitration, which can provide a structured approach to resolving conflicts. If a dispute escalates, consider involving legal counsel familiar with international trade law to navigate the complexities and protect your interests.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What role do certifications play in the sourcing of strand wire?
Certifications are crucial in the sourcing of strand wire as they serve as proof of compliance with industry standards and regulations. They ensure that the wire meets specific safety, quality, and performance criteria, which is particularly important in sectors like construction and manufacturing. When evaluating suppliers, prioritize those with relevant certifications, such as ISO, UL, or CE, as these indicate a commitment to quality and reliability, ultimately reducing risks in your supply chain.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for strand wire
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for strand wire is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize their supply chains. Key takeaways include the importance of understanding the wire manufacturing process, from raw material selection to quality testing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate transparency and a commitment to quality, as this can significantly impact product performance and reliability.
Moreover, embracing technological advancements in manufacturing and logistics can yield cost savings and enhance product availability. Buyers are encouraged to establish strong relationships with suppliers, fostering collaboration and innovation. This approach not only ensures a steady supply of high-quality strand wire but also facilitates adaptability in a rapidly changing market.
Looking ahead, international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should remain proactive in their sourcing strategies. By staying informed about industry trends and emerging technologies, businesses can position themselves for success. Engage with suppliers, explore new markets, and leverage digital tools to enhance procurement processes. The future of strand wire sourcing is promising, and with the right strategies, your business can thrive in this dynamic landscape.