Master Wire Forming: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for wire forming
Wire forming is an essential process in the global manufacturing landscape, enabling the transformation of raw materials into intricate shapes and structures that serve various industries, from automotive to medical equipment. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding wire forming is crucial for sourcing high-quality products that meet specific project requirements. This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, illuminating the diverse types of wire forming techniques, the materials commonly utilized, and the critical manufacturing and quality control processes involved.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In the pages that follow, we will delve into the intricacies of wire forming, exploring its various applications and the nuances of selecting the right suppliers. We will provide insights into cost considerations, market trends, and frequently asked questions that can empower your sourcing decisions. Whether you are looking for durable steel components or precision-formed parts from aluminum or stainless steel, the information contained herein will equip you with the knowledge to navigate this complex market effectively.
By leveraging this guide, you will be better positioned to make informed choices that enhance operational efficiency and drive business growth. The world of wire forming is vast, and understanding its dynamics is key to unlocking new opportunities in your supply chain.
Understanding wire forming Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Wire Forming | Automated, precise bending using computer-controlled machines | Automotive, aerospace, medical devices | Pros: High precision, repeatability; Cons: Higher initial setup cost. |
| Fourslide Forming | Uses multiple cam-controlled slides for complex shapes | High-volume production of intricate parts | Pros: Efficient for large runs; Cons: Setup time can be lengthy. |
| Manual Wire Forming | Handcrafted, labor-intensive process | Custom, low-volume projects | Pros: Flexibility for unique designs; Cons: Slower production speed. |
| Coil Wire Forming | Specializes in producing springs and coils | Electrical, mechanical components | Pros: Ideal for spring applications; Cons: Limited to specific shapes. |
| Roll Forming | Continuous bending process for long sections of wire | Construction, furniture, automotive parts | Pros: High efficiency for long runs; Cons: Less flexibility in design changes. |
CNC Wire Forming
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) wire forming is a highly automated process that utilizes computer programming to control the bending of wire into precise shapes. This method is particularly suitable for industries requiring high accuracy and repeatability, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical device manufacturing. When considering CNC wire forming, buyers should assess the initial investment costs against the long-term benefits of efficiency and reduced labor costs. Additionally, the ability to produce complex geometries with minimal human intervention makes CNC a preferred choice for high-volume orders.
Fourslide Forming
Fourslide forming employs a stamping machine with multiple cam-controlled slides that manipulate wire into intricate shapes. This method is ideal for high-volume production runs where consistent quality and detail are paramount. Industries such as electronics and automotive components frequently utilize this technique for parts that require precision and complexity. Buyers should weigh the efficiency of fourslide forming against the potential for longer setup times, which can impact lead times for initial orders. This method is beneficial for those looking to scale production while maintaining high standards.
Manual Wire Forming
Manual wire forming is a traditional, hands-on method where skilled workers shape wire into forms using basic tools or even their hands. This approach is particularly advantageous for custom or low-volume projects where unique designs are required. Industries ranging from art to specialized machinery often seek out manual wire forming for its flexibility. Buyers should consider the trade-off between the slower production pace and the bespoke nature of the output, which may be essential for niche applications. This method offers a personal touch that can be advantageous in certain markets.
Coil Wire Forming
Coil wire forming focuses on creating springs and coils, making it a vital process in industries such as electrical and mechanical engineering. This method is characterized by wrapping wire around a metal blank to achieve specific tension and shape requirements. Buyers should consider the application needs when selecting coil wire forming, as it is ideal for components like compression, extension, and torsional springs. However, the design options may be limited compared to other methods, so understanding the specific requirements of the intended application is crucial.
Roll Forming
Roll forming is a continuous bending process that produces long sections of wire into uniform shapes. This method is commonly used in the construction, furniture, and automotive industries, where efficiency and consistency are key. Buyers should evaluate roll forming for its ability to handle high-volume production with minimal waste. While it offers excellent efficiency, the design flexibility may be less than other forming techniques, making it essential to have clear specifications before committing to this method. Overall, roll forming is best suited for projects requiring high output and standardization.
Related Video: How Large Language Models Work
Key Industrial Applications of wire forming
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of wire forming | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of wire forms for vehicle components | Enhances vehicle durability and performance | Quality certifications, material specifications, lead times |
| Medical Equipment | Manufacturing of wire forms for surgical tools | Improves precision and safety in medical procedures | Regulatory compliance, biocompatibility, custom designs |
| Aerospace | Creation of wire forms for structural components | Reduces weight while maintaining strength | Aerospace-grade materials, stringent quality standards |
| Construction | Fabrication of wire forms for scaffolding and support | Ensures safety and stability in construction projects | Load-bearing capacities, corrosion resistance, local regulations |
| Electrical & Electronics | Development of wire forms for connectors and terminals | Facilitates reliable electrical connections | Conductivity requirements, compatibility with existing systems |
Automotive
In the automotive industry, wire forming is essential for producing various components such as brackets, clips, and support structures. These wire forms contribute to the overall performance and safety of vehicles by providing structural integrity and durability. International buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers with robust quality certifications and a deep understanding of automotive standards to ensure compliance with safety regulations.
Medical Equipment
Wire forming plays a critical role in the medical sector, particularly in the manufacturing of surgical instruments and medical devices. The precision and customization offered by wire forming techniques allow for the creation of tools that meet stringent safety and performance standards. Buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that adhere to regulatory compliance and can provide materials that are biocompatible, ensuring patient safety and effectiveness of medical procedures.
Aerospace
In aerospace applications, wire forming is utilized to create lightweight yet strong components that are crucial for aircraft performance. Parts such as brackets and support structures benefit from the strength-to-weight ratio achieved through advanced wire forming techniques. Buyers from the aerospace sector should focus on sourcing materials that meet industry-specific standards and require rigorous quality checks to ensure safety and reliability in flight operations.
Construction
The construction industry employs wire forming for scaffolding and support systems, where safety and stability are paramount. Wire forms used in this context must be capable of bearing significant loads while resisting corrosion and environmental wear. B2B buyers in construction should consider local regulations and standards when sourcing wire forms, ensuring that materials used can withstand the conditions of their specific project locations.
Electrical & Electronics
In the electrical and electronics sectors, wire forming is crucial for the creation of connectors, terminals, and various other components that facilitate electrical connections. This application ensures that connections are reliable and efficient, which is vital for system performance. Buyers should evaluate the conductivity requirements and compatibility with existing systems when sourcing wire forms to guarantee optimal functionality and integration in their applications.
Related Video: Forming Sheet Metal & Metal Forming Tools – Uses Explained By Gene Winfield at SEMA
Strategic Material Selection Guide for wire forming
When selecting materials for wire forming, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence product performance, manufacturing complexity, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in wire forming, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its high tensile strength and durability, making it suitable for applications requiring robust components. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°C (752°F) and is less resistant to corrosion compared to stainless steel.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its cost-effectiveness and availability. However, its susceptibility to rust and corrosion limits its use in environments exposed to moisture or chemicals. Additionally, steel can be more challenging to weld and form compared to other materials.
Impact on Application: Steel is ideal for structural components in automotive and construction applications. However, its corrosion sensitivity may restrict its use in marine or food processing environments.
Specific Considerations: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM A36 for structural steel. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing steel may be influenced by local availability and import tariffs.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel, particularly grade 304, offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand temperatures up to 870°C (1598°F). Its non-reactive nature makes it suitable for food and medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust, which makes it ideal for harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive than carbon steel and may require specialized tools for forming.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is commonly used in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications where hygiene and corrosion resistance are critical.
Specific Considerations: Buyers should verify compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets. In Europe, adherence to EN standards is also crucial. Buyers from the Middle East should consider the local climate’s impact on material selection.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, with a melting point of around 660°C (1220°F). It is also highly conductive, making it suitable for electrical applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce shipping costs and improve energy efficiency in applications. However, it is less strong than steel and may not be suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries, where weight savings are crucial. It is also popular in electronics due to its conductivity.
Specific Considerations: Buyers should check for compliance with standards like ASTM B221 for aluminum extrusions. In regions like South America, the availability of aluminum may vary, affecting pricing and lead times.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper has excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties, with a melting point of 1085°C (1985°F). It is also resistant to corrosion and has antimicrobial properties.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of copper is its superior conductivity, making it ideal for electrical applications. However, it is more expensive than aluminum and can be prone to tarnishing over time.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in electrical wiring, plumbing, and heating applications. Its antimicrobial properties also make it suitable for medical equipment.
Specific Considerations: B2B buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM B3 for copper wire. In Europe, buyers should be aware of REACH regulations concerning copper products.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for wire forming | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Structural components in automotive | Cost-effective and durable | Susceptible to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, medical equipment | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Automotive, aerospace | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Less strength than steel | Medium |
| Copper | Electrical wiring, plumbing | Superior conductivity | More expensive and prone to tarnishing | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides essential insights for international B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on the specific requirements of their wire forming applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for wire forming
Wire forming is a critical component in various manufacturing sectors, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods. Understanding the typical manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures involved in wire forming is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This section provides a comprehensive overview of the manufacturing stages, key techniques, and quality control practices that ensure high-quality wire forms.
Manufacturing Processes in Wire Forming
The wire forming process typically consists of four main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that the final product meets the desired specifications and quality standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in wire forming is the selection and preparation of the wire material. Common materials include:
- Steel: Known for its strength and cost-effectiveness, it is suitable for various applications.
- Stainless Steel: Offers corrosion resistance and is ideal for applications requiring hygiene, such as in the medical field.
- Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
- Copper and Brass: Often used for electrical applications due to their conductivity.
Once the material is selected, it is typically fed from a coil or cut to length. The wire is then straightened to ensure uniformity and prepare it for the forming stage.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the wire is manipulated into the desired shapes using various techniques:
- Bending: The most common method, where the wire is bent at specific angles to create three-dimensional shapes.
- Extrusion: Involves pushing the wire through a die to create specific cross-sectional shapes.
- Upsetting: The wire is compressed at specific points to widen or shape it.
- Twisting: Used to create complex shapes or combine multiple wire strands.
- CNC Wire Bending: Utilizes computerized controls for precision and efficiency in producing complex geometries.
Each technique offers unique advantages and is chosen based on the application and design requirements.
3. Assembly
In some cases, wire forms may need to be assembled with other components to create a final product. This can involve welding, fastening, or other joining techniques. The assembly process is crucial, especially for products that require high structural integrity, such as in automotive or aerospace applications.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves surface treatments and finishes, which can include:
- Coating: Applying protective layers such as powder coating or galvanization to enhance corrosion resistance.
- Polishing: Improving the aesthetic appearance and reducing surface roughness.
- Heat Treatment: Altering the physical properties of the wire to enhance strength and durability.
These finishing processes are essential for ensuring that the wire forms meet the specific requirements of their intended applications.
Quality Assurance in Wire Forming
Quality assurance (QA) is a crucial aspect of the wire forming process, ensuring that products meet industry standards and client specifications. Here’s an overview of relevant standards, checkpoints, and testing methods.
International and Industry-Specific Standards
For B2B buyers, understanding the applicable quality standards is critical. Some of the most relevant include:
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized quality management standard that sets criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Manufacturers should be certified to ensure consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates that products conform to European health, safety, and environmental protection standards, essential for buyers in Europe.
- API Standards: Particularly relevant for manufacturers supplying the oil and gas industry, ensuring that products meet specific safety and performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To maintain high-quality standards, manufacturers implement various quality control checkpoints throughout the production process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified requirements.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of finished products to ensure they meet all specifications before shipping.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is an integral part of quality assurance. Common methods used in wire forming include:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the strength and ductility of the wire.
- Dimensional Inspection: Ensures that the wire forms meet specified dimensions and tolerances.
- Visual Inspection: Checks for surface defects, such as scratches or corrosion.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques like ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection are used to detect internal defects without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality control measures. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
- Conduct Audits: Regular on-site audits can help assess the supplier’s adherence to quality standards and their QMS.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of quality control processes and results from testing.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality practices.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers, particularly from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should be aware of specific nuances in quality control:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local manufacturing practices and standards can impact quality expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Familiarity with local regulations regarding product safety and environmental standards is essential, especially when importing products.
- Communication: Establishing clear communication channels with suppliers can mitigate misunderstandings related to quality expectations.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in wire forming is essential for B2B buyers. By being informed about the various stages of production, industry standards, and quality control measures, buyers can make more informed decisions and ensure that they receive high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
Related Video: How to Amazing Electrical Wire Manufacturing in Factory Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for wire forming Sourcing
In the wire forming industry, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. A comprehensive analysis of the cost components and price influencers can lead to better negotiation strategies and overall cost efficiency.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly affects the cost. Common materials include:
– Steel: Economical and strong, but less resistant to corrosion.
– Stainless Steel: Higher cost due to corrosion resistance and durability.
– Aluminum and Copper: Used for specialized applications; these materials can be pricier but offer unique benefits. -
Labor: Labor costs can vary based on the complexity of the wire forms and the manufacturing method used. Manual forming requires skilled labor, while automated processes can reduce labor costs but may involve higher initial capital for machinery.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with running the manufacturing facility, including utilities, maintenance, and administrative expenses. Overhead can vary widely depending on the location and operational efficiency of the supplier.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, especially for specialized forms. The investment in tooling should be factored into the total cost, as it can influence pricing for both low and high volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC processes ensures the finished products meet specified standards. However, this adds to the overall cost structure. Certifications (e.g., ISO) can also influence costs but may be necessary for specific industries.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the location of the supplier and the destination. International shipping can introduce additional expenses such as tariffs, insurance, and handling fees.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover risks and profit. Understanding the standard margins in the industry can help buyers gauge fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) and production volumes directly influence pricing. Larger orders often lead to volume discounts, making it crucial for buyers to negotiate terms that align with their needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Highly customized products will generally incur higher costs due to the added complexity in design and manufacturing. Buyers should clearly communicate specifications to avoid unexpected costs.
-
Materials: The choice of material significantly impacts price. Premium materials will naturally lead to higher costs, so buyers should weigh the benefits against their budget.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality and certifications can increase costs but may be necessary for compliance in certain industries. Buyers should assess whether the added expense aligns with their quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, experience, and location of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may command higher prices but offer reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is crucial for international transactions. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can significantly affect total costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices based on the comprehensive understanding of the cost structure. Leverage volume purchases to secure better rates.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider total cost of ownership rather than just upfront costs. Evaluate all components, including logistics and potential quality issues that might arise.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and local regulations that may affect pricing. Establishing relationships with suppliers can also lead to better terms.
Disclaimer
Prices can vary widely based on numerous factors, including market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. This analysis serves as a guideline; actual costs may differ. Always conduct thorough research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential wire forming Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘wire forming’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for wire forming
Key Technical Properties in Wire Forming
When engaging with wire forming, understanding critical technical properties is essential for B2B buyers. These specifications influence the quality, performance, and suitability of wire forms for various applications.
-
Material Grade
The material grade refers to the specific classification of the metal used in wire forming, such as stainless steel, aluminum, or copper. Different grades offer varying levels of strength, corrosion resistance, and durability. For instance, Grade 304 stainless steel is commonly used for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for food processing applications. Selecting the right material grade is crucial for ensuring that the wire forms meet industry standards and specific operational demands. -
Tolerance
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a wire form’s dimensions. Precise tolerances are critical in applications requiring high accuracy, such as in medical devices or automotive components. A tighter tolerance often means higher manufacturing costs but is essential for ensuring proper fit and function in assemblies. Understanding tolerance requirements can help buyers avoid issues related to compatibility and performance in their applications. -
Wire Diameter
The wire diameter is a fundamental specification that affects the strength and flexibility of the wire forms. It is measured in gauge or millimeters and must be chosen based on the application’s load-bearing requirements. For example, a thicker wire may be needed for structural applications, while thinner wire might suffice for decorative items. Buyers should evaluate the required wire diameter to ensure that the final product can withstand the intended use. -
Finish
The finish of the wire form can significantly impact its aesthetic appeal and functional properties. Common finishes include galvanized, polished, or powder-coated surfaces. The choice of finish affects not only the appearance but also the corrosion resistance and durability of the product. For international buyers, understanding the finish options can help in selecting wire forms that meet both aesthetic and functional requirements for diverse markets.
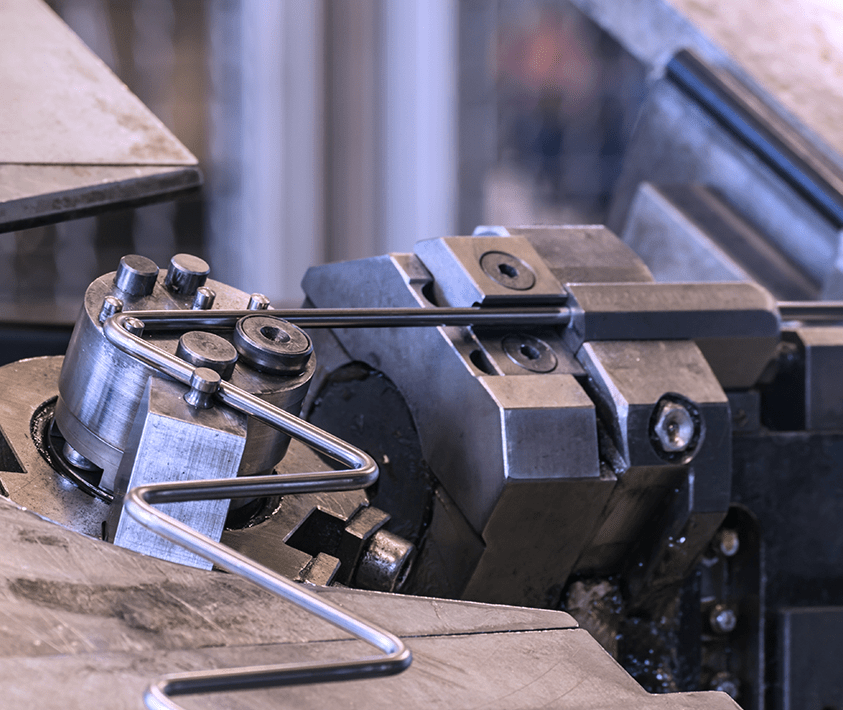
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Load Capacity
Load capacity indicates the maximum weight a wire form can support without deformation or failure. This property is particularly important in industries like construction and automotive, where safety and reliability are paramount. Buyers should assess load capacity to ensure that the wire forms will perform adequately under expected conditions.
Common Trade Terminology in Wire Forming
Familiarity with industry jargon can enhance communication and negotiation with suppliers. Below are some essential terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality wire forms tailored to specific applications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to ensure they can meet their inventory needs without overcommitting financially. This term is particularly relevant for international buyers looking to optimize shipping and production costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. Crafting a detailed RFQ can help buyers receive accurate and competitive pricing while ensuring that all technical specifications are clearly communicated. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are standardized trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, facilitating smoother cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. For wire forming, this can vary based on the complexity of the design and the manufacturing process. Understanding lead times is essential for buyers to plan their supply chain and avoid production delays. -
Customization
Customization refers to the ability to modify standard wire forms to meet specific requirements. Buyers should inquire about customization options to ensure that their unique specifications are met, resulting in optimal product performance and satisfaction.
By understanding these essential properties and terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their wire forming needs are met efficiently and effectively.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the wire forming Sector
The wire forming sector is experiencing dynamic shifts driven by technological advancements, changing consumer demands, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. The global market is increasingly shaped by the integration of automation and digital technologies, such as Computer Numerical Control (CNC) and Industry 4.0 solutions. These innovations enable manufacturers to produce complex wire forms with greater precision and efficiency, making it easier for international B2B buyers to source high-quality products that meet specific application requirements.
Emerging trends indicate a rising preference for customized solutions, particularly in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment manufacturing. Buyers are now seeking suppliers who can deliver tailored wire forms that align with their unique specifications. Additionally, the emphasis on reducing lead times and enhancing supply chain agility is prompting buyers to explore local and regional suppliers, particularly in Africa, South America, and the Middle East. This shift is further fueled by the need for resilience in supply chains, as geopolitical factors and global disruptions continue to impact international trade.
Furthermore, the wire forming market is witnessing a notable increase in the demand for sustainable practices. Buyers are actively looking for suppliers that prioritize environmentally friendly processes and materials, ensuring that their purchasing decisions reflect their corporate social responsibility goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the wire forming sector, with a growing awareness of environmental impacts associated with manufacturing processes. B2B buyers are increasingly focused on sourcing from manufacturers who implement sustainable practices, such as reducing waste, utilizing energy-efficient technologies, and minimizing carbon footprints.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are now demanding transparency in sourcing materials, favoring suppliers who can provide documentation regarding the origin of their raw materials and adherence to ethical labor practices. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and other ‘green’ certifications are becoming essential criteria for supplier selection, as they indicate a commitment to sustainability.
In terms of materials, buyers are encouraged to consider alternatives such as recycled metals or eco-friendly coatings that reduce environmental impact without compromising quality. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, international buyers can not only enhance their corporate image but also align with consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
Wire forming has a rich history that dates back to ancient civilizations, where artisans first manipulated metal wires for practical and decorative purposes. Over the centuries, the techniques have evolved from manual crafting to sophisticated automated processes, reflecting advancements in technology and manufacturing capabilities.
The introduction of CNC machinery in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, allowing for unprecedented precision and efficiency in wire forming. This evolution has enabled manufacturers to meet the diverse needs of various industries, driving the growth of the wire forming sector. Today, as the industry continues to innovate, the focus on sustainability and ethical practices is shaping the future of wire forming, making it a pivotal consideration for international B2B buyers.
Related Video: Global trade will never be the same again, says Christine Lagarde | Power & Politics
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of wire forming
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting wire forming suppliers?
When vetting wire forming suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, technical capabilities, and certifications. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in your specific application area, such as automotive or medical equipment. Assess their production capacity, lead times, and ability to handle custom orders. Additionally, inquire about their quality assurance processes and whether they comply with international standards like ISO 9001. Checking customer reviews and requesting references can also provide insight into their reliability and product quality. -
Can I customize my wire forming orders, and what are the limits?
Most wire forming suppliers offer customization options, allowing you to specify dimensions, shapes, and materials. However, customization limits can vary based on the supplier’s capabilities and the technology they use. Discuss your requirements in detail to understand what is feasible, including design complexity and material choices. Be aware that intricate designs may require longer lead times and higher costs, so it’s essential to balance your specifications with budget and timeline constraints. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for wire forming?
Minimum order quantities (MOQs) for wire forming can vary significantly between suppliers, often depending on the complexity of the item and the production method used. Generally, MOQs can range from a few hundred units for simple items to thousands for more complex forms. Lead times also vary, typically spanning from a few weeks to several months based on the order size, customization level, and supplier location. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid surprises in your supply chain planning. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing wire forming products?
Payment terms for wire forming suppliers often depend on the order size, relationship history, and geographic factors. Common terms include upfront deposits ranging from 30% to 50% of the total order value, with the balance due upon delivery or before shipment. Some suppliers may offer payment options like letters of credit or net 30/60 terms for established customers. Ensure you clarify payment terms in the contract to prevent misunderstandings and ensure smooth transaction processes. -
How do suppliers ensure quality assurance and certifications for wire forming products?
Quality assurance in wire forming involves rigorous testing and compliance with industry standards. Reputable suppliers should hold certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management systems. Ask about their quality control processes, including material inspections, in-process checks, and final product testing. Suppliers may also provide documentation or certifications that verify compliance with specific standards relevant to your industry, ensuring that the products meet necessary safety and performance requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing wire forming products?
Logistics play a crucial role in the timely delivery of wire forming products. Consider factors such as shipping methods, freight costs, and delivery timelines when placing your order. Discuss with suppliers about their shipping capabilities, including options for air or sea freight. Be aware of customs regulations and duties that may apply when importing products into your country. It’s advisable to work with suppliers who can provide comprehensive logistics support, ensuring a smooth import process. -
How can disputes be effectively managed when working with wire forming suppliers?
To manage disputes effectively, establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in your contracts. Include terms related to quality, delivery schedules, and dispute resolution procedures. It is beneficial to have a mediation clause that outlines steps to resolve conflicts amicably before escalating to legal action. Building a strong relationship with your supplier can also mitigate disputes, as trust and understanding can lead to more collaborative problem-solving. -
What common challenges should I be aware of when sourcing wire forming products internationally?
Sourcing wire forming products internationally can present challenges such as cultural differences, language barriers, and varying regulatory standards. Be prepared for potential delays caused by customs or logistical issues. Additionally, fluctuating exchange rates can impact costs, so consider hedging strategies or contracts that account for currency risks. Conducting thorough research on the supplier’s market and establishing clear communication can help navigate these challenges effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for wire forming
In the dynamic world of wire forming, strategic sourcing emerges as a crucial element for international B2B buyers. By understanding the diverse manufacturing processes—ranging from CNC automation to manual techniques—buyers can better assess their options and select suppliers that align with their specific project requirements. Key takeaways include recognizing the versatility of wire forming materials, such as steel and stainless steel, and the importance of choosing the right material for the intended application to ensure durability and performance.
Moreover, establishing strong partnerships with reliable manufacturers can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced product quality. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe continue to evolve, the demand for customized wire forms is set to rise. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to innovation and quality.
Looking ahead, the wire forming sector is poised for growth driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand across various applications. Now is the time to engage with trusted wire forming manufacturers who can meet your needs. Embrace the opportunity to enhance your supply chain and drive your business forward by leveraging strategic sourcing in wire forming.