Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Linear Rail Reach
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for linear rail reach
In today’s fast-paced global marketplace, the significance of linear rail reach cannot be overstated. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for enhanced precision and efficiency, understanding the intricacies of linear rail systems becomes a vital component for success. These systems are essential for automation, machinery, and manufacturing processes, ensuring smooth and accurate motion control that is indispensable for modern production lines.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of linear rail reach, encompassing various types and materials, manufacturing and quality control processes, and insights into reliable suppliers. Additionally, we will explore cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions, all tailored to empower international B2B buyers in making informed sourcing decisions.
By delving into the unique requirements and challenges faced by businesses in diverse regions, including Germany and Saudi Arabia, this guide equips decision-makers with the knowledge necessary to select the right linear rail systems that meet their operational needs. Whether you are looking to enhance automation in manufacturing or ensure precision in electronic machinery, understanding linear rail reach is crucial for driving efficiency and competitiveness in your operations. Prepare to navigate the global market with confidence and make sourcing decisions that propel your business forward.
Understanding linear rail reach Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Rail Systems | High precision, smooth motion, low friction | Automation, Machine tools, Robotics | Pros: Excellent accuracy; Cons: Higher cost due to precision manufacturing. |
| Roller Rail Systems | Increased load capacity, robust design | Heavy machinery, Aerospace, Automotive | Pros: High load-bearing; Cons: Bulkier design may limit application flexibility. |
| Miniature Ball Rail Systems | Compact size, designed for tight spaces | Medical devices, Microelectronics | Pros: Space-efficient; Cons: Limited load capacity. |
| Linear Bushings and Shafts | Self-supporting, offers freedom in peripheral direction | Food industry, Handling, Automation | Pros: Versatile applications; Cons: May require more maintenance. |
| Cam Roller Guides | Suitable for high-speed applications, simple design | Packaging machinery, High-speed conveyors | Pros: Cost-effective for high-speed; Cons: Limited precision compared to other types. |
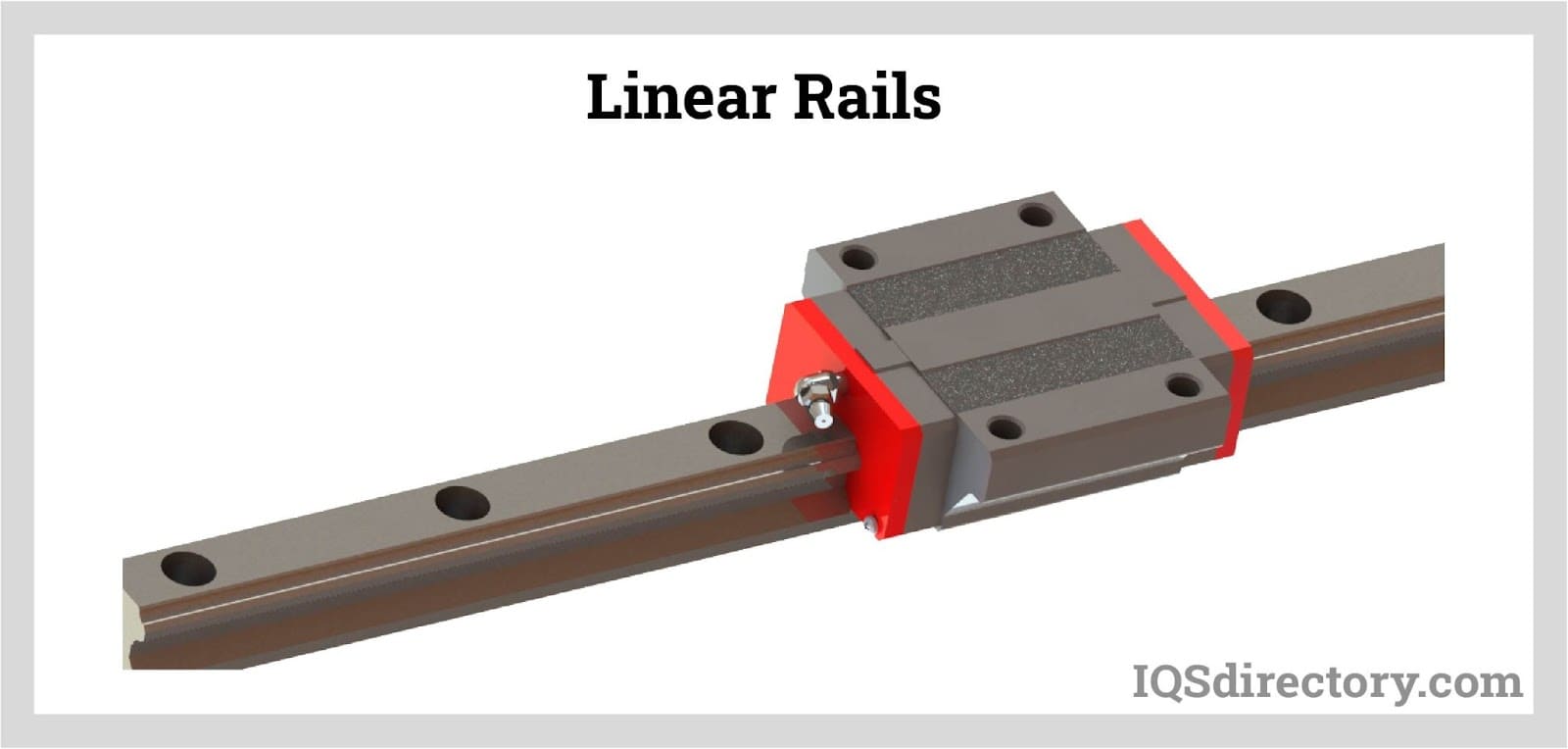
Ball Rail Systems
Ball rail systems are renowned for their high precision and smooth motion, making them ideal for applications requiring exact positioning. They are widely used in automation, machine tools, and robotics. When considering a purchase, B2B buyers should evaluate the operational environment, as these systems often demand higher costs due to their precision manufacturing. However, the investment pays off in applications where accuracy and reliability are paramount.
Roller Rail Systems
Roller rail systems are designed to handle higher loads compared to other types of linear guides. Their robust construction makes them suitable for heavy machinery, aerospace, and automotive applications. Buyers should focus on the load capacity and environmental conditions, as these systems may be bulkier and require more space. While they offer excellent performance, the trade-off is a potentially higher footprint and weight.
Miniature Ball Rail Systems
Miniature ball rail systems cater to industries where space is a premium, such as medical devices and microelectronics. Their compact design allows for integration in tight spaces, making them an attractive option for precision machinery. However, buyers should be aware of their limited load capacity, which may restrict their use in heavier applications. Assessing the specific requirements of the application will be crucial in making an informed purchase decision.
Linear Bushings and Shafts
Linear bushings and shafts are versatile components that provide self-supporting capabilities and freedom in peripheral directions. They find applications in the food industry, handling systems, and automation setups. Buyers should consider the maintenance requirements, as these systems may need more frequent servicing. Their adaptability to various applications makes them a valuable choice for businesses looking for flexibility in their operations.
Cam Roller Guides
Cam roller guides are specifically designed for high-speed applications and feature a simple design that facilitates cost-effectiveness. They are commonly used in packaging machinery and high-speed conveyors. While they excel in speed, buyers should note that they may not offer the same level of precision as other linear guide options. Evaluating the specific speed and precision needs of an application will help buyers choose the right solution.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of linear rail reach
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of linear rail reach | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Precision assembly lines for automotive components | Enhances accuracy and reduces production downtime | Look for suppliers with a proven track record in automotive applications and certifications. |
| Electronics | Automated testing and assembly of circuit boards | Improves efficiency and ensures high precision in production | Consider suppliers who offer customizable solutions tailored to specific electronic components. |
| Medical Devices | Motion systems in surgical robots and imaging equipment | Increases reliability and safety in critical medical applications | Prioritize suppliers with experience in regulatory compliance and certifications in medical technology. |
| Aerospace | Component manufacturing for aircraft assembly | Ensures high precision and durability for safety-critical parts | Evaluate suppliers based on their ability to meet aerospace standards and provide robust support services. |
| Food Processing | Automated packaging and sorting systems | Enhances efficiency and hygiene in food handling processes | Focus on suppliers who specialize in food-grade materials and have experience in the food industry. |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, linear rail reach is essential for precision assembly lines, particularly in the automotive industry. These systems ensure that components are assembled with high accuracy, significantly reducing production downtime caused by misalignments. International buyers should seek suppliers with a strong reputation in automotive applications and relevant certifications to guarantee quality and compliance with industry standards.
Electronics
Linear rail reach plays a crucial role in the automated testing and assembly of circuit boards within the electronics industry. By facilitating smooth and precise motion, these systems enhance production efficiency and ensure that high-precision components are manufactured correctly. Buyers, especially from regions like Europe and South America, should consider suppliers who can provide customizable solutions that cater specifically to their electronic products, ensuring compatibility and performance.
Medical Devices
In the medical device sector, linear rail reach is utilized in motion systems for surgical robots and imaging equipment. These applications require high reliability and precision, as they are critical to patient safety and effective treatment. International buyers should prioritize suppliers with a solid understanding of regulatory compliance and certifications in medical technology, ensuring that their products meet stringent safety standards.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry leverages linear rail reach for the manufacturing of components used in aircraft assembly. The need for high precision and durability in safety-critical parts makes these systems indispensable. Buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to meet aerospace industry standards and their provision of robust support services, which are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and safety.
Food Processing
In food processing, linear rail reach is critical for automated packaging and sorting systems. These systems not only enhance operational efficiency but also ensure high hygiene standards in food handling processes. International buyers should focus on sourcing from suppliers who specialize in food-grade materials and have a proven track record in the food industry, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations.
Related Video: Linear rails guide and test on Ender 3 and Ender 5
Strategic Material Selection Guide for linear rail reach
When selecting materials for linear rail reach, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance characteristics of each material. This analysis will focus on four common materials: aluminum, steel, stainless steel, and plastic. Each material offers unique advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact application suitability and overall performance.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 150°C and can withstand moderate pressures. Its low density makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
Pros & Cons:
Aluminum is durable and easy to machine, which simplifies manufacturing processes. However, it may not be as strong as steel, leading to potential deformation under heavy loads. Additionally, while aluminum is cost-effective, its initial price can be higher than plastic alternatives.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for applications requiring lightweight and corrosion-resistant components, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries. However, it may not be ideal for environments with extreme temperatures or heavy loads.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for aluminum components. Understanding local regulations regarding recycling and material sourcing is also crucial.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is known for its high strength and rigidity, with a temperature rating that can exceed 300°C. It offers excellent load-bearing capabilities and is resistant to wear and tear.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of steel is its durability and strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. However, it is prone to corrosion if not properly treated, which can increase maintenance costs. Steel is generally more affordable than aluminum but may require more complex manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application:
Steel is widely used in industrial applications where high load capacity and durability are essential, such as in manufacturing machinery and construction equipment. Its performance can be affected by environmental factors, necessitating protective coatings in corrosive environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in Africa and South America should consider local availability and pricing of steel, as well as compliance with international standards to ensure quality and safety.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel combines the strength of steel with enhanced corrosion resistance due to its chromium content. It can withstand temperatures up to 800°C and is suitable for high-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to corrosion and staining, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is more expensive than both aluminum and regular steel, and its manufacturing can be more complex due to its toughness.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is often used in food processing, medical equipment, and chemical industries where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical. Its longevity can offset initial costs in applications requiring durability.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Compliance with health and safety standards is vital for buyers in Europe and the Middle East, particularly in food and medical applications. Understanding the specific grades of stainless steel suitable for different applications is also essential.
Plastic
Key Properties:
Plastic materials, such as nylon or POM (polyoxymethylene), are lightweight and have good chemical resistance. They can operate effectively at temperatures up to 100°C and are generally low in weight.
Pros & Cons:
Plastic is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making it suitable for high-volume applications. However, it lacks the strength and rigidity of metals, which can limit its use in high-load scenarios.
Impact on Application:
Plastic is often used in applications requiring lightweight components, such as in consumer electronics and automation equipment. It is also suitable for environments where corrosion resistance is needed but mechanical strength is less critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific types of plastics available and their compliance with international standards. Understanding local regulations regarding plastic use and recycling is also important, particularly in Europe.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for linear rail reach | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Automotive, Aerospace | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Lower strength compared to steel | Medium |
| Steel | Industrial machinery, Construction | High strength and durability | Prone to corrosion | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, Medical equipment | Corrosion-resistant and durable | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Plastic | Consumer electronics, Automation | Cost-effective and lightweight | Limited strength and rigidity | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the key materials used in linear rail reach applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for linear rail reach
Manufacturing Processes for Linear Rail Reach
The manufacturing of linear rail systems involves several critical stages that ensure high quality and precision in the final product. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers who seek reliability and performance in their sourcing.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: The choice of materials, typically high-grade steel or aluminum alloys, is fundamental. These materials are selected for their mechanical properties, such as tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
– Cutting and Shaping: Raw materials are cut into manageable sizes using techniques like laser cutting or CNC machining, ensuring precise dimensions for subsequent processes. -
Forming
– Machining Processes: This involves precision machining to create the specific profiles required for the linear rail. Techniques such as milling and grinding are employed to achieve the necessary tolerances and surface finishes.
– Heat Treatment: To enhance material properties, heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering are often applied. This step is crucial for achieving the desired hardness and durability of the rail. -
Assembly
– Component Assembly: The assembly process involves fitting various components together, including rollers, bearing blocks, and rails. Automated systems may be used to ensure consistency and efficiency in assembly.
– Lubrication Systems Installation: Incorporating lubrication systems at this stage can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of the linear rail systems. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Finishing processes, such as anodizing or powder coating, are applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. These treatments also reduce friction and wear during operation.
– Quality Control Checks: Before the product is finalized, extensive quality checks are performed to ensure that all specifications and standards are met.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is widely recognized globally. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that the manufacturer has established processes for consistent quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking demonstrates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For manufacturers involved in the oil and gas industry, adhering to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is essential for quality assurance.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
– Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet the required specifications. This includes checking for defects, dimensions, and material certifications. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
– During manufacturing, processes are continuously monitored. This can include machine calibration checks, periodic dimensional inspections, and verification of assembly procedures. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
– Once manufacturing is complete, a thorough final inspection is conducted. This includes functional testing of the linear rail systems to ensure they operate smoothly and meet performance specifications.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Inspection: Using precision measuring tools to ensure that all dimensions are within specified tolerances.
- Load Testing: Assessing the load-bearing capacity of the linear rail systems to ensure they can handle specified operational loads without failure.
- Wear Testing: Simulating operational conditions to evaluate the durability and wear characteristics of the rail system over time.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is critical to ensure product reliability.
Steps for Verification
-
Audits:
– Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to evaluate the manufacturing processes and quality control systems directly. This helps identify any potential issues and assess compliance with international standards. -
Requesting Reports:
– Buyers should request quality control reports from suppliers, detailing inspection results, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken for non-conformance. -
Third-Party Inspections:
– Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures. This is particularly useful for buyers unfamiliar with the local manufacturing landscape.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
Understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is essential for B2B buyers. Here are some considerations:
- Cultural Differences: Quality expectations may vary by region. For instance, European manufacturers may adhere to more stringent quality standards than those in other regions. Buyers should be aware of these differences and communicate their requirements clearly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have specific regulations that must be adhered to. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with local laws as well as international standards.
- Language Barriers: Effective communication is vital for quality assurance. Buyers should consider working with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in a language they are comfortable with.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures associated with linear rail systems, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and reliability in sourcing.
Related Video: Lean Manufacturing: MIND-BLOWING Factory Tour! (Behind The Scenes)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for linear rail reach Sourcing
In the international B2B landscape, particularly for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of linear rail reach sourcing is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section delves into the various components that influence pricing and offers actionable insights for optimizing costs.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary raw materials for linear rail systems typically include high-grade steel or aluminum, along with specialized components like bearings and lubrication systems. The choice of material significantly affects the durability, performance, and ultimately, the cost of the product.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary widely depending on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs, such as those in parts of Asia, may offer more competitive pricing. However, it is essential to consider the trade-off between labor cost and quality.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Effective management of these costs can lead to more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific applications can incur additional costs. Buyers should evaluate whether the expected volume justifies the investment in custom tooling.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability but can add to the overall cost. Certifications such as ISO 9001 can also influence pricing due to the associated compliance costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are significant, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties must be accounted for when calculating total costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs, which can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of linear rail reach products:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice between standard and premium materials can significantly impact pricing. Premium materials may offer better performance and longevity but at a higher cost.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with higher quality and recognized certifications typically command higher prices. Buyers should assess the importance of these factors against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their products due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is vital. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can lead to variations in total landed costs, impacting the overall price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing and terms. Leverage your purchasing volume and market knowledge to negotiate better deals.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and operational efficiency over the product’s lifecycle.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Assess all costs associated with the product, from procurement to disposal. A cheaper upfront cost may lead to higher operational costs if the product requires frequent maintenance or replacement.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and tariffs that may affect pricing. Building relationships with local suppliers can mitigate some of these risks.
-
Research and Compare: Utilize platforms that allow for comparisons of suppliers, pricing, and product specifications. This will enable informed decisions and potentially better pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices for linear rail reach components can vary widely based on the factors discussed. The information provided here is for indicative purposes only. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier assessments to obtain accurate pricing relevant to their specific needs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Spotlight on Potential linear rail reach Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘linear rail reach’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for linear rail reach
Key Technical Properties for Linear Rail Reach
Understanding the technical specifications of linear rail reach is crucial for B2B buyers to ensure compatibility and performance in their applications. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the type of material used in the manufacturing of linear rails, commonly including stainless steel, aluminum, and carbon steel.
– Importance: Material selection impacts durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. For example, stainless steel is ideal for applications in humid or corrosive environments, while aluminum is lighter and suitable for applications where weight is a concern. -
Load Rating
– Definition: The maximum load a linear rail can safely support without deforming or failing.
– Importance: Understanding the load rating is critical for ensuring that the linear rail can handle the specific weights and forces in your application. Choosing a rail with an inadequate load rating can lead to premature failure and increased maintenance costs. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension or measured value, often specified in millimeters or micrometers.
– Importance: Tolerances determine the precision of movement and fit between components. In high-precision applications, such as robotics or medical devices, tighter tolerances are essential for ensuring accuracy and reliability. -
Travel Distance
– Definition: The maximum distance over which the linear rail can operate effectively.
– Importance: Knowing the travel distance is vital for applications requiring specific movement ranges. It ensures that the rail meets the operational needs without causing constraints in design or function. -
Speed Rating
– Definition: The maximum speed at which a linear rail can operate safely and effectively.
– Importance: For applications involving automation or rapid movements, understanding the speed rating helps prevent wear and tear, ensuring longevity and reliability of the linear rail system. -
Friction Coefficient
– Definition: A measure of the resistance to motion between the moving parts of the rail system.
– Importance: A lower friction coefficient is desirable in applications requiring smooth and efficient motion. This affects energy consumption and system performance, making it a critical factor in design considerations.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation in B2B transactions. Here are some common terms related to linear rail reach:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Usage: Understanding OEM specifications ensures you are sourcing components that meet your specific requirements and standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Usage: Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and inventory planning, particularly for businesses operating in regions with varying demand levels. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Usage: An RFQ is essential for comparing offers from different suppliers, ensuring that you receive the best value for your procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Usage: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, facilitating smoother international trade. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time between the initiation of a process and its completion, specifically in manufacturing and shipping.
– Usage: Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their projects effectively, ensuring that they can meet production schedules without delays. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Industry-specific standards that products must meet to ensure safety and quality.
– Usage: Awareness of certification standards (such as ISO or CE) is crucial for compliance, particularly in industries like automotive and aerospace where safety is paramount.
By grasping these technical properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product reliability in their linear rail applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the linear rail reach Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The linear rail reach sector is witnessing robust growth, primarily fueled by the increasing adoption of automation across various industries. Global market size is expected to grow from approximately $2.5 billion in 2023 to around $4.3 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.1%. This growth is driven by the rising demand for precision machinery, particularly in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace sectors. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the dynamics of local markets is crucial.
Emerging technologies such as IoT and AI are reshaping sourcing strategies, with manufacturers seeking high-performance linear guides that can integrate seamlessly into automated systems. Notably, companies in Europe, like Germany, are at the forefront of this trend, leveraging advanced technologies to enhance productivity. In contrast, buyers from Africa and South America may focus on cost-effective solutions that do not compromise on quality, presenting unique sourcing opportunities. Furthermore, the trend towards miniaturization in electronics is pushing demand for more precise linear motion systems, which can drive international buyers to consider partnerships with specialized manufacturers.
Key market dynamics include supply chain resilience and the shift towards local sourcing to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers with a proven track record in quality and reliability, as well as those who can provide customized solutions tailored to specific industry needs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of the linear rail reach sector, with increasing pressure on manufacturers to reduce environmental impact. The production and disposal of linear guides can have significant ecological consequences, making it imperative for buyers to consider the sustainability practices of their suppliers. Emphasizing ethical sourcing means seeking suppliers who prioritize energy-efficient manufacturing processes and use environmentally friendly materials.
Buyers should also look for certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or products made from recycled materials. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but can also enhance a company’s brand reputation in an increasingly eco-conscious market. Moreover, the shift towards green technologies is leading to innovations in linear rail products, such as those that require less lubrication and maintenance, thereby reducing waste.
Establishing ethical supply chains is not just a regulatory requirement but also a market differentiator. Buyers who prioritize sustainability can appeal to a growing segment of consumers and businesses that value corporate responsibility, which is particularly relevant in European markets where regulations are stringent.
Brief Evolution/History
The linear rail reach sector has evolved significantly over the decades, transitioning from simple mechanical systems to highly sophisticated automated solutions. Initially developed for industrial machinery, the technology has expanded to serve a diverse range of applications, including robotics, precision manufacturing, and even aerospace.
In the early days, linear guides relied heavily on manual adjustments and maintenance. However, advancements in materials science and engineering have led to the development of high-precision, low-maintenance systems that are now essential in modern manufacturing processes. As industries continue to evolve, so too will the linear rail reach sector, adapting to meet the demands of automation and sustainability in a globalized marketplace. This historical perspective can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers looking to understand the trajectory of the industry and identify future opportunities.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of linear rail reach
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for linear rail reach?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience and expertise in manufacturing linear rail systems. Assess their production capabilities, quality control processes, and certifications (such as ISO 9001). Request references from other international clients, especially those in your region, to gauge reliability. Furthermore, evaluate their responsiveness and willingness to engage in discussions about customization, which is crucial for meeting specific project requirements. -
Can I customize linear rail reach products to fit my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for linear rail reach products. This may include modifications in size, load capacity, or additional features like integrated sensors for monitoring. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and examples of your applications to ensure the supplier fully understands your requirements. Be prepared for potential lead times associated with customized orders, as these can vary significantly. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for linear rail reach products?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers, typically ranging from a few units to several hundred, depending on the product and supplier policies. Lead times also differ based on factors such as product complexity, customization, and current production schedules. It’s advisable to clarify these details early in negotiations to align your project timelines with supplier capabilities. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing linear rail reach products?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon shipment or delivery. Some suppliers may offer net payment terms based on established relationships. Ensure that all payment conditions are clearly outlined in the contract to avoid disputes later. Consider using secure payment methods to protect your financial interests. -
How can I ensure the quality of linear rail reach products?
To ensure product quality, request samples before placing larger orders and conduct thorough inspections upon receipt. Suppliers should provide relevant quality assurance certifications and documentation, such as test reports and compliance with international standards. Additionally, consider implementing a third-party quality inspection service, particularly for larger orders, to validate product quality before shipment. -
What certifications should I look for in linear rail reach suppliers?
Look for suppliers with internationally recognized certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and specific industry standards relevant to linear motion systems. Certifications indicate a commitment to quality and reliability, which are crucial for maintaining operational efficiency in your projects. Request documentation to verify these certifications during the supplier evaluation process. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing linear rail reach products?
Logistics can significantly impact delivery times and costs. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance processes, and potential tariffs or duties specific to your country. It’s advisable to work with a logistics partner experienced in international trade to navigate these complexities effectively. Additionally, ensure that suppliers provide proper packaging to protect the products during transit. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers when sourcing linear rail reach products?
Dispute resolution should begin with clear communication and a thorough review of the contract terms. Establish a procedure for addressing issues such as product defects or delivery delays, ideally outlined in your agreement. If disputes arise, try to resolve them amicably through negotiation. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, which can be costly and time-consuming. Always document all communications and agreements for future reference.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for linear rail reach
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of linear rail reach presents a significant opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The growing demand for automation and precision manufacturing underscores the necessity of incorporating high-quality linear guides into operational frameworks. By understanding the diverse types of linear rails available and their specific applications, buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and product quality.
Key Takeaways:
-
Evaluate Suppliers: Conduct thorough assessments of potential suppliers, focusing on reliability and technological capabilities. Establishing partnerships with reputable manufacturers can mitigate risks associated with procurement.
-
Prioritize Quality and Compatibility: Ensure that the selected linear rail systems are compatible with existing machinery and meet industry standards for quality and performance.
-
Adapt to Market Trends: Stay abreast of market trends, particularly the shift towards automation and miniaturization in manufacturing, to leverage opportunities for innovation and efficiency.
As the linear guide market is projected to grow significantly, now is the time for businesses to invest in these critical components. Embrace the future of manufacturing by integrating advanced linear rail systems into your operations, ensuring that your business remains competitive and responsive to evolving market demands.