Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Bucket Conveyor
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bucket conveyor
In an increasingly interconnected world, bucket conveyors play a pivotal role in optimizing material handling across various industries. From agriculture to manufacturing, these systems are essential for efficiently transporting bulk materials, reducing labor costs, and enhancing productivity. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to streamline their operations, understanding the intricacies of bucket conveyor systems becomes paramount.
This guide offers a comprehensive exploration of bucket conveyors, delving into various types such as standard, inclined, and custom designs tailored for specific applications. It examines the materials utilized in construction, providing insights into durability and maintenance considerations. Additionally, we cover manufacturing processes and quality control measures to ensure that buyers can assess supplier reliability and product integrity effectively.
Understanding the cost factors associated with bucket conveyors is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This guide will help buyers navigate the market landscape, identify reputable suppliers, and leverage frequently asked questions to clarify any uncertainties. By empowering international B2B buyers with this knowledge, we aim to facilitate strategic sourcing decisions that can lead to significant operational improvements and competitive advantages in diverse markets.
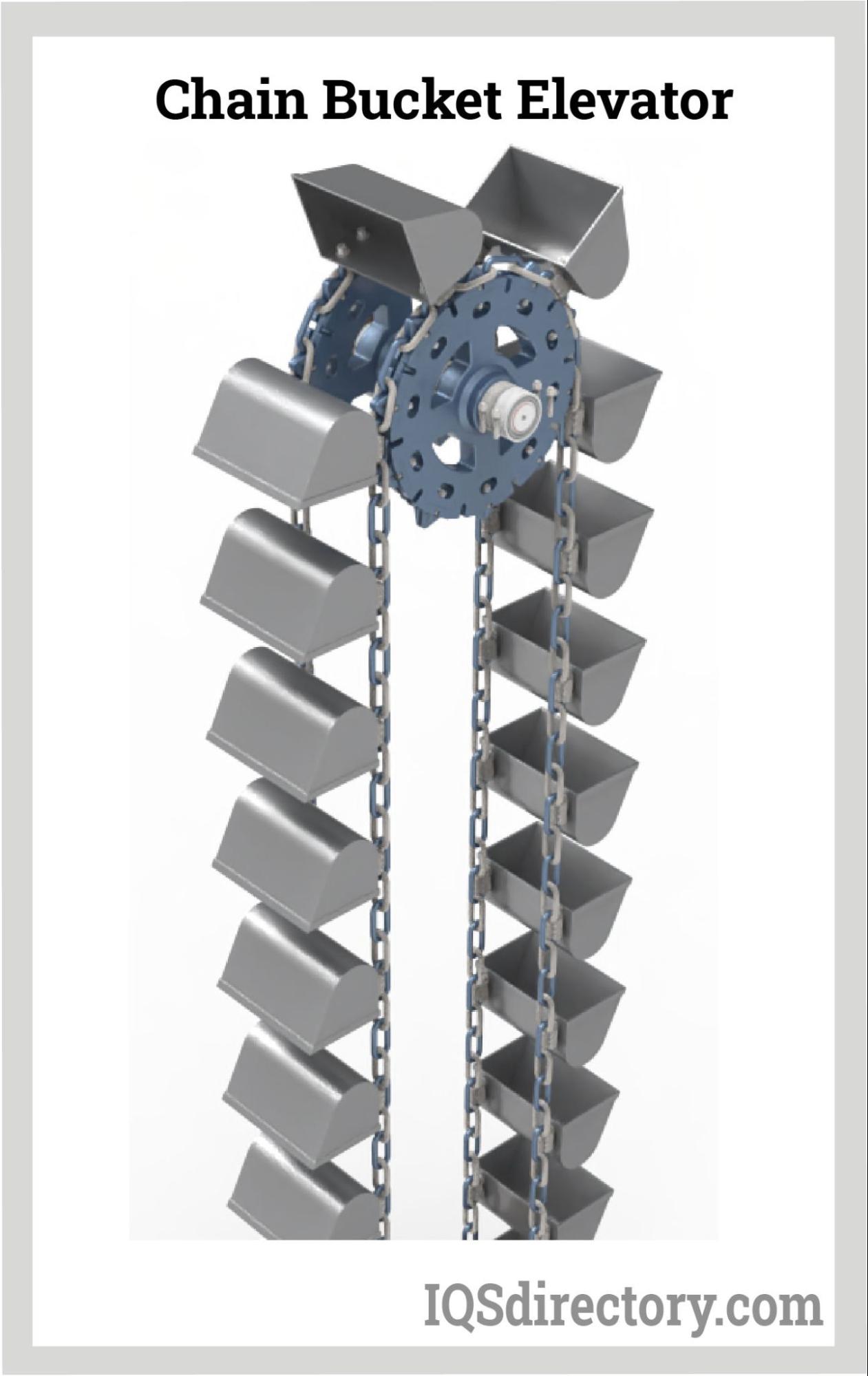
Understanding bucket conveyor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Bucket Conveyor | Fixed design, typically horizontal or inclined. | Manufacturing, agriculture, mining | Pros: Versatile, cost-effective. Cons: Limited flexibility in layout. |
| Z-Type Bucket Conveyor | Vertical configuration with a Z-shaped design. | Food processing, packaging | Pros: Space-saving, ideal for vertical lifts. Cons: More complex installation. |
| C-Type Bucket Conveyor | Curved design allowing for directional changes. | Bulk material handling, recycling | Pros: Efficient in tight spaces, adaptable. Cons: Higher maintenance due to curves. |
| Low Profile Bucket Conveyor | Compact design for low-clearance applications. | Automotive, electronics assembly | Pros: Fits in limited spaces, easy to integrate. Cons: Lower capacity than standard models. |
| Heavy-Duty Bucket Conveyor | Reinforced structure for high-load capacities. | Mining, construction, heavy industries | Pros: Handles large volumes, durable. Cons: Higher initial investment. |
Standard Bucket Conveyor
Standard bucket conveyors are characterized by their fixed design, typically running horizontally or at a slight incline. They are widely used in manufacturing, agriculture, and mining due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. For B2B buyers, the key consideration is the conveyor’s layout and the specific material being transported, as this affects efficiency and operational costs.
Z-Type Bucket Conveyor
The Z-type bucket conveyor features a vertical configuration with a distinctive Z-shaped design. This type is particularly beneficial in food processing and packaging industries where space is at a premium. Buyers should consider the complexity of installation and maintenance, as the vertical lift mechanism can require more intricate engineering compared to standard models.
C-Type Bucket Conveyor
C-type bucket conveyors allow for directional changes, making them suitable for bulk material handling and recycling applications. Their curved design enables efficient operation in tight spaces, which is a significant advantage for facilities with limited room for equipment. However, potential buyers should be aware of the increased maintenance needs due to the complexities introduced by the curves.
Low Profile Bucket Conveyor
Low profile bucket conveyors are designed for applications with low clearance, making them ideal for automotive and electronics assembly lines. Their compact design allows for easy integration into existing systems. Buyers should note that while they fit into tighter spaces, they may have a lower capacity compared to more standard models, which can limit their use in high-volume operations.
Heavy-Duty Bucket Conveyor
Heavy-duty bucket conveyors are built with reinforced structures to handle high-load capacities, making them perfect for industries such as mining and construction. Their durability and capacity to transport large volumes are significant advantages. However, the higher initial investment may be a consideration for buyers, especially those in cost-sensitive markets.
Related Video: Multiple Discharge Locations Z Bucket Conveyor | Vertically Conveying System
Key Industrial Applications of bucket conveyor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bucket conveyor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Transporting bulk ingredients (grains, sugar) | Increases efficiency in material handling, reduces labor costs | Ensure compliance with hygiene standards; consider materials that resist corrosion and are easy to clean |
| Mining and Minerals | Moving ores and aggregates | Enhances productivity by minimizing downtime and manual handling | Assess durability and capacity to handle heavy loads; check for resistance to harsh environmental conditions |
| Construction | Conveying sand, gravel, and concrete mixes | Streamlines construction processes, reducing time on site | Evaluate the conveyor’s adaptability to various terrains; consider modular designs for easy transport |
| Pharmaceuticals | Handling powders and granules | Ensures precise dosing and minimizes contamination risk | Focus on materials that meet FDA regulations; consider automation capabilities for better control |
| Recycling | Sorting and transporting recyclable materials | Increases sorting efficiency and reduces manual labor | Look for systems that can handle a variety of materials; ensure ease of maintenance and adaptability to different waste types |
Food Processing
In the food processing industry, bucket conveyors are essential for transporting bulk ingredients such as grains, sugar, and flour. These systems help streamline operations by automating the movement of materials, which minimizes manual labor and the risk of contamination. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing conveyors that comply with local hygiene regulations and are constructed from corrosion-resistant materials is crucial. This ensures that the equipment remains durable and easy to clean, maintaining product safety standards.
Mining and Minerals
Bucket conveyors are widely used in the mining and minerals sector for moving ores and aggregates from one point to another. Their robust design allows them to handle heavy loads, significantly enhancing productivity while reducing the need for manual handling. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize sourcing durable systems that can withstand harsh mining environments and assess the conveyor’s capacity to handle specific material types. This focus on durability and capacity will ensure continuous operation and lower maintenance costs.
Construction
In construction, bucket conveyors facilitate the efficient transport of materials like sand, gravel, and concrete mixes. This not only accelerates project timelines but also reduces labor costs by minimizing manual handling. For buyers in regions with diverse terrains, such as South Africa, evaluating the adaptability of the conveyor system is essential. Modular designs that are easy to transport and assemble on-site can provide significant advantages, particularly in remote areas where access to heavy machinery may be limited.
Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, bucket conveyors play a critical role in handling powders and granules. They ensure precise dosing and minimize contamination risks, which is vital for maintaining product integrity. International buyers, especially from Europe, should focus on sourcing conveyors that meet stringent FDA regulations. Additionally, systems with automation capabilities can enhance control over the material handling process, providing further assurance of compliance and efficiency.
Recycling
Bucket conveyors are instrumental in the recycling industry, where they are used for sorting and transporting various recyclable materials. These systems improve sorting efficiency and reduce the need for manual labor, which is particularly important in regions with labor shortages. When sourcing conveyor systems, buyers should consider equipment that can handle a wide range of materials and is easy to maintain. Adaptability to different waste types ensures that the conveyor can operate effectively within diverse recycling facilities.
Related Video: Z Type Bucket Elevator/Conveyor by Infinity | Efficient Material Handling
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bucket conveyor
When selecting materials for bucket conveyors, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact performance, durability, and cost. Here, we analyze four common materials used in bucket conveyor systems: steel, plastic, stainless steel, and rubber. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can influence the overall effectiveness of the conveyor system in different environments.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, which is essential in industries like mining and agriculture.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its strength and resistance to wear and tear, which translates to a longer lifespan. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, particularly in humid or chemically aggressive environments, which can lead to increased maintenance costs. Additionally, steel is heavier than other materials, which may affect energy efficiency during operation.
Impact on Application:
Steel is ideal for handling bulk materials such as grains, aggregates, and minerals. Its robustness allows for the transportation of heavy loads, but it may not be suitable for corrosive materials without proper coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure compliance with local and international standards, such as ASTM and DIN, particularly regarding safety and environmental regulations. In regions like Africa and South America, where mining is prevalent, understanding local material sourcing and availability is crucial.
Plastic
Key Properties:
Plastic materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, are lightweight and resistant to corrosion and chemicals. They can operate effectively in a wide range of temperatures.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of plastic reduces energy consumption during operation, and its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for handling various materials, including chemicals and food products. However, plastics may not withstand high temperatures or heavy loads as well as metals, leading to potential deformation or failure under stress.
Impact on Application:
Plastic buckets are often used in food processing and chemical industries, where hygiene and resistance to corrosion are paramount. They are less suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA regulations) when using plastic in food applications. Additionally, understanding regional preferences for materials, particularly in Europe, where sustainability is emphasized, can influence procurement decisions.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures. It is often used in environments where hygiene is critical.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it ideal for food processing and pharmaceutical applications. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which can impact budget considerations.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is suitable for handling food products, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive materials that require strict hygiene standards. Its durability ensures minimal maintenance and downtime.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used meets specific grades (e.g., 304, 316) based on the application. Compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM is also essential, particularly in Europe and the Middle East.
Rubber
Key Properties:
Rubber is known for its flexibility and shock-absorbing properties. It is often used in conjunction with other materials to enhance performance.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of rubber is its ability to reduce noise and vibration, making it suitable for environments where these factors are a concern. However, rubber can degrade over time when exposed to UV light and certain chemicals, leading to a shorter lifespan compared to metals.
Impact on Application:
Rubber is commonly used in bucket conveyor systems for transporting fragile materials or in environments where noise reduction is necessary. It is less effective for heavy-duty applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must consider the local climate and environmental conditions, as these can affect the performance and longevity of rubber components. Ensuring compliance with local standards regarding material safety and environmental impact is also critical.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for bucket conveyor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty applications (mining, agriculture) | High strength and durability | Susceptible to corrosion | High |
| Plastic | Food processing, chemical handling | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited temperature and load capacity | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Rubber | Transporting fragile materials | Noise and vibration reduction | Degrades under UV exposure | Low |
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for bucket conveyors, emphasizing the need for international buyers to consider local regulations, material properties, and application-specific requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bucket conveyor
Manufacturing Processes for Bucket Conveyors
The manufacturing of bucket conveyors involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product is efficient, durable, and meets the specific needs of various industries. The key stages include:
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing bucket conveyors is the selection and preparation of materials. Typically, high-strength steel or stainless steel is used for construction due to its durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. Material preparation involves:
- Cutting: Raw materials are cut into required dimensions using advanced CNC machines to ensure precision.
- Surface Treatment: This can include processes such as sandblasting or chemical cleaning to remove impurities and enhance surface adhesion for coatings.
- Material Inspection: Materials undergo initial quality checks to verify compliance with specified grades and standards.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they are shaped into specific components of the bucket conveyor. This phase may include:
- Bending and Forming: Using hydraulic presses and roll-forming machines, the metal sheets are bent into the required shapes for the frame and buckets.
- Welding: Key components are welded together to create a robust structure. Techniques such as MIG or TIG welding are often employed to ensure strong joints.
- Machining: Precision machining processes may be applied to create slots, holes, or grooves necessary for assembly.
Assembly
In this stage, the formed components are assembled into a complete bucket conveyor system. The assembly process includes:
- Component Fitting: All parts, including the drive system, buckets, and frame, are fitted together. This often requires manual labor for precision alignment.
- Integration of Electrical Systems: If the conveyor includes electrical components, such as sensors or controls, they are integrated during this phase.
- Initial Testing: A preliminary test is conducted to ensure that the assembly functions as intended before moving on to finishing.
Finishing
The final stage involves preparing the conveyor for delivery. This includes:
- Coating: Application of protective coatings, such as powder coating or galvanizing, to enhance durability and corrosion resistance.
- Final Inspection: A thorough inspection is conducted to ensure that all components meet the required specifications and standards before packaging.
- Packaging: Proper packaging techniques are employed to prevent damage during transportation.
Quality Assurance in Bucket Conveyor Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in the manufacturing of bucket conveyors, ensuring that products meet industry standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically involves several international and industry-specific standards, along with systematic checkpoints.
International Standards
For international buyers, compliance with recognized standards is essential. Key standards include:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system, focusing on meeting customer expectations and delivering satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required in Europe, this indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries like oil and gas, API standards ensure that equipment meets specific safety and quality requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is integrated into the manufacturing process through several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before they are used in production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various tests and inspections are conducted to monitor production quality. This can include dimensional checks and weld inspections.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before shipment, the finished product undergoes a comprehensive inspection to confirm it meets all quality and performance standards.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to verify the integrity and functionality of bucket conveyors:
- Load Testing: Ensures the conveyor can handle the specified load without failure.
- Vibration Testing: Assesses the durability of the conveyor under operational conditions.
- Functional Testing: Verifies that all mechanical and electrical components operate correctly.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital. Here are actionable steps to ensure compliance and quality:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct on-site audits to review the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with industry standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask for detailed reports on past quality control checks, including failure rates and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of the manufacturing facility and products before shipment.
- Certification Verification: Confirm that the supplier holds relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) by checking with the certifying bodies.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
Understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions can help mitigate risks associated with international purchases. Key considerations include:
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of varying attitudes towards quality and compliance in different regions. Building relationships with suppliers can help establish trust and understanding.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are familiar with and compliant with the regulations of the countries where the products will be used, particularly in Africa and South America, where regulations can vary significantly.
- Communication Barriers: Establish clear communication channels to address any quality concerns or specifications promptly. Utilize translators if necessary to ensure clarity.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bucket conveyors, ensuring they receive high-quality products tailored to their operational needs.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing – Lean Factory Tour – FastCap
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bucket conveyor Sourcing
When sourcing bucket conveyors, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international buyers. This section outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for negotiating favorable terms, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Bucket Conveyors
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Common materials used in bucket conveyors include steel, plastic, and rubber. Higher-quality materials, such as stainless steel or specialized plastics, can increase costs but may offer better durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely based on the manufacturing location. For instance, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs may reduce overall expenses. However, this can be offset by potential quality control issues, necessitating careful evaluation of labor quality.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Manufacturers with efficient operations may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Customization often requires specialized tooling, which can add to initial costs. Buyers should assess whether the long-term benefits of customized solutions outweigh these initial investments.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that products meet quality standards is essential. QC costs may include testing and inspections, which can be more significant for complex conveyor systems.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are influenced by distance, shipping methods, and import tariffs. Buyers should consider the total logistics expenses when evaluating supplier quotes.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the market rates and the supplier’s position can help in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can greatly affect pricing. Higher volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale.
-
Specifications/Customization: Unique specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the potential for higher expenses.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and compliance with international quality standards (e.g., ISO certifications) can influence prices. Buyers should verify suppliers’ certifications to ensure product quality.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, reliability, and production capabilities of suppliers can vary. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining responsibilities in shipping and logistics. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can significantly affect the total landed cost.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers regarding pricing. Highlighting potential long-term relationships can lead to better pricing or favorable terms.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess not just the initial purchase price, but the overall cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational costs over the conveyor’s lifespan.
-
Consider Local Suppliers: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, local suppliers may offer competitive pricing and reduced shipping costs, despite potentially higher manufacturing prices.
-
Volume Purchases: If possible, consolidate orders to meet MOQs, which can provide significant cost savings.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be cognizant of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and regional economic conditions that can affect pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct thorough research and request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential bucket conveyor Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘bucket conveyor’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bucket conveyor
Essential Technical Properties of Bucket Conveyors
When considering bucket conveyors for your operations, understanding key technical properties is vital. Here are several critical specifications to evaluate:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of material used to construct the bucket and conveyor system, often categorized by strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion or wear.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade is essential for ensuring longevity and reliability in harsh industrial environments. For instance, stainless steel may be preferred for food applications due to its hygienic properties, while plastic might be suitable for lighter, non-abrasive materials. -
Bucket Capacity
– Definition: The volume or weight of material that each bucket can carry, typically measured in liters or kilograms.
– B2B Importance: Understanding bucket capacity helps in calculating the overall throughput of the conveyor system. It allows buyers to ensure that the system meets production requirements without causing bottlenecks. -
Belt Speed
– Definition: The speed at which the conveyor belt moves, often measured in meters per second (m/s).
– B2B Importance: Belt speed directly impacts the efficiency of material handling. A higher speed may increase throughput but could also lead to spillage or wear. Buyers must balance speed with operational requirements to optimize performance. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from specified dimensions in the design and manufacturing of the conveyor system.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance levels affect the precision and fit of components, which is crucial for maintaining the conveyor’s operational integrity. Tight tolerances may be necessary for high-speed applications to prevent misalignment and wear. -
Drive Type
– Definition: The mechanism used to power the conveyor system, which can include electric motors, hydraulic systems, or manual drives.
– B2B Importance: The choice of drive type influences maintenance requirements, energy consumption, and overall operational costs. For example, electric drives are often more efficient and easier to automate than hydraulic systems. -
Length and Height
– Definition: The total distance the conveyor covers and the vertical height it elevates materials.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the length and height is critical for planning the layout of the facility and ensuring that the system fits within spatial constraints while achieving the desired elevation.
Common Trade Terminology in Bucket Conveyor Procurement
Understanding industry jargon is crucial for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some commonly used terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Knowing whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the components being offered. OEM parts often come with warranties and are designed for specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and budget. It is especially significant for smaller operations that may not need large quantities of equipment or parts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that solicits price and other bid information from suppliers for specific goods or services.
– Importance: An RFQ is an essential tool for comparing suppliers and ensuring competitive pricing. Crafting a detailed RFQ can help buyers receive accurate and comparable quotes.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time is vital for planning production schedules and inventory management. Longer lead times can affect project timelines and operational efficiency. -
Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the product and the commitment to repair or replace it if necessary.
– Importance: Understanding warranty terms can protect buyers from potential defects and ensure the reliability of the equipment over its expected lifespan.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing bucket conveyors, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the bucket conveyor Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The bucket conveyor sector is witnessing significant growth driven by the increasing demand for efficient material handling systems across various industries, including mining, agriculture, and manufacturing. Key global drivers include the need for automation, cost efficiency, and the ability to handle bulk materials in a safe and environmentally friendly manner. For international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Emerging technology trends are reshaping the sourcing landscape. The adoption of IoT (Internet of Things) in bucket conveyor systems is enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, thereby reducing downtime and enhancing operational efficiency. Furthermore, advancements in materials science have led to the development of lightweight, durable components that improve the overall performance of bucket conveyors. Buyers should also keep an eye on automation trends, as automated systems are increasingly being integrated into existing infrastructure, allowing for smoother workflows.
The market dynamics are influenced by regional factors. For instance, in Africa and South America, the expansion of mining operations is a significant driver, while in Europe and the Middle East, there is a stronger emphasis on sustainability and compliance with stringent regulations. Buyers should align their sourcing strategies with these regional trends to optimize their investments in bucket conveyor technology.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern in the bucket conveyor sector, with increasing pressure from stakeholders to adopt environmentally responsible practices. The environmental impact of manufacturing and operating bucket conveyors includes energy consumption, waste generation, and emissions. Therefore, international B2B buyers must prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their ecological footprint.
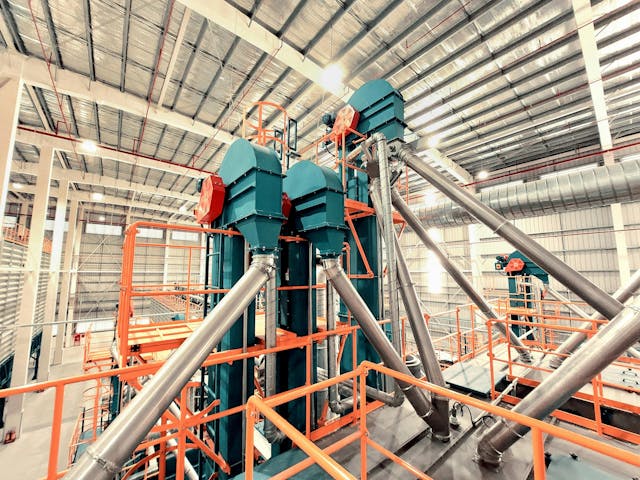

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical sourcing is crucial in ensuring that the materials used in bucket conveyors are obtained responsibly. This involves selecting suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. The use of certified “green” materials, such as recycled metals and sustainably sourced plastics, can also significantly mitigate environmental impacts. Buyers should look for suppliers with certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or similar standards that demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
In addition, integrating sustainability into supply chains can lead to cost savings and improved brand reputation. As consumers and businesses alike become more environmentally conscious, the demand for sustainable practices is likely to influence purchasing decisions. Therefore, incorporating these values into sourcing strategies is essential for long-term success.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of bucket conveyor systems dates back to the late 19th century when they were first introduced to facilitate the efficient transport of bulk materials in industries such as mining and agriculture. Initially, these systems were powered by steam engines and later transitioned to electric motors, enhancing their efficiency and reliability.
Over the decades, advancements in engineering and materials technology have transformed bucket conveyors into sophisticated systems capable of handling a wide range of materials, from grains to heavy ores. The introduction of automation and IoT technologies in recent years marks the latest phase of evolution, enabling real-time monitoring and improved operational efficiency. This history not only highlights the adaptability of bucket conveyors but also underscores the importance of continuous innovation in meeting the evolving needs of global markets.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bucket conveyor
-
How do I vet suppliers for bucket conveyors?
To effectively vet suppliers, start by researching their reputation through industry forums, customer testimonials, and third-party review sites. Request references and case studies that demonstrate their experience with bucket conveyors. It’s also prudent to verify their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate adherence to quality management. Consider visiting their facilities if possible, or utilize video calls to assess their operations and capabilities. Lastly, establish a clear communication channel to gauge their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate. -
Can I customize the bucket conveyor to suit my specific needs?
Yes, most manufacturers offer customization options for bucket conveyors. You can specify dimensions, materials, and features such as bucket size, shape, and configuration based on your operational requirements. Discuss your needs with potential suppliers early in the conversation to ensure they have the capability to meet your specifications. Keep in mind that extensive customization may impact lead times and costs, so be prepared to negotiate and evaluate the trade-offs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities for bucket conveyors can vary significantly between suppliers, often ranging from a single unit to several dozen, depending on the manufacturer’s capabilities and your customization needs. Lead times can also differ, typically spanning from a few weeks to several months. Factors influencing these timelines include the complexity of the design, current production schedules, and shipping logistics. Always confirm MOQs and lead times upfront to avoid potential delays in your supply chain.
-
What payment options should I expect when sourcing internationally?
International B2B transactions often involve various payment methods, including wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. It’s vital to negotiate favorable payment terms that protect your interests, such as partial payments upon order confirmation and the balance upon delivery. Be aware of currency fluctuations and consider using a foreign exchange service to mitigate risks. Additionally, ensure your supplier provides a clear invoice detailing all costs, including shipping and customs duties. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for?
When sourcing bucket conveyors, inquire about the manufacturer’s quality assurance protocols. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicate adherence to international quality standards. Request detailed information about their inspection processes, including in-house testing and third-party audits. Establish a clear agreement on quality expectations and consider requesting samples or conducting site visits to assess product quality before finalizing your order. -
How can I manage logistics and shipping for international orders?
Effective logistics management begins with understanding the shipping options available to you. Discuss with your supplier the best methods for transporting bucket conveyors, whether through air, sea, or land. Evaluate factors such as cost, delivery time, and reliability. Additionally, ensure that the supplier provides all necessary shipping documents, including bills of lading and customs declarations, to facilitate smooth clearance at your destination. Consider partnering with a freight forwarder experienced in international trade to streamline the process. -
What should I do if there’s a dispute with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, it’s crucial to maintain open lines of communication with your supplier to resolve issues amicably. Refer to the contract terms regarding dispute resolution mechanisms, which may include mediation or arbitration. Document all communications and agreements to provide a clear record of interactions. If a resolution cannot be reached, consider seeking legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to understand your rights and potential remedies. -
Are there specific certifications I need to be aware of when importing bucket conveyors?
Yes, importing bucket conveyors may require compliance with various certifications and regulations, depending on your destination country’s import laws. Common certifications include CE marking for products sold in Europe, which indicates compliance with health and safety standards. In some regions, additional certifications might be necessary for materials used in food processing applications. Research the specific requirements for your country and ensure your supplier can provide the necessary documentation to facilitate compliance and avoid customs issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bucket conveyor
Strategic sourcing of bucket conveyors is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. By identifying reliable suppliers and leveraging competitive pricing, companies can ensure they acquire high-quality equipment that meets their specific needs. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating supplier capabilities, understanding local market dynamics, and considering the total cost of ownership rather than just initial purchase price.
Value of Strategic Sourcing:
– Cost Efficiency: Strategic sourcing enables businesses to negotiate better terms and reduce overall expenditure.
– Quality Assurance: Partnering with reputable suppliers ensures access to superior products that enhance productivity.
– Risk Mitigation: A diversified supplier base can safeguard against disruptions in supply chains.
As we look to the future, international B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize strategic sourcing as a means to not only acquire bucket conveyors but also to foster long-term partnerships that drive innovation and sustainability. Now is the time to act—invest in your sourcing strategy today to secure a competitive edge in the global market. Embrace the potential of advanced bucket conveyor systems to streamline operations and propel your business forward.