Mastering Water Evaporators: A Comprehensive B2B Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for water evaporators
Water evaporators play a crucial role in various industries, including food processing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing. As the demand for efficient water management intensifies amid rising operational costs and environmental challenges, understanding the intricacies of evaporator technology becomes vital for international B2B buyers. This guide aims to equip decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe with the essential knowledge needed to navigate the global market for water evaporators effectively.
Within this comprehensive resource, you will find an exploration of various types of evaporators, including batch, forced circulation, and wiped film systems, each tailored to specific applications and product characteristics. We delve into material selection and manufacturing quality control, ensuring that buyers can identify suppliers who meet industry standards and sustainability requirements. Additionally, our guide addresses cost considerations and market trends, providing insights into the economic landscape that influences purchasing decisions.
By demystifying the complexities of water evaporators and highlighting the key factors that affect sourcing, this guide empowers buyers to make informed decisions. Whether you are based in South Africa, the UK, or elsewhere, understanding the nuances of water evaporators will enable you to optimize your operations, reduce costs, and enhance product quality in an increasingly competitive environment.
Understanding water evaporators Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Pan | Low temperature operation; long residence time | Jams, jellies, and some pharmaceuticals | Pros: Simple design; low initial cost. Cons: Limited capacity; not suitable for heat-sensitive products. |
| Natural Circulation | Uses external heating for improved evaporation | Reboiling in distillation processes | Pros: Higher evaporation capacity; flexible design. Cons: Requires larger footprint; may have higher operational costs. |
| Rising Film Tubular | High central core velocity; thin liquid film | Dairy products, fruit juices | Pros: Efficient heat transfer; reduced capital investment. Cons: More complex design; may require precise control systems. |
| Falling Film Tubular | Liquid flows down tube; uniform distribution | Chemical processing; wastewater treatment | Pros: Efficient for viscous products; lower fouling risk. Cons: Higher operational complexity; initial setup can be costly. |
| Wiped Film | Continuous film; effective for heat-sensitive materials | Pharmaceuticals; specialty food products | Pros: Ideal for heat-sensitive products; minimizes residence time. Cons: Higher initial investment; maintenance can be intensive. |
Batch Pan
The batch pan evaporator is one of the oldest methods of concentration, primarily used for products like jams and jellies. Its operation involves a long residence time at low temperatures, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials. However, its limited evaporation capacity and simple design may not meet the demands of larger-scale operations. Buyers should consider the specific product requirements and evaluate whether the lower initial costs align with their production goals.
Natural Circulation
Natural circulation evaporators utilize external heating to enhance evaporation rates, commonly applied in distillation processes. This design allows for larger evaporation capacities compared to batch pans. While the flexibility in design can be a significant advantage, buyers must weigh this against the potential for higher operational costs and the requirement for a larger physical footprint. Careful consideration of production scale and efficiency needs is essential.
Rising Film Tubular
The rising film tubular evaporator is known for its high efficiency, characterized by a thin liquid film that enables rapid heat transfer. This type is particularly effective for products such as dairy and fruit juices, where maintaining product quality is crucial. While its design may be more complex, the benefits of reduced capital investment and shorter processing times make it appealing for B2B buyers. However, precise control systems are necessary to ensure optimal operation.
Falling Film Tubular
Falling film tubular evaporators are designed to distribute liquid evenly across tubes, making them suitable for chemical processing and wastewater treatment. This design allows for efficient processing of viscous products while minimizing fouling risks. However, the operational complexity and initial setup costs can be higher, necessitating a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership for potential buyers. Understanding the specific application requirements is vital for making an informed purchasing decision.
Wiped Film
The wiped film evaporator is particularly well-suited for heat-sensitive materials, as it continuously wipes the product film across the heating surface. This minimizes residence time, making it ideal for pharmaceuticals and specialty food products. While it offers significant advantages in product quality, the higher initial investment and intensive maintenance needs can be drawbacks. Buyers should assess their product characteristics and operational capabilities to determine if this technology meets their needs effectively.
Related Video: Types of Evaporators | HVAC
Key Industrial Applications of water evaporators
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Water Evaporators | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Concentration of fruit juices and dairy products | Enhances flavor and shelf life while reducing transport costs | Equipment efficiency, energy consumption, and maintenance support |
| Chemical Manufacturing | Production of concentrated chemicals and solvents | Improves product quality and reduces waste | Material compatibility, energy efficiency, and regulatory compliance |
| Pharmaceutical | Concentration of active ingredients and formulations | Ensures product potency and stability | Cleanroom compatibility, precision control, and validation support |
| Textile and Dyeing | Concentration of dye solutions and chemicals | Reduces water usage and treatment costs | Environmental regulations, material safety, and process adaptability |
| Wastewater Treatment | Concentration of sludge and recovery of water | Reduces disposal costs and recycles resources | Reliability, scalability, and integration with existing systems |
Food and Beverage
In the food and beverage industry, water evaporators are crucial for concentrating fruit juices and dairy products. By removing excess water, these evaporators enhance the flavor and shelf life of products while significantly reducing transportation costs. For international buyers, especially from regions with varying energy costs, sourcing evaporators with high energy efficiency and low maintenance requirements is essential. Understanding local regulations regarding food safety and equipment hygiene is also critical for compliance and ensuring product quality.
Chemical Manufacturing
Water evaporators play a vital role in chemical manufacturing, particularly in producing concentrated chemicals and solvents. They facilitate the removal of water, improving product quality and minimizing waste. Buyers in this sector should consider the compatibility of materials with the chemicals processed, energy efficiency to reduce operational costs, and compliance with environmental regulations. Additionally, understanding local market dynamics in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can help in selecting the right evaporator technology.
Pharmaceutical
In the pharmaceutical sector, water evaporators are used to concentrate active ingredients and formulations, ensuring product potency and stability. The stringent quality control standards in this industry necessitate equipment that meets cleanroom compatibility and precision control. International buyers must prioritize suppliers who offer robust validation support and can navigate regulatory requirements specific to their region, such as those in the UK or South Africa.
Textile and Dyeing
For the textile and dyeing industry, water evaporators are employed to concentrate dye solutions and chemicals, significantly reducing water usage and treatment costs. This application is particularly relevant in regions facing water scarcity. When sourcing evaporators, buyers should consider environmental regulations, the safety of materials used in dyeing processes, and the adaptability of the equipment to different dye types and processes, ensuring operational flexibility.
Wastewater Treatment
In wastewater treatment, water evaporators are used to concentrate sludge and recover water, effectively reducing disposal costs and recycling valuable resources. This application is increasingly important as industries face stricter environmental regulations and the need for sustainable practices. Buyers should focus on the reliability and scalability of evaporators to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, as well as the overall operational efficiency to maximize resource recovery in their specific regional contexts.
Related Video: Wastewater treatment & ZLD evaporators powered by solar energy – Solarvap
Strategic Material Selection Guide for water evaporators
When selecting materials for water evaporators, it’s crucial to consider their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and how they align with specific applications. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of water evaporators, focusing on their relevance to international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its high corrosion resistance, strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 800°C and can handle pressures exceeding 200 psi.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for various applications, including food and chemical processing. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other materials, which can impact initial capital costs. Manufacturing complexity is moderate, as stainless steel requires specialized welding techniques.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including corrosive chemicals and high-purity water, making it ideal for industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel grades. In regions like Europe and South Africa, certifications related to food safety and chemical processing are critical.
Carbon Steel
Key Properties: Carbon steel is characterized by its high tensile strength and ability to withstand high pressures. It has a temperature rating of up to 400°C but is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of carbon steel is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for large-scale evaporators. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its use in certain applications, particularly those involving corrosive substances. The manufacturing process is simpler than that of stainless steel.
Impact on Application: Carbon steel is suitable for applications where the media is non-corrosive, such as water or certain oils. Its use in corrosive environments may require additional protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A36. In regions with high humidity or corrosive environments, additional coatings or treatments may be necessary to extend the lifespan of carbon steel evaporators.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium offers exceptional corrosion resistance and can withstand high temperatures, with a typical rating of up to 600°C. It also has a lower density compared to stainless steel, making it lighter.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of titanium is its outstanding resistance to corrosion, especially in seawater and acidic environments. However, it is significantly more expensive than both stainless and carbon steel, and its manufacturing process is complex, requiring specialized techniques.
Impact on Application: Titanium is ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals or high-purity requirements, such as in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B265. In regions with stringent environmental regulations, titanium’s properties can provide a competitive advantage despite its higher cost.
Glass-Lined Steel
Key Properties: Glass-lined steel combines the strength of steel with the non-reactive properties of glass. It can handle temperatures up to 300°C and is resistant to corrosion from a wide range of chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage is its excellent resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making it suitable for sensitive applications. However, it is prone to chipping and cracking, which can lead to maintenance issues. The manufacturing process is more complex due to the glass lining.
Impact on Application: Glass-lined steel is particularly well-suited for applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where product purity is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards like DIN 12100 for glass-lined equipment. In regions with strict food safety regulations, glass-lined evaporators may be preferred.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for water evaporators | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | High corrosion resistance | Higher initial capital cost | High |
| Carbon Steel | Non-corrosive media applications | Cost-effective | Susceptible to rust | Low |
| Titanium | Aggressive chemical environments | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Very high cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Glass-Lined Steel | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Excellent chemical resistance | Prone to chipping and cracking | Medium |
This material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions when sourcing water evaporators, ensuring that they choose materials that align with their operational needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for water evaporators
Manufacturing Processes for Water Evaporators
When sourcing water evaporators, understanding the manufacturing processes is critical for B2B buyers. The production of these systems involves several key stages, each requiring precision and adherence to specific techniques to ensure high-quality output.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
- Material Preparation
– Selection of Raw Materials: High-quality materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys are essential due to their corrosion resistance and durability. Buyers should inquire about the source and grade of materials used.
– Material Testing: Before use, materials undergo rigorous testing to check for structural integrity and compliance with industry standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Forming
– Fabrication Techniques: Common methods include welding, machining, and bending. Each technique must be chosen based on the design requirements of the evaporator.
– Precision Engineering: Advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often employed to ensure exact dimensions and tolerances, which are crucial for optimal performance. -
Assembly
– Component Integration: The assembly process involves integrating various components such as heat exchangers, pumps, and control systems. Each part must align perfectly to ensure efficiency.
– Quality Checks During Assembly: Periodic inspections are conducted to ensure that components meet specified tolerances and fit correctly. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Processes like passivation, polishing, and coating are applied to enhance corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. This is particularly important for evaporators used in food and beverage applications.
– Final Inspection: A thorough final inspection is performed to ensure that the finished product meets all design specifications and quality standards.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is vital in the manufacturing of water evaporators, ensuring that products meet the necessary standards for safety, performance, and reliability.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines requirements for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold within the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For evaporators used in oil and gas applications, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards ensures industry-specific quality and safety.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Conducts inspections on raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards before production begins. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Ongoing assessments during the manufacturing process help identify defects or deviations early, allowing for immediate corrective actions. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– The final product undergoes comprehensive testing to verify that it meets all operational and safety requirements before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
- Hydrostatic Testing: Ensures that the evaporator can withstand internal pressures without leaking.
- Performance Testing: Assesses the efficiency of the evaporator under operational conditions, verifying heat transfer rates and energy consumption.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic and radiographic testing check for internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers should take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits of potential suppliers helps assess their manufacturing practices and quality control systems.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed reports on past performance, including any non-conformities and corrective actions taken.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection bodies can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality assurance practices.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of specific nuances when it comes to quality control and certification:
- Regional Standards Variability: Different regions may have varying compliance requirements. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are familiar with the regulations applicable in their target markets.
- Documentation and Traceability: It’s essential for suppliers to maintain clear documentation of the manufacturing process and quality control measures. This facilitates easier audits and compliance verification.
- Cultural Considerations: Understanding the cultural context of the supplier’s country can impact negotiation and communication regarding quality expectations. Buyers should establish clear lines of communication and set expectations early in the procurement process.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers of water evaporators, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance is crucial. By focusing on the key stages of production and the relevant quality control measures, buyers can ensure that they procure reliable and efficient systems tailored to their operational needs. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and actively verifying their quality practices will further safeguard investment and enhance operational performance.
Related Video: Korean drinking water plastic bottles mass production process in alkaline water factory
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for water evaporators Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of water evaporators is critical for international B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. This analysis covers essential cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing water evaporators include stainless steel and specialized alloys that can withstand corrosion and high temperatures. The quality and source of these materials significantly impact the overall cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and are influenced by local wage standards and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Skilled labor is often required for assembly and quality assurance, particularly for high-end or customized evaporators.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Overhead can differ based on the manufacturing location and the efficiency of production processes.
-
Tooling: The cost of tooling can be substantial, especially for custom designs. Tooling expenses should be considered when requesting quotes for specialized evaporators.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC processes ensure that the evaporators meet industry standards and customer specifications. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the equipment and the certifications required.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are significant, especially for international transactions. Factors such as the distance from the supplier, shipping method, and customs duties can heavily influence logistics costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the evaporator.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Bulk orders often qualify for discounts, making it essential for buyers to consider their purchasing volume when negotiating prices.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized evaporators designed for specific applications may incur additional costs. Understanding the necessary specifications beforehand can help buyers avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can affect both performance and cost. High-quality materials may lead to higher initial costs but can offer better durability and efficiency, impacting the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications, such as ISO standards or industry-specific approvals, can influence pricing. Higher quality assurance standards typically lead to higher costs but may justify the investment through improved reliability and performance.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their products, but they often provide better support and warranty services.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipment (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect the final cost. Buyers should clearly understand their responsibilities and the associated costs to avoid surprises.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can lead to significant savings. Buyers should be prepared to discuss volume discounts, payment terms, and shipping costs.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership, which includes purchase price, maintenance, and operational costs over the equipment’s lifespan. Investing in higher-quality evaporators may reduce operational costs and downtime.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the regional factors influencing pricing. For instance, tariffs and import duties can significantly affect costs for buyers in Africa and South America compared to those in Europe.
-
Supplier Assessment: Evaluate potential suppliers not only on price but also on their service capabilities, reliability, and the quality of their products. This holistic approach can lead to better long-term partnerships.
Disclaimer
The pricing analysis provided here is indicative and subject to change based on market fluctuations, specific project requirements, and supplier negotiations. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential water evaporators Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘water evaporators’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for water evaporators
Key Technical Properties of Water Evaporators
When considering the procurement of water evaporators, international B2B buyers should focus on several critical specifications that directly impact performance, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Here are the essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
The construction material of evaporators, often stainless steel or specialized alloys, is crucial for corrosion resistance and longevity. The choice of material affects not only durability but also the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures, which are common in evaporation processes. For buyers in industries such as food processing or pharmaceuticals, using food-grade materials is essential to meet health and safety regulations. -
Thermal Efficiency
This specification refers to the ability of an evaporator to transfer heat effectively. High thermal efficiency reduces energy consumption, which is particularly important in regions with high energy costs. Buyers should request data on the heat transfer coefficients and overall energy consumption figures to assess long-term operational costs. -
Capacity
The evaporation capacity, usually measured in liters per hour or gallons per hour, indicates how much water the system can evaporate in a given time. Understanding the required capacity is critical for ensuring that the evaporator meets production demands without downtime. Buyers should align their capacity needs with the expected production volume to avoid under or over-sizing the equipment. -
Operating Pressure
Evaporators operate under various pressure conditions, which can significantly affect boiling points and evaporation rates. Buyers should consider the operating pressure required for their specific applications and ensure the evaporator can handle these conditions. Higher pressures often lead to increased efficiency but may require more robust and expensive equipment. -
Tolerance Levels
Tolerances refer to the allowable variations in dimensions and operational parameters. In B2B contexts, precise tolerances are critical for ensuring that evaporators fit into existing systems and perform reliably. Buyers should inquire about the manufacturing tolerances of the equipment, especially if integrating with other machinery. -
Control Systems
Modern evaporators often come equipped with advanced control systems that enhance automation and monitoring. Features like automated temperature control, pressure monitoring, and flow regulation are vital for optimizing performance and reducing labor costs. Buyers should evaluate the level of automation required for their operations to determine the best control systems.
Common Trade Terminology in the Water Evaporator Industry
Understanding industry jargon can facilitate smoother transactions and negotiations. Here are key terms that buyers should familiarize themselves with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
This term refers to companies that manufacture products that are sold under another company’s brand. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers ensure they are sourcing quality products and can provide insights into warranty and support services. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQ terms to align with their production needs while minimizing excess inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products or services. It is a vital tool for buyers to gather competitive quotes and make informed purchasing decisions. Clarity in the RFQ can lead to better responses from suppliers. -
Incoterms
Short for International Commercial Terms, these are standardized trade terms used in international shipping. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand cost implications and risk management in transportation. -
Lead Time
This term refers to the amount of time between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and supply chain management. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly to suppliers to ensure timely delivery. -
Warranties and Service Agreements
These are contracts that outline the support and services provided by the manufacturer post-purchase. Understanding the terms of warranties and service agreements can protect buyers from unexpected repair costs and ensure equipment reliability.
By comprehensively understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the water evaporators Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global water evaporators market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across diverse sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical processing. Key factors influencing this market include the rising need for efficient water management solutions due to water scarcity, particularly in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where climate change exacerbates existing challenges.
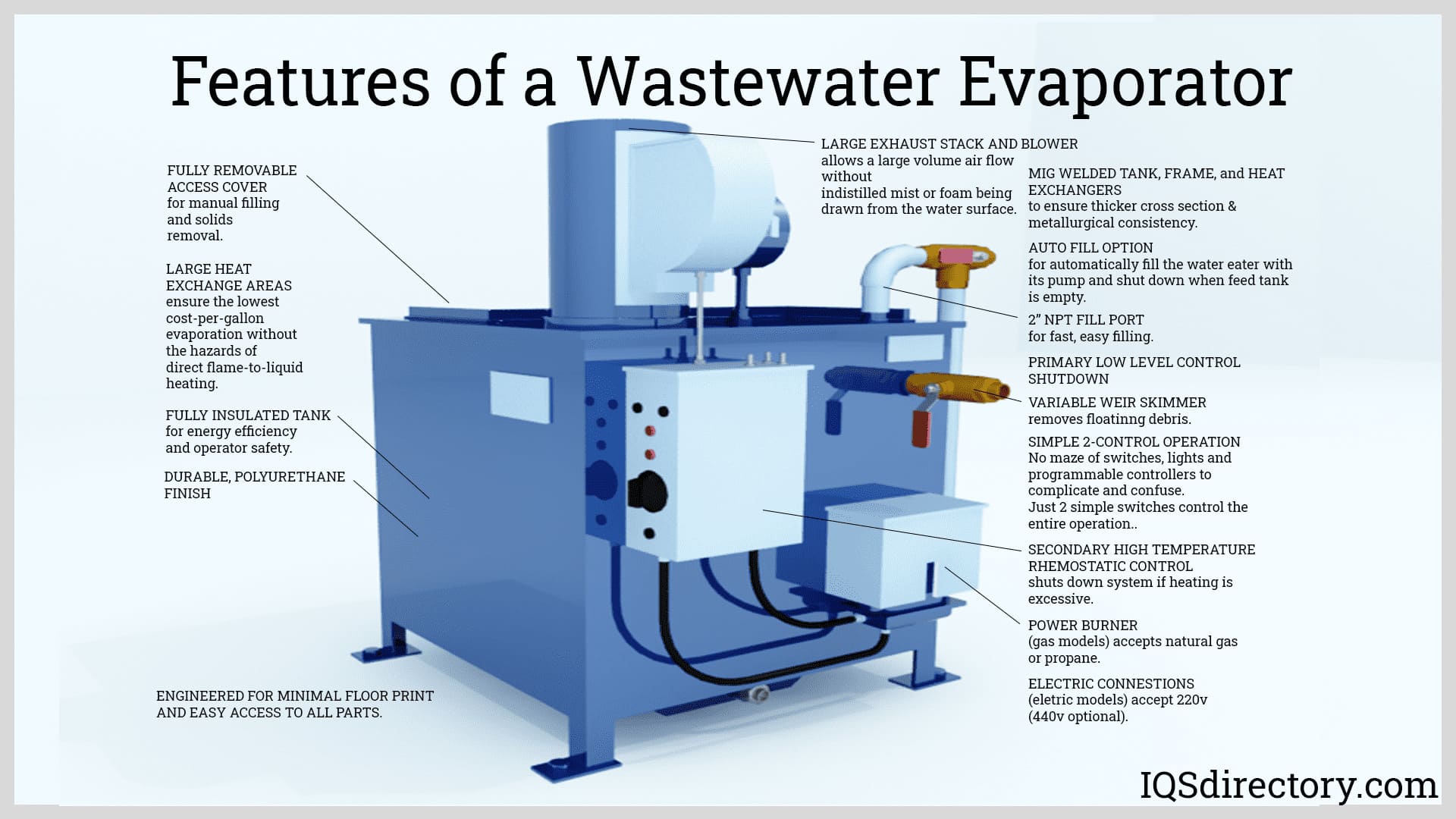
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Emerging technologies such as Mechanical Vapor Recompression (MVR) and advanced automation systems are reshaping sourcing trends. These technologies not only enhance energy efficiency but also reduce operational costs, making them highly attractive for international B2B buyers. In addition, the trend towards modular and preassembled evaporators is gaining traction, offering businesses flexibility and quicker installation times.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional energy costs and regulations promoting sustainable practices. Buyers from Europe, for example, are increasingly seeking suppliers that align with stringent environmental standards, while those in South America and Africa may prioritize cost-effectiveness and local support. Understanding these regional nuances is crucial for international buyers aiming to navigate the complex landscape of water evaporators.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal concern in the water evaporators sector, reflecting a broader commitment to environmental stewardship among manufacturers and buyers alike. The production and operation of evaporators can significantly impact water usage and energy consumption. As such, B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to reducing their environmental footprint through innovative technologies and sustainable practices.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. Buyers should consider suppliers who uphold fair labor practices and transparency in their supply chains, particularly in regions where regulations may vary. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED for energy efficiency can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. By choosing partners with ‘green’ certifications, international buyers can not only enhance their corporate social responsibility profiles but also mitigate risks associated with environmental regulations.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of water evaporators has been marked by significant technological advancements since their inception. Initially, traditional methods like batch pans and natural circulation systems dominated the landscape. However, the introduction of more efficient technologies, such as rising and falling film evaporators, revolutionized the industry by improving heat transfer and reducing energy consumption.
As the demand for high-quality, concentrated products grew, so did the need for more sophisticated evaporator designs. Today, the focus is on enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and adaptability to various industrial needs. Understanding this historical context can provide B2B buyers with insights into the reliability and performance of different evaporator types, guiding their sourcing decisions effectively.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of water evaporators
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of water evaporators?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, technological capabilities, and client references. Evaluate their production capacity and quality assurance processes. Check for relevant certifications such as ISO and industry-specific standards. It’s also beneficial to assess their financial stability and after-sales support. Engaging with local industry associations or trade fairs can provide insights into the supplier’s reputation and reliability. -
Can water evaporators be customized to meet specific processing needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for water evaporators. Customization can include adjustments in size, materials, and specific operational parameters to accommodate unique product characteristics. When discussing customization, clearly communicate your operational requirements, such as the type of liquid to be evaporated and desired concentration levels. Ensure that the supplier has a proven track record in delivering custom solutions. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead time for water evaporators?
The MOQ for water evaporators can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the equipment. Generally, MOQs range from one unit for specialized systems to several units for standard models. Lead times are influenced by the order size, customization requests, and the supplier’s production schedule, often ranging from a few weeks to several months. Always clarify these details upfront to align expectations. -
What payment terms are common in international B2B transactions for water evaporators?
Common payment terms include a deposit upon order confirmation (typically 30-50%), with the balance due prior to shipment or upon delivery. Consider using letters of credit (LC) for larger transactions to mitigate risk. Be aware of the payment methods accepted by the supplier, which may include bank transfers, credit cards, or escrow services. Ensure that the terms are clearly outlined in the purchase agreement to avoid disputes later.
-
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for the evaporators I purchase?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes and relevant certifications from the supplier. Look for international certifications such as ISO 9001, which ensures adherence to quality management standards. Ask for test reports or performance guarantees, especially for custom orders. Consider conducting factory inspections or third-party audits to verify the manufacturing process and quality control measures. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when importing water evaporators?
Logistics for importing water evaporators involve shipping methods, customs clearance, and local regulations. Choose a reliable freight forwarder experienced in handling industrial equipment. Understand the shipping terms (Incoterms) and ensure that all necessary documentation, including invoices and certificates of origin, is in order. Be aware of potential duties, taxes, and compliance with local safety and environmental regulations. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier?
If a dispute arises, first attempt to resolve the issue amicably through direct communication. Document all correspondence and agreements made. If resolution fails, refer to the contract for dispute resolution clauses, which may include mediation or arbitration. Engage legal counsel familiar with international trade laws if necessary, and consider escalating the matter to relevant trade associations or regulatory bodies for support. -
How can I assess the long-term viability of a supplier?
To assess a supplier’s long-term viability, analyze their financial health, market presence, and technological innovation capabilities. Look for indicators such as continuous investment in R&D, customer retention rates, and growth in their client base. Regularly review their performance through feedback from other clients and industry reports. Establishing a partnership with suppliers who prioritize sustainability and adaptability can enhance your supply chain resilience.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for water evaporators
In conclusion, strategic sourcing of water evaporators is crucial for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize production processes and enhance operational efficiency. Understanding the various types of evaporators, such as rising film and falling film systems, allows businesses to select equipment that aligns with their specific needs, ensuring not only effective concentration but also significant energy savings. Buyers should consider local energy costs, product characteristics, and technological advancements when making procurement decisions.
As global water scarcity intensifies, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, the demand for innovative and efficient evaporator technologies will only grow. Engaging with reputable manufacturers who offer customizable solutions can lead to improved product quality and sustainability.
Actionable Insight: Prioritize partnerships with suppliers who are committed to energy efficiency and sustainable practices. This not only enhances your competitive edge but also positions your operations favorably in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Looking forward, it is essential for buyers to stay informed about emerging technologies and trends in the evaporator market. By doing so, they can make informed decisions that drive operational excellence and contribute to long-term success.