Master Sourcing Strategies for Broaching Machines in Global
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for broaching machine
In an increasingly interconnected world, the demand for precision engineering solutions has never been higher. The broaching machine, a key player in the realm of metalworking, offers unparalleled efficiency and accuracy for shaping complex components. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of broaching technology is vital for competitive advantage. These machines facilitate the production of intricate designs with minimal waste, making them essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
This guide is designed to empower you with comprehensive insights into the global broaching machine market. We will explore various types of broaching machines, including vertical and horizontal models, and delve into the materials best suited for specific applications. Additionally, we will cover manufacturing processes and quality control standards that ensure the reliability and performance of these machines.
Buyers will benefit from a detailed analysis of suppliers, pricing structures, and market trends, enabling informed sourcing decisions. Addressing frequently asked questions, this guide aims to demystify the complexities of the broaching machine landscape, ensuring you can navigate it effectively. By equipping yourself with the right knowledge, you can optimize your procurement strategies, enhance operational efficiency, and ultimately drive your business forward in the global marketplace.
Understanding broaching machine Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Broaching | Operates with the broach moving horizontally; ideal for longer workpieces. | Automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery. | Pros: Efficient for long cuts; lower tooling costs. Cons: Requires significant floor space. |
| Vertical Broaching | Utilizes a vertical setup; suitable for shorter, thicker materials. | Precision parts in electronics and small machinery. | Pros: Compact design; high precision. Cons: Limited to shorter strokes. |
| Continuous Broaching | Features a continuous feed system; suitable for high-volume production. | Mass production in automotive and manufacturing. | Pros: Extremely efficient; reduces cycle time. Cons: High initial investment. |
| Rotary Broaching | Uses a rotating broach; effective for creating complex shapes and holes. | Manufacturing of gears and keyways. | Pros: Versatile; excellent for intricate designs. Cons: Slower than linear broaching methods. |
| Push Broaching | Involves pushing the broach through the workpiece; suitable for softer materials. | General machining in various industries. | Pros: Simple operation; cost-effective. Cons: Limited to softer materials; less precision. |
Horizontal Broaching
Horizontal broaching machines are distinguished by their horizontal movement of the broach, making them ideal for processing longer workpieces. These machines are predominantly used in industries such as automotive and aerospace, where large components require precise machining. When considering a horizontal broaching machine, buyers should evaluate the available floor space, as these machines typically require a significant footprint. Additionally, they offer lower tooling costs due to the efficiency of the broaching process, making them a cost-effective choice for large-scale production.
Vertical Broaching
Vertical broaching machines operate with a vertical broach movement, making them suitable for shorter and thicker materials. Commonly found in the electronics sector and small machinery manufacturing, these machines provide high precision and a compact design, which is advantageous for facilities with limited space. Buyers should consider the specific dimensions and weight of the materials being machined, as vertical broaching is limited to shorter strokes. The precision offered by these machines often justifies the investment, especially for industries requiring meticulous work.
Continuous Broaching
Continuous broaching machines are designed for high-volume production, featuring a feed system that allows the broach to operate without interruption. This type of machine is widely used in the automotive industry and other manufacturing sectors where efficiency and speed are paramount. While the initial investment may be high, the reduction in cycle time and increased production rates can lead to significant long-term savings. B2B buyers should assess their production needs carefully, as continuous broaching is best suited for businesses with consistent, high-demand output.
Rotary Broaching
Rotary broaching machines utilize a rotating broach to create complex shapes and holes, making them particularly effective for manufacturing gears and keyways. This versatility allows for intricate designs that linear broaching methods may struggle to achieve. However, rotary broaching is generally slower than other methods, which may be a consideration for businesses focused on rapid production. Buyers should evaluate the specific applications and material requirements, as rotary broaching is ideal for projects demanding detailed work.
Push Broaching
Push broaching machines involve the broach being pushed through the workpiece, making them suitable for softer materials. They are commonly used in general machining across various industries, providing a simple and cost-effective solution for basic broaching needs. While push broaching is less precise than other methods, its straightforward operation appeals to businesses with budget constraints or those requiring less intricate machining. Buyers should consider the material hardness and desired precision when selecting this type of broaching machine.
Related Video: Horizontal Broaching Machine: Pull Type Broach Nomenclature, Design Construction & Working Principle
Key Industrial Applications of broaching machine
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of broaching machine | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Gear and spline broaching | High precision in manufacturing complex components | Supplier reliability, machine capacity, and lead times |
| Aerospace | Turbine blade shaping | Enhanced performance and weight reduction | Certification standards, material compatibility, and custom tooling |
| Manufacturing & Fabrication | Keyway and slot broaching | Increased efficiency and reduced machining time | Cost of ownership, maintenance support, and local service availability |
| Oil & Gas | Broaching of valve seats and ports | Improved product lifespan and operational reliability | Material quality, technical support, and industry compliance |
| Medical Devices | Broaching for precise fittings and connectors | Enhanced product accuracy and patient safety | Regulatory compliance, customization options, and supplier expertise |
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, broaching machines are essential for producing gears and splines with high precision. This application addresses the need for complex shapes that require tight tolerances, which are critical for performance and safety. International buyers must consider supplier reliability and machine capacity to ensure that production schedules are met without compromising on quality. Additionally, lead times can significantly impact the overall production timeline, making timely sourcing crucial.
Aerospace Sector
Broaching is extensively used in shaping turbine blades within the aerospace industry. This application not only enhances the performance of the blades but also contributes to weight reduction, which is vital for fuel efficiency. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that adhere to strict certification standards and can provide tooling compatible with advanced materials. Understanding the specific requirements for durability and precision is essential for maintaining safety and compliance in aviation applications.
Manufacturing & Fabrication
In the broader manufacturing and fabrication sector, broaching machines are employed for creating keyways and slots in various components. This application streamlines the production process, significantly increasing efficiency while reducing machining time. For international buyers, considerations around cost of ownership and maintenance support are critical. Additionally, the availability of local service and technical assistance can greatly influence the decision-making process, especially in regions where technical expertise may be limited.
Oil & Gas Industry
The oil and gas sector utilizes broaching for the machining of valve seats and ports, which are crucial for the operational reliability of equipment. The precision achieved through broaching enhances the lifespan of these components, reducing the frequency of replacements and maintenance. Buyers should focus on the quality of materials used in the broaching process, as well as the supplier’s ability to provide technical support and ensure compliance with industry standards. This is particularly important in regions with stringent regulatory requirements.
Medical Devices
In the medical device industry, broaching is used to create precise fittings and connectors that ensure product accuracy and enhance patient safety. This application highlights the importance of regulatory compliance and the need for customization options to meet specific design requirements. International buyers should seek suppliers with expertise in the medical sector who can navigate the complexities of compliance and provide innovative solutions tailored to their needs. Understanding the nuances of medical device manufacturing will help in selecting the right broaching machines for optimal results.
Related Video: VERTICAL BROACHING MACHINE BM25 | NARGESA
Strategic Material Selection Guide for broaching machine
When selecting materials for broaching machines, it’s essential to consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below, we analyze four common materials used in broaching machines, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for international B2B buyers.
Steel
Key Properties:
Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and durability. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 300°C and exhibits good wear resistance. Corrosion resistance can vary based on the alloy composition, with stainless steel offering superior protection.
Pros & Cons:
Steel is generally cost-effective and widely available, making it a popular choice for many applications. However, its manufacturing complexity can increase with specific alloy formulations. While steel is suitable for a variety of broaching applications, its weight may be a disadvantage in some designs.
Impact on Application:
Steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including oils and coolants, which are commonly used in machining processes. Its strength makes it ideal for heavy-duty applications, but it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments without proper treatment.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM and DIN. In Africa and South America, sourcing local steel can mitigate costs and support regional industries.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C, though its strength is lower than that of steel.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can enhance machine speed and efficiency. However, it is generally more expensive than steel and may require specialized manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is particularly effective in applications involving non-ferrous materials. Its compatibility with various coolants and lubricants allows for smooth operation, but it may not be suitable for high-stress applications where strength is paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers in regions like Saudi Arabia and Argentina should be aware of the higher costs associated with aluminum and ensure that their suppliers can meet specific quality standards. Understanding local market dynamics can help in negotiating better pricing.
Cast Iron
Key Properties:
Cast iron is characterized by its excellent machinability and vibration-damping properties. It can handle temperatures up to 400°C and offers good wear resistance, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of cast iron is a significant advantage, particularly in high-load scenarios. However, it is brittle and can be prone to cracking under stress, which may limit its use in certain applications. Additionally, cast iron is heavier than steel or aluminum, which can affect machine design.
Impact on Application:
Cast iron is ideal for applications involving high-impact forces and is often used in the construction of machine frames. Its compatibility with various machining fluids makes it versatile, though care must be taken in environments with extreme temperature fluctuations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of cast iron in their region and ensure compliance with local standards. In the Middle East and Africa, sourcing locally can reduce shipping costs and support local economies.
Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite materials offer a combination of properties, including high strength-to-weight ratios and excellent corrosion resistance. They can be engineered to withstand specific temperature and pressure ratings, often exceeding those of traditional materials.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of composites is their versatility and ability to be tailored for specific applications. However, they can be significantly more expensive than traditional materials and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application:
Composites are particularly beneficial in applications that require lightweight solutions without sacrificing strength. They are compatible with various media but may not be suitable for extremely high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should assess the availability of composite materials in their region and ensure that suppliers can meet stringent quality standards. Understanding local regulations regarding composites is crucial, especially in Europe, where compliance can be stringent.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for broaching machine | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty machining | High strength and durability | Heavier weight | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight applications | Low weight and corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
| Cast Iron | Machine frames and bases | Excellent machinability | Brittle and heavy | Low |
| Composite Materials | Specialized lightweight applications | Tailored properties | High cost and complex manufacturing | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for broaching machine
Manufacturing a broaching machine is a complex process that requires precision engineering, adherence to quality standards, and thorough quality control measures. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section delves into the key stages of manufacturing, quality assurance practices, and how buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of a broaching machine typically involves several key stages, each integral to ensuring the final product meets industry standards and buyer expectations.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Broaching machines are primarily constructed from high-strength steel alloys to withstand the rigors of operation.
- Material Selection: Buyers should inquire about the specific grades of steel used, as this impacts durability and performance. Common choices include AISI 4140 or AISI 8620, known for their hardness and wear resistance.
- Initial Treatment: Materials often undergo heat treatment processes such as annealing or quenching to enhance mechanical properties before machining.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next phase is forming the machine components. This stage typically includes:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are utilized for precise shaping and cutting of components. This ensures high tolerances and repeatability in manufacturing.
- Casting or Forging: Depending on the design specifications, some components may be cast or forged. Forging generally offers better mechanical properties due to the alignment of the grain structure.
3. Assembly
The assembly of a broaching machine involves integrating various components into a cohesive unit.
- Sub-Assembly: Individual components such as the broach tool, drive mechanism, and work table are first assembled separately.
- Final Assembly: The sub-assemblies are then brought together, requiring skilled labor to ensure alignment and functionality.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional qualities of the machine.
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as grinding, polishing, and coating are employed to reduce friction, improve wear resistance, and enhance appearance.
- Calibration: Each machine is calibrated to ensure it operates within specified parameters, which is critical for precision machining.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is essential in the manufacturing of broaching machines, particularly for international buyers who require compliance with various standards.
International Standards
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international and industry-specific standards is crucial:
- ISO 9001: This quality management standard ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. Buyers should verify that suppliers have ISO 9001 certification.
- CE Marking: For buyers in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For industries such as oil and gas, adherence to API standards ensures that equipment meets stringent safety and quality requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, involving several checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular inspections are conducted during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify issues early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The completed machine undergoes a final inspection to ensure it meets all operational and safety standards before shipping.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods are vital for validating the quality and performance of broaching machines:
- Functional Testing: Machines are tested under operational conditions to ensure they perform as expected.
- Dimensional Inspection: Precision measuring tools are used to verify that all components meet design specifications.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or magnetic particle testing help detect material flaws without damaging the components.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is essential to ensure that they receive a reliable product. Here are actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing environment, processes, and adherence to quality standards.
- Requesting Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including inspection reports and test results.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s capabilities and product quality.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
When dealing with international suppliers, buyers must be aware of specific nuances related to quality control and certification:
- Cultural Differences: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. It’s important to understand these differences and how they might affect product quality.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should be aware of local regulations that may impact the import and usage of machinery. Ensuring that suppliers comply with these regulations can prevent future legal and operational issues.
- Communication: Clear communication regarding quality expectations is essential. Buyers should articulate their requirements and verify that suppliers understand and can meet these standards.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for broaching machines are integral to ensuring that buyers receive high-quality, reliable equipment. By understanding these processes and actively engaging in quality verification, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, minimize risks, and establish long-lasting partnerships with suppliers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Related Video: Manufacturing Process: Broaching
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for broaching machine Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of broaching machines is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their procurement strategies. This section delves into the critical cost components, factors influencing pricing, and actionable tips for negotiating better deals.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in broaching machines include high-grade steel and specialized alloys. Fluctuations in raw material prices can significantly impact overall costs. Buyers should consider sourcing from regions with stable material supply chains to mitigate risks.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and skill availability. In regions like Europe, labor tends to be more expensive due to higher living costs, whereas in Africa and South America, labor may be more cost-effective. Understanding local labor markets can aid in selecting suppliers that align with budgetary constraints.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturers minimize overhead, which can lead to competitive pricing. Evaluating potential suppliers’ operational efficiency is crucial.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary significantly based on machine specifications and customization requirements. Buyers should assess the tooling needs early in the procurement process to avoid unexpected expenses later.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes ensure the reliability and performance of broaching machines. Suppliers with advanced QC systems may charge higher prices, but this often translates into lower failure rates and maintenance costs over time.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can add a substantial amount to the overall price, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties must be accounted for. Effective logistics management can lead to significant savings.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins can vary widely based on market conditions and competition. Understanding typical margins within the industry can provide insight into whether a quoted price is fair.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) and total order volume can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often qualify for discounts, so consolidating purchases can be a strategic approach.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-built machines or those with specialized features usually come at a premium. Buyers must balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts both price and machine durability. High-performance materials may increase upfront costs but can reduce long-term maintenance expenses.
-
Quality/Certifications: Machines that meet international standards or have specific certifications typically command higher prices. However, these machines may offer better performance and reliability.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide better support and reliability.
-
Incoterms: The agreed terms of delivery (Incoterms) can affect the final cost. Understanding these terms helps buyers calculate total landed costs more accurately.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation is key to securing favorable terms. Consider leveraging relationships with suppliers and exploring long-term partnerships to enhance negotiation outcomes.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just upfront pricing. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and potential downtime when evaluating machine costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers must be aware of currency fluctuations, trade tariffs, and regional pricing strategies. Engaging local experts or consultants can provide valuable insights into market dynamics.
-
Local Market Insights: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should familiarize themselves with local suppliers who may offer competitive pricing and shorter lead times.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost structures discussed are indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure the best value for your investment.
Spotlight on Potential broaching machine Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘broaching machine’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for broaching machine
Key Technical Properties of Broaching Machines
Understanding the technical specifications of broaching machines is crucial for international B2B buyers. These specifications impact performance, efficiency, and the overall cost of ownership. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The type of material used in the construction of the broaching machine, typically steel or cast iron.
– Importance: Higher-grade materials ensure durability and resistance to wear and tear, which is vital for high-volume production environments. Buyers should evaluate the material grade to ascertain the machine’s longevity and maintenance requirements. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension, often expressed in millimeters or microns.
– Importance: Precision is critical in manufacturing processes. A tighter tolerance means higher accuracy in the finished product, which is essential for industries like automotive or aerospace. Buyers should ensure that the machine meets their specific tolerance requirements to avoid costly rework. -
Stroke Length
– Definition: The distance the broach travels in a single operation.
– Importance: A longer stroke length can improve productivity by allowing for larger workpieces or multiple operations in a single pass. Buyers should consider the stroke length in relation to their production needs to optimize workflow. -
Speed
– Definition: The operational speed of the broaching machine, often measured in strokes per minute (SPM).
– Importance: Higher speeds can enhance productivity; however, they may also affect the quality of the finished product. It’s essential for buyers to balance speed with quality assurance to meet their production goals. -
Power Rating
– Definition: The amount of power the machine consumes, typically measured in horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW).
– Importance: A higher power rating can indicate the ability to handle tougher materials or larger workpieces. Buyers should assess their power requirements based on the materials they intend to work with. -
Tooling Compatibility
– Definition: The types of broaching tools that can be utilized with the machine.
– Importance: Different industries may require specific tooling solutions. Ensuring compatibility with existing tools can minimize costs and downtime. Buyers should evaluate the tooling options available for the machines they are considering.
Common Trade Terms in Broaching Machine Procurement
Navigating the procurement landscape requires familiarity with specific trade terminology. Here are key terms that B2B buyers should understand:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding whether a machine is an OEM product can affect warranty, service, and support options. Buyers should verify the OEM status to ensure they receive genuine parts and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Buyers need to be aware of MOQs as they can impact inventory costs. Understanding these limits can help in planning purchases and managing cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting price quotes for specific products or services.
– Importance: RFQs are essential for comparing prices and terms among different suppliers. Buyers should prepare comprehensive RFQs to ensure they receive accurate and competitive offers. -
Incoterms
– Definition: International commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Knowledge of Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks. This understanding is crucial for effective budgeting and logistics planning. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to delivery.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time helps in planning production schedules. Buyers should factor lead time into their procurement strategies to avoid delays in their operations. -
Warranty
– Definition: A guarantee provided by the manufacturer regarding the condition of the machine.
– Importance: Warranties can vary significantly, affecting the total cost of ownership. Buyers should assess warranty terms to ensure they are adequately protected against defects or failures.
In summary, understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with broaching machines is essential for international B2B buyers. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making and can lead to optimized procurement strategies that enhance operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the broaching machine Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The broaching machine sector is witnessing significant growth driven by several global factors. The demand for precision machining in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing is a key driver. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it’s essential to recognize the shift towards automation and Industry 4.0 technologies. This shift is not only enhancing productivity but also enabling real-time data analytics, which helps in optimizing production processes.
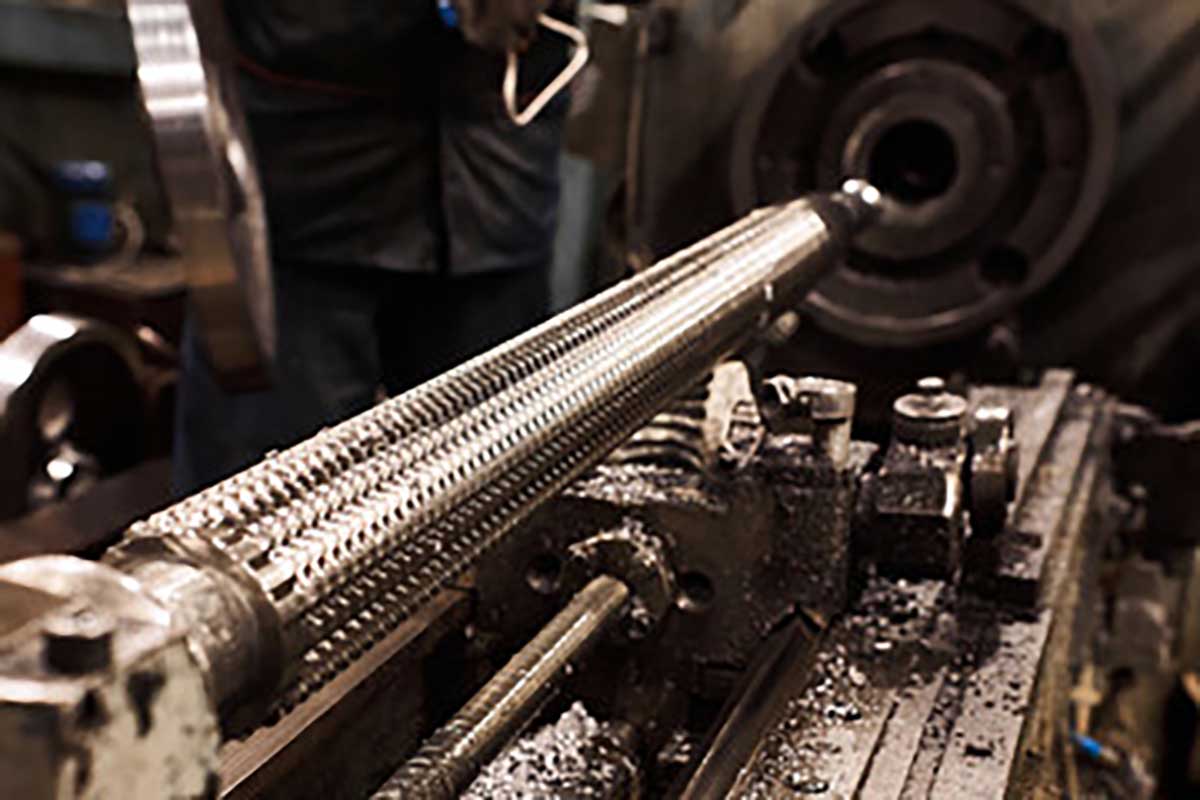

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Emerging trends in sourcing include a preference for suppliers that offer integrated solutions, combining equipment with software for better operational efficiency. Buyers are increasingly interested in vendors that can provide customizable broaching machines tailored to specific manufacturing needs, which is especially relevant for industries in developing markets that require flexibility in their production capabilities. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on local sourcing, driven by supply chain disruptions from global events and a desire to reduce lead times.
Another trend is the rise of smart manufacturing, where IoT-enabled broaching machines are becoming commonplace. These machines can communicate performance data, allowing for predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. For B2B buyers, understanding these technological advancements is critical in making informed purchasing decisions that align with future industry standards.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a priority in the broaching machine sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, is under scrutiny. As a result, international buyers are encouraged to partner with suppliers who prioritize sustainability through energy-efficient machines and waste-reducing practices.
Ethical sourcing is also a crucial aspect for B2B buyers. Ensuring that suppliers maintain fair labor practices and comply with environmental regulations is essential for mitigating risks associated with unethical supply chains. Buyers should seek out manufacturers that possess certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety.
Moreover, the adoption of ‘green’ materials in the production of broaching machines can significantly enhance a company’s sustainability profile. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but can also appeal to eco-conscious clients, opening new market opportunities. As such, B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their commitment to sustainability and ethical practices, integrating these factors into their procurement strategies.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Brief Evolution/History
The broaching machine has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 19th century. Initially used for simple shaping tasks, the technology has progressed to accommodate complex machining needs with high precision. This evolution has been marked by the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology in the late 20th century, which revolutionized the sector by allowing for more intricate designs and automated operations.
Today, the focus is on integrating advanced technologies such as AI and IoT into broaching machines, further enhancing their capabilities. Understanding this historical context is vital for B2B buyers as it highlights the continuous innovation in the sector, informing purchasing decisions and future investments. As the market progresses, staying abreast of technological advancements will be key to maintaining a competitive edge.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of broaching machine
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of broaching machines?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their manufacturing capabilities and technological expertise. It’s beneficial to request case studies or references from previous clients, especially those in your region, to understand their service levels and reliability. -
Can broaching machines be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options based on your specific needs. When discussing your requirements, detail the materials you intend to work with, the complexity of parts, and production volumes. Ensure the supplier has a proven track record in customization and can provide examples of previous projects. This will help ensure that the machine is tailored to your operational needs and efficiency goals. -
What are typical lead times and minimum order quantities (MOQ) for broaching machines?
Lead times can vary widely depending on the complexity of the machine and the supplier’s production capacity. Generally, expect lead times of 6 to 12 weeks for standard machines. For custom solutions, it may take longer. Regarding MOQs, many suppliers may have flexible options, especially if they are looking to establish a long-term relationship. Always clarify these terms upfront to avoid misunderstandings. -
What payment methods are commonly accepted by international suppliers?
Payment methods can vary, but most international suppliers accept wire transfers, letters of credit, and PayPal. It’s advisable to negotiate payment terms that protect both parties, such as a deposit upfront and the balance upon delivery or installation. Additionally, consider using escrow services for large transactions to mitigate risks, ensuring the supplier meets their obligations before payment is released. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from suppliers?
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in manufacturing broaching machines. Look for suppliers that implement rigorous QA protocols, including in-process inspections and final testing before shipment. Request documentation related to their QA processes, such as inspection reports and certifications. Additionally, inquire if they offer a warranty or after-sales support, which can be indicative of their confidence in the machine’s quality. -
How can I effectively manage logistics when importing broaching machines?
Managing logistics involves understanding shipping routes, customs regulations, and duties applicable to your country. Work closely with your supplier to determine the best shipping method, whether by sea or air, considering factors like cost and delivery time. It’s also advisable to partner with a logistics provider experienced in international trade, ensuring compliance with local regulations and facilitating smooth customs clearance. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract, which should include a dispute resolution clause. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, as they can be less costly and time-consuming. Keeping thorough documentation of all communications and agreements will support your position during any dispute. -
Are there specific certifications I should look for when sourcing broaching machines?
Yes, when sourcing broaching machines, seek suppliers with relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems and CE marking for compliance with European health, safety, and environmental standards. Additionally, certifications specific to your industry, such as AS9100 for aerospace applications, can provide further assurance of quality and reliability. Always request proof of these certifications to ensure compliance with international standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for broaching machine
As we conclude this exploration of broaching machines, it is clear that strategic sourcing plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency and driving profitability for international B2B buyers. By focusing on key factors such as supplier reliability, cost-effectiveness, and technological advancements, businesses can streamline their procurement processes and ensure they are equipped with the best tools for their manufacturing needs.
Key takeaways include the importance of understanding local market dynamics, leveraging global supplier networks, and investing in training for personnel to maximize the utility of broaching machines. For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, these insights are crucial in navigating the complexities of international trade and securing competitive advantages.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced broaching technology is expected to grow, driven by the ongoing industrialization and automation trends. Now is the time for B2B buyers to engage with suppliers who not only offer superior products but also provide comprehensive support and insights. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your sourcing strategies and position your business for future success in a rapidly evolving marketplace.