Master Plastic Crate Sourcing: Essential Guide for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for plastic crate
In the competitive landscape of global trade, plastic crates have emerged as essential tools for optimizing supply chains across various industries. Their versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness make them invaluable for businesses aiming to streamline logistics and enhance product protection during transit. As international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to improve operational efficiencies, understanding the complexities of plastic crate procurement becomes critical.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad aspects of plastic crates, covering essential topics including types of crates, materials used, and manufacturing and quality control standards. We will also explore the landscape of suppliers and their geographical strengths, enabling you to identify reliable partners suited to your specific needs. Cost considerations and market trends are examined in detail, equipping buyers with the insights necessary to make informed purchasing decisions.
Additionally, the guide addresses common FAQs, ensuring that you have access to valuable information that empowers you to navigate the market effectively. By leveraging this resource, B2B buyers can enhance their sourcing strategies, mitigate risks, and ultimately achieve a competitive edge in their operations. Whether you are in the manufacturing, agriculture, or retail sectors, understanding the nuances of plastic crate sourcing will pave the way for successful international trade.
Understanding plastic crate Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stackable Crates | Designed for efficient stacking; often with interlocking features. | Warehousing, distribution, retail. | Pros: Space-saving, easy to transport. Cons: Limited weight capacity. |
| Collapsible Crates | Can be folded down when not in use; lightweight materials. | E-commerce, logistics, storage. | Pros: Saves space when stored, versatile. Cons: May lack durability under heavy loads. |
| Ventilated Crates | Features holes or slats for airflow; prevents spoilage. | Agriculture, food transport, fisheries. | Pros: Keeps contents fresh, reduces moisture. Cons: May be less sturdy than solid crates. |
| Heavy-Duty Crates | Reinforced structure for maximum strength; often used for machinery. | Manufacturing, heavy equipment shipping. | Pros: High load capacity, durable. Cons: Higher cost and weight. |
| Returnable Crates | Designed for multiple uses and easy return; often made from durable plastic. | Automotive, retail, and supply chain. | Pros: Cost-effective over time, sustainable. Cons: Initial investment can be high. |
Stackable Crates
Stackable crates are engineered to maximize storage efficiency, featuring interlocking designs that enable secure stacking without toppling. They are primarily used in warehousing and distribution environments, allowing for optimized space utilization during transport and storage. When purchasing stackable crates, buyers should consider the weight capacity, material durability, and compatibility with existing storage systems to ensure that they meet operational needs.
Collapsible Crates
Collapsible crates are designed for flexibility and ease of storage. They can be folded down when not in use, making them ideal for e-commerce businesses and logistics companies that require adaptable solutions. Buyers should evaluate the material strength and the locking mechanism to ensure that the crates can handle the required load while maintaining ease of use. These crates are particularly beneficial for companies looking to minimize storage space when shipping products.
Ventilated Crates
Ventilated crates feature holes or slats that allow for airflow, making them essential for transporting perishable goods such as fruits, vegetables, and seafood. They help maintain freshness by reducing moisture buildup and preventing spoilage. When selecting ventilated crates, buyers should consider the size and design of the ventilation features to ensure they meet the specific requirements of the products being shipped. Durability is also crucial, as these crates must withstand various handling conditions.
Heavy-Duty Crates
Heavy-duty crates are constructed with reinforced materials to handle substantial loads, making them suitable for shipping heavy machinery and equipment. These crates provide maximum strength and protection, which is vital in manufacturing and industrial applications. Buyers should assess the load capacity, dimensions, and whether additional features such as shock absorption are necessary for their specific shipping needs. While these crates are typically more expensive, their durability can lead to long-term cost savings.
Returnable Crates
Returnable crates are designed for multiple uses, often made from high-quality plastic that withstands repeated handling. They are particularly popular in the automotive and retail sectors, where sustainability and cost-effectiveness are priorities. Buyers should consider the initial investment and the potential for reduced costs over time through reusability. Additionally, understanding the logistics of returning these crates is essential for maximizing their benefits within the supply chain.
Related Video: Top 14 Plastic Crates Reviewed: Find The Best One For Your Needs | ImMould.com
Key Industrial Applications of plastic crate
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Plastic Crate | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Transporting fruits and vegetables from farms to markets | Reduces spoilage and damage during transit | Ensure crates are durable, ventilated, and food-safe |
| Logistics and Shipping | Storing and shipping consumer goods | Enhances efficiency, reduces costs associated with damages | Look for stackable designs, lightweight materials |
| Retail | In-store display and storage of products | Improves organization and accessibility of merchandise | Consider aesthetics and durability for public display |
| Pharmaceuticals | Secure transport of medical supplies | Ensures compliance with safety and sanitation standards | Verify material compliance with health regulations |
| Manufacturing | Parts storage and inventory management | Streamlines production processes and reduces handling time | Assess load capacity and customization options |
Agriculture
In the agriculture sector, plastic crates are essential for transporting fruits and vegetables from farms to markets. Their design minimizes spoilage and damage during transit, which is critical for maintaining product quality and maximizing profitability. International buyers should consider crates that are durable, ventilated, and made from food-safe materials to comply with health standards and ensure the freshness of produce upon arrival.
Logistics and Shipping
Plastic crates play a vital role in the logistics and shipping industries by providing a reliable method for storing and transporting consumer goods. Their stackable design enhances efficiency in storage and reduces costs associated with damages during transit. Buyers should focus on lightweight materials that do not compromise strength, ensuring that the crates can handle various loads while remaining cost-effective.
Retail
In retail environments, plastic crates are used for both in-store display and storage of products. They improve organization and accessibility, making it easier for customers to find items while also optimizing space. When sourcing plastic crates for retail, buyers should consider the aesthetic appeal of the crates, as well as their durability, to withstand daily use in a public setting.
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry relies on plastic crates for the secure transport of medical supplies. These crates help ensure compliance with safety and sanitation standards, which are paramount in this sector. Buyers should verify that the materials used in the crates meet health regulations to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of sensitive products during transport.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, plastic crates are utilized for parts storage and inventory management, streamlining production processes and reducing handling time. Their ability to organize components efficiently can significantly enhance workflow. When selecting crates for manufacturing, it is important to assess their load capacity and explore customization options to fit specific operational needs.
Related Video: Automated bread crate filling and stacking, plastic tray stacker/destacker
Strategic Material Selection Guide for plastic crate
When selecting materials for plastic crates, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, limitations, and how they align with specific applications. Below are analyses of four common materials used in the manufacturing of plastic crates, providing insights tailored for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Polyethylene (PE)
Key Properties:
Polyethylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance, low-temperature flexibility, and impact resistance. It can withstand temperatures ranging from -50°C to 80°C, making it suitable for various environments.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PE crates are lightweight, durable, and resistant to moisture and chemicals, which makes them ideal for food storage and agricultural applications. They are also recyclable, contributing to sustainability efforts.
– Disadvantages: While PE is durable, it can become brittle in extreme cold and may not withstand high temperatures over prolonged periods. Additionally, its lower tensile strength compared to other plastics may limit its use for heavy loads.
Impact on Application:
PE is compatible with food products and is often used in the agricultural sector for transporting fruits and vegetables, where moisture resistance is crucial.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with food safety standards (e.g., FDA regulations) and consider local recycling capabilities. Understanding local preferences for materials can also influence purchasing decisions, especially in regions with strong sustainability initiatives.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is characterized by its high melting point (up to 160°C), good chemical resistance, and low density. It is also resistant to fatigue, making it suitable for repeated use.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PP crates are robust, lightweight, and have excellent resistance to chemicals and moisture. They are often used in automotive and industrial applications due to their durability.
– Disadvantages: The material can be more expensive than PE, and its UV resistance is lower unless treated, which may limit outdoor applications without additional protective measures.
Impact on Application:
PP is ideal for industrial and automotive parts, where strength and resistance to various chemicals are required. Its ability to withstand repeated handling makes it suitable for logistics and distribution.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of ASTM and ISO standards for material specifications. Additionally, understanding the regional market for automotive parts can guide sourcing decisions.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties:
PVC is known for its rigidity, strength, and resistance to environmental degradation. It can handle temperatures between -15°C and 60°C, making it suitable for various applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PVC crates are highly durable, resistant to chemicals, and can be manufactured in various colors and designs. They are often used in construction and packaging industries.
– Disadvantages: PVC can be more expensive than PE and PP, and its environmental impact is a concern due to its non-biodegradable nature. Additionally, it can become brittle over time if exposed to UV light.
Impact on Application:
PVC is commonly used in construction for transporting materials and in packaging for products requiring a sturdy crate.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider compliance with local environmental regulations and standards. PVC alternatives may be preferred in regions with stringent sustainability requirements.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Key Properties:
ABS is a thermoplastic known for its toughness and impact resistance, with a temperature range of -20°C to 80°C. It exhibits good chemical resistance and is easy to process.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: ABS crates are strong, lightweight, and have excellent impact resistance, making them suitable for high-stress applications. They are also easy to mold into complex shapes.
– Disadvantages: The cost of ABS is generally higher than that of PE and PP, and it has lower UV resistance, which may limit outdoor use without additional treatment.
Impact on Application:
ABS is often used in consumer goods and electronics packaging, where protection from impact is critical.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of using ABS for specific applications and ensure compliance with any relevant safety standards.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for plastic crate | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Food storage, agricultural transport | Lightweight and moisture-resistant | Brittle in extreme cold | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Industrial and automotive applications | High durability and chemical resistance | More expensive than PE | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Construction material transport | Highly durable and customizable | Environmental concerns and brittleness | Medium |
| Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) | Consumer goods and electronics packaging | Excellent impact resistance | Higher cost and lower UV resistance | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a framework for international B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding plastic crate materials, ensuring that their choices align with operational needs and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for plastic crate
The manufacturing of plastic crates involves several critical stages, each designed to ensure that the final product meets the specifications required by international B2B buyers. Understanding these processes, as well as the quality assurance measures in place, is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines the key manufacturing processes, quality control standards, and verification methods relevant to plastic crates.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The primary materials used in plastic crate manufacturing are typically high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene (PP). The preparation phase involves:
– Material Selection: Choosing the right type of plastic based on the intended use of the crate (e.g., food-grade, heavy-duty).
– Compounding: Mixing the raw plastic with additives like UV stabilizers and colorants to enhance performance and durability.
– Pelletizing: Extruding the compounded material into small pellets that are easier to handle and process in subsequent stages.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the actual shape of the crate is created. Key techniques include:
– Injection Molding: This is the most common method for producing plastic crates. The plastic pellets are heated until they melt and then injected into molds. This technique allows for high precision and the ability to create complex shapes.
– Blow Molding: This method is often used for producing hollow crates. Air is blown into a heated tube of plastic, which expands to fill a mold.
– Thermoforming: Involves heating a plastic sheet until soft and then forming it over a mold. This method is more suitable for thinner, lighter crates.
3. Assembly
Depending on the design, some crates may require assembly. This could involve:
– Joining Components: For crates made of multiple parts, assembly may include snapping, welding, or using adhesives to secure different sections.
– Adding Features: Incorporating additional elements such as handles, lids, or ventilation holes to enhance functionality.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the crates. This includes:
– Surface Treatment: Applying coatings or treatments to improve resistance to chemicals and UV light.
– Printing and Labeling: Adding logos or identification marks, which is especially important for branding in B2B contexts.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in ensuring that plastic crates meet international standards and customer expectations. Key components of a robust quality assurance program include:
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is crucial for manufacturers looking to demonstrate consistent quality in their processes.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, particularly important for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: Relevant for crates used in the oil and gas industry, ensuring they meet specific performance and safety criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain high-quality standards, manufacturers typically implement various quality control checkpoints throughout the production process:
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon delivery to ensure they meet specified requirements.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to detect any deviations from standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing and inspection of the finished crates before they are packaged for shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are used to ensure the durability and reliability of plastic crates:
– Load Testing: Assessing the crate’s ability to withstand weight and pressure.
– Environmental Testing: Evaluating performance under various temperature and humidity conditions.
– Chemical Resistance Testing: Ensuring that the material can withstand exposure to various chemicals, which is particularly important for food and agricultural applications.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality control measures is crucial. Here are some effective strategies:
Supplier Audits
Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturer’s processes, equipment, and quality management systems firsthand. This can help identify potential risks and ensure compliance with international standards.
Quality Assurance Reports
Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can provide insight into their testing procedures, results, and any corrective actions taken. These documents should include information on IQC, IPQC, and FQC processes.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of verification. These independent entities can perform audits and testing to ensure that the products meet specified standards before shipment.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
Understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions can help buyers navigate the complexities of international trade. Factors to consider include:
– Cultural Differences: Awareness of varying standards and practices in different countries can facilitate better communication with suppliers.
– Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that products meet local regulations in the buyer’s country, which may differ from the manufacturer’s standards.
– Supply Chain Transparency: Building relationships with suppliers that prioritize transparency in their operations can lead to better quality assurance and trust.
In conclusion, international B2B buyers must be well-informed about the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for plastic crates. By understanding the intricacies of material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside robust quality control practices, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their specific needs and regulatory requirements.
Related Video: Plastic Container Manufacturing Process. Polyethylene Mass Production Factory in Korea
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for plastic crate Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing of plastic crates is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The following analysis outlines the key cost components, price influencers, and buyer tips to help you make informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary material used in plastic crates is polyethylene or polypropylene, with prices fluctuating based on global oil prices and availability. High-quality materials may increase costs but enhance durability and longevity.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary significantly by region. In countries with lower labor costs, the overall production price may be more competitive. However, this can also affect quality if not managed properly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can lower overhead and should be factored into the total cost.
-
Tooling: Custom designs or specialized molds require upfront investment in tooling, which can be substantial. This cost is often amortized over larger production runs, making it important for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQs).
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC measures ensures that the crates meet specified standards and certifications. This can incur additional costs but is vital for minimizing returns and ensuring customer satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transportation, and freight forwarding arrangements. International buyers should consider both shipping and customs duties when budgeting for crates.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically mark up prices to cover their risks and profit margins. Understanding market rates for your specific needs can help in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders often lead to significant cost reductions. Suppliers may offer tiered pricing based on order volume, encouraging larger purchases.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific features can increase costs. It’s essential to balance customization needs with budget constraints.
-
Materials Quality/Certifications: Higher quality and certified materials will increase upfront costs but may result in lower total costs over time due to reduced damage rates and longer lifespan.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence pricing. Partnering with established suppliers can often justify a higher price due to better quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of shipping and delivery can significantly impact overall costs. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) dictate who bears the shipping and insurance costs, which can alter the final price.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate Effectively: Don’t hesitate to negotiate prices, especially for larger orders. Be prepared to discuss specific requirements and show willingness to explore different suppliers.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Assess the total cost of ownership, which includes not just the purchase price but also logistics, maintenance, and eventual disposal costs.
-
Be Aware of Pricing Nuances: International buyers should consider currency fluctuations, tariffs, and local market conditions that can affect pricing. Understanding the local economic context can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Request Detailed Quotes: Ensure that all quotes include a breakdown of costs, so you can identify potential savings or areas of concern.
-
Consider Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a strong partnership with a supplier can lead to better pricing and service over time, particularly if you consistently order from them.
In summary, a thorough understanding of the cost structure and pricing dynamics for plastic crates enables international B2B buyers to make strategic decisions that align with their operational needs and budget constraints. By focusing on the key components and influencers of pricing, buyers can better navigate the complexities of sourcing in a global market.
Spotlight on Potential plastic crate Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘plastic crate’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for plastic crate
When selecting plastic crates for your business needs, understanding essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here, we explore key specifications and common industry terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with.
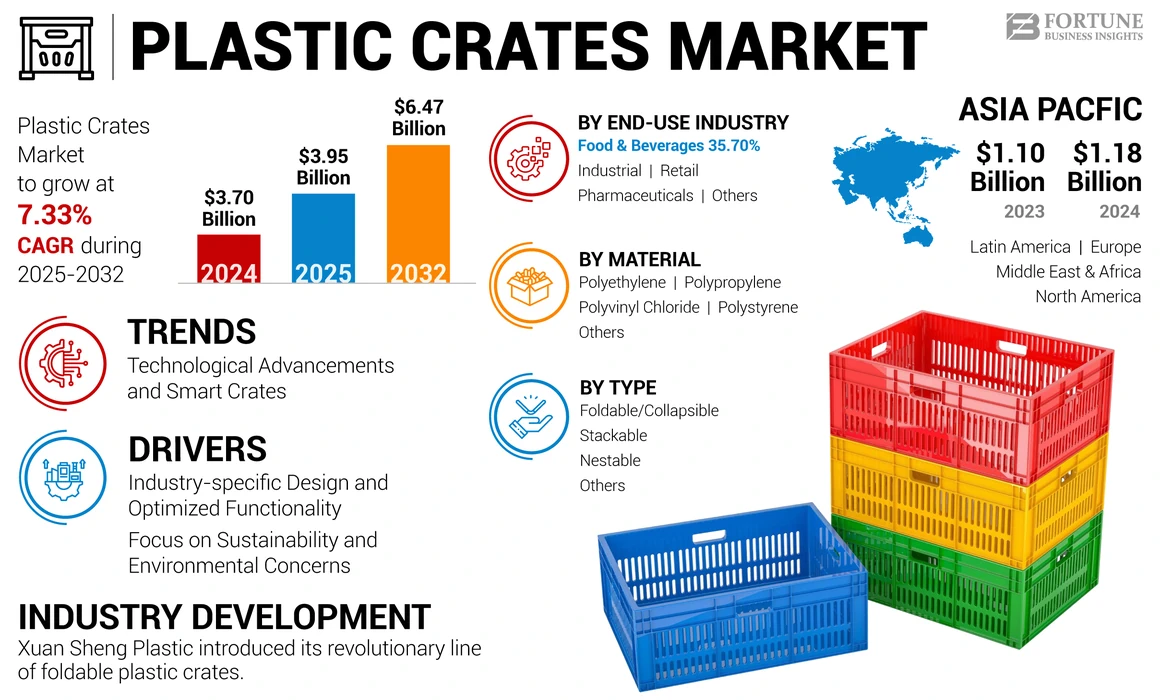
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Technical Properties of Plastic Crates
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of plastic used in crate manufacturing, typically ranging from low-density polyethylene (LDPE) to high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
– Importance: Higher-grade materials offer better durability, UV resistance, and temperature tolerance. Selecting the right material is vital for ensuring that the crate meets specific handling and storage requirements, particularly in demanding environments. -
Load Capacity
– Definition: The maximum weight a crate can safely carry without compromising its structural integrity.
– Importance: Understanding load capacity is essential for logistics and inventory management. Overloading a crate can lead to damage not only to the crate itself but also to the products it carries, potentially leading to financial losses. -
Dimensional Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable variation in the dimensions of a crate, which can affect its compatibility with pallets, shelving systems, and transportation methods.
– Importance: Proper dimensional tolerance ensures that crates fit snugly on pallets and in storage systems. This is critical for optimizing space and reducing the risk of product damage during transit. -
Stackability
– Definition: The ability of crates to be stacked securely without collapsing or deforming.
– Importance: Stackable crates maximize storage efficiency and minimize the footprint required for warehousing. This is particularly beneficial in regions where space is at a premium, such as urban areas in Africa and Europe. -
Impact Resistance
– Definition: The ability of a crate to withstand drops and impacts without cracking or breaking.
– Importance: Crates with high impact resistance are crucial for industries that involve heavy handling or transportation over rough terrain. This characteristic helps reduce product loss and damage. -
Chemical Resistance
– Definition: The ability of a crate to resist degradation when exposed to various chemicals, including oils, acids, and cleaning agents.
– Importance: For industries such as agriculture and pharmaceuticals, chemical resistance is vital to ensure the integrity of the products stored in the crates, particularly when dealing with hazardous materials.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing equipment and systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory planning. This term can affect your purchasing strategy, especially for small businesses or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing information and terms for specific products.
– Importance: An RFQ helps businesses compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, enabling better negotiation and cost management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers for the delivery of goods under sales contracts.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international trade, as they clarify who pays for shipping, insurance, and tariffs, thereby reducing potential disputes. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times helps businesses plan their inventory and supply chain effectively, ensuring that products are available when needed. -
Customization
– Definition: The ability to modify a product to meet specific requirements, such as size, color, or branding.
– Importance: Customization can enhance brand visibility and ensure that crates meet unique logistical needs, making it a valuable consideration for B2B buyers.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terminologies, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing plastic crates more effectively, ensuring they select the right solutions for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the plastic crate Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The plastic crate sector is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. Increased demand for efficient logistics and sustainable packaging solutions is reshaping the industry landscape. International B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are focusing on sourcing solutions that enhance operational efficiency while minimizing costs. The rise of e-commerce and online retailing has also accelerated the need for durable and versatile packaging, resulting in a surge in the demand for plastic crates.
Emerging technologies are reshaping how companies design and manufacture plastic crates. Innovations such as advanced polymer materials and smart packaging solutions are gaining traction. These technologies not only improve the durability and functionality of crates but also contribute to cost reductions in shipping and storage. Furthermore, the increasing integration of Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities into logistics processes is enabling real-time tracking and management of shipments, enhancing supply chain visibility and efficiency.
For international buyers, understanding local market dynamics is crucial. Factors such as regional regulations, trade tariffs, and economic conditions can significantly affect sourcing decisions. Buyers must conduct thorough market research to identify reliable suppliers who can meet their specific needs, ensuring that they are well-informed about the latest trends and technologies shaping the plastic crate sector.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of plastic waste has led to a growing emphasis on sustainability within the plastic crate sector. International B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recycled materials and eco-friendly production processes. This shift is not only beneficial for the environment but also enhances brand reputation and consumer trust.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical supply chains are becoming a focal point for buyers. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to responsible sourcing practices and maintain fair labor standards is essential. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that have received certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) or other recognized ‘green’ certifications. These certifications serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the use of biodegradable plastics and recyclable materials in the production of crates is gaining popularity. Buyers should inquire about the materials used by suppliers and consider options that minimize environmental impact. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can contribute to a circular economy while securing a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of plastic crates can be traced back to the mid-20th century when they were first introduced as an alternative to wooden crates. Initially popularized for their lightweight and durable characteristics, plastic crates quickly gained traction in various industries, including agriculture, food distribution, and manufacturing. Over the years, advancements in polymer technology have led to the development of specialized crates designed for specific applications, enhancing their functionality and efficiency.
As global trade expanded, the demand for standardized, stackable, and reusable crates increased, prompting manufacturers to innovate continuously. Today, the plastic crate sector is characterized by a diverse range of products that cater to the unique needs of international B2B buyers, reflecting ongoing trends toward sustainability, efficiency, and adaptability in logistics and supply chain management.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of plastic crate
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for plastic crates?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Request samples to assess product quality and durability. Look for suppliers with robust quality assurance processes and positive customer feedback. Check their capacity to meet your order volume and delivery timelines. Additionally, verify their compliance with international standards relevant to your industry, such as ISO certifications, to ensure reliability and safety in your supply chain. -
Can I customize plastic crates to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options. Discuss your requirements regarding size, color, material, and design features. Provide detailed specifications, including dimensions, weight capacity, and intended use. Collaborate with the supplier early in the design phase to ensure that your needs are met without compromising functionality or increasing costs unnecessarily. Customization can enhance efficiency in your operations, especially if you handle unique products. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for plastic crates?
MOQs vary by supplier and can range from a few dozen to several hundred units, depending on the complexity of the crate design and materials used. Lead times typically range from 2 to 8 weeks, contingent on the supplier’s production schedule and your order size. To optimize your supply chain, negotiate MOQs based on your purchasing capacity and plan your orders ahead of peak seasons to avoid delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when ordering plastic crates internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common practices include deposits (often 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due prior to shipping. Some suppliers may offer credit terms for established customers. Always clarify payment methods, such as wire transfers or letters of credit, and ensure you understand the implications of each. Establishing clear payment terms upfront can help prevent disputes and build trust in your supplier relationship. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the plastic crates I purchase?
Request documentation of the supplier’s quality assurance processes and relevant certifications. Look for ISO 9001 certification or specific industry-related certifications that demonstrate compliance with safety and quality standards. Conduct regular audits of your suppliers if possible, and consider third-party inspections before shipment. This proactive approach helps mitigate risks associated with product defects and ensures that the crates meet your operational requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing plastic crates?
Logistics plays a crucial role in the timely delivery of your plastic crates. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including freight costs, shipping methods, and estimated delivery times. Consider the total landed cost, which includes shipping, customs duties, and taxes. If you’re sourcing from overseas, factor in potential delays at ports or during customs clearance. Building a buffer into your timeline can help manage unexpected disruptions. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding plastic crate orders?
Disputes can arise over quality, delivery timelines, or product specifications. To minimize conflicts, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in contracts. If a dispute occurs, address it promptly by discussing the issue directly with your supplier. Use evidence, such as emails and contracts, to support your claims. If resolution efforts fail, consider mediation or arbitration as a structured approach to resolving issues without damaging the business relationship. -
What are the best practices for maintaining a long-term relationship with plastic crate suppliers?
To cultivate a successful long-term partnership, maintain open lines of communication and provide regular feedback on product performance. Schedule periodic reviews to discuss potential improvements and evolving needs. Timely payments and consistent orders can enhance trust and reliability. Additionally, be transparent about your business goals and challenges, which can help suppliers align their offerings with your requirements and foster collaborative problem-solving.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for plastic crate
In the dynamic landscape of global trade, strategic sourcing of plastic crates emerges as a critical factor for success. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must prioritize understanding the diverse types and specifications of plastic crates to ensure they meet their unique shipping needs. Leveraging insights into crate design, material durability, and cost-effectiveness can significantly reduce logistics challenges, such as damage during transit and inefficiencies in handling.
To enhance supply chain resilience, buyers should foster relationships with reliable manufacturers and suppliers, emphasizing collaboration for tailored solutions. This proactive approach not only mitigates risks but also opens avenues for innovation in packaging solutions that can adapt to evolving market demands.
Looking ahead, the trend towards sustainable practices is set to influence the plastic crate industry significantly. Buyers should remain vigilant about emerging technologies and eco-friendly materials that can provide a competitive edge. By embracing these changes and leveraging strategic sourcing, businesses can position themselves for growth and sustainability in an increasingly interconnected global marketplace. Engage with your suppliers today to explore how you can optimize your sourcing strategy and enhance your operational efficiency.