Master Compression Mold Sourcing: Your Comprehensive Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for compression mold
In today’s competitive landscape, understanding the nuances of compression molding is essential for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their manufacturing processes. This versatile method is integral for producing durable, high-quality components across various industries, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. By mastering compression molding, businesses can enhance product performance, reduce costs, and meet the evolving demands of global markets.
This comprehensive guide delves into the critical aspects of compression molding, covering a broad spectrum of topics essential for informed sourcing decisions. Buyers will explore various types of compression molds, suitable materials like rubber and silicone, and the intricacies of manufacturing and quality control processes. Additionally, insights into supplier selection, cost considerations, and current market trends will empower decision-makers to navigate their options confidently.
Special attention is given to the unique challenges and opportunities faced by buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including specific examples relevant to markets like Thailand and the UK. By equipping themselves with this knowledge, businesses can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they partner with the right suppliers who meet their quality and efficiency standards.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital resource, enabling B2B buyers to make strategic, informed decisions in the global market for compression molds.
Understanding compression mold Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Compression Mold | Simple two-part molds, suitable for high-volume production | Automotive parts, seals, gaskets | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to maintain; Cons: Limited design flexibility. |
| Multi-Cavity Mold | Contains multiple cavities to produce several parts simultaneously | Consumer goods, electronics | Pros: Increases production efficiency; Cons: Higher initial tooling costs. |
| Insert Mold | Incorporates inserts (like metal components) into the mold | Medical devices, industrial components | Pros: Enhances part functionality; Cons: More complex design and setup. |
| Transfer Mold | Uses a separate chamber to transfer material into the mold | Specialty items, complex geometries | Pros: Better control over material flow; Cons: Slower production rates. |
| Automated Compression Mold | Integrated with robotics for automated loading and unloading | High-volume manufacturing, automotive | Pros: Reduces labor costs, increases consistency; Cons: High initial investment. |
Standard Compression Mold
Standard compression molds are the most basic type, typically featuring a two-part design that allows for the easy production of high volumes of parts. They are predominantly used in industries such as automotive and consumer goods for components like seals and gaskets. For B2B buyers, the primary considerations include cost-effectiveness and maintenance ease; however, the trade-off is a lack of design flexibility, which may limit innovation.
Multi-Cavity Mold
Multi-cavity molds are designed to produce several identical parts in one cycle, significantly increasing production efficiency. These molds are ideal for applications in consumer goods and electronics, where high volume is necessary. While they offer substantial advantages in terms of throughput, buyers should be aware of the higher initial tooling costs associated with their complexity and precision requirements.
Insert Mold
Insert molds are characterized by their ability to incorporate additional components, such as metal inserts, directly into the molded part. This feature is particularly valuable in the medical and industrial sectors, where part functionality is critical. Buyers should consider the added complexity in design and setup, which may increase lead times, but the benefits of enhanced product performance can justify the investment.
Transfer Mold
Transfer molds utilize a separate chamber to push the material into the mold cavity, offering greater control over the flow of the material. This type is well-suited for specialty items and complex geometries, making it a preferred choice in industries requiring precision. While they provide superior control, buyers need to consider the slower production rates, which may impact overall efficiency.
Automated Compression Mold
Automated compression molds integrate robotics and automation to streamline the loading and unloading process, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing environments, such as the automotive industry. The main advantages include reduced labor costs and increased consistency in production. However, the high initial investment required for automation technology may be a barrier for some businesses, necessitating careful financial planning.
Related Video: Compression Moulding Process – A Detailed explanation.
Key Industrial Applications of compression mold
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Compression Mold | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of rubber seals and gaskets | Enhances vehicle durability and reduces maintenance costs | Ensure suppliers have experience with automotive-grade materials. |
| Medical Devices | Manufacturing of custom silicone components | Ensures compliance with stringent health regulations | Verify certifications and quality assurance processes. |
| Consumer Goods | Creation of durable rubber grips and handles | Improves product usability and customer satisfaction | Assess material compatibility and design flexibility. |
| Electronics | Production of insulating components | Reduces risk of electrical failures and enhances safety | Check for suppliers with expertise in thermal and electrical properties. |
| Aerospace | Manufacturing of lightweight seals and insulators | Increases fuel efficiency and performance of aircraft | Focus on sourcing from manufacturers with aerospace certifications. |
Automotive
In the automotive sector, compression molding is crucial for producing high-performance rubber seals and gaskets that are essential for preventing leaks and ensuring vehicle integrity. This method allows for the creation of complex shapes that meet specific design requirements, thus enhancing the durability of components. For international buyers, especially from Africa and South America, it is vital to source from suppliers who are experienced with automotive-grade materials and can provide compliance with local automotive standards.
Medical Devices
Compression molding is extensively used in the medical device industry to manufacture custom silicone components such as seals, valves, and tubing. These parts must meet stringent health regulations, ensuring safety and efficacy in medical applications. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should prioritize suppliers who can demonstrate robust quality assurance protocols and relevant certifications, ensuring that products are compliant with international health standards.
Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods sector, compression molding is employed to create durable rubber grips and handles for various products. This process enhances usability and comfort, directly impacting customer satisfaction. International buyers, particularly from Europe and Africa, should evaluate potential suppliers based on their ability to offer design flexibility and material compatibility to meet diverse product needs.
Electronics
The electronics industry benefits from compression molding through the production of insulating components that protect against electrical failures. The process allows for the creation of precise, durable parts that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. Buyers from regions like South America and Europe should focus on sourcing from manufacturers with expertise in materials that possess excellent thermal and electrical properties to ensure safety and reliability.
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, compression molding is utilized to manufacture lightweight seals and insulators that contribute to the overall efficiency of aircraft. These components must meet rigorous safety standards while minimizing weight to enhance fuel efficiency. Buyers from Africa and the Middle East should seek manufacturers with aerospace certifications and a proven track record in producing high-quality, compliant components to ensure optimal performance and safety in their applications.
Related Video: Compression Molding
Strategic Material Selection Guide for compression mold
When selecting materials for compression molding, it is essential to consider various factors that influence product performance and suitability for specific applications. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in compression molding, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Silicone Rubber
Key Properties: Silicone rubber exhibits excellent temperature stability, with a service range from -60°C to 200°C. It is also resistant to UV light, ozone, and various chemicals, making it suitable for outdoor applications.
Pros & Cons: Silicone rubber is highly durable and maintains its properties over a wide range of temperatures. However, it can be more expensive than other elastomers, which may increase production costs. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized equipment for precise molding.
Impact on Application: Silicone rubber is ideal for applications requiring flexibility and resistance to extreme conditions, such as seals and gaskets in automotive and aerospace industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with relevant standards like ASTM D2000 for rubber materials. Additionally, understanding the local market’s acceptance of silicone products is crucial, as preferences can vary across regions such as Africa and Europe.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Key Properties: EPDM is known for its excellent weather resistance, high-temperature tolerance (up to 150°C), and good electrical insulating properties.
Pros & Cons: This material is cost-effective and provides good durability against environmental factors. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to silicone, which may limit its applications in high-stress environments. The manufacturing process is relatively straightforward, making it accessible for many manufacturers.
Impact on Application: EPDM is commonly used in roofing membranes, automotive weather stripping, and electrical insulation due to its resilience against aging and environmental stressors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific performance standards relevant to EPDM in their region, such as DIN 7863 in Europe. Understanding local sourcing capabilities can also influence cost-effectiveness.
Nitrile Rubber (NBR)
Key Properties: Nitrile rubber is characterized by its excellent oil and fuel resistance, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: NBR is relatively inexpensive and offers good mechanical properties, making it a popular choice for seals and gaskets. However, it has limited resistance to ozone and UV light, which can lead to degradation in outdoor applications. The complexity of manufacturing is moderate, requiring careful handling during the molding process.
Impact on Application: NBR is widely used in applications involving petroleum products, such as fuel hoses and seals, due to its resistance to oil and grease.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D1418 is essential for NBR products. Buyers should also consider the availability of NBR in their local markets, as sourcing can vary significantly between regions.
Polyurethane (PU)
Key Properties: Polyurethane exhibits high abrasion resistance and can be formulated to achieve a wide range of hardness levels. It can withstand temperatures from -30°C to 80°C, depending on the formulation.
Pros & Cons: PU is versatile and can be tailored for specific applications, offering excellent durability and performance. However, it can be more expensive than other elastomers, and the manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precise formulations and curing times.
Impact on Application: Polyurethane is often used in applications requiring high wear resistance, such as wheels, rollers, and cushioning components.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PU products meet relevant safety and performance standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management. Understanding the local regulatory landscape is crucial for compliance and market acceptance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for compression mold | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicone Rubber | Seals and gaskets in automotive | Excellent temperature stability | Higher cost compared to other elastomers | High |
| EPDM | Automotive weather stripping | Cost-effective and durable | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Nitrile Rubber | Fuel hoses and seals | Good oil and fuel resistance | Limited ozone and UV resistance | Low |
| Polyurethane | Wheels and cushioning components | High abrasion resistance | More expensive with complex manufacturing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on performance requirements, cost considerations, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for compression mold
Compression molding is a widely utilized manufacturing process that produces high-quality, durable components across various industries. For international B2B buyers, especially those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in compression molding is essential for making informed procurement decisions.
Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process of compression molding can be divided into several main stages:
1. Material Preparation
The success of compression molding begins with the careful preparation of raw materials. Typically, thermosetting elastomers like rubber or silicone are used. The material is often preheated to optimize its flow properties and ensure uniform distribution within the mold. Precise weighing and mixing of additives are crucial to prevent defects, such as incomplete fills or surface imperfections.
- Key Techniques:
- Preform Creation: Preforms are shaped and sized to fit the mold, ensuring minimal waste and optimal cavity filling.
- Material Testing: Conducting tests to verify material properties (e.g., viscosity, thermal stability) before use.
2. Forming
This stage is where the actual molding occurs. The prepared preform is placed into a heated mold, which is then closed, and pressure is applied. The heat causes the material to flow and fill the mold cavity, while the pressure ensures that any trapped air is expelled, preventing voids.
- Key Techniques:
- Temperature Control: Maintaining precise temperature settings throughout the process to avoid defects.
- Pressure Application: Utilizing hydraulic or mechanical presses to apply uniform pressure.
3. Assembly
After forming, the components may require additional assembly steps, depending on the complexity of the final product. This could involve bonding multiple parts or integrating inserts and fasteners.
- Key Techniques:
- Inserts Integration: Using pre-formed inserts to enhance the functionality of the molded part.
- Bonding: Employing adhesives or heat to bond different materials together.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage involves trimming excess material (deflashing), surface treatment, and any necessary post-processing. This ensures that the final product meets the precise dimensional and aesthetic requirements.
- Key Techniques:
- Trimming: Removing excess material carefully to maintain product integrity.
- Surface Treatment: Applying coatings or finishes to enhance performance or appearance.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in compression molding is vital to ensure that products meet industry standards and customer expectations. Here are some key aspects:
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS), ensuring consistent quality in products and services.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: In the oil and gas sector, the American Petroleum Institute (API) provides standards for quality assurance in manufacturing components.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in compression molding typically includes several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of raw materials to ensure they meet specified standards before entering production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect and rectify any issues immediately.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of finished products to ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are employed to validate the quality of the molded parts, including:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and gauges to verify that parts meet specified dimensions.
- Material Testing: Assessing mechanical properties such as tensile strength and elasticity to ensure performance under specified conditions.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for surface defects, color consistency, and overall aesthetics.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must be diligent in verifying the quality assurance practices of their suppliers. Here are several approaches:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to review the supplier’s manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed reports on quality control processes, including results of tests and inspections.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the supplier’s operations and product quality, ensuring unbiased assessments.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from diverse regions, it’s essential to understand the nuances of quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with local standards and regulations that may differ from international norms. For example, medical devices in Europe must comply with the Medical Device Regulation (MDR).
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and inspection rigor. Engage in clear communication with suppliers to align on quality expectations.
- Documentation and Traceability: Ensure that suppliers provide comprehensive documentation for all materials and processes, which is critical for regulatory compliance and traceability.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with compression molding, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality standards and operational needs. This knowledge not only enhances product quality but also strengthens supply chain resilience in an increasingly competitive global market.
Related Video: The Silicone Rubber Compression Molding Process Explained
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for compression mold Sourcing
When analyzing the cost structure and pricing for compression mold sourcing, it is essential to break down the various cost components and factors that influence pricing. This understanding will aid international B2B buyers in making informed decisions, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts the overall cost. Compression molding typically uses thermoset materials like rubber and silicone, which can vary in price based on quality and supplier. Bulk purchasing can lead to cost savings.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass skilled operators and technicians who manage the molding process. In regions with higher labor costs, such as parts of Europe, these expenses can represent a significant portion of the total cost. Outsourcing to manufacturers in countries with lower labor costs may present cost advantages.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing practices can help minimize these overheads, contributing to overall cost savings.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom molds. The complexity of the mold design, the materials used, and the need for precision engineering all contribute to this cost. Investing in high-quality tooling can enhance durability and reduce long-term expenses.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing strict quality control measures is vital for ensuring that the molded products meet required specifications. While QC adds to the initial cost, it can prevent costly reworks and defects, which can be more expensive in the long run.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are often overlooked but can significantly influence the total cost of sourcing. Factors such as shipping methods, distances, and customs duties must be considered. Choosing the right Incoterms can help clarify responsibilities and costs.
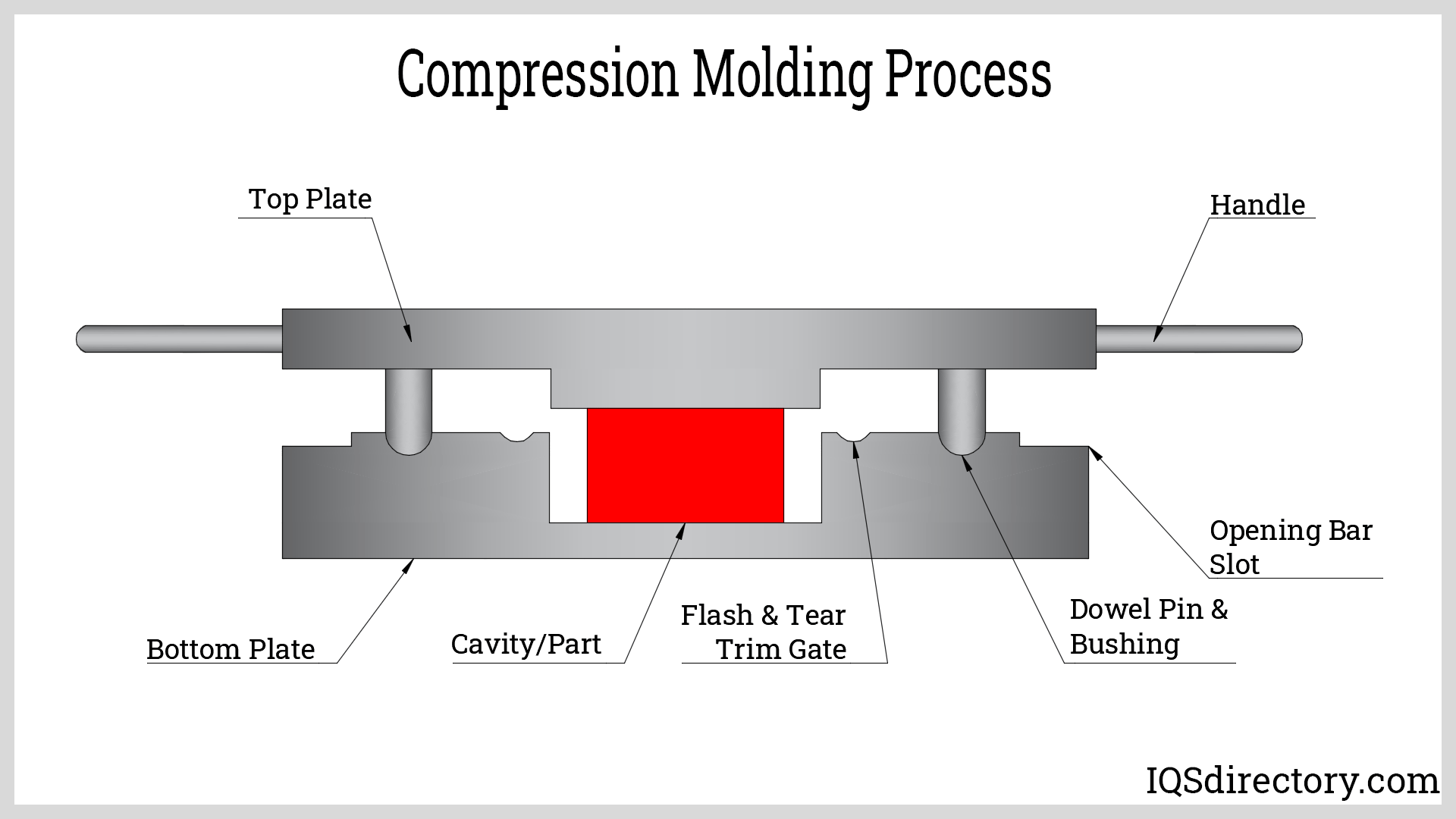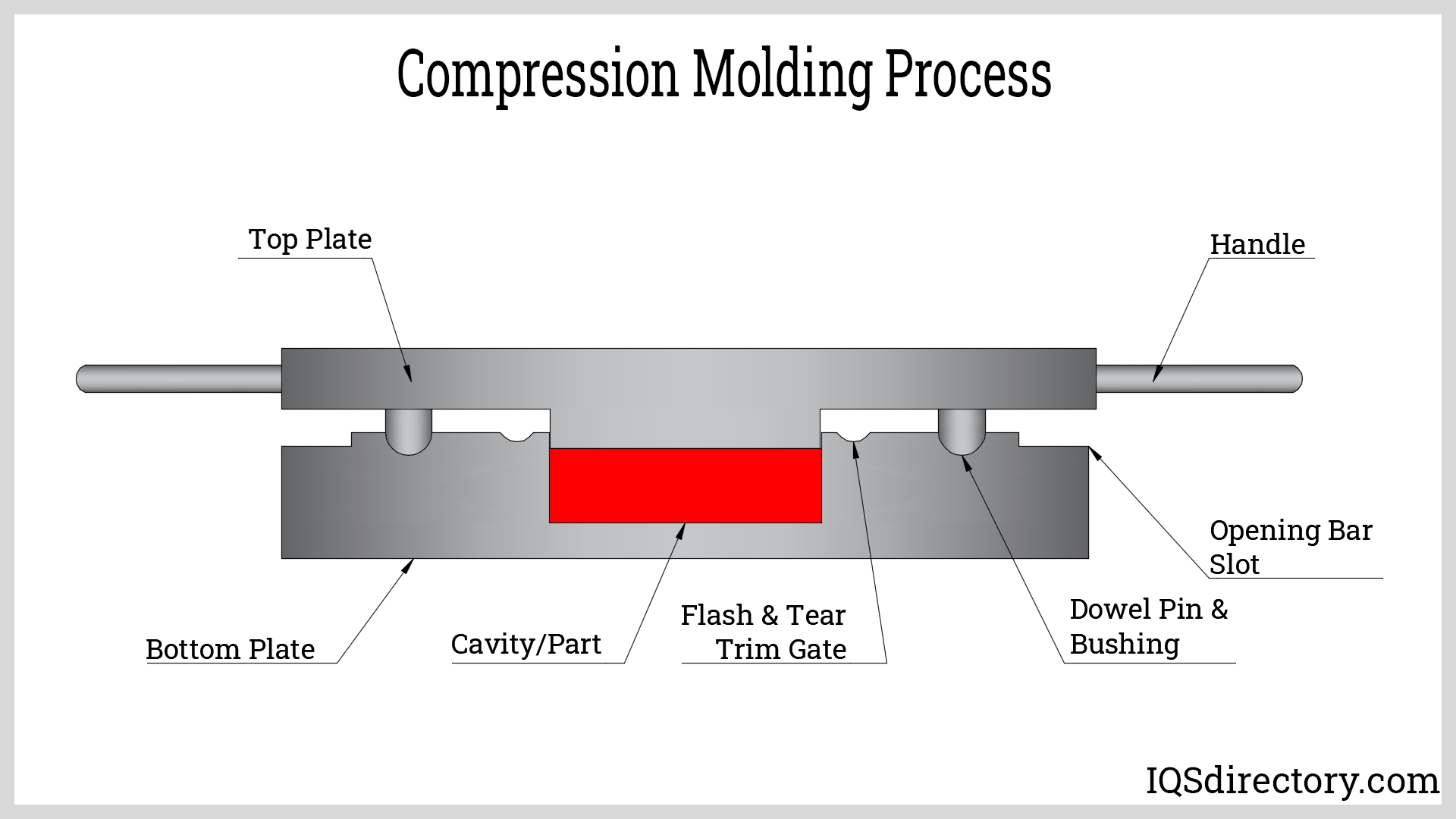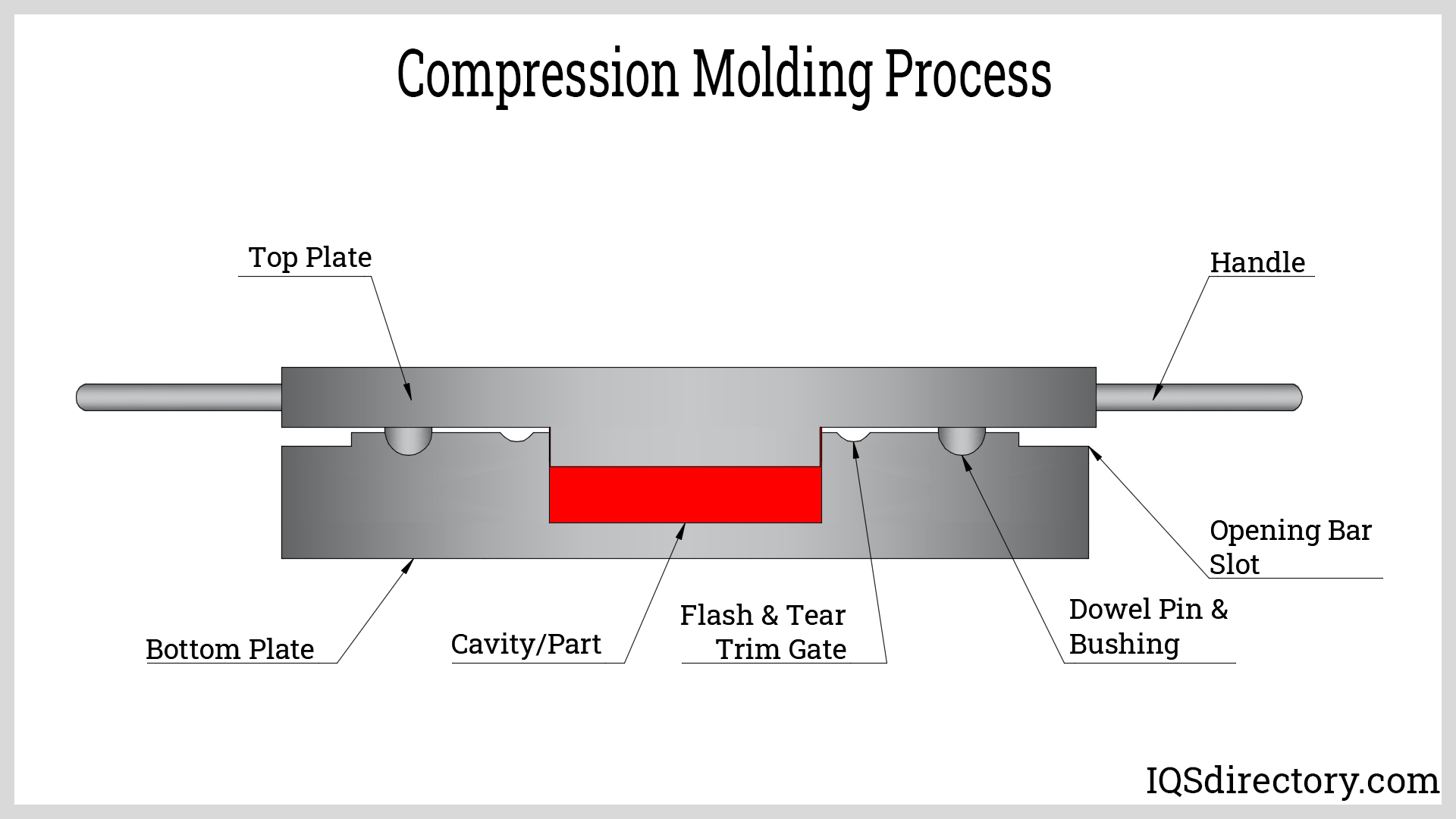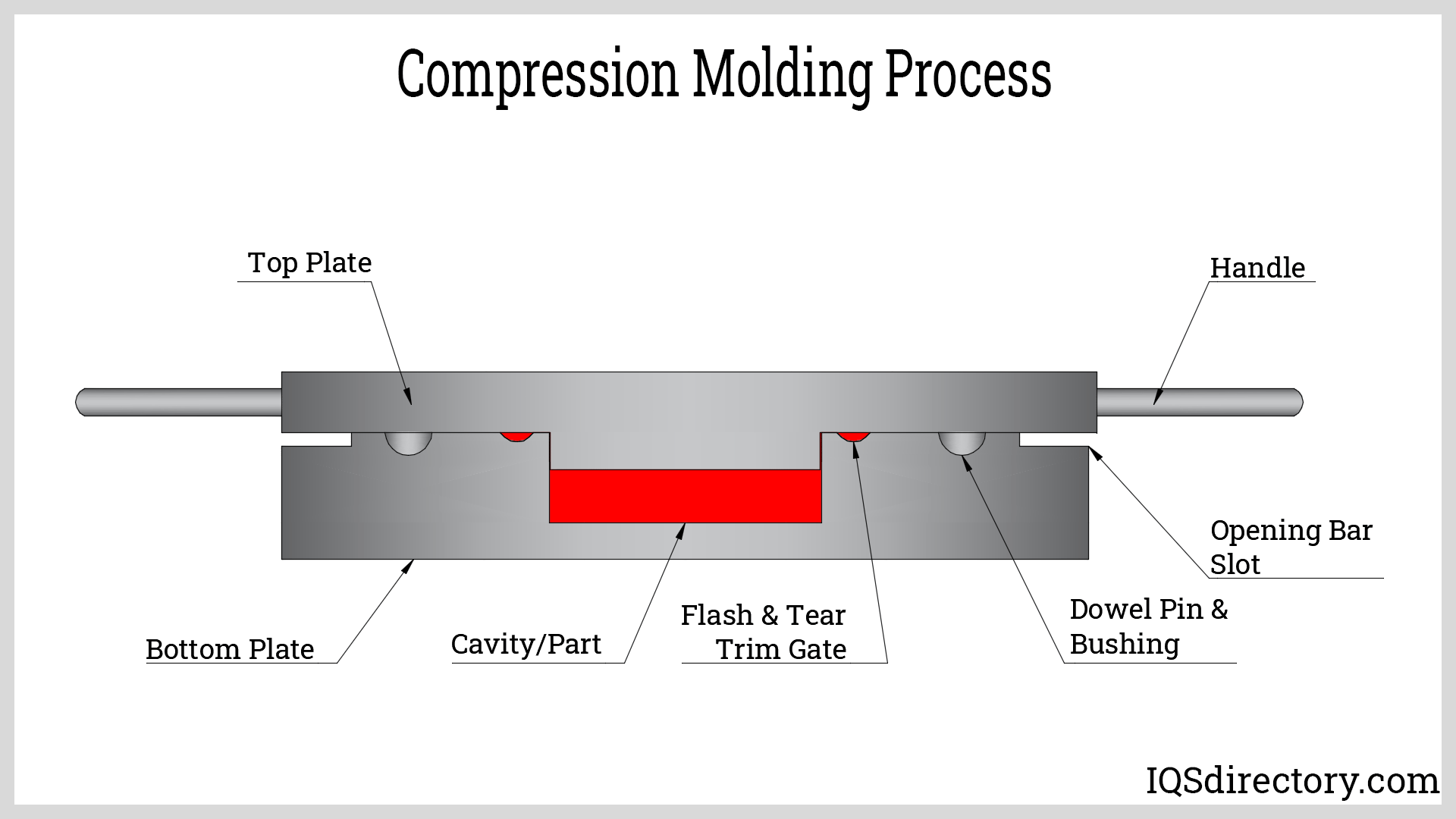
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the supplier’s business model. Understanding the typical margins in your industry can help in negotiating better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can affect pricing. Larger volumes typically lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their production needs to negotiate favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements can increase costs. Clear communication of specifications upfront can help suppliers provide accurate quotes and avoid misunderstandings.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that meet industry standards and certifications may come at a premium. However, investing in quality can lead to enhanced performance and reduced risk of failure.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier play a critical role in pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their track record and quality assurance processes, while newer suppliers may offer lower prices to attract business.
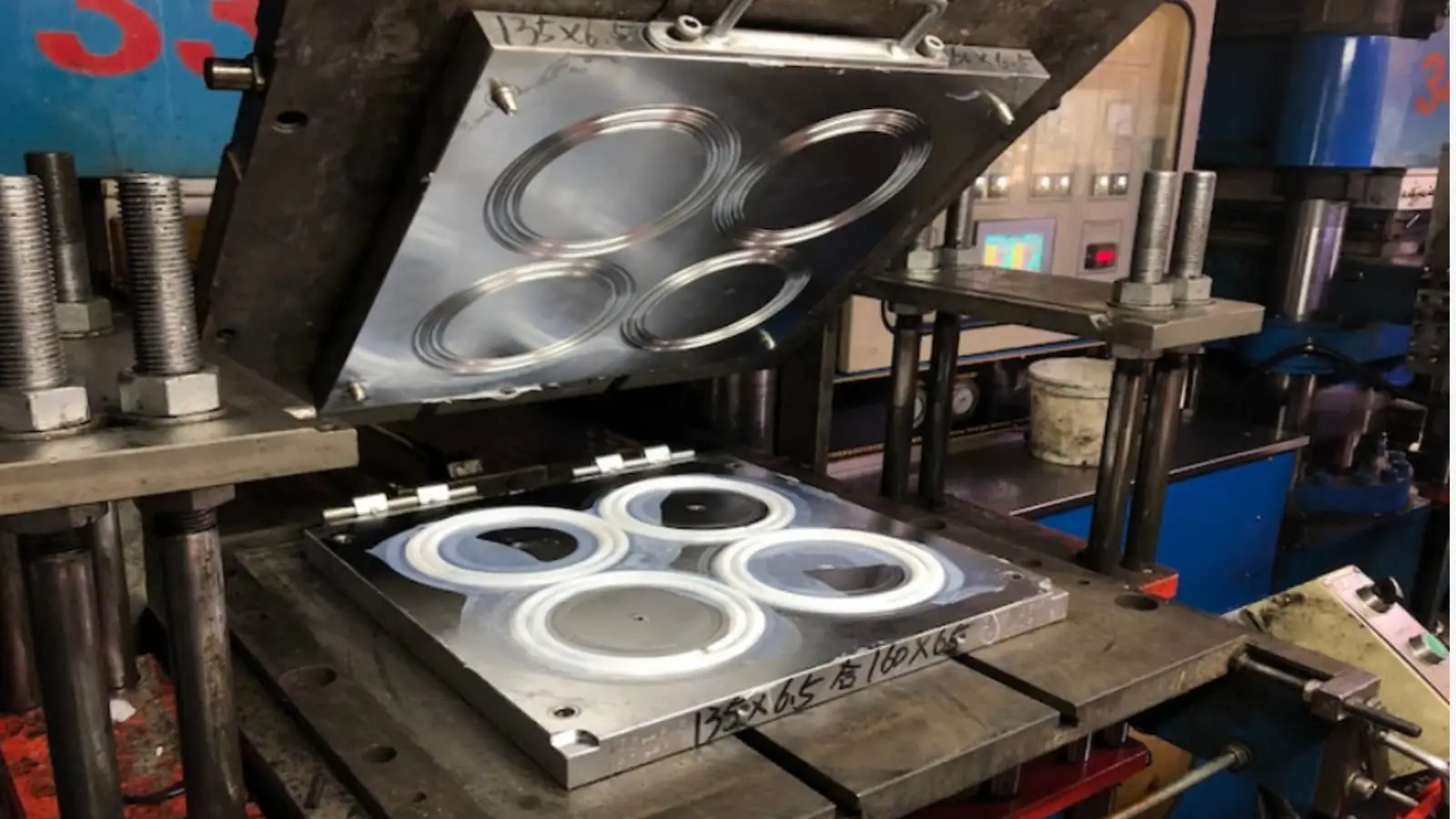

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can affect logistics costs and responsibilities. Familiarizing oneself with these terms can help buyers avoid unexpected charges and delays.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to offer discounts for bulk purchases or long-term contracts.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront price. This includes maintenance, operational costs, and potential savings from higher quality products.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect final costs. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can provide stability in pricing.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Prices can vary widely based on market conditions, material choices, and production specifics. It is advisable to request detailed quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
By thoroughly understanding these components and factors, international B2B buyers can make strategic decisions that enhance their sourcing efficiency and overall profitability in compression molding.
Spotlight on Potential compression mold Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘compression mold’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for compression mold
Compression molding is a pivotal process in manufacturing, particularly for producing high-quality components in various industries. Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with this method is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when sourcing products or partnering with manufacturers.
Key Technical Properties of Compression Molding
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the specific classification of the raw materials used in the molding process, such as silicone, rubber, or thermoset materials.
– Importance: Selecting the appropriate material grade ensures that the final products meet performance requirements and regulatory standards. Buyers must specify material grades to align with application needs, such as flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. -
Tolerances
– Definition: Tolerances refer to the allowable variations in dimensions and physical properties of molded parts.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are crucial for components that fit into assemblies or require precise functionality. Understanding tolerances helps buyers negotiate specifications and ensures that the parts will integrate seamlessly into their products. -
Curing Time
– Definition: Curing time is the duration required for the material to harden and achieve its final properties after being molded.
– Importance: Curing time directly affects production schedules and inventory management. Buyers must consider this factor when planning for delivery timelines and product availability, particularly in industries where time-to-market is critical. -
Compression Ratio
– Definition: The compression ratio is the ratio of the volume of the preform to the volume of the mold cavity.
– Importance: A higher compression ratio can indicate a denser, more compact part, which may enhance strength and durability. Buyers should understand this property to ensure that the end products meet their performance criteria. -
Temperature Control
– Definition: This involves maintaining specific temperatures during the molding process to ensure optimal material flow and curing.
– Importance: Effective temperature control is essential for achieving consistent product quality. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturer’s capabilities in temperature management to avoid defects and variability in their components.
Common Trade Terminology in Compression Molding
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships is vital for buyers looking to source components that fit into larger systems or devices. It helps ensure compatibility and quality assurance in the supply chain. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management. Buyers must align their purchasing strategies with the supplier’s MOQ to avoid excess costs or stock shortages. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Relevance: Issuing an RFQ is a critical step in the procurement process. It allows buyers to compare costs and capabilities, enabling informed decision-making when selecting suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Relevance: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for buyers involved in cross-border purchases, as they clarify shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, ensuring smoother transactions. -
Deflashing
– Definition: Deflashing is the process of removing excess material (flash) from molded parts after they have been cured.
– Relevance: This term is significant for buyers concerned about the aesthetic and functional quality of the final products. Understanding the deflashing process helps ensure that the delivered components meet quality standards.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing compression molded products, enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the compression mold Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global compression molding market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing demand across various sectors, including automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods. The rising need for durable and high-quality components is prompting manufacturers to adopt advanced compression molding techniques. Notably, the integration of Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is reshaping sourcing strategies, enabling real-time monitoring of production processes and supply chain dynamics. This transition is particularly advantageous for B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as it enhances operational efficiency and reduces time-to-market.
Emerging trends in the market include a shift towards customization and small batch production, allowing businesses to meet specific client needs without incurring significant costs. Additionally, the focus on sustainability is compelling manufacturers to explore eco-friendly materials and processes. Buyers should be aware of the growing preference for suppliers who can demonstrate responsible sourcing practices and adherence to environmental regulations.
Furthermore, the global supply chain landscape is evolving, with a notable shift towards nearshoring. This trend is driven by geopolitical factors and the desire to mitigate risks associated with long-distance supply chains. For international buyers, this offers opportunities to engage with local suppliers who can provide more responsive service and flexibility.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As sustainability becomes a central focus for industries worldwide, the compression molding sector is not exempt. The environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes has prompted a reevaluation of sourcing practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who implement sustainable practices, such as minimizing waste and optimizing energy use during production.
Ethical sourcing is also critical. Buyers should assess their suppliers’ adherence to fair labor practices and environmental regulations. Certification programs such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 9001 for quality management can serve as benchmarks for evaluating supplier commitment to sustainability.
Moreover, the adoption of green materials—such as bio-based elastomers and recycled rubber—can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with compression molding. By collaborating with suppliers that prioritize these materials, B2B buyers can enhance their sustainability profiles while satisfying increasingly eco-conscious customers.
Brief Evolution/History
Compression molding has its roots in the late 19th century, emerging as a reliable method for producing rubber components. Initially popularized by Harvey Firestone, the technique has evolved significantly, adapting to the needs of various industries over time. The basic principles of placing preheated materials into molds remain unchanged, but advancements in technology and materials have enhanced its efficiency and versatility.
Today, compression molding stands out for its ability to produce high-strength, durable components that meet stringent quality standards. As markets expand and evolve, the historical significance of this method continues to inform contemporary practices, providing a solid foundation for future innovations in the sector.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of compression mold
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for compression molds?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in the compression molding process, especially with materials relevant to your industry. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Additionally, request samples of previous work to assess their capabilities. Evaluate their production capacity and lead times to ensure they can meet your demand. Finally, consider their communication skills and responsiveness, as effective collaboration is crucial for successful partnerships. -
Can compression molds be customized to meet specific design requirements?
Yes, compression molds can be highly customized to accommodate specific design needs. Work closely with your supplier to discuss your unique requirements, including dimensions, material types, and features like textures or inserts. Many manufacturers offer design assistance to optimize the mold for your application, ensuring functionality and aesthetic appeal. Be prepared to provide detailed specifications and drawings to facilitate the design process, which may also influence lead times and costs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for compression molds?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the mold. Generally, MOQs for compression molds range from 100 to 1,000 units, depending on the supplier’s production capabilities. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks, factoring in design, tooling, and production times. For urgent projects, some suppliers may offer expedited services, but this often incurs additional costs. Always clarify these details upfront to avoid surprises during the procurement process. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing compression molds?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, so it’s essential to establish clear agreements before proceeding. Common practices include partial upfront payments (20-50%) with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms, allowing a certain period post-delivery for payment. Discussing payment methods, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, is crucial, especially for international transactions, to ensure security and compliance with financial regulations. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and compliance with international standards?
To ensure quality assurance, request detailed information about the supplier’s quality control processes. Look for suppliers with relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards, which demonstrate adherence to quality management practices. Ask about their testing methods for final products, including material integrity and dimensional accuracy. Regular audits and inspections can also be scheduled to ensure compliance with your specifications and international standards, fostering transparency and trust in the partnership. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing compression molds?
Logistics play a critical role in the procurement of compression molds, especially for international buyers. Consider shipping options, including air freight for urgent needs or sea freight for cost efficiency. Evaluate the supplier’s location in relation to shipping routes to minimize transportation costs and time. Additionally, factor in customs regulations and duties that may apply to your imports. Collaborating with a logistics partner can streamline the process and help navigate any complexities related to international shipping. -
How should disputes be handled in international B2B transactions involving compression molds?
Establishing clear terms in your contract can significantly mitigate disputes. Include clauses that specify dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration, and identify the governing law. Maintain thorough documentation of all communications, agreements, and transactions to support your position if conflicts arise. In case of a dispute, approach the supplier with a focus on resolution, emphasizing open communication to find a mutually beneficial solution. If necessary, consider involving legal counsel experienced in international trade. -
What are the common challenges in the compression molding process, and how can they be mitigated?
Common challenges include material handling issues, tooling design complexities, and maintaining optimal process conditions. To mitigate these, ensure proper training for your team on material preparation and mold handling. Collaborate with your supplier on mold design to enhance durability and ease of use. Establish stringent process controls and regular inspections during production to identify and rectify issues early. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also facilitate better communication and problem-solving when challenges arise.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for compression mold
As global industries continue to evolve, the strategic sourcing of compression molding presents a compelling opportunity for businesses aiming to enhance product quality and operational efficiency. By understanding the intricacies of compression molding, buyers can leverage its advantages, including high durability, design versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
Key takeaways include the importance of partnering with experienced contract manufacturers who possess specialized knowledge and advanced equipment, ensuring consistent quality and compliance with industry standards. Furthermore, outsourcing not only mitigates the challenges of tooling and process control but also provides scalability to adapt to fluctuating market demands.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should proactively explore collaborations that align with their strategic goals. The continued demand for high-quality, flexible parts in various sectors—from automotive to healthcare—highlights the need for a robust supply chain. Invest in relationships with reputable manufacturers to secure a competitive edge and drive innovation in your product offerings. Embrace the future of compression molding and position your business for sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected marketplace.