Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Manufacturing On Demand
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for manufacturing on demand
In an era where agility and responsiveness are paramount, manufacturing on demand (MOD) emerges as a transformative solution for international B2B buyers. This innovative approach allows businesses to produce goods only when needed, eliminating the burdens of excess inventory and associated costs. By leveraging advanced digital platforms, MOD streamlines the production process, enabling rapid quoting, enhanced supplier communication, and real-time order tracking.
For buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, this model is not just a trend but a strategic advantage. It empowers companies to tailor their production to specific market demands, facilitating customized solutions that resonate with local consumers while reducing waste. This guide will delve deep into the multifaceted landscape of manufacturing on demand, covering various types of manufacturing processes, material considerations, quality control measures, and supplier selection.
Moreover, we will provide insights on cost structures, market trends, and frequently asked questions, equipping buyers with the knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are in Kenya exploring local suppliers or in Mexico seeking global partners, understanding the dynamics of MOD will enhance your competitive edge in the global marketplace. Embrace the future of manufacturing—where efficiency meets customization—and unlock the potential of on-demand solutions for your business growth.
Understanding manufacturing on demand Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Additive Manufacturing | Utilizes 3D printing technology to create parts layer by layer. | Prototyping, custom tooling, and low-volume production. | Pros: High customization, reduced waste. Cons: Slower production speed compared to traditional methods. |
| CNC Machining | Computer-controlled tools for precision cutting and shaping. | Aerospace, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. | Pros: High precision, versatile material options. Cons: Setup time can be lengthy for small batches. |
| Injection Molding | Produces parts by injecting molten material into molds. | High-volume production of plastic components. | Pros: Cost-effective for large quantities, excellent surface finish. Cons: High initial tooling costs, less flexibility for design changes. |
| Digital Textile Printing | Directly prints designs onto fabric using digital technology. | Fashion, home decor, and promotional products. | Pros: Quick turnaround for custom designs, minimal waste. Cons: Limited to specific fabric types, potential color matching issues. |
| Micro-Manufacturing | Focuses on producing small, precise parts using specialized equipment. | Electronics, medical devices, and specialized components. | Pros: High precision in small-scale production. Cons: Limited scalability and higher per-unit costs. |
Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is characterized by its layer-by-layer approach to creating parts. This method is particularly suitable for industries requiring rapid prototyping, custom tooling, or low-volume production. Buyers should consider the material compatibility and the complexity of designs, as intricate geometries can be achieved with this technology. However, the slower production speed compared to traditional methods may impact timelines for larger orders.
CNC Machining
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining employs computer-controlled tools to achieve high precision in cutting and shaping materials. This method is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices where tolerances are critical. When purchasing CNC services, buyers should assess the machine capabilities and the expertise of the operators. While CNC machining offers versatility in material selection, setup times can be a drawback for smaller batch orders.
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material into molds to create parts. This method is particularly advantageous for high-volume production of plastic components, making it ideal for industries like consumer goods and automotive. Buyers must weigh the high initial tooling costs against the cost-effectiveness for large quantities. The design flexibility is limited once the mold is created, so thorough planning is essential before starting production.
Digital Textile Printing
Digital textile printing allows for direct printing of designs onto fabrics using advanced digital technology. This method is increasingly popular in the fashion industry, home decor, and promotional products due to its quick turnaround for custom designs. B2B buyers should consider the types of fabrics compatible with this technology and potential color matching issues. While it minimizes waste, it may not be suitable for all fabric types, limiting its application in certain markets.
Micro-Manufacturing
Micro-manufacturing focuses on the production of small, precise components using specialized equipment. This approach is particularly relevant in sectors like electronics and medical devices, where high precision is paramount. Buyers should be aware that while micro-manufacturing offers exceptional quality for small-scale production, it may come with higher per-unit costs and limited scalability. Understanding the specific capabilities of micro-manufacturers is crucial for ensuring compatibility with project requirements.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of manufacturing on demand
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Manufacturing on Demand | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Custom components for aircraft and drones | Reduces lead time and inventory costs, ensures compliance with safety regulations | Need for high precision, certification requirements, and reliable supply chains |
| Automotive | Prototyping and production of custom parts | Enables rapid prototyping, reduces waste, and supports JIT production strategies | Demand for flexibility in order quantities and material selection |
| Consumer Electronics | Tailored electronic housings and enclosures | Facilitates customization, reduces time to market, and minimizes excess inventory | Importance of rapid turnaround times and adherence to design specifications |
| Medical Devices | Personalized medical equipment and implants | Enhances patient outcomes through customization, reduces regulatory risks | Compliance with health regulations and need for biocompatible materials |
| Fashion and Apparel | Custom clothing and accessories | Allows for personal branding, reduces unsold inventory, and improves customer satisfaction | Understanding of local market trends and sustainable sourcing options |
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, on-demand manufacturing is critical for producing custom components for aircraft and drones. This approach significantly reduces lead times and inventory costs, as parts are manufactured only when needed. International B2B buyers in this sector must prioritize suppliers that meet stringent safety regulations and certification requirements, ensuring that all components are compliant with industry standards. Additionally, establishing reliable supply chains is essential to prevent delays in production and maintain operational efficiency.
Automotive
The automotive sector benefits from on-demand manufacturing through rapid prototyping and the production of custom parts. This flexibility allows manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands while minimizing waste associated with overproduction. Buyers, particularly from emerging markets in Africa and South America, should seek suppliers who can accommodate varying order quantities and provide a diverse selection of materials to meet specific design needs. The ability to implement just-in-time (JIT) production strategies further enhances operational efficiency.
Consumer Electronics
On-demand manufacturing is transforming the consumer electronics industry by enabling the production of tailored electronic housings and enclosures. This customization capability not only facilitates faster time-to-market but also minimizes excess inventory, which is crucial in a fast-paced market. For international buyers, especially in Europe, it is vital to partner with manufacturers that can deliver rapid turnaround times while adhering to detailed design specifications. This ensures that products meet consumer expectations and maintain competitive advantages.
Medical Devices
In the medical device sector, on-demand manufacturing allows for the creation of personalized equipment and implants tailored to individual patient needs. This customization enhances patient outcomes and reduces regulatory risks associated with mass-produced devices. Buyers in this field, particularly from regions like the Middle East, must ensure that their suppliers comply with rigorous health regulations and can provide biocompatible materials. Establishing strong relationships with manufacturers who understand these requirements is essential for success.
Fashion and Apparel
On-demand manufacturing is revolutionizing the fashion and apparel industry by enabling the production of custom clothing and accessories. This model allows brands to offer personalized products, reducing the risk of unsold inventory and enhancing customer satisfaction. For international buyers in markets like Kenya and Mexico, understanding local trends and consumer preferences is critical. Additionally, sourcing sustainably can create a competitive edge, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers while optimizing supply chains.
Related Video: New method of manufacturing using powder bed: Additive Manufacturing with Selective Laser Melting
Strategic Material Selection Guide for manufacturing on demand
When selecting materials for manufacturing on demand, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that impact product performance, cost, and application suitability. Below is a detailed analysis of four common materials used in on-demand manufacturing, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight yet strong, with excellent corrosion resistance and good thermal conductivity. It typically withstands temperatures up to 600°F (315°C) and has a low density.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for applications in aerospace and automotive sectors. However, it can be more expensive than steel and may require specialized machining processes, which can complicate manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and chemicals, making it suitable for components in automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with international standards such as ASTM and ISO. Additionally, sourcing aluminum from local suppliers can mitigate import costs and lead times, particularly in regions like Africa and South America.
2. Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its exceptional corrosion resistance and strength, with temperature ratings often exceeding 1500°F (815°C). It is also non-reactive, making it ideal for food and medical applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability and longevity of stainless steel are significant advantages, particularly in harsh environments. However, it can be costly and challenging to machine, leading to longer lead times and higher manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is highly compatible with various media, including acids and bases, making it suitable for chemical processing equipment.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel grades meet local regulations and standards, such as DIN or JIS. Understanding the specific grade requirements can help avoid costly compliance issues.
3. PLA (Polylactic Acid)
Key Properties: PLA is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable resources. It has a lower melting point (around 160°F or 70°C) and is suitable for low-stress applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PLA is its environmental friendliness and ease of use in 3D printing. However, it has lower strength and heat resistance compared to metals and can be unsuitable for high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: PLA is ideal for prototyping, educational tools, and packaging. Its compatibility with food items makes it a popular choice for disposable cutlery and containers.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should consider local regulations regarding biodegradable materials and ensure that PLA products meet relevant safety standards. Sourcing from local manufacturers can also reduce shipping costs and environmental impact.
4. Nylon
Key Properties: Nylon is a synthetic polymer known for its toughness and flexibility. It has good temperature resistance (up to 400°F or 204°C) and excellent wear resistance.
Pros & Cons: The flexibility and durability of nylon make it suitable for various applications, including gears and bearings. However, it can absorb moisture, which may affect its mechanical properties over time.
Impact on Application: Nylon is compatible with various media, including oils and fuels, making it suitable for automotive and industrial applications.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the moisture absorption properties of nylon and consider this in their product design. Compliance with relevant international standards is crucial, especially in regulated industries.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for manufacturing on demand | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Aerospace components, automotive parts | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher cost and complex machining | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing equipment | Exceptional durability and corrosion resistance | Costly and challenging to machine | High |
| PLA | Prototyping, disposable cutlery | Environmentally friendly | Lower strength and heat resistance | Low |
| Nylon | Gears, bearings | Toughness and flexibility | Moisture absorption affects properties | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to empower international B2B buyers by providing insights into material properties, advantages, and considerations that can impact their manufacturing decisions. By understanding these factors, buyers can make informed choices that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for manufacturing on demand
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing on demand (MOD), understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for B2B buyers. This insight becomes particularly vital for international buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, where diverse market conditions and regulatory environments exist. Below, we delve into the typical manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and actionable strategies for verifying supplier quality.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing process in an on-demand model is streamlined and highly adaptable, focusing on producing only what is needed, when it is needed. Here are the primary stages involved:
1. Material Preparation
The first step involves selecting and preparing raw materials that meet the specific requirements of the order. Buyers should ensure that suppliers have robust material sourcing strategies, including certifications that guarantee quality and compliance with international standards. Common techniques include:
- Material Inspection: Verifying the quality of incoming materials through visual checks and testing.
- Cutting and Shaping: Utilizing advanced technologies such as laser cutting or CNC machining to prepare materials accurately.
2. Forming
In this stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the desired forms. Techniques used may vary based on the product type but often include:
- 3D Printing: Ideal for complex designs and small batches, offering flexibility and customization.
- Injection Molding: Effective for producing precise components in larger quantities when needed.
3. Assembly
The assembly process involves putting together various components to create the final product. Key techniques include:
- Automated Assembly: Utilizing robotics and automated systems to enhance efficiency and consistency.
- Manual Assembly: Skilled labor may be required for intricate parts, emphasizing the need for well-trained workers.
4. Finishing
Finishing touches add the final details to the product, enhancing aesthetics and functionality. Techniques may involve:
- Surface Treatment: Processes such as anodizing or powder coating to improve durability and appearance.
- Quality Checks: Conducting inspections at this stage to ensure the final product meets specified standards.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is a cornerstone of the manufacturing on demand model, ensuring that products meet the required specifications and standards. B2B buyers should be familiar with international and industry-specific standards that govern quality.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard that outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance signifies a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in the European market, indicating conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for manufacturers in the oil and gas sector, focusing on quality and safety in equipment and processes.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during the manufacturing process to identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive evaluations of the finished product to ensure it meets all quality standards before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure compliance with quality standards, various testing methods are employed, including:
- Destructive Testing: Assessing the limits of materials under stress, often used for metals and composites.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic testing or X-ray inspection that evaluate materials without causing damage.
- Functional Testing: Verifying that the product operates as intended under real-world conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in international markets, verifying the quality assurance practices of suppliers is crucial. Here are some strategies:
Supplier Audits
Conducting regular audits can help assess a supplier’s compliance with quality standards. Buyers should look for:
- Documentation: Ensure that suppliers maintain detailed records of their quality management processes.
- Certifications: Verify that suppliers possess relevant quality certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) that guarantee adherence to international standards.
Quality Reports
Requesting quality reports can provide insights into a supplier’s performance over time. Key metrics to review include:
- Defect Rates: Understanding the frequency of defects can help gauge the reliability of the supplier.
- Corrective Actions: Review how suppliers address quality issues to ensure continuous improvement.
Third-Party Inspections
Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control processes. These services can conduct:
- Random Sampling: To test a portion of the production run for quality assurance.
- Compliance Checks: Ensuring that products meet both local and international regulations.
Navigating QC Nuances for International Buyers
International buyers must navigate various quality control nuances specific to their regions. For instance:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the local business culture can aid in establishing effective communication with suppliers regarding quality expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Buyers should be aware of the specific regulations in their target markets, especially in industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, where compliance is critical.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is vital; consider employing translators or bilingual staff to facilitate discussions about quality standards and expectations.
By comprehensively understanding manufacturing processes and implementing robust quality assurance practices, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can significantly enhance their procurement strategies in the on-demand manufacturing landscape. This approach not only fosters better supplier relationships but also ensures that products meet the highest quality standards, ultimately driving business success.
Related Video: Mercedes C-Class CAR FACTORY – HOW IT’S MADE Assembly Production Line Manufacturing Making of
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for manufacturing on demand Sourcing
When engaging in manufacturing on demand (MOD), understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing analysis is crucial for international B2B buyers. This model offers significant advantages over traditional manufacturing, but it also presents unique cost components and pricing influences that buyers must navigate effectively.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials is a primary factor in MOD pricing. Buyers should consider the type and quality of materials required for their specific products, as this can vary greatly. Sourcing high-quality materials can enhance product durability and appeal but may increase costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs in on-demand manufacturing can fluctuate based on the complexity of the product and the skill level required. Custom products often necessitate skilled labor, which can drive up costs. Buyers should inquire about the labor structure of suppliers to understand how it affects pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to equipment maintenance, utilities, and facility expenses. Since on-demand manufacturing often involves smaller batches, overhead costs can be higher per unit compared to traditional mass production. Buyers should assess how suppliers allocate these costs to their pricing.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can vary significantly depending on the customizations required. Initial tooling investments may be higher, but these costs can be spread across multiple orders if the buyer continues to source from the same supplier. It is essential to negotiate tooling costs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses later.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring product quality is paramount in MOD. QC processes may add to the overall cost but are essential for maintaining standards. Buyers should verify the QC measures in place and how they are reflected in pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on destination, shipment size, and delivery speed. For international buyers, understanding Incoterms is vital as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping, impacting overall logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers will add a profit margin to cover their costs and risks. The margin can vary based on the supplier’s pricing strategy and market demand. Engaging in discussions about margin expectations can lead to more favorable terms.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing structure in MOD:
-
Volume/MOQ: While MOD typically allows for smaller orders, suppliers may still have minimum order quantities (MOQs) that influence pricing. Higher volumes can lead to discounts, making it worthwhile to explore bulk purchasing options when feasible.
-
Specifications/Customization: The more complex the product specifications, the higher the associated costs. Buyers should provide clear specifications to avoid miscommunication and unexpected costs.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that require specific certifications or meet stringent quality standards may incur higher costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of these requirements against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s location, reputation, and production capabilities can significantly influence costs. Building relationships with reliable suppliers can often lead to better pricing and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms on pricing is crucial for international buyers. Different terms can affect who bears the cost of shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which can alter the total cost structure.
Buyer Tips
To navigate the complexities of MOD pricing, international B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially when discussing large orders or long-term partnerships. Being transparent about budget constraints can foster goodwill and potentially lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Analyze the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) rather than just the upfront costs. Consider long-term costs associated with quality, durability, and potential wastage.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of the regional differences in pricing structures. For instance, suppliers in Africa may have different cost bases compared to those in Europe or South America. Understanding these nuances can enhance negotiation tactics.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Always request a detailed breakdown of costs and be wary of indicative prices that may not reflect final costs. Prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, so ensure there’s clarity on any potential price adjustments.
By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing from on-demand manufacturers, optimizing both cost and quality in their procurement strategies.
Spotlight on Potential manufacturing on demand Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘manufacturing on demand’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for manufacturing on demand
Key Technical Properties for Manufacturing on Demand
When engaging in manufacturing on demand, understanding specific technical properties is crucial for B2B buyers. These properties not only define the quality and functionality of the products but also influence the overall production process. Here are some essential specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of materials based on their mechanical and physical properties, often specified by industry standards (e.g., ASTM, ISO).
– Importance: Selecting the right material grade ensures that the final product meets performance criteria, durability, and regulatory requirements, which is particularly significant for industries such as automotive and aerospace. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension of a part, indicating how much a measurement can deviate from a specified value.
– Importance: Tolerances are critical in ensuring that parts fit together properly. Tight tolerances may be necessary for intricate assemblies, while looser tolerances might suffice for less critical applications, affecting production costs and timelines.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Surface Finish
– Definition: The texture and smoothness of a part’s surface, often described in terms of Ra (roughness average).
– Importance: The surface finish can affect both aesthetic appeal and functional performance, such as friction and wear. Different applications may require specific finishes, influencing manufacturing processes and costs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The amount of time from the placement of an order to the delivery of the finished product.
– Importance: Understanding lead times helps in planning inventory and production schedules. On-demand manufacturing typically offers shorter lead times, enabling businesses to respond quickly to market demands. -
Production Capacity
– Definition: The maximum output a manufacturing facility can produce in a given timeframe, often measured in units or weight.
– Importance: Assessing production capacity is vital for B2B buyers to ensure that suppliers can meet their order volumes without delays, especially in high-demand scenarios. -
Customizability
– Definition: The ability to modify product features or specifications to meet specific customer requirements.
– Importance: The degree of customizability can differentiate a supplier in the market, allowing businesses to offer tailored solutions that meet unique client needs.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation in the manufacturing on-demand landscape. Here are several key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify the original source of components, which can be crucial for quality assurance and supply chain management. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers, as it can impact order sizes and inventory management. On-demand manufacturing often reduces or eliminates MOQs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to request pricing information from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Relevance: RFQs streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms efficiently. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, used in international trade.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms is critical for understanding responsibilities and liabilities regarding shipping, delivery, and insurance, especially for international transactions.
-
Just-In-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
– Definition: A strategy that aligns raw-material orders with production schedules to reduce inventory costs.
– Relevance: JIT is a core principle of on-demand manufacturing, allowing companies to minimize waste and improve efficiency. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from the initiation of an order to its fulfillment.
– Relevance: As mentioned previously, understanding lead times is essential for efficient supply chain management and planning, particularly in fast-paced markets.
By grasping these technical properties and terminology, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making process and foster more effective partnerships in the manufacturing on-demand landscape.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the manufacturing on demand Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The on-demand manufacturing sector is rapidly evolving, driven by several global dynamics that particularly benefit international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Key drivers include the acceleration of digital transformation, which has made cloud-based platforms more accessible for manufacturers and buyers alike. This digital shift not only facilitates real-time communication and order management but also enhances responsiveness to market changes.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced analytics are reshaping sourcing trends. For instance, AI can optimize production schedules and supply chain logistics, while IoT devices can monitor machinery and inventory levels in real-time. These advancements reduce lead times and improve the accuracy of order fulfillment, which is critical for B2B buyers managing just-in-time inventory systems.
Moreover, the demand for customization is increasing, with buyers seeking tailored solutions that traditional manufacturing processes struggle to deliver. This trend is particularly relevant for sectors like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods, where specific requirements often dictate the need for smaller batch sizes. As B2B buyers from diverse regions engage with on-demand manufacturers, they gain the advantage of flexible production capabilities that align with their unique market demands.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, and on-demand manufacturing aligns closely with environmentally responsible practices. By producing goods only as needed, this model significantly reduces waste associated with overproduction and excess inventory. For B2B buyers, partnering with manufacturers that embrace sustainability can enhance their brand image and appeal to increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
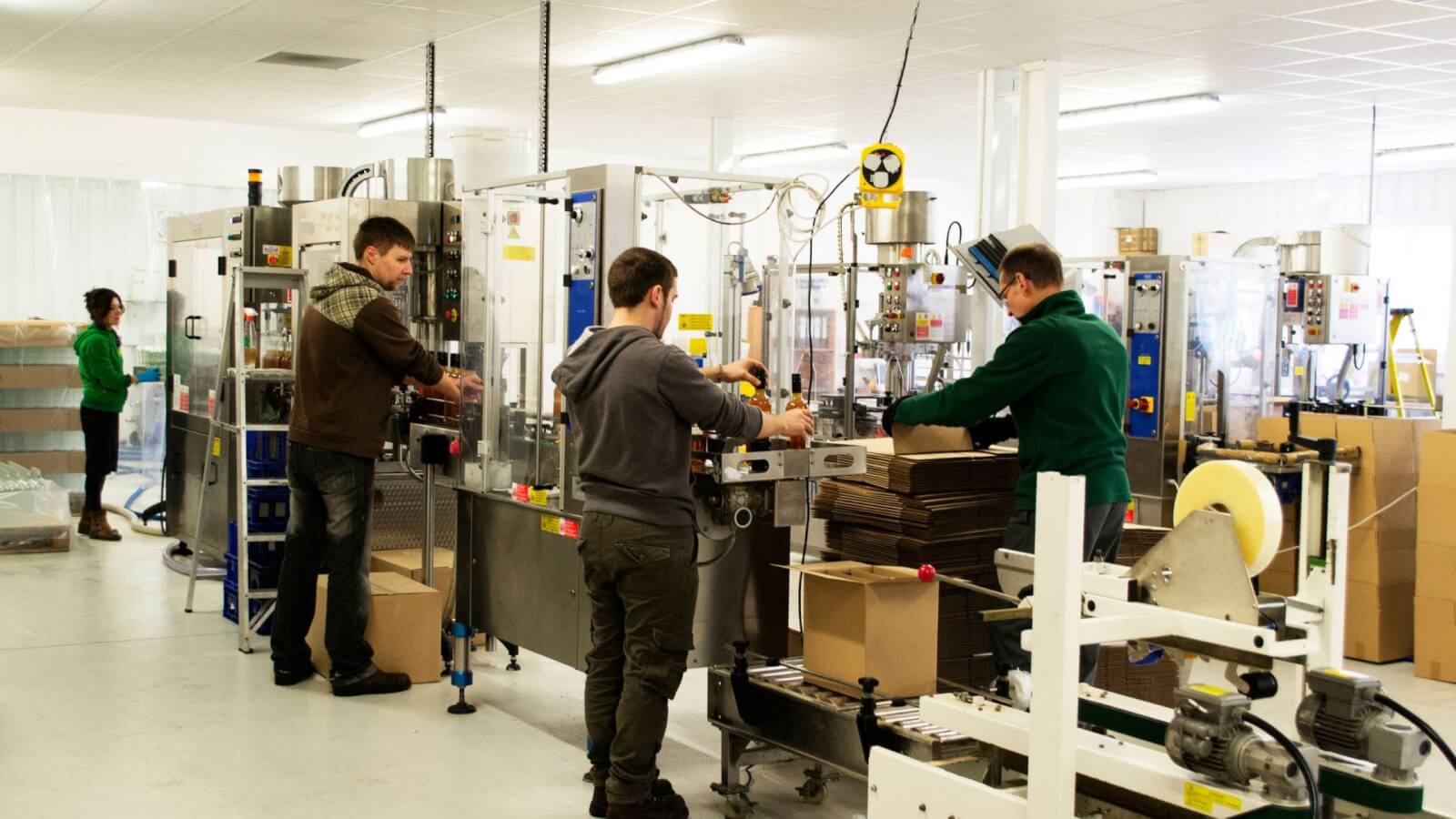

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are encouraged to seek suppliers who prioritize fair labor practices and sustainable sourcing of materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to ethical practices. Additionally, materials such as recycled plastics or sustainably sourced metals are increasingly available, allowing B2B buyers to align their procurement strategies with their sustainability goals.
As the market for sustainable products grows, buyers should actively evaluate their suppliers’ practices and seek out partnerships that contribute to a greener supply chain. This not only helps mitigate environmental impact but also positions companies to meet regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for sustainability.
Brief Evolution/History
The concept of on-demand manufacturing has its roots in the desire to optimize production efficiency and minimize waste. Initially, traditional manufacturing relied heavily on mass production techniques, often resulting in significant excess inventory. As technology advanced, particularly with the advent of digital tools and platforms, the manufacturing landscape began to shift.
The rise of the Internet and cloud computing in the early 2000s facilitated the development of on-demand manufacturing, enabling companies to produce only what was needed when it was ordered. This evolution has empowered businesses across various sectors to adopt more flexible and responsive manufacturing strategies, paving the way for a sustainable and efficient approach to production that resonates well with today’s B2B buyers. As the market continues to evolve, the emphasis on technology, customization, and sustainability will remain pivotal in shaping the future of on-demand manufacturing.
Related Video: Made in the world: Better understanding global trade flows
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of manufacturing on demand
-
How do I vet suppliers for on-demand manufacturing?
When vetting suppliers for on-demand manufacturing, prioritize their experience in your specific industry and their technological capabilities. Request case studies or references from previous clients, particularly those in your region, to gauge their reliability and quality. Utilize platforms that provide supplier ratings and reviews. Additionally, assess their responsiveness during initial communications, as this indicates their commitment to customer service and problem-solving capabilities. -
Can I customize products with on-demand manufacturing?
Yes, one of the primary advantages of on-demand manufacturing is the ability to customize products according to your specifications. Many platforms allow you to upload CAD files or design specifications directly, enabling real-time feedback on manufacturability. Always discuss your customization needs early in the process to ensure that the supplier can meet your design requirements and production timelines. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
On-demand manufacturing typically has lower MOQs compared to traditional manufacturing, often allowing for single-unit orders. Lead times can vary based on complexity and production capacity but are generally shorter, ranging from a few days to weeks. To avoid delays, communicate your timeline and urgency upfront, and ensure the supplier can meet your production schedule. -
How are payments handled in on-demand manufacturing?
Payment methods can vary by supplier but typically include options like credit cards, bank transfers, or escrow services. Some platforms may require upfront payment, while others allow partial payments upon order confirmation. Be sure to clarify payment terms, including any applicable deposits or payment milestones, to avoid misunderstandings later in the process. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect?
Reputable on-demand manufacturing suppliers implement rigorous QA processes, including material inspections, in-process checks, and final product evaluations. Inquire about their certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and whether they provide quality reports or documentation with each order. Establish clear quality expectations and discuss how issues will be addressed if they arise during production. -
What certifications should I look for in suppliers?
Look for suppliers with relevant industry certifications that demonstrate their compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications for quality management and environmental standards. Additionally, check for any specific certifications pertinent to your industry (e.g., FDA approval for medical devices). These certifications provide assurance of the supplier’s commitment to quality and regulatory compliance. -
How does logistics work with on-demand manufacturing?
Logistics in on-demand manufacturing typically involves coordination between the supplier and third-party logistics providers for shipping. Confirm how the supplier handles shipping logistics, including packaging, tracking, and delivery timelines. Depending on your location, discuss potential customs and import regulations that may affect the shipping process, especially for cross-border transactions. -
What should I do if a dispute arises with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. If that fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution processes. Many platforms offer mediation services or an escalation process. It’s crucial to document all communications and agreements to support your case if further action is needed.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for manufacturing on demand
As the landscape of manufacturing evolves, on-demand manufacturing presents an opportunity for international B2B buyers to streamline operations and reduce costs. By leveraging cloud-based platforms, businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe can access a wide network of suppliers, enabling real-time quotes and efficient order management. This model not only minimizes excess inventory but also allows for greater customization, catering to the specific needs of customers while enhancing responsiveness.
Key Takeaways:
– Cost Efficiency: On-demand manufacturing reduces the financial burden of holding large inventories.
– Flexibility: Businesses can adapt quickly to market demands without the risk of overproduction.
– Improved Collaboration: Digital platforms enhance communication and facilitate better supplier relationships.
Looking ahead, the shift towards on-demand manufacturing is poised to redefine traditional supply chains. International B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace this model to optimize their sourcing strategies. By doing so, they can not only stay competitive but also innovate in product offerings tailored to their markets. Engage with on-demand manufacturing today to future-proof your supply chain and drive sustainable growth.