Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Nickle Metal
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for nickle metal
Navigating the intricate landscape of the global nickel market is essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving industries. Nickel metal plays a pivotal role in various applications, from stainless steel production to the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) battery sector. As the demand for sustainable and high-performance materials rises, understanding the nuances of nickel sourcing, processing, and pricing becomes increasingly critical.
This guide is designed to equip international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like the UAE and Saudi Arabia—with the insights necessary for informed sourcing decisions. Throughout the guide, we will delve into the different types of nickel, explore materials and manufacturing processes, and examine quality control standards that ensure product reliability.
Buyers will also find an analysis of leading suppliers, comprehensive cost structures, and an overview of the market dynamics influencing pricing trends. Moreover, a dedicated section addressing frequently asked questions will provide clarity on common concerns, enabling businesses to navigate complexities with confidence.
By leveraging the actionable insights presented in this guide, B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance supply chain resilience and foster sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive global market.
Understanding nickle metal Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel 200 | Pure nickel (99.6% Ni) with excellent corrosion resistance | Chemical processing, food processing | Pros: High purity, good mechanical properties. Cons: Limited strength at high temperatures. |
| Nickel 201 | Similar to Nickel 200, but with lower carbon content | Electronics, aerospace | Pros: Improved ductility, good for welding. Cons: Lower strength than other nickel alloys. |
| Inconel 600 | Nickel-chromium alloy with high oxidation resistance | Aerospace, chemical processing | Pros: Excellent high-temperature strength. Cons: Higher cost, requires specialized machining. |
| Monel 400 | Nickel-copper alloy known for its toughness and corrosion resistance | Marine applications, oil and gas | Pros: Excellent resistance to seawater. Cons: More expensive than standard nickel. |
| Nickel Alloy 625 | Nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy with high strength and corrosion resistance | Oil and gas, chemical processing | Pros: Versatile, strong, and resistant to pitting. Cons: Difficult to machine, higher cost. |
Nickel 200
Nickel 200 is a commercially pure nickel alloy, notable for its high corrosion resistance and excellent mechanical properties. It is particularly suitable for applications in chemical processing and food processing industries, where purity and resistance to corrosive environments are paramount. When considering purchasing Nickel 200, buyers should prioritize its suitability for low to moderate temperatures and its welding capabilities, while noting its limitations in high-temperature applications.
Nickel 201
Nickel 201 is an alloy similar to Nickel 200 but with a lower carbon content, enhancing its ductility and making it more suitable for welding. This alloy is often utilized in electronics and aerospace applications, where its superior formability is advantageous. Buyers should consider Nickel 201 for projects requiring high reliability and performance under stress, while being aware that it may not offer the same strength as other nickel alloys.
Inconel 600
Inconel 600 is a nickel-chromium alloy recognized for its outstanding oxidation and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures. It is extensively used in the aerospace sector and chemical processing industries. B2B buyers should evaluate Inconel 600 for applications that demand high-temperature performance; however, the cost and the need for specialized machining can be barriers for some organizations.
Monel 400
Monel 400 is a nickel-copper alloy prized for its toughness and resistance to corrosion, especially in marine environments. It is widely used in the oil and gas industry and various marine applications. Buyers should weigh Monel 400’s excellent resistance to seawater and acidic environments against its higher cost compared to standard nickel alloys, making it a strategic choice for demanding applications.
Nickel Alloy 625
Nickel Alloy 625 is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloy known for its exceptional strength and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. It is commonly applied in oil and gas industries and chemical processing. When considering Nickel Alloy 625, buyers should recognize its versatility and high-performance characteristics, but also prepare for potential challenges related to machining and higher material costs.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of nickle metal
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Nickel Metal | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Storage | Nickel in lithium-ion batteries | Enhances battery capacity and longevity | Ensure compliance with international standards; assess supplier reliability. |
| Aerospace | Nickel alloys in aircraft components | Provides high strength and corrosion resistance | Verify certifications and quality assurance processes. |
| Automotive | Nickel in catalytic converters | Improves emissions control and fuel efficiency | Evaluate supplier’s sustainability practices; consider local sourcing options. |
| Electronics | Nickel in electronic components | Ensures conductivity and durability in devices | Focus on suppliers with advanced manufacturing capabilities. |
| Construction | Nickel in stainless steel for building materials | Increases durability and resistance to environmental factors | Assess raw material sourcing and traceability of nickel content. |
Energy Storage
Nickel metal is crucial in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which are widely used in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage solutions. The inclusion of nickel enhances the energy density of batteries, leading to longer-lasting power sources. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America where renewable energy is gaining traction, sourcing high-quality nickel is essential. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who adhere to global environmental standards and can demonstrate reliable delivery capabilities.
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, nickel alloys are integral to manufacturing components that require exceptional strength and corrosion resistance, such as turbine blades and engine parts. These materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, making them essential for safety and performance. B2B buyers in this industry must ensure that suppliers have the necessary certifications, such as AS9100, to meet stringent aerospace standards. Additionally, understanding the alloy composition and sourcing practices is vital to ensure quality and performance.
Automotive
Nickel plays a significant role in the production of catalytic converters, which are critical for reducing harmful emissions in vehicles. By enhancing the efficiency of these components, nickel helps automotive manufacturers meet stringent environmental regulations while improving fuel efficiency. Buyers in the automotive sector should evaluate suppliers based on their commitment to sustainability and the traceability of their nickel sources. Local sourcing may also be advantageous to reduce lead times and transportation costs.
Electronics
In the electronics industry, nickel is used in various components, including connectors, circuit boards, and batteries. Its excellent conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it a preferred choice for manufacturers aiming for durability and performance in their products. International B2B buyers should focus on suppliers with advanced manufacturing technologies and quality control measures to ensure the reliability of electronic components. Additionally, assessing the supplier’s capacity for innovation can provide a competitive edge.
Construction
Nickel is often incorporated into stainless steel, which is widely used in construction for its strength and resistance to environmental factors. This application is particularly relevant in regions with harsh climates, where materials must withstand corrosion. Buyers in the construction sector should consider the sourcing of nickel to ensure that it meets industry standards for quality and environmental impact. Establishing partnerships with suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices can enhance the overall value of construction projects.
Related Video: Forming Sheet Metal & Metal Forming Tools – Uses Explained By Gene Winfield at SEMA
Strategic Material Selection Guide for nickle metal
When selecting nickel metal for various applications, international B2B buyers must consider several common materials that incorporate nickel. Each material has unique properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common nickel-containing materials.
1. Nickel Alloy 625
Key Properties:
Nickel Alloy 625 is known for its exceptional strength and resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. It maintains its mechanical properties even at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for high-stress applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, especially in acidic environments; high-temperature strength; good weldability.
– Cons: Higher cost compared to other nickel alloys; manufacturing complexity due to its high strength.
Impact on Application:
This alloy is particularly effective in marine, aerospace, and chemical processing industries, where exposure to harsh environments is common. Its compatibility with various media makes it a preferred choice for critical applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM B443 and DIN 2.4856. Understanding local sourcing capabilities and potential tariffs is also crucial, especially for buyers in Africa and South America.
2. Nickel-Copper Alloy (Monel)
Key Properties:
Monel is a nickel-copper alloy that offers excellent resistance to corrosion in seawater and acidic environments. It exhibits good mechanical properties and is non-magnetic.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Outstanding resistance to corrosion and oxidation; good mechanical properties; easy to fabricate.
– Cons: More expensive than standard steel; limited availability in some regions.
Impact on Application:
Monel is widely used in marine applications, chemical processing, and oil and gas industries due to its ability to withstand harsh conditions. It is particularly effective in applications where seawater exposure is prevalent.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the availability of Monel in their region and consider compliance with standards like ASTM B164. Understanding the local market dynamics is essential for cost-effective procurement.
3. Stainless Steel (with Nickel)
Key Properties:
Stainless steel, particularly grades like 304 and 316, contains nickel to enhance corrosion resistance and improve mechanical properties. These alloys perform well in a variety of environments.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Good corrosion resistance; widely available; relatively low cost compared to pure nickel alloys.
– Cons: Lower strength at high temperatures compared to nickel alloys; may require additional treatments for specific applications.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is commonly used in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and architectural applications. Its versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of media, although it may not perform as well in extreme conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 and JIS G4303. Awareness of local regulations regarding stainless steel grades is also vital for ensuring product suitability.
4. Nickel-Plated Steel
Key Properties:
Nickel-plated steel is a cost-effective alternative that combines the strength of steel with the corrosion resistance of nickel. The plating process enhances the surface properties of the steel substrate.
Pros & Cons:
– Pros: Cost-effective; improved corrosion resistance; good mechanical properties of the underlying steel.
– Cons: Plating can wear off; limited resistance to high temperatures compared to solid nickel alloys.
Impact on Application:
This material is often used in automotive and appliance applications where a balance of cost and performance is required. It is suitable for environments with moderate exposure to corrosive elements.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the thickness of the nickel plating and ensure compliance with relevant standards such as ASTM B456. Understanding the durability of the coating in specific applications is also critical.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for nickel metal | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel Alloy 625 | Aerospace, chemical processing | Excellent high-temperature strength | Higher cost, manufacturing complexity | High |
| Nickel-Copper Alloy (Monel) | Marine applications, oil and gas | Outstanding corrosion resistance | More expensive, limited availability | High |
| Stainless Steel (with Nickel) | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Good corrosion resistance | Lower strength at high temps | Medium |
| Nickel-Plated Steel | Automotive, appliances | Cost-effective | Plating can wear off | Low |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of key nickel materials, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for nickle metal
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for nickel metal are critical for international B2B buyers, particularly those involved in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and energy. This section delves into the comprehensive stages of manufacturing nickel metal, the essential quality control measures, and how buyers can ensure they are sourcing high-quality products from reliable suppliers.
Manufacturing Processes
Nickel metal production involves several key stages, each requiring precision and adherence to best practices. Understanding these processes helps buyers evaluate the capabilities of potential suppliers.
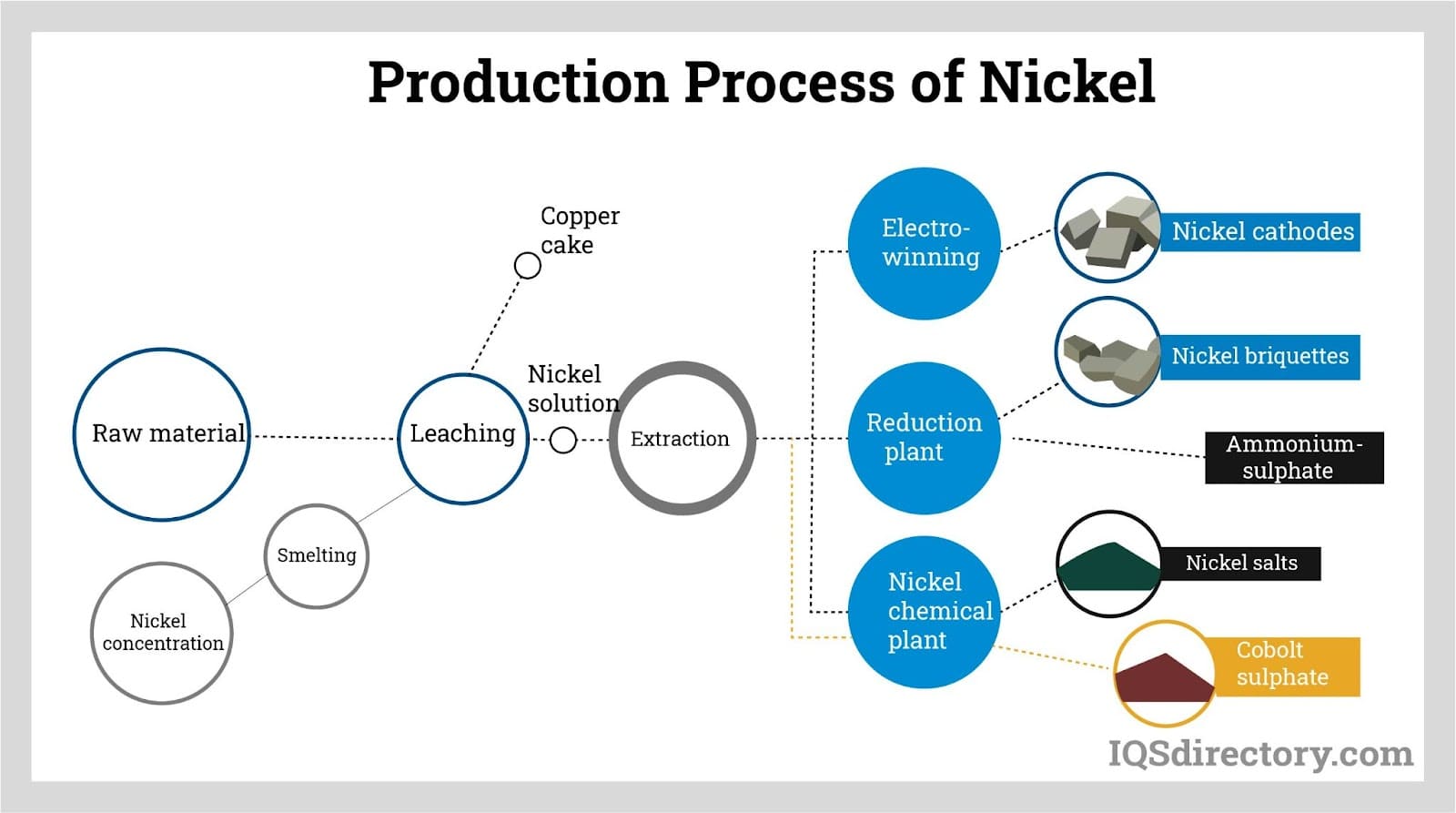
1. Material Preparation
The manufacturing process begins with the preparation of raw materials. Nickel ore, typically sourced from lateritic or sulfide deposits, undergoes several treatments to extract nickel. Key steps include:
- Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed and ground to liberate nickel particles from other minerals.
- Concentration: Techniques such as flotation or magnetic separation are used to concentrate nickel content, which increases efficiency in subsequent processing stages.
- Roasting and Leaching: For sulfide ores, roasting is employed to convert nickel sulfide into nickel oxide, followed by leaching to extract nickel using sulfuric acid.
2. Forming
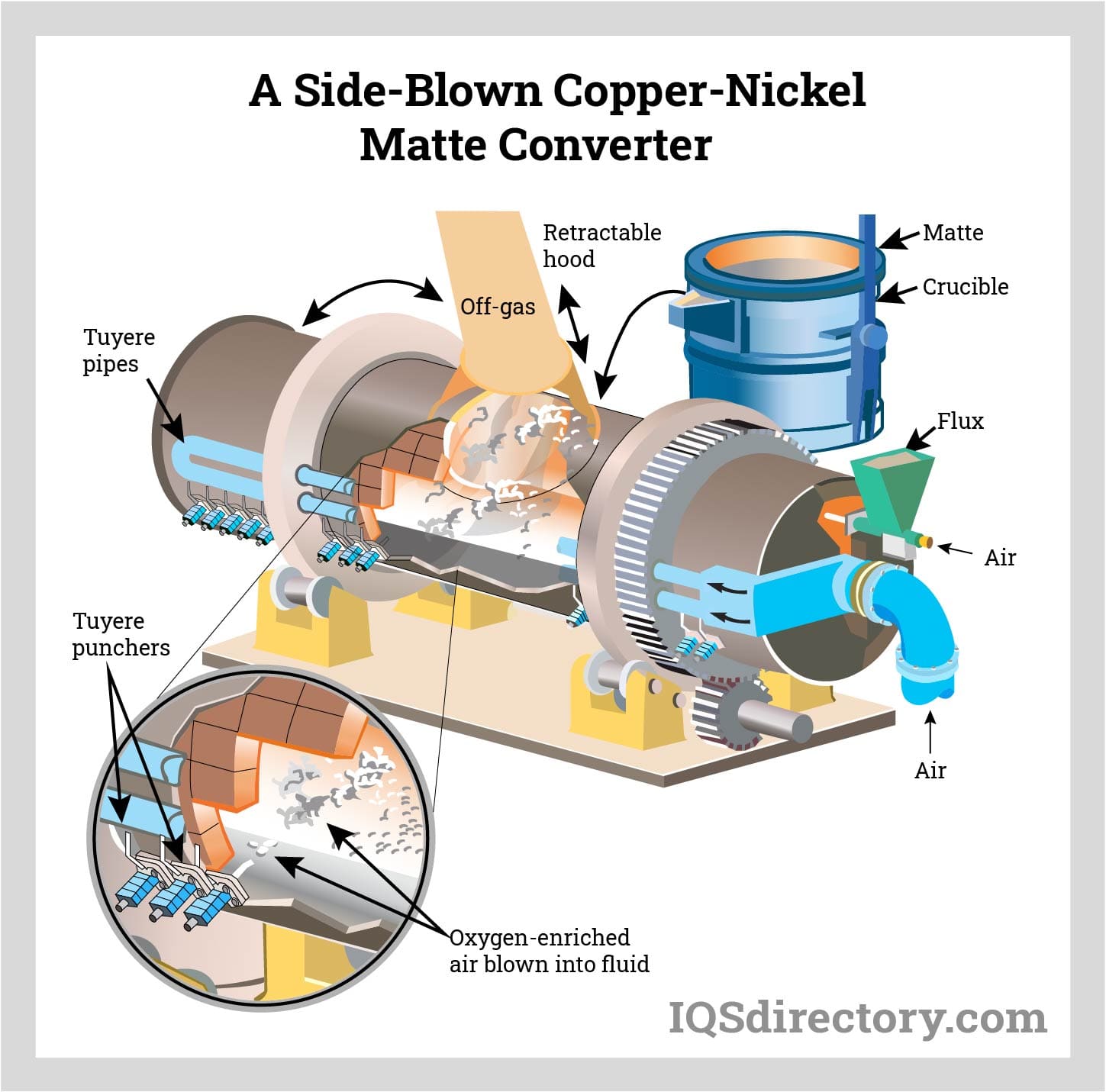
Once the raw material is prepared, the next phase is shaping the nickel into usable forms. This includes:
- Smelting: The concentrated nickel is smelted in a furnace to separate nickel from impurities, producing nickel matte.
- Refining: The matte undergoes refining processes, such as electrolytic refining or carbonyl refining, to achieve high-purity nickel. This stage is crucial for applications requiring specific nickel grades.
3. Assembly
In cases where nickel is part of an alloy or composite material, the assembly process is vital. Key techniques include:
- Alloying: Nickel is often alloyed with other metals (like copper or chromium) to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance or strength.
- Casting and Forging: Depending on the final product requirements, nickel can be cast into molds or forged into specific shapes through mechanical processes.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves preparing the nickel for final use or shipment. This includes:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like electroplating or passivation are applied to improve surface properties, such as resistance to oxidation.
- Packaging: Proper packaging ensures that the nickel products are protected during transportation and storage, maintaining quality.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the nickel metal industry, especially given the material’s applications in critical sectors. Buyers must be aware of relevant international standards and the quality control checkpoints employed by suppliers.
International Standards
Several standards govern the quality of nickel metal production, including:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and emphasizes continual improvement and customer satisfaction.
- ASTM Standards: Various ASTM standards specify the chemical composition and mechanical properties of nickel and nickel alloys, ensuring they meet industry requirements.
Industry-Specific Certifications
In addition to general standards, specific certifications may apply, such as:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA), indicating compliance with safety and environmental requirements.
- API Standards: Relevant for nickel used in oil and gas applications, ensuring materials can withstand harsh environments.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control encompasses multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to identify and rectify issues promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducting thorough inspections and testing of finished products before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Buyers should be familiar with common testing methods used to ensure quality:
- Chemical Analysis: Determining the chemical composition of nickel to verify compliance with standards.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength, ductility, and hardness through standardized tests.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or radiography are employed to detect internal flaws without damaging the material.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality control practices is essential. Here are actionable steps:
- Conduct Audits: Regularly audit suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards.
- Request Documentation: Obtain quality assurance reports, certifications, and test results to assess the supplier’s commitment to quality.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilize independent inspection services to verify that products meet specified quality standards before shipment.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
Buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification processes that may vary by region. For instance:
- Regional Standards: Different regions may have unique regulations governing nickel production. Understanding these can help buyers ensure compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
- Cultural Differences: Approaches to quality assurance can differ based on cultural practices. Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better communication and understanding of quality expectations.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with nickel metal, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality materials that meet their specific requirements.
Related Video: Top 5 Mass Production Techniques: Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for nickle metal Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Nickel Metal Sourcing
Nickel metal sourcing entails a multifaceted cost structure that international B2B buyers must navigate effectively. The primary components influencing the cost include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin.
-
Materials: The cost of nickel itself is subject to fluctuations based on global supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical factors, and production levels from major producing countries, including Indonesia, Australia, and the Philippines. Prices can vary significantly, making it essential to monitor market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ based on the region of production. For instance, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may reduce overall expenses. However, quality and expertise must also be considered, as cheaper labor may not always equate to superior product quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, equipment maintenance, and indirect labor. Buyers should evaluate suppliers’ operational efficiencies, as higher overheads can lead to inflated pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized products can add significant costs. Buyers should assess whether they need bespoke solutions or if standard products will suffice, as the latter can minimize tooling expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality through rigorous QC processes is critical, especially for industries requiring strict compliance with standards. Investing in robust QC can prevent costly defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, including freight, insurance, and handling fees, can vary widely depending on the origin and destination of the nickel. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) play a crucial role in determining who bears these costs and risks.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. Understanding the typical margins in the nickel market can aid in negotiating better pricing.
Key Influencers on Pricing
Several factors can influence the pricing of nickel metal:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Suppliers often provide better pricing tiers for larger orders. Buyers should negotiate based on their expected consumption to leverage volume discounts.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized nickel products often incur higher costs due to additional processing and production adjustments. Buyers should clarify their requirements upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or those with specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may demand premium pricing. Buyers must balance the need for quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and historical performance can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but provide better quality assurance and service.
-
Incoterms: Different Incoterms can significantly impact the overall cost structure. For example, choosing CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) may shift more responsibility and cost to the supplier, while EXW (Ex Works) places the onus on the buyer.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
To optimize nickel sourcing costs, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Leverage competitive offers from multiple suppliers to negotiate better prices and terms. Building long-term relationships can also yield better deals over time.
-
Assess Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Beyond the purchase price, evaluate the TCO, which includes logistics, maintenance, and potential downtime. A lower upfront cost may lead to higher long-term expenses.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and trade policies that may affect pricing. Staying informed about geopolitical developments can also provide insights into potential price changes.
-
Engage Local Experts: For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, engaging local sourcing experts can help navigate the complexities of international trade and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing for their specific requirements.
Spotlight on Potential nickle metal Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘nickle metal’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for nickle metal
Nickel metal is increasingly recognized for its essential role in various industries, particularly in the context of energy transition and sustainable technologies. Understanding its technical properties and industry terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Critical Technical Properties of Nickel Metal
-
Material Grade
Nickel is classified into several grades based on its purity and alloying elements. Common grades include Nickel 200 (99.6% pure) and Nickel 201 (99.6% pure with reduced carbon content). Buyers must consider the material grade as it affects the metal’s strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific applications, such as in aerospace or chemical processing. -
Tensile Strength
This property measures the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing. For nickel alloys, tensile strength can vary significantly, impacting their performance in high-stress environments. Buyers should evaluate tensile strength to ensure that the nickel products will perform adequately under operational conditions. -
Corrosion Resistance
Nickel’s natural resistance to corrosion makes it ideal for use in harsh environments, such as marine or chemical applications. Understanding the corrosion resistance of different nickel grades helps buyers select the right material for longevity and reduced maintenance costs. -
Thermal Conductivity
This property indicates how well a material can conduct heat. Nickel has good thermal conductivity, which is essential in applications where heat dissipation is critical, such as in electronics and batteries. Buyers should assess thermal conductivity to ensure effective heat management in their applications. -
Machinability
This term refers to how easily a material can be cut, shaped, or finished using machining processes. Nickel alloys can present machining challenges; hence, understanding the machinability of specific grades is crucial for manufacturers to optimize production efficiency.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the nickel industry, buyers often deal with OEMs for components that require nickel alloys, making it important to understand OEM relationships and their implications for supply chains. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers should be aware of MOQs when negotiating contracts to ensure that they can meet their production needs without excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services. In the nickel market, submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standardized terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms, such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), helps buyers clarify shipping responsibilities and costs, ensuring smoother logistics. -
Alloying Elements
These are additional metals or materials mixed with nickel to enhance specific properties, such as strength or corrosion resistance. Common alloying elements include copper, chromium, and molybdenum. Buyers should consider the effects of alloying elements when selecting nickel products for specific applications.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions regarding nickel metal procurement, ultimately leading to better project outcomes and enhanced supply chain efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the nickle metal Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The nickel market is currently experiencing significant shifts driven by the global transition to renewable energy and the increasing demand for electric vehicles (EVs). As countries push for decarbonization, nickel’s role in battery production—particularly for lithium-ion batteries—has surged. This trend is especially relevant for international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as they look to diversify their sourcing strategies amidst fluctuating prices and geopolitical tensions.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Emerging Sourcing Trends:
1. Digital Transformation: The integration of digital platforms and technologies in sourcing processes is becoming essential. Buyers are increasingly leveraging data analytics and AI to enhance supply chain transparency and efficiency.
2. Local Sourcing: As sustainability becomes a priority, there is a notable shift towards local sourcing to reduce transportation emissions and support local economies. This trend is particularly relevant in regions like Africa and South America, where local nickel production is on the rise.
3. Partnerships and Collaborations: Strategic alliances among companies, governments, and NGOs are forming to secure reliable supply chains. This is vital for B2B buyers seeking stable sources of nickel, especially in politically volatile regions.
Market Dynamics:
Global nickel demand is projected to grow significantly, primarily fueled by the EV sector. However, supply constraints due to environmental regulations and mining challenges in key producing countries like Indonesia and the Philippines could lead to price volatility. B2B buyers must stay informed about these dynamics to navigate the market effectively and secure favorable procurement agreements.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of nickel mining and processing has prompted a growing emphasis on sustainability within the industry. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to ethical practices and environmentally friendly operations.
Importance of Ethical Supply Chains:
1. Environmental Stewardship: Buyers are seeking suppliers who minimize ecological damage, such as deforestation and water pollution, during nickel extraction and processing. This is crucial not only for regulatory compliance but also for brand reputation.
2. Certifications and Standards: Green certifications, such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the ResponsibleSteel™ certification, are becoming essential criteria for sourcing decisions. These certifications assure buyers of sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
Adopting Green Materials:
The trend toward using recycled nickel is gaining momentum. Sourcing nickel from recycled materials not only reduces the environmental footprint but also helps mitigate the impact of supply chain disruptions. B2B buyers should consider suppliers that utilize recycled nickel and can provide transparency regarding their sourcing practices.
Brief Evolution/History
Nickel has been utilized for thousands of years, but its modern industrial applications began in the late 19th century with the rise of stainless steel production. The growing demand for nickel in batteries, particularly since the early 2000s, has transformed its market dynamics significantly. The advent of electric vehicles in the last decade has further accelerated this trend, positioning nickel as a critical material in the energy transition. As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of nickel can provide valuable insights into current market behaviors and future opportunities.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of nickle metal
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of nickel metal?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience and reputation in the nickel industry. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Check their financial stability through credit reports and seek references from existing clients. It’s also important to assess their supply chain transparency and sustainability practices, especially given the increasing focus on ethical sourcing in global markets. -
Can suppliers customize nickel metal products to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for nickel products, including variations in size, alloy composition, and surface treatment. When discussing customization, clearly outline your specifications and intended applications. Collaborate closely with the supplier’s engineering team to ensure that the customizations meet industry standards and are feasible within your desired timeframe. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for nickel metal?
MOQs for nickel metal can vary significantly based on supplier capabilities and product types. Generally, MOQs range from 1 ton to 10 tons for standard products. Lead times also fluctuate based on the complexity of the order and supplier location, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to discuss your specific needs early in negotiations to ensure the supplier can accommodate your requirements. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing nickel metal internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely, but common practices include payment in advance, letters of credit, and net 30 or 60 days after delivery. For larger orders, consider negotiating staggered payments based on production milestones. Ensure that all payment terms are clearly outlined in your contract to avoid misunderstandings and protect both parties’ interests. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and necessary certifications for nickel metal?
Request detailed quality assurance documentation from your supplier, including material test reports and compliance certificates. Key certifications to look for include ASTM standards and ISO certifications. Additionally, consider third-party inspections during production to validate quality and adherence to specifications. Establishing a clear QA process in your contract can help mitigate risks associated with product quality. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing nickel metal?
Logistics for importing nickel metal involve several factors, including shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and insurance coverage. Work with a freight forwarder experienced in handling metals to navigate international shipping complexities. Ensure that all customs documentation is accurate and complete to avoid delays. Additionally, factor in potential tariffs and import duties in your budgeting. -
What steps should I take in case of disputes with a nickel metal supplier?
In case of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. If this fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, including dispute resolution procedures. Consider mediation or arbitration as a less confrontational approach than litigation. Keeping thorough documentation of all communications and transactions can strengthen your position in any dispute resolution process. -
How can I stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations for nickel metal?
To stay updated on market trends, subscribe to industry reports from reputable sources, follow market analysis from financial institutions, and join relevant trade associations. Networking with industry peers can also provide valuable insights. Additionally, consider using digital platforms that provide real-time data on nickel pricing and supply chain developments to make informed purchasing decisions.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for nickle metal
The strategic sourcing of nickel metal is becoming increasingly critical as industries pivot towards sustainable practices and innovative technologies. Key takeaways for B2B buyers include the importance of understanding the nickel supply chain, evaluating suppliers based on sustainability metrics, and leveraging regional advantages. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize partnerships with suppliers who are not only cost-effective but also committed to ethical mining practices and environmental stewardship.
Value of Strategic Sourcing:
Strategic sourcing enhances supply chain resilience, reduces costs, and fosters innovation. By developing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers, businesses can secure better pricing and consistent quality, which are vital in a fluctuating market. Additionally, engaging with suppliers who invest in sustainable practices can boost corporate reputation and attract eco-conscious customers.
As the demand for nickel continues to rise, particularly in electric vehicle batteries and renewable energy technologies, international B2B buyers are encouraged to act decisively. Explore diverse sourcing options, assess the sustainability of your suppliers, and position your business at the forefront of the nickel market. Embrace this opportunity to drive growth while contributing to a more sustainable future.