Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Heating Element
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for heating element manufacturers
The global market for heating element manufacturers is a vital segment of the industrial landscape, providing essential components for a wide range of applications, from manufacturing to healthcare. For B2B buyers, understanding the intricacies of this market is critical. Heating elements play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, safety, and reliability in various processes, making informed sourcing decisions imperative.
This comprehensive guide offers a deep dive into the world of heating element manufacturing. It covers various types of heating elements—including cartridge, tubular, and immersion heaters—along with the materials used in their production. Additionally, the guide delves into manufacturing quality control processes, supplier evaluations, cost considerations, and market trends.
By exploring this guide, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—countries like Nigeria and Argentina—will be empowered to make informed decisions that enhance their operational effectiveness. With insights into supplier capabilities and market dynamics, buyers will be equipped to navigate the complexities of sourcing heating elements effectively. The guide aims to bridge the gap between manufacturers and buyers, fostering successful partnerships that drive innovation and efficiency in their respective industries.
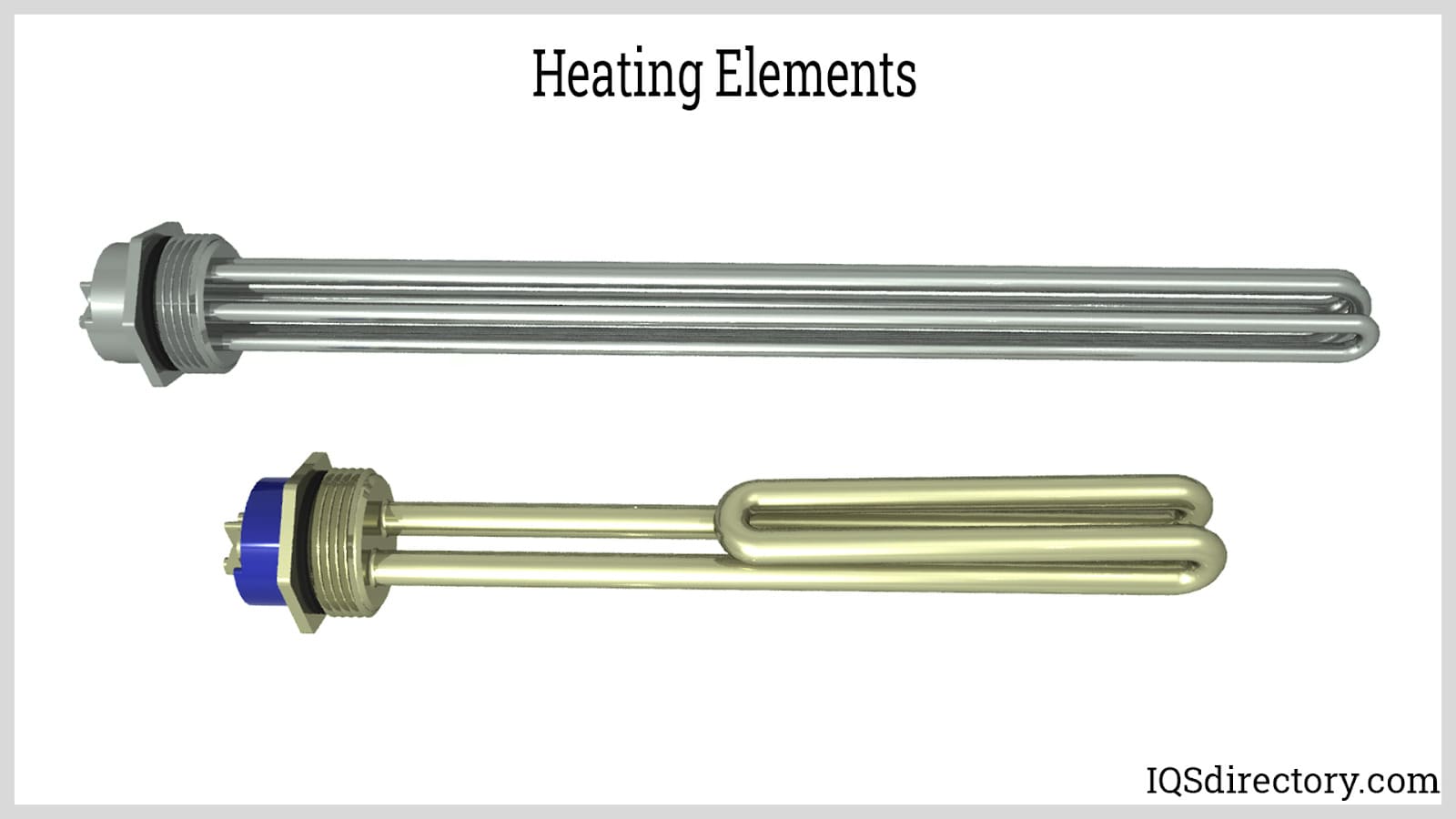
Understanding heating element manufacturers Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cartridge Heaters | Compact, versatile, customizable wattage | Industrial heating, medical device manufacturing | Pros: High efficiency, space-saving. Cons: Higher initial cost, limited specialty options. |
| Tubular Heaters | Durable, high watt density, various shapes available | Food processing, chemical processing, HVAC | Pros: Versatile design, long lifespan. Cons: Potentially slower heat-up time. |
| Immersion Heaters | Direct heating through fluid immersion | Water heating, oil heating, chemical processing | Pros: Efficient heat transfer, customizable sizes. Cons: Requires careful installation, maintenance needed. |
| Flexible Heaters | Lightweight, conformable, can be shaped to fit | Aerospace, medical devices, packaging machinery | Pros: Space-efficient, versatile. Cons: May not withstand high temperatures for long. |
| Band Heaters | Wrap-around design, often used for cylindrical objects | Plastic processing, packaging, food industry | Pros: Uniform heat distribution, easy to install. Cons: Limited to specific applications, may require additional insulation. |
Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge heaters are known for their compact design and versatility, making them ideal for various industrial applications, particularly in medical device manufacturing and heat-treating processes. They can be customized to meet specific wattage requirements, enhancing their efficiency. When purchasing, consider the compatibility with your existing equipment and the potential for higher initial costs compared to standard options.
Tubular Heaters
These heaters are characterized by their durability and high watt density, allowing them to be used in a wide range of applications, including food processing and HVAC systems. Tubular heaters can be manufactured in various shapes, making them adaptable for different setups. Buyers should evaluate the required heating capacity and the environment in which these heaters will operate, as some configurations may have slower heat-up times.
Immersion Heaters
Immersion heaters are designed to heat liquids directly by being submerged, making them highly efficient for applications such as water and oil heating. They can be customized in size and power to suit specific needs. Buyers should consider installation requirements and maintenance needs, as proper setup is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Flexible Heaters
Lightweight and conformable, flexible heaters can be shaped to fit various surfaces, making them popular in industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Their space-efficient design allows for innovative applications where traditional heaters may not fit. However, buyers should be aware that while they offer versatility, they may not withstand high temperatures for extended periods.
Band Heaters
These heaters are designed to wrap around cylindrical objects, providing uniform heat distribution essential in processes like plastic molding and packaging. They are relatively easy to install and can be tailored to specific applications. When considering band heaters, assess the specific heating requirements and whether additional insulation may be necessary to enhance efficiency.
Related Video: How PTC Heating Element Technology Works
Key Industrial Applications of heating element manufacturers
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of heating element manufacturers | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Heating elements in ovens and cookers | Improved cooking efficiency and uniform temperature control | Compliance with food safety standards and energy efficiency |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Immersion heaters for process heating | Enhanced control over chemical reactions and safety | Material compatibility and resistance to corrosive substances |
| HVAC | Heating elements in air conditioning systems | Better climate control and energy savings | Energy ratings and adaptability to local climate conditions |
| Medical Equipment | Heating elements in sterilizers and incubators | Reliable sterilization and patient safety | Regulatory compliance and precision temperature control |
| Automotive | Heating elements in component manufacturing and testing | Increased production efficiency and quality assurance | Customization options and response times for urgent needs |
Food Processing
In the food processing sector, heating elements are integral in ovens and cookers, where they facilitate cooking and baking processes. They provide precise temperature control, ensuring consistent quality and safety in food products. For international buyers, especially those in regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to source heating elements that comply with local food safety regulations and energy efficiency standards. This can enhance operational efficiency while reducing energy costs.
Chemical Manufacturing
Immersion heaters are widely used in chemical manufacturing for process heating. They allow for precise temperature control, which is critical for effective chemical reactions and maintaining safety standards. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider the material compatibility of heating elements with various chemicals, particularly in corrosive environments. This ensures durability and reduces maintenance costs, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient production processes.
HVAC
In the HVAC industry, heating elements play a vital role in air conditioning systems, providing warmth and comfort in various climates. They contribute to energy savings and better climate control, which is increasingly important for businesses looking to reduce operational costs. Buyers should focus on the energy ratings of heating elements and their adaptability to local climate conditions, especially in diverse markets like Africa and Europe, where environmental regulations may vary.
Medical Equipment
Heating elements are essential in medical equipment, particularly in sterilizers and incubators. They ensure reliable sterilization processes and maintain optimal conditions for sensitive medical applications. For B2B buyers in the medical sector, regulatory compliance with health standards is paramount. Additionally, precision in temperature control is crucial, making it important to work with manufacturers who can provide high-quality, certified heating elements.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, heating elements are used in various applications, including component manufacturing and testing. They enhance production efficiency and ensure quality assurance through consistent heating processes. Buyers should look for manufacturers that offer customization options to meet specific production needs and can provide quick response times for urgent requirements. This is especially relevant for international buyers in fast-paced markets like South America and Europe, where production timelines can be critical.
Related Video: Uses Of Polymers | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Strategic Material Selection Guide for heating element manufacturers
When selecting materials for heating elements, manufacturers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below are analyses of four common materials used in heating element manufacturing, detailing their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
1. Nickel-Chromium Alloys (NiCr)
Key Properties:
Nickel-chromium alloys are known for their high-temperature resistance, typically operating effectively up to 1200°C. They exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in oxidizing environments, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of NiCr alloys is a significant advantage, as they can withstand thermal cycling without degrading. However, they tend to be more expensive than other materials, which may affect overall production costs. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized equipment for shaping and forming.
Impact on Application:
These alloys are particularly compatible with air and gas heating applications, as well as in environments where oxidation is a concern. They are commonly used in industrial furnaces and heating elements for ovens.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN, as these materials are often subject to strict regulations regarding performance and safety.
2. Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Key Properties:
Silicon carbide is renowned for its high thermal conductivity and ability to operate at extreme temperatures (up to 1600°C). It also boasts excellent resistance to thermal shock and oxidation.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of SiC is its ability to maintain performance in harsh conditions, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. However, it is generally more brittle than metals, which can complicate manufacturing and increase the risk of breakage during handling.
Impact on Application:
SiC is often used in applications involving molten metals and high-temperature furnaces, where durability is paramount. Its compatibility with aggressive media makes it a preferred choice in the metallurgical industry.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers, especially from the Middle East, should be aware of the material’s compliance with local environmental regulations and standards for thermal efficiency.
3. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is a highly conductive material, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat transfer. It can operate at temperatures up to 300°C and is known for its excellent ductility and malleability.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of copper is its low cost and ease of manufacturing, as it can be easily shaped and formed into various configurations. However, its susceptibility to corrosion and oxidation at higher temperatures limits its application scope.
Impact on Application:
Copper is widely used in heating elements for domestic appliances and low-temperature industrial applications. Its compatibility with water and non-corrosive media makes it suitable for heating water and other fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Europe should consider the implications of using copper in terms of compliance with RoHS directives, particularly regarding lead content and environmental impact.
4. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel offers a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity. It can withstand temperatures up to 800°C, depending on the specific alloy used.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel makes it a popular choice for heating elements in various industries. However, it is generally more expensive than other metals like copper, and its manufacturing process can be more complex.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is commonly used in food processing and medical applications due to its hygienic properties and resistance to corrosion from various chemicals. It is also suitable for use in environments where cleanliness is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers from Africa and South America should ensure that the selected stainless steel grades meet the relevant international standards for food safety and corrosion resistance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for heating element manufacturers | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium | Industrial furnaces, heating elements for ovens | High-temperature resistance | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Silicon Carbide | High-temperature furnaces, metallurgical processes | Excellent thermal shock resistance | Brittle, risk of breakage | Medium |
| Copper | Domestic appliances, low-temperature industrial use | Low cost, excellent heat transfer | Corrosion and oxidation susceptibility | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical applications | Durability and corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | Medium |
This material selection guide provides valuable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions that align with their specific application needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for heating element manufacturers
Manufacturing heating elements involves a series of well-defined processes that ensure product quality and compliance with industry standards. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes not only aids in selecting the right supplier but also enhances negotiation and quality assurance strategies.
Typical Manufacturing Processes for Heating Elements
1. Material Preparation
The initial stage of manufacturing heating elements focuses on sourcing high-quality materials. Common materials include:
– Nickel-chromium alloys for resistance heating.
– Stainless steel for durability and corrosion resistance.
– Ceramics for insulation.
Key Techniques:
– Material Sourcing: Suppliers should provide certificates of material quality to ensure compliance with specifications.
– Pre-treatment: Materials often undergo cleaning and surface treatment to remove contaminants that could affect performance.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, they are shaped into the desired configurations. This stage includes:
– Cutting: Materials are cut to size using precision equipment.
– Bending and Shaping: Techniques such as stamping or rolling are employed to create specific geometries, especially for tubular heating elements.
Key Techniques:
– CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines ensure high precision in shaping components.
– 3D Printing: Emerging technologies like additive manufacturing allow for intricate designs and rapid prototyping.
3. Assembly
The assembly phase involves integrating various components into a complete heating element. This process typically includes:
– Wiring: Electrical connections are established, often using high-temperature resistant wires.
– Insulation: Insulation materials are added to prevent heat loss and protect surrounding components.
Key Techniques:
– Automated Assembly Lines: Enhance efficiency and consistency in the assembly process.
– Manual Assembly: In cases requiring high customization, skilled labor may be utilized.
4. Finishing
The final stage focuses on surface treatments and coatings that enhance performance and longevity. This can include:
– Coating: Applying heat-resistant paints or coatings to protect against oxidation.
– Testing: Initial testing is conducted to ensure that the elements meet predefined specifications.
Key Techniques:
– Electroplating: Improves corrosion resistance and extends product life.
– Polishing: Enhances the aesthetic quality and reduces surface imperfections.
Quality Assurance in Heating Element Manufacturing
Quality assurance is critical to ensuring that heating elements perform reliably under various conditions. International buyers should be familiar with the following standards and checkpoints.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized quality management standard that ensures consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For heating elements used in the oil and gas sector, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) is typically structured around several key checkpoints:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections throughout the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to verify performance and compliance.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Checks for resistance, insulation, and operational performance.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluates how well heating elements perform under specified temperature conditions.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the lifespan and reliability of heating elements under various environmental conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is vital. Here are actionable steps:
1. Conduct Audits
Regular audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing practices and adherence to quality standards. Buyers should consider:
– On-site Audits: Visiting manufacturing facilities to observe processes firsthand.
– Third-party Audits: Engaging external firms to conduct impartial assessments.
2. Request Quality Reports
Suppliers should provide detailed quality assurance reports that include:
– Testing Results: Documentation of all testing conducted on products.
– Certification Copies: Proof of compliance with international standards (e.g., ISO, CE).
3. Engage Third-party Inspection Services
Consider hiring third-party inspection services, especially for large orders, to ensure that products meet specified quality standards before shipment. This step can mitigate risks associated with international sourcing.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing heating elements internationally, buyers should be aware of specific nuances:
– Cultural Differences: Understand how quality assurance practices may vary by region. For instance, suppliers in Europe may have stricter regulations compared to those in developing markets.
– Communication Barriers: Establish clear communication channels to discuss quality expectations and resolve issues quickly.
– Local Regulations: Be aware of local compliance requirements in the buyer’s country, which may differ from the manufacturer’s standards.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they procure high-quality heating elements that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Top 10 Fantastic Mass Production Factory Process Videos
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for heating element manufacturers Sourcing
When sourcing heating elements from manufacturers, it’s essential to understand the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics involved. This analysis is particularly relevant for international B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where various factors can significantly influence costs and pricing.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as metals and ceramics, can vary greatly depending on market fluctuations and sourcing locations. High-quality materials often lead to higher initial costs but can improve longevity and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs can differ widely based on the manufacturer’s location. Countries with higher labor costs may provide superior craftsmanship and more rigorous quality controls, while lower-cost regions might compromise on these factors.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, such as utilities, equipment depreciation, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturers manage overhead effectively, which can translate into better pricing for buyers.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific heating element designs can be a significant upfront investment. Manufacturers typically pass these costs on to buyers, particularly for small or one-off orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure product reliability but can add to overall costs. Buyers should assess the manufacturer’s QC practices and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) to determine the balance between cost and quality.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary based on the distance from the manufacturer to the buyer, shipping method, and any tariffs or duties applicable. Efficient logistics planning can reduce these costs significantly.
-
Margin: Manufacturers will include a profit margin in their pricing. This margin can vary based on brand reputation, market demand, and competitive positioning.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Prices often decrease with larger order volumes. Understanding the manufacturer’s Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can help buyers negotiate better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized products usually carry a premium price. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials affects both performance and cost. Buyers should weigh the long-term benefits of premium materials against initial costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality and certified products may cost more upfront but can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over time.
-
Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong track record may command higher prices due to perceived reliability and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can help buyers manage logistics costs effectively, as these terms dictate who bears responsibility for shipping and insurance at various points.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate terms, especially for larger orders. Leverage competitive quotes to secure better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the purchase price. Consider long-term operational costs, including maintenance and energy efficiency.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of local market conditions that may influence pricing. For instance, tariffs or import duties can significantly affect the final cost in regions like Africa and South America.
-
Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Consider long-term partnerships that foster trust and collaboration.
-
Research and Benchmarking: Conduct thorough research on various suppliers, including their pricing structures and customer feedback. This will provide a benchmark for making informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures mentioned are indicative and can fluctuate based on various market conditions. Always consult multiple suppliers and perform due diligence to ensure you receive the best value for your investment.
Spotlight on Potential heating element manufacturers Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘heating element manufacturers’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for heating element manufacturers
Key Technical Properties for Heating Elements
Understanding the technical specifications of heating elements is essential for international B2B buyers looking to make informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in manufacturing heating elements, commonly including stainless steel, Inconel, or ceramic.
– B2B Importance: Material grade directly affects the performance, durability, and resistance to corrosion and oxidation of heating elements. Selecting the right material is crucial for applications exposed to harsh conditions or requiring high-temperature operation. -
Watt Density
– Definition: The amount of power (watts) supplied per unit area of the heating element, typically expressed in watts per square inch or watts per square centimeter.
– B2B Importance: Higher watt density can lead to quicker heating times, making it vital for processes requiring rapid temperature changes. However, it can also result in shorter element life if not managed properly, so understanding the application requirements is critical. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The acceptable range of deviation from specified dimensions or performance characteristics, often expressed as a percentage.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance affects how well the heating element fits into its intended application. Tight tolerances may be essential in precision applications, ensuring the element performs efficiently without risking damage to surrounding equipment. -
Insulation Resistance
– Definition: The resistance of the insulating material surrounding the heating element, measured in ohms.
– B2B Importance: High insulation resistance is crucial to prevent electrical leakage, which can lead to safety hazards or equipment malfunction. It is particularly important in industrial applications where safety and reliability are paramount. -
Operating Temperature
– Definition: The maximum temperature at which the heating element can operate effectively without degradation.
– B2B Importance: Knowing the operating temperature helps in selecting elements that can withstand specific operational conditions, ensuring safety and longevity. Different applications may require elements that operate at varying temperatures, making this a critical specification. -
Thermal Efficiency
– Definition: The effectiveness with which a heating element converts electrical energy into heat.
– B2B Importance: Higher thermal efficiency leads to reduced energy costs and better performance. Buyers should consider this property to enhance energy savings in their operations, especially in large-scale industrial applications.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and better communication with suppliers. Here are some essential terms for buyers:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM partnerships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing from reputable manufacturers that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their purchasing strategy and manage inventory effectively, particularly for large-scale operations or specific projects. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and other details for specific products or services.
– Relevance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best value and terms for their procurement needs. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions, covering shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping costs and risks associated with international purchases, enabling better financial planning.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Relevance: Knowing lead times allows buyers to manage project timelines and ensure timely delivery of critical components, particularly in industries with tight schedules. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Compliance with industry-specific standards (e.g., ISO, CE) that ensure quality and safety.
– Relevance: Certifications indicate a manufacturer’s commitment to quality and can influence buyer confidence, particularly in regulated industries.
By understanding these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they select the right heating elements for their specific applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the heating element manufacturers Sector
Global heating element manufacturing is shaped by various market dynamics and sourcing trends, significantly influenced by regional demands and technological advancements. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, navigate this sector, understanding these trends is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global heating element market is experiencing robust growth driven by increasing industrialization, the demand for energy-efficient solutions, and advancements in technology. Key sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare are rapidly adopting electric heating elements due to their efficiency and reliability. For B2B buyers in regions like Nigeria and Argentina, this presents an opportunity to source innovative heating solutions that meet specific industry requirements.
Emerging technologies, such as IoT-enabled heating systems, are changing the landscape. These systems offer real-time monitoring and control, enhancing operational efficiency. Buyers should consider suppliers that integrate smart technologies into their products, as this can lead to reduced operational costs and improved maintenance capabilities.
Additionally, the shift towards localized sourcing is gaining momentum. International buyers are increasingly looking for manufacturers closer to their operations to mitigate supply chain risks and reduce lead times. This trend is particularly relevant for buyers in the Middle East and Africa, where logistical challenges can impact timely delivery.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal focus for heating element manufacturers, reflecting a growing awareness of environmental impact. Buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as utilizing recyclable materials and reducing energy consumption during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. This involves ensuring that suppliers maintain fair labor practices and transparency in their supply chains. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) indicate a commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. B2B buyers should seek partners who possess these certifications, as they reflect a dedication to minimizing environmental impact and ensuring responsible sourcing.
Furthermore, the adoption of “green” materials, such as bio-based plastics and low-emission metals, is gaining traction. By investing in products made from sustainable materials, buyers can enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles while also meeting regulatory requirements in their respective regions.
Brief Evolution/History
The heating element industry has evolved significantly over the past century. Initially dominated by simple resistance-based heating technologies, the sector has seen the introduction of advanced materials and manufacturing processes. The rise of electric heating elements, particularly in industrial applications, has transformed how heat is generated and managed in various settings. This evolution has led to increased efficiency, safety, and versatility, allowing manufacturers to cater to diverse market needs. Understanding this historical context can help B2B buyers appreciate the technological advancements that underpin modern heating solutions and make informed sourcing decisions.
By staying informed about market dynamics, sourcing trends, and sustainability practices, international B2B buyers can better navigate the complexities of the heating element manufacturing sector, ultimately leading to enhanced operational efficiency and sustainability in their supply chains.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of heating element manufacturers
-
How can I effectively vet heating element manufacturers?
To vet heating element manufacturers, start by researching their reputation through online reviews, industry forums, and social media platforms. Request references and case studies to understand their previous projects. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001 or RoHS compliance to ensure quality standards. Additionally, inquire about their production capabilities, experience in your specific industry, and any partnerships with recognized entities. If possible, visit their facility or arrange for a virtual tour to assess their operations and quality control processes firsthand. -
Can I customize heating elements according to my specifications?
Most reputable manufacturers offer customization options to meet specific requirements. Discuss your application needs, including dimensions, wattage, and material preferences, with potential suppliers. Ensure they have the technical capability to produce tailored solutions and request samples or prototypes before placing a larger order. Additionally, clarify the extent of customization available, such as design modifications or unique features, to ensure the final product aligns with your operational demands. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly between manufacturers, often depending on the complexity and type of heating element required. Commonly, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times can also differ based on the manufacturer’s location and production capacity, typically ranging from 2 to 12 weeks. Always confirm these details during the negotiation phase to avoid any production delays that could impact your supply chain. -
What payment terms should I expect when dealing with international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among manufacturers, especially in international transactions. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. Negotiate terms that provide you with adequate protection and flexibility, such as partial upfront payments with the remainder upon delivery. Be cautious of manufacturers requiring full payment in advance, as this may indicate financial instability. Always ensure clarity in payment terms to avoid disputes later. -
What quality assurance processes should heating element manufacturers have in place?
A robust quality assurance (QA) process is crucial for maintaining product standards. Manufacturers should implement regular inspections at various production stages, including raw material checks, in-process monitoring, and final product testing. Ask for documentation of their QA procedures and any third-party certifications that validate their compliance with industry standards. Additionally, inquire about their return policy and warranty terms to safeguard your investment. -
How do logistics and shipping arrangements work for international orders?
Logistics can be complex when sourcing heating elements from international suppliers. Discuss shipping options, including Incoterms, to clarify responsibilities for costs and risks during transportation. Understand the expected delivery times and any potential customs clearance challenges. It’s advisable to work with logistics providers experienced in international trade to ensure a smooth process. Furthermore, confirm whether the manufacturer offers support in managing logistics or if you will need to handle it independently. -
What steps should I take in case of a dispute with a manufacturer?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue directly with the manufacturer through open communication. Document all correspondence and agreements made during the negotiation process. If resolution fails, refer to the contractual terms agreed upon, including any mediation or arbitration clauses. Engaging legal counsel familiar with international trade laws may also be necessary. Maintaining a professional demeanor throughout the process can help facilitate a more amicable resolution. -
What certifications should I look for in heating element manufacturers?
Certifications are a key indicator of a manufacturer’s adherence to quality and safety standards. Look for ISO certifications, particularly ISO 9001 for quality management systems. Compliance with RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) ensures that products are free from harmful substances. Additionally, certifications specific to your industry, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) for electrical safety, can provide further assurance. Request documentation of these certifications to verify the manufacturer’s claims and maintain compliance with your local regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for heating element manufacturers
In navigating the complex landscape of heating element manufacturing, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial factor for international B2B buyers. Key takeaways emphasize the importance of understanding supplier capabilities, evaluating product quality, and assessing compliance with international standards such as RoHS and REACH. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should prioritize manufacturers who offer customizable solutions and robust support to meet specific industry needs.
Value of Strategic Sourcing: By adopting a strategic sourcing approach, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions. Engaging with diverse suppliers not only broadens options but also fosters innovation through collaborative partnerships.
As we look toward the future, the demand for high-performance heating solutions will likely increase, driven by advancements in technology and sustainability initiatives. International B2B buyers are encouraged to take proactive steps: conduct thorough market research, leverage online platforms for supplier discovery, and build relationships with manufacturers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and innovation. By doing so, you position your organization to thrive in a competitive marketplace while ensuring the reliability and efficiency of your heating applications.