Master Electric Motor Makers: Essential Guide for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric motor makers
Electric motors are the unsung heroes of modern industry, driving efficiency and innovation across sectors from manufacturing and agriculture to logistics and infrastructure. For international B2B buyers—especially those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—the process of sourcing electric motors is fraught with complexities. Understanding the nuances of motor types, materials, manufacturing standards, and quality control is essential for making informed procurement decisions that align with operational goals.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource tailored specifically for B2B buyers. It delves into various electric motor types, such as AC induction and brushless DC motors, highlighting their unique features and applications. You will gain insights into the materials and construction that influence performance and durability, alongside critical evaluations of supplier qualifications and cost management strategies. Furthermore, the guide addresses frequently asked questions and provides up-to-date market intelligence, ensuring you are well-equipped to navigate the global landscape.
By leveraging the actionable insights and structured frameworks presented in this guide, you can enhance your sourcing strategies and secure reliable suppliers. Whether you are in Mexico seeking efficient motors for agriculture or in Saudi Arabia looking for durable solutions for industrial applications, this guide empowers you to make strategic decisions that foster long-term operational success.
Understanding electric motor makers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC Induction Motor | Simple, robust design; operates on AC power; squirrel cage or wound rotor types | Pumps, compressors, conveyors, fans | Reliable and widely available; less efficient at variable speeds |
| Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor | Electronic commutation; high efficiency; reduced maintenance due to no brushes | Electric vehicles, HVAC, medical equipment | Long lifespan and compact; higher upfront cost, requires electronic control |
| Synchronous Motor | Rotor speed synchronized with supply frequency; precise speed regulation | Process plants, mills, power factor correction | High efficiency and precise speed; complex start-up, higher cost |
| Servo Motor | Precise position/speed control; closed-loop feedback | Robotics, CNC, high-precision automation | Exceptional accuracy; more expensive, complex commissioning |
| Gear Motor | Integrated gearbox for torque and speed adaptation | Packaging, materials handling, agitators | Simplifies system design; gearbox wear, modest efficiency loss |
AC Induction Motor
AC induction motors are the backbone of many industrial applications, known for their durability and cost-effectiveness. They operate on alternating current and can handle voltage fluctuations, making them suitable for diverse environments, particularly in Africa and South America. When sourcing these motors, buyers should ensure compatibility with local electrical standards and assess the availability of spare parts and service support, as these factors can significantly influence operational reliability.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brushless DC (BLDC) Motor
Brushless DC motors are characterized by their high efficiency and minimal maintenance, owing to the absence of brushes. They are compact and ideal for applications where space and energy efficiency are critical, such as in electric vehicles and HVAC systems. B2B buyers should consider the initial investment versus long-term savings on maintenance and energy costs. Additionally, familiarity with electronic controllers among local technicians is essential for effective integration and support.
Synchronous Motor
Synchronous motors are designed for applications requiring precise speed control, making them suitable for process plants and power factor correction in industrial settings. Their operation is synchronized with the supply frequency, ensuring consistent performance. While they offer high efficiency, buyers should be aware of the complexities involved in starting these motors and the potentially higher costs associated with them. Understanding the application requirements is crucial for selecting the right motor type.
Servo Motor
Servo motors provide exceptional precision in position and speed control, making them indispensable in robotics and high-precision automation applications. They operate using closed-loop feedback systems, which enhance their accuracy. However, they come with a higher price point and may require complex commissioning processes. Buyers should evaluate their specific application needs and the technical expertise available in their teams to ensure proper installation and maintenance.
Gear Motor
Gear motors combine an electric motor with a gearbox to optimize torque and speed for specific applications. They are particularly useful in packaging, materials handling, and agitator systems. While gear motors simplify design and integration, buyers should consider the potential for gearbox wear and a modest loss in efficiency. It’s important to assess the operational demands and ensure that the selected gear motor can meet the necessary performance specifications.
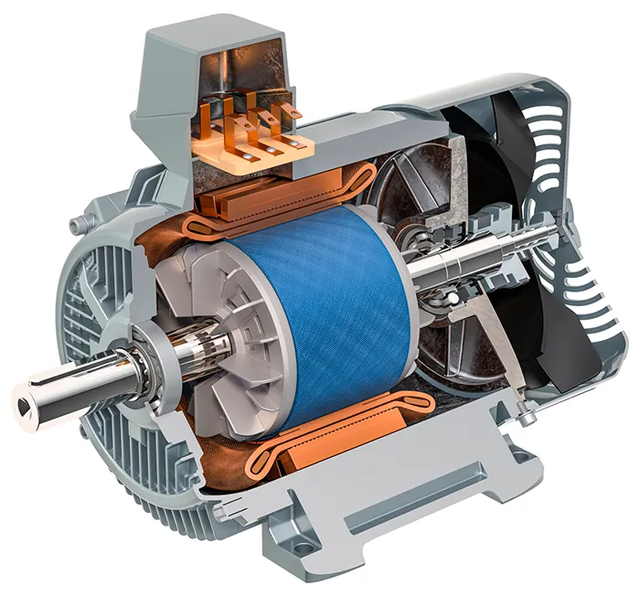
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of electric motor makers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric motor makers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Increased productivity and efficiency in production | Compatibility with local voltages, availability of parts |
| Agriculture | Irrigation systems and pumps | Enhanced crop yield and resource efficiency | Durability in harsh conditions, energy efficiency |
| Logistics & Transportation | Conveyor systems for material handling | Streamlined operations and reduced labor costs | Space constraints, maintenance support availability |
| HVAC Systems | Fans and compressors for heating and cooling | Improved energy efficiency and climate control | Compliance with regional energy standards, after-sales support |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine generators | Sustainable energy production and reduced carbon footprint | Technical specifications for local regulations, reliability |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, electric motors are crucial for driving automated assembly lines, which enhance production efficiency. These motors allow for precise control over machinery, reducing downtime and increasing output. International buyers must ensure that the motors are compatible with local electrical standards and can withstand the operational demands of their specific production processes. Additionally, evaluating the availability of spare parts and local service providers is essential to maintain uptime.
Agriculture
Electric motors are extensively used in agricultural applications, particularly in irrigation systems and pumps. They enable efficient water delivery, which is vital for enhancing crop yields, especially in regions facing water scarcity. For buyers in Africa and South America, sourcing motors that can operate in challenging environmental conditions is critical. Energy efficiency is also a key consideration, as it directly impacts operational costs and sustainability efforts.
Logistics & Transportation
In logistics, electric motors power conveyor systems that facilitate the smooth handling of materials. These systems significantly streamline operations, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing errors in material transport. B2B buyers should consider the spatial requirements of their facilities when sourcing motors, as well as the availability of maintenance support to ensure continuous operation. Understanding the specific load requirements and compatibility with existing systems is also vital.
HVAC Systems
Electric motors play a pivotal role in HVAC systems, driving fans and compressors that regulate heating and cooling. By improving energy efficiency, these motors help businesses reduce operational costs while ensuring optimal climate control. Buyers should focus on sourcing motors that comply with regional energy standards and have robust after-sales support. This is particularly important in regions with fluctuating temperatures, where reliable performance is crucial for comfort and operational efficiency.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, electric motors are integral to wind turbine generators, converting kinetic energy into electrical power. This not only supports sustainable energy initiatives but also contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of businesses. Buyers need to ensure that the motors meet specific technical specifications required by local regulations. Reliability and performance under varying environmental conditions are also key factors that influence sourcing decisions, particularly in remote or off-grid locations.
Related Video: Ultimate Beginners Guide to Using Electric Motors for Makers and DIY Projects; #068
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric motor makers
When selecting materials for electric motor manufacturing, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of common materials is crucial for B2B buyers. This analysis will focus on four widely used materials: Copper, Aluminum, Steel, and Insulation Materials. Each material has unique characteristics that impact performance, cost, and application suitability.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. It can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications where heat dissipation is critical.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, which enhances motor efficiency and performance. However, copper is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can increase overall production costs. Additionally, its weight can be a concern in applications where reducing weight is essential.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in windings and electrical connections within motors. Its high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, making it ideal for high-performance motors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of copper and its price volatility. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM B170 for copper wire may also be relevant.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum has good electrical conductivity, is lightweight, and offers excellent corrosion resistance. It can operate effectively in a range of temperatures and is often used in applications requiring reduced weight.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight compared to copper, making it an attractive option for many manufacturers. However, aluminum has lower conductivity than copper, which can impact motor efficiency. Additionally, it may require more complex manufacturing processes to ensure adequate performance.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is often used for motor housings and rotor components. Its lightweight nature can enhance the overall efficiency of motors, especially in automotive and aerospace applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that aluminum components meet local and international standards, such as DIN 17615 for aluminum alloys. The availability of aluminum in various regions can vary, impacting sourcing strategies.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength, durability, and magnetic properties. It can withstand high pressures and temperatures, making it suitable for demanding industrial applications.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s primary advantage is its robustness and ability to handle heavy loads, which is essential in high-torque applications. However, it is heavier than both copper and aluminum, which can be a disadvantage in weight-sensitive designs. Additionally, steel can be prone to corrosion if not properly treated.
Impact on Application: Steel is commonly used in the construction of motor frames, shafts, and rotor cores. Its magnetic properties enhance the efficiency of electric motors, particularly in industrial environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for corrosion-resistant coatings, especially in humid or corrosive environments like those found in parts of the Middle East. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel is also important.
Insulation Materials
Key Properties: Insulation materials, such as polyimide and epoxy, provide electrical insulation and thermal stability. They are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electric motors.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of high-quality insulation materials is their ability to withstand high temperatures and prevent electrical shorts. However, the cost of advanced insulation materials can be high, and their manufacturing processes can be complex.
Impact on Application: Insulation materials are used in windings and other electrical components to prevent short circuits and improve thermal management. They are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of electric motors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that insulation materials comply with relevant standards, such as UL 1446 for insulation systems. Additionally, understanding local temperature and humidity conditions can inform material selection.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric motor makers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Windings and electrical connections | Superior electrical conductivity | High cost and weight | High |
| Aluminum | Motor housings and rotor components | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower conductivity than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Motor frames, shafts, and rotor cores | Robustness and magnetic properties | Heavier and prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Insulation Materials | Windings and electrical component insulation | High thermal stability and safety | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
This analysis provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for electric motor makers, highlighting key considerations for international B2B buyers. Understanding these materials will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric motor makers
Electric motors are critical components in various industrial applications, and understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is essential for B2B buyers. This section delves into the typical stages of manufacturing electric motors and the quality control (QC) protocols that ensure reliability and performance. By grasping these aspects, international buyers—especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—can make informed sourcing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of electric motors involves several key stages, each crucial for producing high-quality products. These stages typically include material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Electric motors primarily consist of metals like copper, aluminum, and steel, as well as insulation materials.
- Material Selection: Suppliers should use high-grade materials that meet international standards to ensure durability and efficiency. For instance, copper is essential for windings due to its excellent conductivity.
- Material Testing: Before production, materials undergo testing for properties such as conductivity, tensile strength, and corrosion resistance. This initial quality check helps prevent defects in the final product.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into components that will later be assembled into the motor.
- Techniques Used:
- Stamping: This process is used to create stator and rotor laminations from sheets of metal. High-speed stamping machines ensure precision and reduce waste.
- Winding: Copper wire is wound around the stator and rotor. Automated winding machines enhance the consistency of coil turns, which is vital for performance.
- Quality Checks: During forming, visual inspections are performed to identify any physical defects, such as misalignment or surface irregularities.
3. Assembly
Once the individual components are formed, the next step is assembly.
- Assembly Techniques:
- Mechanical Assembly: Components are joined using mechanical fasteners or press fits. This method ensures strong connections without the need for adhesives, which can degrade over time.
- Soldering: Electrical connections are made through soldering, ensuring low resistance and high conductivity.
- Integration of Electronics: For modern electric motors, especially brushless DC motors, integration with electronic control units (ECUs) is crucial. This requires precision in both assembly and alignment.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves applying finishes that enhance the motor’s performance and aesthetics.
- Coating: Motors are often coated with protective layers to prevent corrosion and wear. Common techniques include powder coating and enamel painting.
- Final Inspection: Before the motors are packaged, a thorough inspection is conducted to ensure all assembly processes have been completed correctly and that the motor meets performance specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a vital component of the manufacturing process for electric motors. It ensures that products meet both international and industry-specific standards.
International Standards
B2B buyers should look for suppliers that comply with recognized quality standards:
- ISO 9001: This standard ensures that a manufacturer has a quality management system in place. It focuses on continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: In Europe, products must meet health, safety, and environmental protection standards to obtain CE marking, which is crucial for market acceptance.
Industry-Specific Standards
In addition to general standards, specific industries may require compliance with additional guidelines:
- API (American Petroleum Institute): For motors used in oil and gas applications, compliance with API standards ensures reliability under demanding conditions.
- NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association): In North America, NEMA standards specify performance and efficiency requirements for electric motors.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): At this stage, raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing process, random samples are taken to check for defects and adherence to specifications.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Once the motors are assembled, they undergo rigorous testing, including performance testing and safety checks, to verify that they meet all specified standards.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are commonly employed to ensure the quality and reliability of electric motors:
- Electrical Testing: This includes testing for insulation resistance, winding resistance, and current consumption to ensure efficient operation.
- Thermal Testing: Motors are subjected to temperature tests to determine their thermal performance under load conditions.
- Vibration Testing: This assesses the motor’s mechanical integrity and helps identify potential failures that could arise during operation.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control practices. Here are several strategies to verify supplier QC:
- Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the supplier’s manufacturing processes, QC measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Certification Verification: Buyers should request copies of relevant certifications and ensure they are up to date.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide unbiased assessments of the supplier’s quality control processes and product reliability.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of QC is essential for successful procurement:
- Local Regulations: Familiarize yourself with local regulations that may impact the import of electric motors, such as customs standards and safety regulations.
- Supply Chain Reliability: Assess the supplier’s ability to provide after-sales support and spare parts, as this can significantly affect operational uptime.
- Cultural Differences: Be aware of cultural differences in business practices that may affect communication and expectations regarding quality.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in electric motor production, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source reliable products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Electric Motor FACTORY – HOW IT’S MADE a Industrial Motor Assembly
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric motor makers Sourcing
In the complex landscape of electric motor sourcing, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will delve into the key cost components involved in electric motor manufacturing, the factors influencing prices, and actionable tips for buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in electric motor manufacturing includes raw materials such as copper for windings, steel for the core, and rare earth metals for certain motor types. Prices can fluctuate based on global commodity markets, so buyers should stay informed about material trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Africa and South America, manufacturers may offer competitive pricing. However, this can sometimes come at the expense of quality, so evaluating labor standards is essential.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, facility maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, impacting the final price.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific motor designs can represent a significant investment. Buyers requiring unique specifications should factor in these costs, as they can lead to higher initial pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC measures ensure product reliability and compliance with international standards. Suppliers investing in quality assurance may charge a premium, but this often results in lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) due to reduced failure rates.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs are a critical factor, especially for international shipments. Factors such as shipping methods, distance, and local infrastructure can significantly influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin varies based on the supplier’s business model, market positioning, and competitive landscape.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQ terms to achieve better pricing, especially when sourcing for large projects.
-
Specifications/Customization: Tailored solutions can increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization with the potential for standard models that may offer cost savings.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. For instance, opting for standard materials rather than specialized ones can yield significant savings.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with recognized quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) may command higher prices. However, these certifications often correlate with better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: Reputation, location, and production capabilities of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more, but they often provide added value through reliability and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for cost management. Terms like CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) or FOB (Free on Board) dictate who bears shipping and insurance costs, impacting the final price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of your needs and market benchmarks. Leverage volume commitments to secure better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate total costs, not just the purchase price. Consider factors like energy efficiency and maintenance when assessing TCO.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international buyers may face additional costs, such as tariffs and taxes. These can significantly impact the final acquisition cost.
-
Market Intelligence: Stay informed about global market trends and pricing fluctuations. This knowledge can enhance negotiation strategies and supplier selection.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing, improved service, and preferential treatment during supply chain disruptions.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed are indicative and can vary significantly based on the specific requirements, supplier negotiations, and market conditions. Always conduct thorough due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing in your sourcing endeavors.
Spotlight on Potential electric motor makers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electric motor makers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric motor makers
Key Technical Properties of Electric Motors
When sourcing electric motors, understanding specific technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of components, particularly the rotor and stator, influences the motor’s durability and performance. Common materials include silicon steel for magnetic components and aluminum or copper for windings. Buyers should consider the environmental conditions in which the motor will operate, as higher-grade materials can enhance resistance to corrosion and wear, ensuring longevity and reliability. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In electric motors, tight tolerances are crucial for ensuring proper fit and function of components, which directly affects efficiency and performance. A motor with precise tolerances will have better alignment, reduced vibration, and increased lifespan, making it a key consideration for buyers seeking high-quality, reliable solutions. -
Efficiency Rating
The efficiency of an electric motor indicates how well it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Higher efficiency ratings (like IE3 or IE4 classifications) are beneficial for reducing operational costs and energy consumption. For businesses in regions with high energy costs, investing in efficient motors can lead to significant long-term savings and improved sustainability. -
Operating Temperature
Each electric motor has a defined operating temperature range, beyond which performance can degrade or components can fail. Understanding this specification is critical, especially in industries with extreme environments, such as manufacturing or agriculture. Selecting a motor with an appropriate temperature rating helps to avoid premature failures and costly downtimes. -
Torque and Speed Characteristics
Torque indicates the rotational force produced by the motor, while speed is measured in revolutions per minute (RPM). The right balance of torque and speed is crucial for various applications, from conveyor systems to pumps. B2B buyers must match these characteristics with their specific operational needs to ensure optimal performance.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some common terms used in electric motor procurement:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For electric motors, working with an OEM can ensure that the components are designed to meet specific standards and integrate seamlessly into existing systems. This is crucial for buyers looking for reliability and compatibility in their supply chains. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their consumption rates to avoid excess inventory or stockouts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that solicits price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Crafting a clear RFQ helps buyers communicate their needs accurately, leading to better pricing and service terms. It’s a critical step in the procurement process that can influence overall costs and supplier relationships. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, which clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping costs, risk, and insurance responsibilities, helping buyers navigate logistics and avoid unexpected expenses. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the duration from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for planning and inventory management, particularly in industries where downtime can be costly. Buyers should always factor in lead times when assessing supplier reliability and planning for maintenance or production schedules.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they procure the right electric motors for their specific needs while minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electric motor makers Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electric motor market is undergoing transformative changes driven by several global factors. As industries pivot towards automation and electrification, there is a significant increase in demand for high-efficiency electric motors across diverse sectors such as manufacturing, automotive, and renewable energy. Emerging markets in Africa and South America are experiencing rapid industrial growth, creating new opportunities for international suppliers. In the Middle East, investments in infrastructure and energy diversification are fueling demand for electric motors, while Europe is emphasizing efficiency and sustainability due to stringent environmental regulations.
Current sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital procurement tools that enhance transparency and streamline supplier evaluations. Technologies such as IoT and AI are being integrated into motor design and manufacturing, allowing for smarter, more adaptable motor solutions. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can provide not only competitive pricing but also innovation in product design and application. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on local sourcing helps mitigate risks associated with global supply chain disruptions, especially in regions with fluctuating political and economic climates.
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should focus on understanding local market dynamics, including regulatory requirements and regional electrical standards, to ensure compatibility and efficiency in their procurement strategies.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the electric motor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly concerning energy consumption and waste generation, has raised awareness about the importance of ethical sourcing. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates effective environmental management systems.
Furthermore, the use of ‘green’ materials in the production of electric motors can significantly reduce their carbon footprint. Buyers should look for suppliers that utilize recyclable materials, energy-efficient manufacturing processes, and sustainable supply chain practices. This not only contributes to environmental stewardship but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for responsible business practices.
As regulatory frameworks globally tighten around environmental standards, B2B buyers must proactively seek partnerships with manufacturers that prioritize sustainability, ensuring compliance and enhancing brand reputation.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electric motors dates back to the early 19th century, with foundational work by inventors such as Michael Faraday and Nikola Tesla. Initially, electric motors were bulky and inefficient, primarily used in industrial applications. However, advancements in materials and manufacturing technologies over the decades have led to the development of more compact, efficient, and versatile motor designs.
The late 20th century marked a significant shift towards automation and electronic control systems, enabling the rise of various motor types, including brushless DC and servo motors. Today, electric motors are pivotal in sectors ranging from manufacturing to renewable energy, continually adapting to meet the demands of modern technology. For B2B buyers, understanding this evolution is crucial for making informed decisions about the types of motors that best suit their operational needs.
Related Video: How Car Makers Are Switching To EVs | CNBC Marathon
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric motor makers
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting electric motor suppliers?
When vetting electric motor suppliers, focus on their experience and reputation in the industry, checking for customer reviews and references. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can indicate adherence to quality standards. Assess their manufacturing capabilities and quality control processes to ensure they can meet your specifications. Additionally, verify their financial stability to mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions, particularly important in regions with fluctuating economic conditions. -
Can electric motors be customized to fit specific applications?
Yes, many electric motor manufacturers offer customization options. Buyers can request specific voltage ratings, power outputs, and form factors tailored to their applications. It’s crucial to communicate your requirements clearly and discuss any potential impact on lead times and costs. Ensure that the supplier has a robust engineering team capable of providing effective solutions, and request samples or prototypes to evaluate performance before finalizing your order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for electric motors?
MOQs and lead times vary significantly based on the manufacturer and the complexity of the motor. Standard electric motors may have lower MOQs, often starting at 50 to 100 units, while customized solutions could require higher quantities. Lead times can range from 2 to 12 weeks, depending on the supplier’s production capacity and the availability of raw materials. Always discuss these factors upfront to align expectations and avoid delays in your operations. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by electric motor suppliers?
Payment terms can vary, but many suppliers offer options such as 30% upfront deposit and the balance upon delivery. Some may accept letters of credit or deferred payment arrangements, particularly for large orders. It’s essential to negotiate favorable terms that protect your interests while ensuring the supplier feels secure in their transaction. Be clear about currency preferences and any potential import duties that could affect the total cost. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the electric motors I purchase?
To ensure quality, request documentation of certifications such as ISO, CE, or UL, which indicate compliance with international standards. Ask for test reports or quality assurance processes the supplier follows. A reputable supplier should be transparent about their quality control measures, including regular inspections and testing protocols. Consider conducting an on-site visit if feasible, or utilize third-party inspection services to verify the quality before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing electric motors internationally?
Logistics play a critical role in international sourcing. Assess the shipping methods available, such as air freight for speed or sea freight for cost-effectiveness. Consider customs regulations and potential tariffs or import duties that may apply. Work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping terms (Incoterms) and ensure that insurance coverage is in place during transit. Having a reliable logistics partner can help mitigate delays and unforeseen costs. -
How should I handle disputes with electric motor suppliers?
Establish clear terms of engagement and communication channels before issues arise. In case of a dispute, attempt to resolve it through direct communication to reach an amicable solution. If necessary, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, particularly regarding warranty claims or product defects. Consider involving a mediation service or legal counsel if direct negotiations fail. Having a well-drafted contract can provide clarity on dispute resolution procedures. -
What should I do if the electric motors do not meet my specifications upon delivery?
Upon delivery, immediately inspect the motors against the agreed specifications. If discrepancies arise, document the issues with photos and detailed descriptions. Contact the supplier promptly to report the non-conformance, referencing your contract terms regarding returns or adjustments. Many suppliers will have a return policy or warranty in place, and it’s crucial to follow the outlined procedures to ensure a smooth resolution. Maintain a record of all communications for future reference.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric motor makers
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of electric motors is pivotal for B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and reliability. By thoroughly defining needs, conducting comprehensive supplier research, and evaluating potential partners based on quality, service, and price, businesses can mitigate risks associated with procurement. The emphasis on compatibility with local standards and availability of support services cannot be overstated, particularly for buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
As the landscape for electric motor sourcing continues to evolve, staying informed about market trends and technological advancements will be crucial. Buyers are encouraged to leverage global networks, engage in strategic partnerships, and participate in industry events to gain insights and foster relationships with reliable suppliers.
The future holds immense potential for those who embrace a proactive approach to sourcing electric motors, ensuring not just immediate operational needs are met, but also positioning their businesses for long-term growth and sustainability. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—invest in strategic partnerships that will drive your organization forward.