Master Sourcing Electric Heat Elements: A Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for electric heat element
In today’s rapidly evolving global marketplace, the significance of electric heat elements cannot be overstated. These components play a crucial role in diverse applications, from industrial heating processes to advanced smart garments, enhancing energy efficiency and thermal comfort. As industries across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for sustainability and innovation, understanding the nuances of electric heat elements becomes vital for informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide serves as a valuable resource for international B2B buyers, detailing the various types of electric heat elements, including flexible heating fabrics and high-performance conductive materials. We delve into manufacturing and quality control processes, ensuring that buyers can identify reliable suppliers who adhere to stringent standards. Furthermore, we explore cost considerations, market trends, and essential FAQs to equip decision-makers with the insights needed to navigate this complex landscape.
By empowering buyers with actionable information, this guide facilitates strategic procurement and fosters partnerships that drive business growth. Whether you are in the aerospace, textile, or electronics sector, understanding electric heat elements will enhance your competitive edge and support your commitment to sustainability and innovation in a challenging global environment.
Understanding electric heat element Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexible Heating Elements | Lightweight, adaptable to various surfaces; includes conductive fabrics and films | Smart garments, industrial heating | Pros: High flexibility, customizable; Cons: Potential durability issues depending on materials used. |
| Ceramic Heating Elements | Robust, offers high thermal efficiency; ideal for high-temperature applications | Industrial furnaces, HVAC systems | Pros: Long lifespan, efficient heat transfer; Cons: Heavier and less flexible than other types. |
| Metal Heating Elements | Made from conductive metals; includes wire and foil types | Commercial cooking, industrial ovens | Pros: High durability, excellent heat conduction; Cons: Can be bulky and less energy-efficient than other types. |
| Carbon Heating Elements | Utilizes carbon-based materials; often lightweight and flexible | Heating pads, electric blankets | Pros: Good thermal performance, lightweight; Cons: May require careful handling to avoid damage. |
| PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Elements | Self-regulating; resistance increases with temperature | Automotive applications, space heaters | Pros: Safety features due to self-regulation; Cons: Limited to specific temperature ranges. |
Flexible Heating Elements
Flexible heating elements are innovative solutions that integrate conductive materials into fabrics or films. These elements are particularly suitable for applications in smart garments and various industrial heating processes. When considering B2B purchases, buyers should evaluate the adaptability and integration capabilities of these elements with their existing products. The flexibility allows for a variety of applications, but durability can vary based on the materials used, which is a crucial factor for long-term investments.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ceramic Heating Elements
Ceramic heating elements are known for their robustness and high thermal efficiency. They are ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnaces and HVAC systems. Buyers should consider the longevity and efficiency of these elements, particularly in environments where consistent heat is necessary. While they offer excellent performance, the weight and rigidity of ceramic elements might limit their use in applications requiring flexibility.
Metal Heating Elements
Metal heating elements, including wire and foil types, are widely used in commercial cooking and industrial ovens due to their durability and excellent heat conduction. When purchasing, B2B buyers should assess the specific metal composition and its thermal properties, as these factors can influence performance and energy efficiency. While metal elements are reliable, they can be bulkier, which might not suit all applications, especially those requiring space efficiency.
Carbon Heating Elements
Carbon heating elements utilize carbon-based materials, providing a lightweight and flexible heating solution. Commonly found in heating pads and electric blankets, they offer good thermal performance. Buyers should focus on the handling requirements, as carbon elements can be sensitive to physical damage. Their flexibility makes them appealing for various applications, but understanding the material’s limitations is essential for ensuring longevity and effectiveness.
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Elements
PTC heating elements are unique in that they self-regulate, meaning their resistance increases with temperature, providing a safety feature in automotive and space heater applications. B2B buyers should evaluate the specific temperature ranges and operational limits of PTC elements to ensure they meet application needs. While their self-regulating nature enhances safety, their functionality is often limited to particular temperature ranges, which may restrict their use in certain scenarios.
Related Video: What Are The Different Atomic Models? Dalton, Rutherford, Bohr and Heisenberg Models Explained
Key Industrial Applications of electric heat element
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of electric heat element | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Textile Manufacturing | Heating elements in smart garments | Enhances thermal comfort and safety for workers in cold environments | Quality of materials, flexibility, durability, and safety standards |
| Food Processing | Electric heating for cooking and pasteurization | Increases efficiency and reduces energy costs in food production | Compliance with food safety regulations, energy efficiency ratings |
| Chemical Production | Process heating for chemical reactions | Ensures precise temperature control, improving product quality | Material compatibility, temperature range, and safety certifications |
| Aerospace | Thermal management in aircraft components | Enhances safety and performance under extreme conditions | Lightweight materials, resistance to thermal stress, and reliability |
| Electronics | Soldering and component heating | Improves manufacturing precision and reduces defects | Energy efficiency, temperature control accuracy, and integration ease |
Textile Manufacturing
In the textile industry, electric heating elements are integral to the production of smart garments, which actively provide warmth to users. These garments are particularly beneficial for workers in cold environments, enhancing comfort and safety. For international buyers, especially those in Africa and Europe, sourcing high-quality flexible heating elements that are durable and comply with safety standards is crucial. The ability to integrate these elements seamlessly into fabrics while maintaining their flexibility is a key consideration.
Food Processing
Electric heating elements are widely used in food processing for applications such as cooking and pasteurization. They offer significant benefits in terms of efficiency and energy savings, leading to lower operational costs. For buyers in South America and the Middle East, it is essential to ensure that the heating elements meet local food safety regulations and energy efficiency standards. Sourcing from suppliers that provide reliable, high-performance heating solutions can improve productivity and product quality in this sector.
Chemical Production
In chemical manufacturing, electric heat elements are employed for process heating, crucial for maintaining specific temperature conditions necessary for chemical reactions. This precise temperature control enhances product quality and consistency, which is vital for competitive advantage. Buyers, particularly from Europe and the Middle East, should focus on sourcing heating elements that are compatible with various chemicals, can withstand high temperatures, and have necessary safety certifications to mitigate risks associated with chemical processing.
Aerospace
Electric heating elements play a critical role in the aerospace industry, particularly in thermal management systems for aircraft components. These elements help maintain optimal temperatures, ensuring safety and performance under extreme conditions. For international buyers, especially in Europe and Australia, sourcing lightweight and reliable heating solutions is essential. Suppliers must provide components that can withstand thermal stress and offer long-term durability to meet stringent aerospace standards.
Electronics
In the electronics sector, electric heating elements are utilized for soldering and heating components during manufacturing processes. They enhance precision and reduce defects, which is vital for maintaining quality standards. For buyers in Africa and South America, it is important to consider the energy efficiency and temperature control accuracy of the heating elements. Additionally, ease of integration into existing manufacturing systems is a key factor in sourcing decisions, ensuring that the heating solutions align with production capabilities.
Related Video: A Detailed Explanation of the Electric Arc Furnace – What It is and How It Works
Strategic Material Selection Guide for electric heat element
When selecting materials for electric heat elements, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including the properties of the materials, their advantages and disadvantages, and their suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in electric heat elements: Nickel-Chromium Alloys, Carbon Fiber, Conductive Polymers, and Copper.
Nickel-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties: Nickel-chromium alloys, such as Nichrome, exhibit excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures. They can typically withstand temperatures up to 1,200°C (2,192°F) and are known for their high electrical resistivity.
Pros & Cons: These alloys are highly durable and can provide consistent heating performance. However, they can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, especially when forming intricate shapes.
Impact on Application: Nickel-chromium alloys are particularly suitable for applications requiring high-temperature resistance, such as industrial furnaces and heating elements in appliances. Their compatibility with various media makes them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN for safety and performance. The availability of these alloys can vary by region, particularly in Africa and South America, where sourcing may be more challenging.
Carbon Fiber
Key Properties: Carbon fiber materials are lightweight and possess excellent thermal conductivity. They can operate effectively at temperatures around 300°C (572°F) and have good resistance to thermal shock.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of carbon fiber is its high strength-to-weight ratio, making it ideal for portable heating applications. However, it can be costly and may not be as durable as metal options under extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Carbon fiber is often used in flexible heating elements for garments and portable devices, providing efficient heating without adding significant weight.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may find carbon fiber products more readily available due to established supply chains. Compliance with environmental regulations is also a consideration, as carbon fiber production can be energy-intensive.
Conductive Polymers
Key Properties: Conductive polymers, such as polyaniline and polypyrrole, are flexible and can operate at moderate temperatures (up to 200°C or 392°F). They are also lightweight and can be integrated into textiles.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of conductive polymers is their flexibility and ease of integration into various substrates. However, they generally have lower thermal stability and conductivity compared to metals, which can limit their application in high-temperature environments.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for smart garments and flexible heating applications, where comfort and adaptability are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific standards for conductive polymers in their regions. In Europe, for instance, adherence to REACH regulations regarding chemical safety is crucial.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper is known for its excellent electrical conductivity and thermal properties, with a melting point of approximately 1,085°C (1,985°F). It is also resistant to corrosion in many environments.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of copper include its high conductivity and relatively low cost. However, it is heavier than other materials and can be prone to oxidation if not properly coated or treated.
Impact on Application: Copper is commonly used in electric heating elements for applications requiring efficient heat transfer, such as in heating coils and industrial heaters.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards is essential, particularly for electrical safety. Buyers should also consider the sourcing and availability of copper, which may fluctuate based on global market conditions.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for electric heat element | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickel-Chromium Alloys | Industrial furnaces, heating appliances | High-temperature resistance | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Carbon Fiber | Flexible heating elements in garments | Lightweight, high strength | Lower durability under extreme conditions | Medium |
| Conductive Polymers | Smart garments, portable heating devices | Flexibility and adaptability | Lower thermal stability | Medium |
| Copper | Heating coils, industrial heaters | Excellent conductivity | Prone to oxidation, heavier | Low |
This comprehensive analysis provides international B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding material selection for electric heat elements, considering both performance and regional compliance factors.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for electric heat element
Manufacturing Processes for Electric Heat Elements
The production of electric heat elements involves a series of well-defined stages that ensure the final product meets performance and safety standards. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers assess potential suppliers and make informed purchasing decisions.
1. Material Preparation
Material Selection: The manufacturing process begins with the selection of appropriate materials. Common conductive materials include metallic options like copper and aluminum, as well as non-metallic materials like carbon fibers and conductive polymers. The choice depends on the desired thermal properties, flexibility, and application.
Processing Techniques:
– Metallic Materials: These often undergo processes like extrusion or drawing to form wires and sheets.
– Non-Metallic Materials: Conductive polymers are typically synthesized through chemical processes, while carbon fibers may be woven into fabrics or formed into films.
Quality Control: During material preparation, samples are often tested for conductivity, tensile strength, and thermal stability to ensure they meet industry standards.
2. Forming
Shaping Techniques: The forming stage involves shaping the selected materials into the desired configuration for heating elements. This can be accomplished through:
– Weaving or Knitting: For flexible heating fabrics, conductive fibers are woven or knitted into textiles.
– Coating: A conductive layer can be applied to a substrate material using techniques like screen printing or spray coating to create heating films.
Quality Assurance: Continuous monitoring during forming ensures dimensional accuracy and material integrity. Any defects can be identified early, reducing waste and improving efficiency.
3. Assembly
Component Integration: After forming, the components are assembled. This may involve:
– Incorporating Insulation: Insulation materials are added to prevent heat loss and ensure user safety.
– Integration with Control Systems: Electrical connections are made to integrate the heating element with temperature sensors and control modules.
Testing During Assembly: In-process quality checks (IPQC) are critical at this stage to ensure that all components are correctly aligned and functioning.
4. Finishing
Final Treatments: The finishing stage includes protective coatings or treatments that enhance durability and resistance to environmental factors.
– Coating for Protection: Elements may be coated with materials that provide moisture and chemical resistance.
– Final Assembly: The finished product is assembled into its final form, such as clothing or appliance components.
Final Quality Control: A final inspection (FQC) is conducted to ensure that the product meets all specifications and performance standards before shipping.
Quality Assurance Standards and Practices
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of electric heat elements. International B2B buyers should be familiar with relevant standards and practices that ensure product safety and efficacy.
International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is crucial for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate consistent quality. Compliance with ISO 9001 ensures that processes are standardized and continuously improved.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements. Manufacturers must conduct thorough testing and documentation to obtain CE certification for their electric heat elements.
-
API Standards: For applications in specific industries, such as oil and gas, compliance with American Petroleum Institute (API) standards may be necessary to ensure safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during manufacturing to identify and rectify issues in real-time.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of finished products to verify they meet all quality and safety standards before dispatch.
Common Testing Methods
- Electrical Testing: Conductivity tests ensure that heating elements can effectively conduct electricity without excessive resistance.
- Thermal Testing: Evaluates the heating performance and efficiency under various conditions.
- Durability Testing: Assess the product’s longevity and performance under stress, including environmental exposure.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is crucial. Here are actionable steps to ensure compliance and reliability:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and compliance with international standards.
-
Request Quality Reports: Ask for documentation of quality control processes, including IQC, IPQC, and FQC reports, to understand how the supplier maintains product quality.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to conduct independent evaluations of manufacturing facilities and product quality. This is particularly valuable for buyers from regions with varying regulatory environments.
Navigating QC and Certification Nuances
International B2B buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate diverse regulatory landscapes. Here are some considerations:
-
Regional Regulations: Be aware of local regulations that may impact the acceptance of products, including additional certifications required for specific markets.
-
Cultural Expectations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding product quality and safety. Understanding these nuances can help in selecting suppliers that align with market needs.
-
Documentation: Ensure that suppliers provide all necessary documentation for certifications, including test results and compliance reports. This documentation is vital for customs clearance and market entry.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for electric heat elements, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
Related Video: Amazing factories | Manufacturing method and top 4 processes | Mass production process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for electric heat element Sourcing
In the context of sourcing electric heating elements, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This analysis will cover the key cost components, price influencers, and strategic buyer tips, particularly focusing on markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in electric heat elements is the raw materials used, which typically include conductive metals (like copper and aluminum), conductive polymers, and insulation materials. The choice of materials significantly affects both the performance and durability of the heating elements.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the manufacturing location. Countries with lower labor costs can offer more competitive pricing, but this may impact quality and lead times. Consideration of skilled versus unskilled labor is also essential, particularly for precision manufacturing processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facilities, utilities, and administrative expenses. Efficient production processes can reduce overhead, which is often passed on to buyers in the form of lower prices.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specialized heating elements can be a substantial upfront cost. Buyers should assess whether the tooling costs can be amortized over a large production run, as this can significantly affect per-unit pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the heating elements meet required specifications and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it is critical for maintaining quality, especially in industries where safety is paramount.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary based on the origin of the product and the delivery location. Understanding the logistics involved, including potential tariffs and import duties, is essential for calculating the total landed cost.
-
Margin: Supplier margins will vary based on market conditions, competitive pressures, and the perceived value of the product. Understanding the market landscape can help buyers negotiate better terms.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for bulk orders, making it advantageous for buyers to consolidate orders whenever possible.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized heating elements typically incur higher costs due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes. Buyers should carefully evaluate the necessity of custom features against standard options.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can influence both the cost and performance characteristics of the heating elements. Buyers should assess the trade-offs between material quality and pricing.
-
Quality/Certifications: Compliance with international quality standards and certifications can impact pricing. While certified products may cost more upfront, they can lead to savings over time through reduced failure rates and warranty claims.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge a premium, but the reliability and support they provide can justify the cost.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the terms of trade (Incoterms) is crucial for calculating total costs. Different terms can shift responsibilities for costs and risks between buyers and suppliers.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage multiple quotes from different suppliers to enhance negotiation power. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can also lead to better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, operating costs, and potential maintenance expenses. A lower initial price may not always equate to better value.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, geopolitical factors, and local market conditions that can impact pricing.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand regional pricing trends and supplier options. This knowledge will empower buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for electric heating elements can vary widely based on the factors discussed. This analysis provides indicative pricing insights, and buyers are encouraged to seek specific quotes tailored to their unique requirements and circumstances.
Spotlight on Potential electric heat element Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘electric heat element’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for electric heat element
Key Technical Properties of Electric Heat Elements
When selecting electric heat elements for industrial applications, understanding their technical properties is crucial. Here are the essential specifications that international B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
– The material used in electric heat elements significantly affects their performance. Common materials include stainless steel, copper, and conductive polymers. Each material has unique thermal and electrical conductivity properties, which impact heating efficiency and durability. Buyers must assess the material grade to ensure it meets the specific environmental conditions and operational demands of their applications. -
Power Rating (Watts)
– The power rating indicates the amount of heat generated by the element per unit time, typically measured in watts. This specification is vital for determining whether the heating element can achieve the desired temperature within a specific time frame. Understanding power requirements helps buyers match heating elements with their operational needs, avoiding underperformance or energy inefficiencies. -
Temperature Range
– Electric heat elements operate within specified temperature ranges. Knowing the maximum and minimum temperature limits is essential for application safety and effectiveness. Buyers should ensure that the selected elements can withstand the operating conditions without degrading or failing, particularly in demanding environments like industrial processes or outdoor applications. -
Resistance Tolerance
– Resistance tolerance refers to the permissible variation in resistance values of the heating element. This specification is crucial for ensuring consistent performance and energy efficiency. Buyers should consider elements with resistance tolerances that align with their operational stability requirements to avoid fluctuations in heating performance that could lead to product quality issues. -
Flexibility and Form Factor
– The design and flexibility of electric heat elements, such as flexible heating fabrics or rigid plates, are vital depending on the application. Flexibility allows integration into various products, including smart garments. Buyers need to evaluate the form factor to ensure compatibility with their design specifications and operational constraints.
Common Trade Terminology
Understanding industry jargon can enhance communication and streamline transactions. Here are some key terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of electric heat elements, OEMs can provide customized solutions tailored to specific industrial applications. This term is important for buyers looking to source components from manufacturers that can meet their unique requirements.
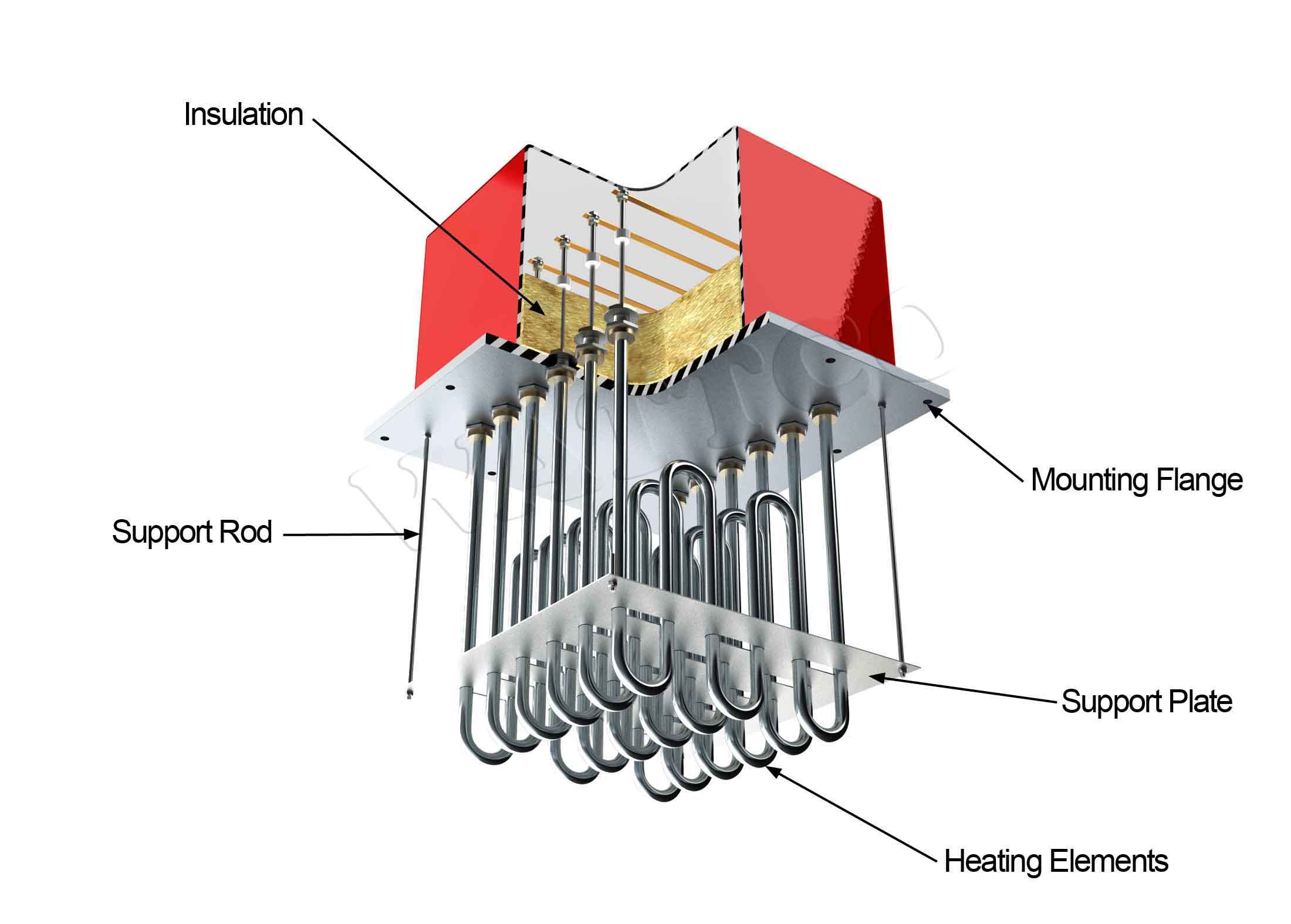
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding the MOQ is crucial for B2B buyers to manage their inventory effectively and avoid overstocking or stockouts. Suppliers often set MOQs based on production costs and logistics, so buyers should assess their purchasing strategy accordingly. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a formal process where buyers request price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. This process is essential for obtaining competitive pricing and understanding market conditions. B2B buyers should prepare detailed RFQs that outline their requirements to receive accurate and comprehensive quotes from suppliers. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify aspects such as shipping costs, risk transfer, and delivery points. Familiarity with Incoterms helps B2B buyers navigate logistics and ensure that both parties understand their obligations, thereby reducing the risk of disputes. -
Lead Time
– Lead time is the duration between placing an order and receiving the product. Understanding lead times is crucial for buyers to plan their production schedules and manage inventory. Buyers should communicate their timelines clearly to suppliers to ensure timely delivery, especially when dealing with complex manufacturing processes. -
Certification Standards
– Certification standards refer to the regulatory and safety standards that products must meet to be sold in specific markets. Compliance with these standards is essential for ensuring product safety and legality. Buyers should verify that electric heat elements meet relevant certifications to avoid potential legal and operational issues.
By grasping these technical properties and industry terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing electric heat elements, ultimately enhancing their operational efficiency and product quality.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the electric heat element Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The electric heat element sector is undergoing transformative changes driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Global drivers include the urgent need to reduce carbon emissions, the rising cost of fossil fuels, and the push for renewable energy sources. International B2B buyers are seeing a shift towards flexible electric heating solutions that offer improved thermal comfort, especially in industries such as textiles, automotive, and construction. Emerging technologies in conductive materials, such as conductive polymers and carbon nanomaterials, are enhancing the performance and safety of electric heating elements.
Current sourcing trends indicate a growing interest in smart heating garments and systems that provide real-time monitoring and control capabilities. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer integrated solutions that not only meet performance standards but also align with sustainability goals. Furthermore, digitalization in supply chains is allowing for better tracking of materials and production processes, which is essential for meeting the evolving demands of eco-conscious consumers.
Market dynamics are also shifting towards collaborative partnerships between manufacturers and buyers. This collaboration is crucial for developing tailored solutions that address specific regional challenges, such as extreme weather conditions in Africa and Europe. As a result, B2B buyers should seek suppliers that demonstrate innovation, flexibility, and a commitment to quality and sustainability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the electric heat element sector. The environmental impact of traditional heating methods, primarily based on fossil fuels, has led to a significant focus on green alternatives. Electric heating solutions, particularly those utilizing renewable energy sources, present an effective way to reduce carbon footprints.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses face increasing pressure to ensure that their supply chains are transparent and responsible. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to ethical practices, such as fair labor conditions and sustainable material sourcing. Additionally, certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Energy Star can help in identifying suppliers committed to sustainable practices.
Investing in green materials, such as recyclable or biodegradable conductive polymers, not only enhances the sustainability of electric heat elements but also appeals to environmentally conscious consumers. B2B buyers must engage with suppliers who are proactive in their sustainability efforts, as this can enhance brand reputation and customer loyalty in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of electric heat elements can be traced back to the early 20th century when electric heating was first introduced as a viable alternative to traditional fossil fuel methods. Initially utilized in industrial settings, advancements in material science and technology have expanded their applications into consumer products, including smart garments and flexible heating solutions.
Recent innovations focus on enhancing efficiency and flexibility, addressing the needs of modern industries and consumers alike. As electric heat elements continue to evolve, their integration into smart technologies signifies a promising future, aligning with global sustainability goals and the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions.
This historical context provides B2B buyers with insight into the trajectory of the electric heat element sector, emphasizing the importance of partnering with forward-thinking suppliers committed to innovation and sustainability.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of electric heat element
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for electric heating elements?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry reputation, production capacity, and quality assurance processes. Request references and case studies to evaluate their experience with similar projects. It’s also crucial to assess their compliance with international standards and certifications, such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their ability to provide customized solutions tailored to your specific needs, as well as their responsiveness and communication skills. -
Can electric heating elements be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for electric heating elements, including size, shape, and material composition. It’s essential to communicate your specific requirements clearly, including operational temperature ranges and application context. Discussing these details early in the procurement process can help ensure that the final product meets your expectations and operational needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for electric heating elements?
MOQs for electric heating elements can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs range from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times also depend on the supplier’s production capacity and customization requirements, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s advisable to confirm these details during initial discussions to avoid delays in your supply chain. -
What payment terms are standard for international purchases of electric heating elements?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the balance before shipment. For larger orders, suppliers may offer more flexible terms, such as letters of credit or staggered payments based on delivery milestones. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure the payment method is secure to mitigate financial risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for electric heating elements?
Request detailed documentation from suppliers regarding their quality assurance processes and certifications. Ask for product samples to evaluate quality firsthand and consider third-party testing for compliance with relevant standards (e.g., CE, UL). Establishing a clear quality control process, including inspections at different production stages, will help ensure that the products meet your specifications and regulatory requirements. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing electric heating elements internationally?
Logistics considerations include understanding shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs regulations, and import duties applicable to your region. Collaborate with your supplier to ensure that they have experience in international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs clearance. It’s also wise to plan for potential delays in transit and to choose a logistics partner that can handle your specific needs effectively. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding electric heating elements?
To handle disputes effectively, first, maintain open communication with the supplier to address concerns directly. If issues arise, refer to your contract’s terms and conditions, particularly those related to warranties and returns. Consider involving a third-party mediator if necessary, especially for significant disputes. Having a clear dispute resolution process outlined in your contracts can help mitigate potential conflicts. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing electric heating elements internationally?
Common challenges include language barriers, cultural differences, and varying quality standards across regions. Additionally, fluctuations in currency exchange rates can impact pricing. To navigate these challenges, conduct thorough market research and build relationships with reliable suppliers. Regular communication and clear expectations will also help minimize misunderstandings and ensure a smoother procurement process.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for electric heat element
In the evolving landscape of electric heat elements, strategic sourcing emerges as a critical component for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality, sustainability, and innovation, companies can significantly enhance their operational efficiencies while minimizing environmental impacts. The shift towards electric heating solutions not only addresses pressing climate challenges but also aligns with global trends in energy efficiency and reduced carbon footprints.
B2B buyers must focus on establishing robust partnerships with reliable suppliers who offer flexible heating solutions and innovative materials, such as conductive polymers and carbon-based technologies. This approach ensures access to the latest advancements in electric heating technology, enabling businesses to remain competitive in their respective markets.
As we look to the future, the demand for sustainable heating solutions will only increase. It is essential for buyers to stay informed about emerging technologies and market trends to make educated sourcing decisions. Engaging with thought leaders and attending industry events can provide valuable insights. By embracing these strategic sourcing practices, international B2B buyers can position themselves at the forefront of the electric heat element market, driving growth and sustainability in their operations.