Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Particle Size Reduction
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for particle size reduction equipment
In today’s competitive landscape, particle size reduction equipment plays a pivotal role in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to food processing. The ability to manipulate particle size can significantly impact product quality, efficiency, and safety. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of this equipment is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of particle size reduction equipment. It explores various types of machinery, the materials they process, and the manufacturing and quality control standards that ensure optimal performance. Buyers will find insights into leading suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends that can influence their purchasing strategies. Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section addresses common queries, empowering buyers with the knowledge to navigate complex procurement processes confidently.
By equipping themselves with this information, international buyers can enhance their operational capabilities, ensuring they select the right equipment that meets their specific needs. Whether you’re in South Africa, Kenya, or elsewhere, this guide serves as a valuable resource, enabling you to leverage particle size reduction technology effectively and strategically in your business operations.
Understanding particle size reduction equipment Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hammer Mill | High-speed rotor with hammers; versatile for various materials. | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Chemicals | Pros: Cost-effective, efficient for bulk materials. Cons: Generates heat, may require cooling. |
| Ball Mill | Utilizes balls to grind materials; suitable for fine particle size reduction. | Mining, Ceramics, Pharmaceuticals | Pros: Produces very fine particles. Cons: High energy consumption, longer processing time. |
| Jet Mill | Uses high-velocity air jets to achieve size reduction; ideal for heat-sensitive materials. | Pharmaceuticals, Food, Chemicals | Pros: Minimal heat generation, precise particle size control. Cons: Higher capital costs, requires specialized maintenance. |
| Conical Mill (Cone Mill) | Cone-shaped design for controlled particle size reduction; adaptable for various applications. | Food, Pharmaceuticals, Chemical Processing | Pros: Versatile, low noise levels. Cons: Limited to medium particle sizes, may require frequent cleaning. |
| Roller Mill | Uses cylindrical rollers to crush and grind materials; efficient for large-scale operations. | Agriculture, Food, Mining | Pros: Efficient for large volumes, consistent particle size. Cons: Limited to certain materials, potential for wear on rollers. |
Hammer Mill
Hammer mills are characterized by their high-speed rotating hammers, which pulverize materials into fine particles. They are widely used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals due to their versatility in handling various materials. When considering a hammer mill, buyers should evaluate the material being processed, as the equipment can generate heat during operation, necessitating cooling systems to protect sensitive ingredients.
Ball Mill
Ball mills are designed for grinding materials using balls that tumble within a rotating cylindrical chamber. This method is particularly effective for achieving very fine particle sizes, making them popular in mining, ceramics, and pharmaceuticals. However, buyers should be aware of the high energy consumption associated with ball mills and the longer processing times required, which can impact production efficiency.
Jet Mill
Jet mills utilize high-velocity air jets to create a particle size reduction effect without introducing heat, making them ideal for processing heat-sensitive materials. Common applications include pharmaceuticals, food products, and chemicals. Buyers should consider the higher initial investment and maintenance requirements of jet mills, but they benefit from precise control over particle size distribution, which is crucial in many industries.
Conical Mill (Cone Mill)
The conical mill features a cone-shaped design that allows for controlled particle size reduction while being adaptable for various applications. It is often used in food, pharmaceutical, and chemical processing. When purchasing a conical mill, buyers should note its versatility and lower noise levels, but they should also consider the limitations in achieving very fine particle sizes and the potential need for frequent cleaning to maintain product quality.
Roller Mill
Roller mills operate using cylindrical rollers to crush and grind materials, making them particularly efficient for large-scale operations in agriculture, food production, and mining. They provide consistent particle sizes and are suitable for high-volume processing. Buyers should evaluate the types of materials they intend to process, as roller mills may be limited to certain materials and could experience wear on the rollers, necessitating regular maintenance.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of particle size reduction equipment
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Particle Size Reduction Equipment | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceutical | Milling active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Improved drug efficacy and bioavailability | Compliance with regulatory standards and quality control processes |
| Food & Beverage | Grinding spices and flavoring agents | Enhanced taste, texture, and shelf life | Need for hygienic designs and food-grade materials |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Reducing pigment particle size for coatings | Better dispersion and color consistency | Equipment durability and resistance to chemical wear |
| Cosmetics & Personal Care | Micronizing powders for creams and lotions | Improved texture and absorption in formulations | Precision in achieving desired particle size distribution |
| Mining & Minerals | Crushing and milling ores for extraction | Increased yield and efficiency in processing | Equipment adaptability to different ore types and hardness |
Pharmaceutical Applications
In the pharmaceutical industry, particle size reduction equipment is crucial for milling active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This process enhances the drug’s efficacy and bioavailability by creating smaller particles that dissolve more readily in the body. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should prioritize sourcing equipment that meets stringent regulatory standards and quality control processes, ensuring compliance with local and international pharmaceutical guidelines.
Food & Beverage Applications
In the food and beverage sector, grinding spices and flavoring agents is a common application of particle size reduction equipment. This process not only enhances the taste and texture of products but also extends their shelf life. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should consider equipment that features hygienic designs and food-grade materials, ensuring safety and compliance with food safety regulations while maintaining product integrity.
Chemical Manufacturing Applications
The chemical manufacturing industry often utilizes particle size reduction equipment to reduce pigment particle size for coatings. This application is vital for achieving better dispersion and color consistency in final products. B2B buyers from Africa and Europe should focus on sourcing durable equipment that can withstand chemical wear and tear, while also ensuring that the machinery is adaptable to various materials and processing requirements.
Cosmetics & Personal Care Applications
In the cosmetics and personal care sector, micronizing powders for creams and lotions is a significant application of particle size reduction technology. This process improves the texture and absorption of products, enhancing the overall user experience. Buyers in South America and Europe should ensure precision in achieving the desired particle size distribution, as this directly impacts product performance and consumer satisfaction.
Mining & Minerals Applications
In the mining and minerals sector, crushing and milling ores for extraction is a critical application of particle size reduction equipment. This process increases yield and efficiency in mineral processing, making it essential for maximizing resource recovery. International buyers, particularly from Africa, should seek equipment that is adaptable to different ore types and hardness levels, ensuring effective processing across various mining operations.
Related Video: Tietjen Hammer Mills and Grinders – Particle Size Reduction and Grinding
Strategic Material Selection Guide for particle size reduction equipment
When selecting materials for particle size reduction equipment, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the properties, advantages, and limitations of various materials. This knowledge will facilitate informed decisions that align with operational requirements and compliance standards prevalent in different regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and mechanical strength. It can withstand pressures up to 3000 psi, making it suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it is resistant to wear and tear. However, the cost of stainless steel can be high compared to other materials, and manufacturing complexities can arise during machining and welding processes. End products made from stainless steel are generally suitable for food and pharmaceutical applications due to their non-reactive nature.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel’s compatibility with various media makes it ideal for industries that require stringent hygiene standards, such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN. In regions like South Africa and Kenya, local regulations may dictate specific grades of stainless steel for food and drug applications.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is characterized by its high tensile strength and hardness, with a temperature rating that can reach up to 600°F. However, it is more susceptible to corrosion than stainless steel.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon steel is its lower cost compared to stainless steel, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion can limit its application in moisture-rich environments, necessitating additional coatings or treatments.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is often used in applications where high strength is required, but its limitations in corrosive environments may restrict its use in food and pharmaceutical sectors.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should assess the environmental conditions of their operations. In regions with high humidity, such as parts of South America, additional protective measures may be necessary to prevent corrosion.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and lightweight nature. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°F and is resistant to many acids and bases.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of polypropylene is its low cost and ease of fabrication, making it suitable for various applications. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals and may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is ideal for applications involving corrosive substances, particularly in the chemical industry. Its lightweight nature also facilitates easier handling and installation.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific chemical compatibility of polypropylene with the materials they intend to process. Compliance with local standards is also essential, especially in regions like Europe, where stringent regulations govern material use.
Ceramic Materials
Key Properties: Ceramics are known for their hardness, wear resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 3000°F). They are also chemically inert, making them suitable for aggressive environments.
Pros & Cons: The durability of ceramic materials is a significant advantage, particularly in high-wear applications. However, they can be brittle and prone to cracking under impact, and their cost can be relatively high.
Impact on Application: Ceramics are often used in applications requiring high precision and durability, such as in the pharmaceutical and food industries, where contamination must be minimized.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider the fragility of ceramics and ensure that their equipment design minimizes the risk of breakage. Additionally, compliance with international standards is crucial, especially in markets like the Middle East, where regulations can be strict.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for particle size reduction equipment | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | High cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Carbon Steel | General industrial applications | Lower cost compared to stainless steel | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Chemical processing | Low cost and easy fabrication | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Ceramic Materials | High-precision applications | High durability and wear resistance | Brittle and high cost | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of common materials used in particle size reduction equipment, equipping international B2B buyers with the insights necessary for making informed purchasing decisions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for particle size reduction equipment
The manufacturing and quality assurance processes for particle size reduction equipment are critical components that B2B buyers need to understand. This knowledge not only helps in selecting the right equipment but also ensures compliance with international standards and operational efficiency.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing particle size reduction equipment involves the selection and preparation of raw materials. This step is crucial as it directly affects the durability and performance of the final product. Common materials used include high-grade stainless steel and other alloys that resist wear and corrosion. Buyers should inquire about the source and quality of these materials, as they influence the equipment’s lifespan and maintenance requirements.
2. Forming Techniques
The forming process typically involves several techniques, including:
- Casting: Used for creating complex shapes with high precision.
- Machining: Essential for ensuring that components meet specific tolerances and surface finishes.
- Welding: This technique joins various parts together, and the quality of the weld can impact the structural integrity of the equipment.
It’s advisable for buyers to ask suppliers about the forming techniques employed, as well as any technological innovations that enhance precision and efficiency.
3. Assembly
Once components are formed, they undergo assembly. This stage may involve:
- Sub-assembly: Smaller components are assembled before the final assembly.
- Integration: All subsystems are integrated into the final product, ensuring that each part functions correctly within the larger system.
Buyers should verify whether suppliers follow standardized assembly protocols, which can significantly reduce the risk of operational failures.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves surface treatment and finishing processes that enhance the equipment’s performance and appearance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Polishing: Improves surface smoothness, which can be critical for reducing friction.
- Coating: Provides additional protection against corrosion and wear.
Understanding the finishing processes helps buyers assess the long-term maintenance needs of the equipment.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of particle size reduction equipment. Suppliers often adhere to various international and industry-specific standards.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- ISO 14001: This standard relates to environmental management, important for companies focused on sustainability.
Industry-Specific Standards
- CE Certification: This mark indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for equipment used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring that products meet stringent safety and efficacy requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials and components upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitors the manufacturing process to detect and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conducts a comprehensive evaluation of the finished product before it is shipped to customers.
Each of these checkpoints is critical for maintaining high-quality standards and minimizing defects.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods used in the QC process include:
- Mechanical Testing: Assesses the strength and durability of materials.
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that all components meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates the efficiency and effectiveness of the equipment in real-world scenarios.
B2B buyers should request detailed reports on these testing methods from suppliers to ensure the equipment meets their specific requirements.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, buyers should consider the following strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of the manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation detailing the QC processes and results of previous inspections.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspectors to verify the quality and compliance of the equipment before purchase.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC and certification is essential. Different regions may have varying standards, and suppliers must be knowledgeable about these differences to ensure compliance.
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may affect equipment standards and certifications.
- Global Standards: Ensure that suppliers are capable of meeting both local and international standards, as this will facilitate smoother operations and compliance.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in particle size reduction equipment is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming techniques, assembly, finishing, and robust QC practices, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and product quality.
Related Video: Honda factory tour – Production in Japan plant
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for particle size reduction equipment Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of particle size reduction equipment is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis will cover the key components that contribute to the overall cost, the factors influencing pricing, and provide actionable tips for buyers to optimize their sourcing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost of particle size reduction equipment. High-quality, durable materials are essential for ensuring longevity and efficiency, but they also come at a premium. Buyers should consider the trade-off between upfront costs and long-term performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely by region and can affect the overall pricing of equipment. In countries with higher wage standards, labor costs will be reflected in the final price. It is important for buyers to understand the labor market in the supplier’s location, as this can influence negotiation strategies.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with the production process, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Suppliers with efficient operations may offer more competitive pricing, so buyers should inquire about the supplier’s production capabilities and efficiency metrics.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be required for specialized equipment, which can add significant costs. Buyers should assess whether standard equipment can meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that equipment meets specified standards, which is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. While higher QC standards may increase costs, they can prevent costly failures and downtime in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are critical components, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs duties can all influence the final price. Understanding Incoterms and logistics strategies can help buyers manage these costs effectively.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s positioning. Buyers should engage in discussions about pricing structures to understand how margins are calculated and to negotiate effectively.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in bulk or meeting minimum order quantities (MOQ) often leads to significant discounts. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to take advantage of these opportunities.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate whether customization is necessary or if existing models can suffice, which could lead to cost savings.
-
Quality/Certifications: Equipment that meets specific industry certifications may command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and reliability of suppliers play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms can help buyers avoid unexpected costs related to shipping and insurance. This knowledge is essential for managing overall expenses effectively.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in open discussions about pricing, highlighting long-term relationships and potential bulk orders. Effective negotiation can lead to better pricing structures.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond the initial purchase price. Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential downtime. Investing in higher-quality equipment can yield savings over time.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences due to local market conditions. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have different pricing strategies compared to those in Africa or South America, influenced by local demand and competition.
Disclaimer
Prices for particle size reduction equipment can vary widely based on specifications, supplier relationships, and market fluctuations. It is recommended that buyers conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure they secure the best value for their investments.
Spotlight on Potential particle size reduction equipment Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘particle size reduction equipment’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for particle size reduction equipment
Essential Technical Properties of Particle Size Reduction Equipment
When selecting particle size reduction equipment, international B2B buyers should consider several critical technical properties that impact performance, efficiency, and overall product quality. Understanding these specifications helps ensure the chosen equipment meets operational needs and regulatory requirements.
-
Material Grade
– The material used in the construction of the equipment, such as stainless steel or carbon steel, significantly affects durability, corrosion resistance, and hygiene standards, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing. High-grade materials minimize contamination risks and enhance the lifespan of the equipment. -
Particle Size Distribution (PSD)
– PSD refers to the range of particle sizes produced by the milling process. It is crucial for determining product quality and functionality. For instance, in pharmaceuticals, a narrow PSD can enhance drug efficacy and absorption rates. Buyers should specify their target PSD to ensure the equipment can deliver the desired results. -
Capacity
– This refers to the volume of material that the equipment can process in a given time. Buyers must evaluate their production needs and select equipment that can handle their desired throughput without compromising quality. A mismatch can lead to inefficiencies and increased operational costs. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance indicates the acceptable deviation from the specified particle size. Tight tolerances are essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, where even minor variations can affect product safety and effectiveness. Understanding tolerance requirements helps buyers choose equipment that can consistently meet their specifications. -
Power Consumption
– The energy efficiency of the equipment is a key consideration for reducing operational costs. Equipment that consumes less power while delivering high performance can significantly impact the overall cost of ownership. Buyers should inquire about the power requirements and operational efficiency of potential equipment. -
Safety Standards
– Compliance with international safety standards is vital, particularly in industries that handle hazardous materials. Equipment should meet relevant certifications to ensure safe operation. Buyers should request documentation that confirms compliance with standards such as ISO or CE.
Common Trade Terminology in Particle Size Reduction
Familiarity with industry-specific terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that manufacture products or components that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM partnerships can help buyers evaluate the reliability and quality of the equipment they are considering. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest order size that a supplier is willing to process. Buyers must consider their production needs against MOQ requirements to avoid excess inventory and manage costs effectively.
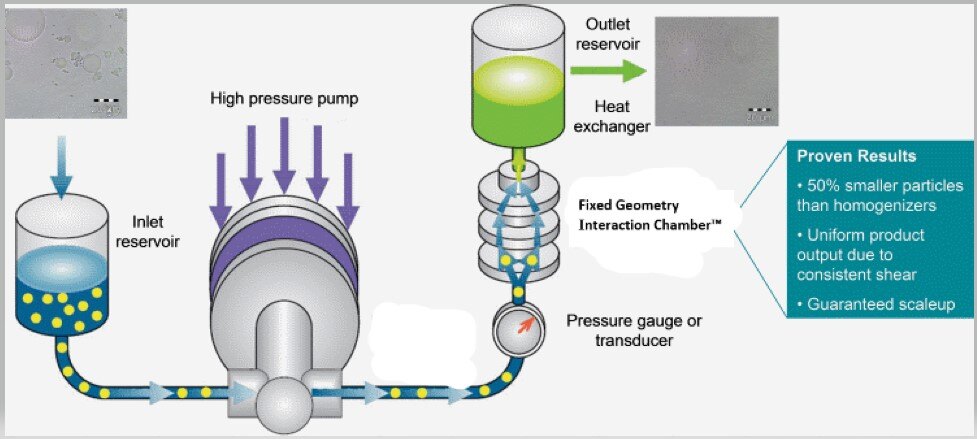
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal document issued by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific equipment or services. This process is crucial for comparing options and ensuring competitive pricing. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk management, and delivery obligations, which is essential for smooth international procurement. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the equipment. Understanding lead times is critical for planning production schedules and ensuring timely delivery of materials. -
After-Sales Support
– This term encompasses the services provided by suppliers after the equipment has been sold, including maintenance, repairs, and technical support. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer robust after-sales support to minimize downtime and ensure operational efficiency.
By grasping these essential properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when investing in particle size reduction equipment, ultimately enhancing their operational effectiveness and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the particle size reduction equipment Sector
Global drivers are significantly shaping the particle size reduction equipment market, influencing B2B purchasing decisions. The demand for finely milled products is surging across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemicals. Key trends include the increasing adoption of advanced technologies such as automation and digitalization, which enhance efficiency and precision in particle size reduction processes. Furthermore, the push for customized solutions is rising as manufacturers seek equipment tailored to specific material characteristics and end-product requirements.
In regions like Africa and South America, emerging markets are experiencing rapid industrialization, leading to a greater need for high-quality milling equipment. On the other hand, Europe and the Middle East are focusing on compliance with stringent regulations and quality standards, which necessitates advanced particle size reduction technologies. The integration of data analytics and IoT into machinery is enabling manufacturers to optimize processes and improve product quality, making these technologies attractive to B2B buyers looking to enhance operational efficiencies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern for B2B buyers in the particle size reduction equipment sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly prioritizing equipment that minimizes resource usage and reduces carbon footprints.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, such as sourcing raw materials responsibly and implementing environmentally friendly manufacturing processes. Certifications like ISO 14001 for environmental management and FSC for sustainable forestry can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, opting for equipment made from recyclable materials and designed for energy efficiency is critical in aligning with green initiatives and corporate social responsibility goals.
Brief Evolution/History
The particle size reduction equipment sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by simple mechanical milling processes, advancements in technology have led to the development of sophisticated equipment capable of achieving precise particle sizes. The introduction of high-energy milling and wet milling technologies has allowed for greater control over particle size distribution, which is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals where product efficacy is closely tied to particle size.
As the industry continues to innovate, the integration of smart technologies and automation is expected to further transform the landscape, providing B2B buyers with enhanced options for optimizing production and ensuring quality. This evolution underscores the importance of staying informed about technological advancements and sourcing trends to make strategic purchasing decisions.
Related Video: Trump Deals Set To Fall Short of Sweeping Trade Reforms | Bloomberg: The Asia Trade 6/30/25
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of particle size reduction equipment
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers of particle size reduction equipment?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by checking their industry reputation and experience, especially in your specific market (Africa, South America, Middle East, or Europe). Request references from previous clients and assess their product quality through certifications like ISO or CE. Additionally, evaluate their customer service and support capabilities, as these are crucial for long-term partnerships. Engage in discussions about their manufacturing processes, technologies used, and their commitment to compliance with local regulations. -
Is customization of equipment possible, and how should I approach this with suppliers?
Many suppliers offer customization options to meet specific application needs. When approaching suppliers, clearly outline your requirements, including desired particle size distribution, throughput, and material characteristics. Ask about their previous customization projects to gauge their capabilities. A collaborative approach during the design phase can lead to a more tailored solution. Ensure that any customization adheres to industry standards and regulations pertinent to your region. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for particle size reduction equipment?
MOQs can vary significantly among suppliers based on the equipment type and customization requirements. Generally, expect MOQs to range from one unit for specialized machinery to multiple units for standard models. Lead times can also differ, typically ranging from 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity and availability of components. It’s advisable to discuss these details upfront and consider lead times when planning your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by suppliers, and how can I negotiate favorable conditions?
Common payment terms include upfront payments, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Suppliers may require a deposit, particularly for customized equipment. To negotiate favorable conditions, build a relationship with the supplier and demonstrate your reliability as a buyer. Discussing bulk orders or long-term contracts may also provide leverage for better payment terms. Always ensure that the payment methods comply with international trade regulations. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for?
Look for suppliers who have robust quality assurance processes in place, including ISO 9001 certification. Ask about their testing protocols for equipment to ensure performance standards are met before shipment. Additionally, inquire about post-sale support, including maintenance services and spare parts availability. Certifications related to safety and environmental standards, such as CE marking for Europe, are also critical, as they ensure compliance with regional regulations. -
How should I handle logistics for international shipments of equipment?
Managing logistics for international shipments requires careful planning. Verify the supplier’s shipping capabilities and whether they handle logistics directly or use third-party logistics providers. Discuss incoterms to understand who bears responsibility for shipping costs and risks. Additionally, consider customs clearance processes in your country, as delays can occur. Partnering with a logistics expert familiar with international trade can streamline the process and avoid costly mistakes. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, maintain open communication with the supplier to resolve issues amicably. Refer to your contract for terms regarding conflict resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration clauses. Document all communications and agreements to support your position. If necessary, consider involving a legal expert familiar with international trade laws to assist in resolving the dispute. Establishing a clear dispute resolution process upfront can help mitigate potential conflicts.
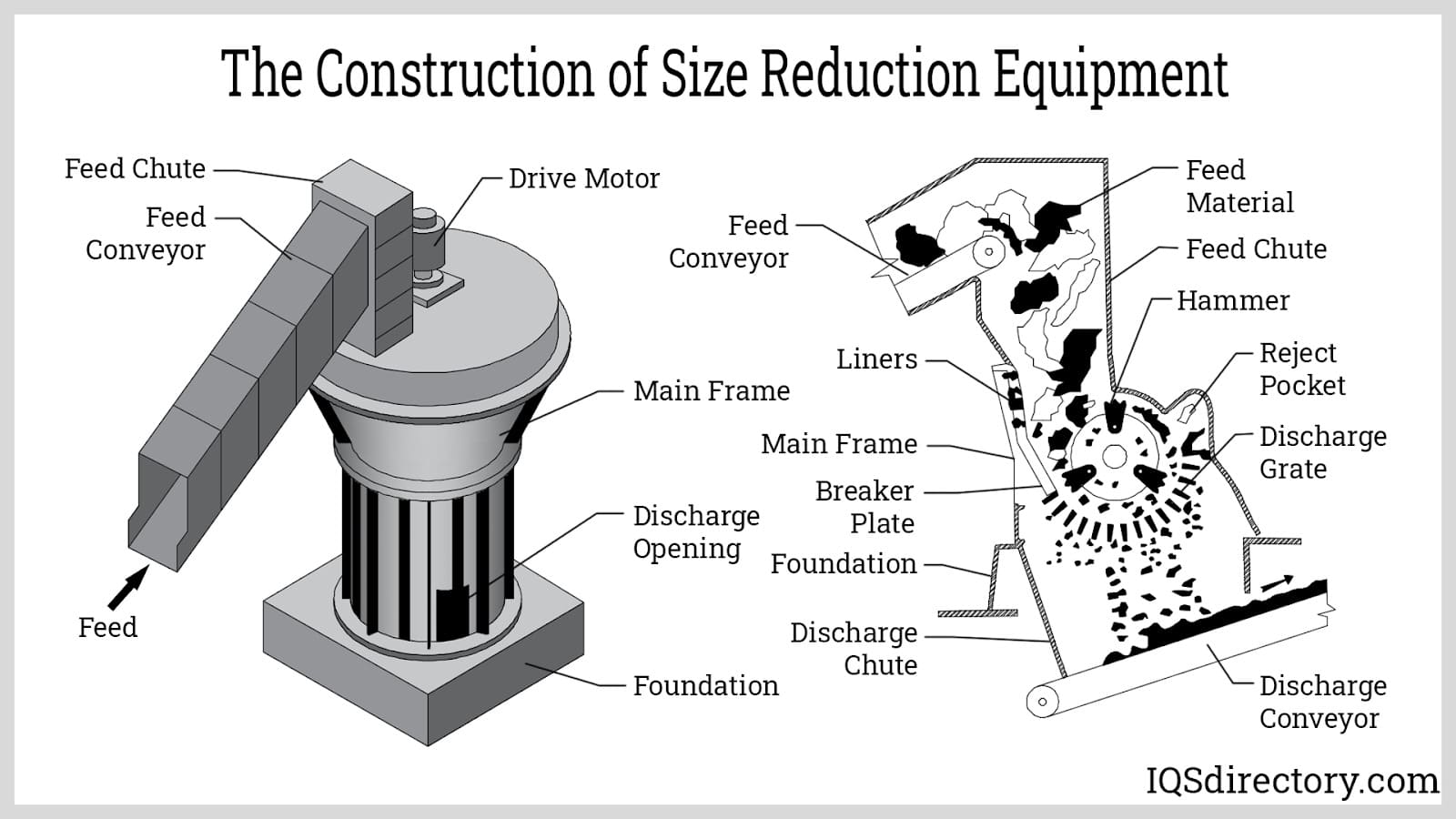
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Are there specific regulatory considerations I need to be aware of when importing particle size reduction equipment?
Yes, regulatory considerations vary by region and can include compliance with safety standards, environmental regulations, and import tariffs. Research the specific regulations in your country regarding machinery imports, such as certifications required for safety and environmental impact. Engage with local customs authorities to ensure you have all necessary documentation and permits. Consulting with a trade compliance expert can also help navigate complex regulations and avoid delays in customs clearance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for particle size reduction equipment
As the global demand for particle size reduction equipment continues to rise, strategic sourcing becomes increasingly crucial for international B2B buyers. Key considerations include understanding the specific requirements of your industry—whether pharmaceutical, food, or chemicals—while also evaluating suppliers based on their technological expertise and product reliability. Buyers should prioritize equipment that not only meets desired particle size distribution (PSD) but also enhances operational efficiency and product quality.
In regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, fostering relationships with established manufacturers can lead to better support and tailored solutions. Leveraging local suppliers can also facilitate smoother logistics and reduce costs, enhancing overall procurement strategies.
Looking ahead, the market for particle size reduction equipment is poised for growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing regulatory standards. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with innovative suppliers who can offer insights into emerging trends and technologies. Engage with industry experts, attend trade shows, and participate in forums to stay informed and make strategic decisions that will position your business for success in an evolving landscape.