Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Thermoplastic Injection
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for thermoplastic injection molding
Thermoplastic injection molding stands as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling the production of high-quality, complex parts across a multitude of industries. This process is critical for international B2B buyers seeking to optimize their supply chains and enhance product performance. With its ability to deliver precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, thermoplastic injection molding is essential for sectors ranging from automotive to consumer electronics, and even medical devices.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of thermoplastic injection molding, encompassing various types of materials, manufacturing techniques, quality control measures, and sourcing strategies. It delves into the nuances of selecting the right thermoplastics, understanding manufacturing processes, and evaluating suppliers to make informed purchasing decisions. Key insights on cost analysis and market trends will empower buyers from diverse regions—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—to navigate the complexities of the global market effectively.
By engaging with this guide, B2B buyers will gain the knowledge required to streamline their sourcing strategies, ensuring they select the most suitable materials and partners for their specific needs. The information presented here is designed to enhance decision-making capabilities, ultimately driving innovation and competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Understanding thermoplastic injection molding Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Injection Molding | Utilizes a single mold for high-volume production | Consumer goods, automotive parts | Pros: Cost-effective for large runs. Cons: High initial mold costs. |
| Multi-material Injection Molding | Combines different thermoplastics in a single process | Electronics, automotive, medical devices | Pros: Enhanced functionality and aesthetics. Cons: Complex machinery and higher costs. |
| Gas-Assisted Injection Molding | Uses gas to create hollow parts, reducing material use | Automotive, furniture, and packaging | Pros: Lightweight parts with reduced material costs. Cons: Requires specialized equipment. |
| Structural Foam Injection Molding | Creates lightweight, rigid foam structures | Packaging, automotive, and consumer products | Pros: Good insulation properties and low weight. Cons: Limited design flexibility compared to solid parts. |
| Insert Molding | Integrates metal or other materials into the plastic part | Electronics, automotive, and industrial components | Pros: Improved strength and functionality. Cons: Increased complexity in design and production. |
Standard Injection Molding
Standard injection molding is the most common method for producing thermoplastic parts. It involves injecting molten thermoplastic into a single mold, making it ideal for high-volume production runs. This method is particularly suitable for manufacturing consumer goods and automotive components. Buyers should consider the initial investment in mold design and production, as it can be significant. However, the cost per unit decreases with higher production volumes, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale applications.
Multi-material Injection Molding
This innovative technique allows for the simultaneous injection of multiple thermoplastics, resulting in parts that leverage the unique properties of each material. It is commonly used in industries such as electronics and automotive, where complex components require different functionalities. Buyers should weigh the benefits of enhanced part performance and aesthetics against the higher costs and complexity of the machinery involved. This method is ideal for products that demand a combination of durability and visual appeal.
Gas-Assisted Injection Molding
Gas-assisted injection molding employs gas to create hollow sections within parts, which can significantly reduce material usage while maintaining structural integrity. This technique is particularly effective for automotive and packaging applications, where lightweight components are advantageous. Buyers should consider the potential for lower material costs and enhanced design flexibility but remain aware of the need for specialized equipment and expertise to implement this method effectively.
Structural Foam Injection Molding
Structural foam injection molding generates lightweight, rigid parts by injecting a gas into the molten thermoplastic, creating a foam-like structure. This method is widely used in the packaging and automotive sectors due to its excellent insulation properties and reduced weight. While it offers significant advantages in terms of material efficiency, buyers must consider the limitations in design flexibility compared to solid parts. The initial setup costs may also be higher, but the long-term benefits often justify the investment.
Insert Molding
Insert molding integrates metal or other materials into thermoplastic components, enhancing their strength and functionality. This technique is prevalent in the electronics and automotive industries, where durability and performance are critical. Buyers should evaluate the added value of improved part performance against the increased complexity and costs associated with design and production. Insert molding is particularly beneficial for applications requiring a combination of plastic and metal components, enabling innovative product designs.
Related Video: Technology of Injection Molding Level 3, lesson 1, plastic types
Key Industrial Applications of thermoplastic injection molding
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of thermoplastic injection molding | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Production of interior and exterior components | Lightweight, durable parts that enhance vehicle performance | Material selection for impact resistance and aesthetics |
| Consumer Electronics | Manufacturing of housings and components | Cost-effective, high-volume production of intricate designs | Compliance with international safety and quality standards |
| Medical Devices | Creation of non-invasive medical equipment | High precision and biocompatibility for patient safety | Certification requirements and material traceability |
| Building & Construction | Fabrication of fittings and structural components | Improved durability and resistance to environmental factors | Availability of local suppliers and logistics efficiency |
| Packaging | Development of containers and protective packaging | Enhanced product protection and shelf appeal | Sustainability of materials and recyclability options |
Automotive
In the automotive industry, thermoplastic injection molding is crucial for producing both interior and exterior components such as dashboards, bumpers, and trims. These components require materials that are lightweight yet durable, contributing to overall vehicle efficiency and performance. International buyers should focus on sourcing high-quality engineering thermoplastics that meet specific standards for impact resistance and aesthetic appeal, ensuring compliance with regional automotive regulations.
Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics sector relies heavily on thermoplastic injection molding for the manufacturing of housings, connectors, and intricate components. This process allows for the cost-effective production of complex designs at high volumes, which is essential for competitive pricing. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that adhere to international safety and quality standards, ensuring that all products meet the necessary certifications for electronics.
Medical Devices
Thermoplastic injection molding is employed in the medical device industry to create non-invasive equipment, such as syringes, inhalers, and diagnostic tools. The precision of this manufacturing process is vital for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of medical devices. International buyers must consider stringent certification requirements and material traceability to guarantee that all products meet regulatory standards for patient safety and efficacy.
Building & Construction
In the building and construction sector, thermoplastic injection molding is used for fabricating fittings, pipes, and structural components that require high durability and resistance to environmental factors. These components are essential for maintaining structural integrity and ensuring longevity in construction projects. Buyers should evaluate the availability of local suppliers and consider logistics efficiency to minimize costs and lead times.
Packaging
The packaging industry utilizes thermoplastic injection molding to develop containers, bottles, and protective packaging solutions. This application is crucial for enhancing product protection and shelf appeal, directly influencing consumer purchasing decisions. Buyers should focus on the sustainability of materials used in packaging, looking for options that are recyclable or made from recycled content to meet growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Related Video: Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) Injection Molding
Strategic Material Selection Guide for thermoplastic injection molding
When selecting materials for thermoplastic injection molding, international B2B buyers must consider several factors, including mechanical properties, cost implications, and compliance with regional standards. Below are analyses of four common thermoplastic materials used in injection molding, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, application impacts, and specific considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Key Properties:
ABS is known for its excellent impact resistance, toughness, and surface hardness. It performs well at temperatures ranging from -20°C to 80°C and has good chemical resistance against acids and alkalis.
Pros & Cons:
The material is relatively easy to mold and provides a good balance of mechanical toughness and aesthetic qualities. However, it can be susceptible to stress cracking when exposed to certain chemicals, which may limit its applications in harsh environments.
Impact on Application:
ABS is widely used in automotive components, consumer goods, and electronic housings. Its compatibility with various media makes it suitable for a range of applications, but care must be taken in environments with aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that ABS products comply with relevant standards such as ASTM and ISO. In regions like the UK and Saudi Arabia, understanding local regulations regarding plastic materials is crucial for market entry.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Key Properties:
Polycarbonate is characterized by its high impact resistance, transparency, and thermal stability, with a temperature range of -40°C to 120°C. It also exhibits good dimensional stability under heat.
Pros & Cons:
While PC offers exceptional durability and is suitable for applications requiring transparency, it can be more expensive than other thermoplastics. Additionally, it may require special handling during processing due to its sensitivity to moisture.
Impact on Application:
Commonly used in safety glasses, automotive components, and electronic housings, polycarbonate’s optical clarity makes it ideal for applications where visibility is essential. However, its moisture sensitivity can affect the final product’s quality if not managed properly.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the potential for regulatory scrutiny regarding the use of polycarbonate in consumer products, especially in Europe, where REACH regulations may apply. Ensuring compliance with local standards is vital.
Nylon (Polyamide)
Key Properties:
Nylon is known for its excellent mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and low friction properties. It can withstand temperatures from -40°C to 120°C and has good chemical resistance, particularly to oils and fuels.
Pros & Cons:
Nylon’s durability and versatility make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive to textiles. However, it can absorb moisture, which may lead to dimensional changes and affect mechanical properties if not properly dried before processing.
Impact on Application:
Nylon is often used in applications requiring high strength and wear resistance, such as gears and bearings. Its moisture absorption can impact performance in humid environments, which is a critical consideration for buyers in tropical regions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of moisture-resistant grades of nylon, especially in regions with high humidity. Compliance with ASTM and ISO standards is also important for ensuring product quality and safety.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is lightweight, flexible, and has excellent chemical resistance, with a temperature range of -20°C to 100°C. It also exhibits good fatigue resistance and low moisture absorption.
Pros & Cons:
The material is cost-effective and easy to process, making it a popular choice for a variety of applications. However, its lower impact resistance compared to other thermoplastics can limit its use in demanding applications.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is commonly used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for applications involving various media, but its lower strength may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that polypropylene products meet local compliance standards, as regulations can vary significantly across regions. Understanding the specific needs of local markets is essential for successful product development.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for thermoplastic injection molding | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Automotive components, consumer goods | Good impact resistance and toughness | Susceptible to stress cracking | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Safety glasses, automotive parts | High impact resistance and clarity | More expensive, moisture sensitive | High |
| Nylon | Gears, bearings, textiles | Excellent mechanical strength | Moisture absorption can affect properties | Medium |
| Polypropylene | Packaging, automotive parts, consumer goods | Cost-effective and flexible | Lower impact resistance | Low |
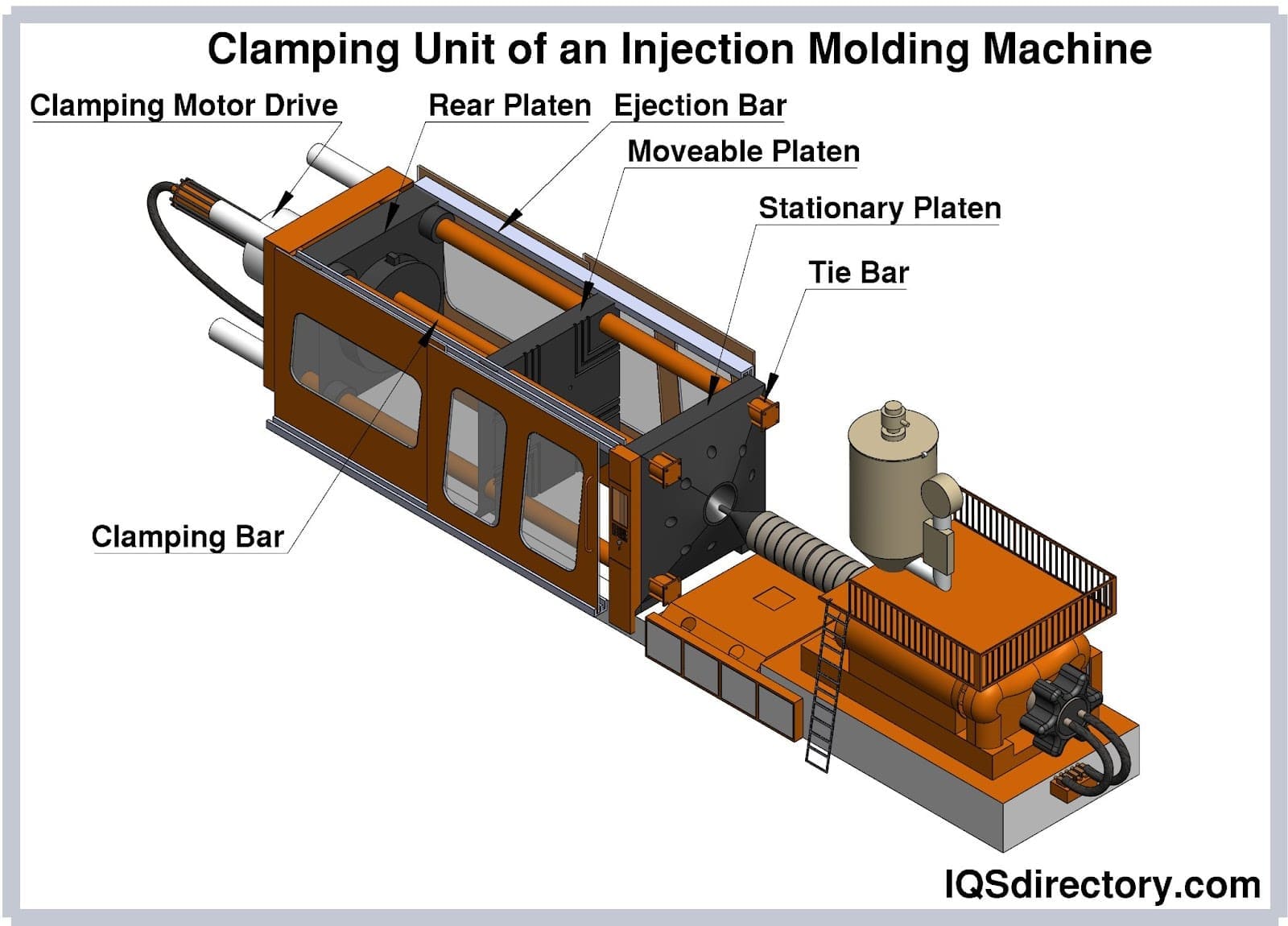
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for thermoplastic injection molding
The manufacturing process for thermoplastic injection molding involves several critical stages, each with its own set of techniques that ensure the production of high-quality components. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these stages and the associated quality assurance measures is vital for making informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in thermoplastic injection molding is material preparation. This involves selecting and processing the thermoplastic resin, which typically comes in the form of pellets. Key steps include:
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Drying: Most thermoplastics require drying to remove moisture that can cause defects during molding.
- Coloring and Additives: Depending on the final application, additives such as colorants, stabilizers, or fillers may be mixed with the resin to enhance properties like strength, flexibility, or UV resistance.
2. Forming
The forming stage is where the actual molding occurs. This includes several key techniques:
- Injection: The dried resin pellets are fed into a heated barrel where they are melted and then injected into a mold under high pressure. The precision of this step is critical to ensure that the molten material fills the mold completely and uniformly.
- Cooling: Once injected, the material is cooled to solidify into the desired shape. The cooling rate can significantly affect the physical properties of the final product, influencing factors such as strength and surface finish.
3. Assembly
In many cases, thermoplastic parts require assembly to form a complete product. This may involve:
- Joining Techniques: Various methods such as welding, adhesive bonding, or mechanical fastening can be used depending on the materials and design.
- Incorporation of Other Components: This stage often includes integrating electronic components, seals, or other functional parts into the thermoplastic assembly.
4. Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which enhances the product’s appearance and performance. Common finishing techniques include:
- Trimming and Deburring: Removing excess material and sharp edges to ensure safety and aesthetic appeal.
- Surface Treatments: Processes like painting, plating, or coating can be applied for improved durability or visual characteristics.
Quality Assurance in Injection Molding
Quality assurance is an essential component of the manufacturing process, ensuring that products meet specified standards and customer expectations. For international B2B buyers, understanding quality control measures is crucial for minimizing risks associated with product defects.
International Standards and Certifications
Several international standards govern quality assurance in manufacturing:
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing consistent quality and continuous improvement. Suppliers with ISO 9001 certification demonstrate their commitment to quality.
- CE Marking: Particularly relevant for products sold in the European market, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For buyers in the oil and gas sector, API (American Petroleum Institute) certification ensures that products meet industry-specific quality and safety standards.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control typically involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components before they enter the production line. This ensures that only materials meeting specified criteria are used.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects in real-time. This may include checking temperatures, pressures, and cycle times.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of finished products to ensure they meet all specifications and standards before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to verify product quality:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluates properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and hardness.
- Dimensional Inspection: Uses tools like calipers and gauges to ensure that products meet dimensional specifications.
- Visual Inspection: A straightforward method to identify surface defects and ensure overall product quality.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is essential. Here are several actionable steps:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include both announced and unannounced visits.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports that outline inspection results, testing methods used, and any corrective actions taken in response to defects.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to provide unbiased evaluations of product quality before shipment. This can help identify potential issues that may not be caught in standard inspections.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
International buyers should be aware of specific nuances in quality control that may vary by region:
- Regional Standards Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are compliant with both international and local regulations relevant to your market. For example, regulations may differ significantly between the EU and Middle Eastern countries.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying approaches to quality assurance. Understanding these differences can help buyers communicate their expectations more effectively.
- Logistics and Transportation: Quality assurance doesn’t end at production. Consider how products are packaged and transported, as improper handling can lead to defects even after passing quality checks.
By understanding the comprehensive manufacturing processes and robust quality assurance measures associated with thermoplastic injection molding, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring that they source high-quality products that meet their specifications and standards.
Related Video: Automotive Dashboard Injection Molding | Plastic Injection molding | Large Mold Manufacturing | Mold
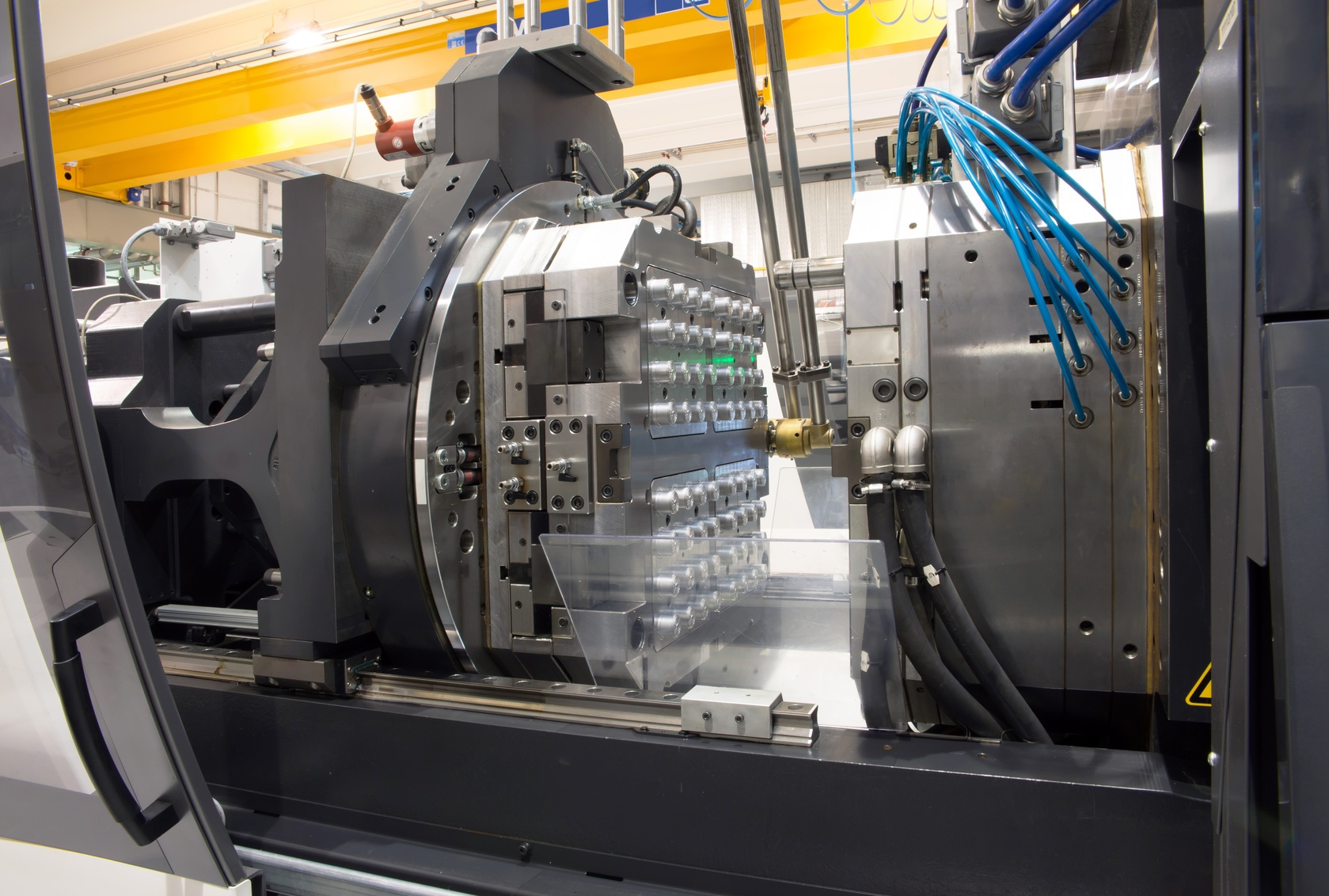
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for thermoplastic injection molding Sourcing
The cost structure for thermoplastic injection molding is multifaceted and requires careful consideration by international B2B buyers. Understanding the various components that contribute to the overall cost can facilitate better negotiation and sourcing strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of thermoplastic resin significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials like ABS, polycarbonate, and nylon vary in price based on their properties and market demand. Buyers should evaluate the specific requirements of their application to select the most cost-effective material without compromising quality.
-
Labor: Labor costs can vary widely depending on the location of the manufacturing facility. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing, but buyers should also consider the skill level and expertise of the workforce, which can impact the quality of the final product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with running the production facility, such as utilities, equipment maintenance, and administrative expenses. Efficient operations can help reduce overhead costs, thus lowering the overall price.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs are significant in injection molding. Custom molds can be expensive to produce, with costs ranging from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars. Buyers should consider the volume of production; higher volumes can justify the initial tooling investment, leading to lower per-unit costs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures that the products meet the required specifications and certifications. While this adds to the cost, it can prevent expensive recalls or rework, ultimately saving money in the long run.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen shipping method. Understanding Incoterms is crucial, as they dictate who bears the risk and costs associated with transportation.
-
Margin: Supplier margins can vary based on their operational efficiencies and market positioning. Buyers should explore multiple suppliers to understand the typical margins in their specific market segment.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence pricing in thermoplastic injection molding:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes often lead to reduced unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) that align with their production needs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific material requirements may increase costs. It is essential to balance customization needs with budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products that require specific quality certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) may incur additional costs. Buyers should assess whether these certifications are necessary for their applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms can help buyers manage shipping costs and risks effectively. Terms like FOB (Free On Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) influence total landed costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiate: Leverage competitive quotes from multiple suppliers to negotiate better prices. Transparency about competing offers can be beneficial.
-
Cost Efficiency: Focus on total cost of ownership rather than just unit price. Consider long-term costs associated with quality, maintenance, and potential rework.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, suppliers in Europe may have higher operational costs compared to those in Africa or South America, impacting pricing structures.
-
Long-term Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and improved service. Consider entering into contracts for consistent volume to secure favorable terms.
Disclaimer
Prices in thermoplastic injection molding can vary widely based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and specific project requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential thermoplastic injection molding Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘thermoplastic injection molding’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for thermoplastic injection molding
Thermoplastic injection molding is a sophisticated manufacturing process that relies on specific technical properties and industry terminology. Understanding these elements is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, as they navigate sourcing and procurement.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of thermoplastics based on their mechanical and thermal properties, which dictate their performance in specific applications.
– Importance: Different material grades offer varying strength, flexibility, and resistance to heat and chemicals. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate grade ensures that the final product meets industry standards and application requirements. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The allowable deviation from a specified dimension in the manufacturing process.
– Importance: Tolerance is critical in ensuring that parts fit and function correctly within assemblies. High precision can reduce rework costs and enhance product quality, making it an essential consideration for buyers focused on operational efficiency. -
Melt Flow Index (MFI)
– Definition: A measure of the viscosity of a thermoplastic resin when melted, indicated by the rate at which it flows through a standard die at a specified temperature and load.
– Importance: MFI affects how well a material can be processed in injection molding. Understanding MFI helps buyers select materials that will perform optimally in their specific molding conditions, impacting production speed and quality. -
Impact Resistance
– Definition: The ability of a thermoplastic to withstand sudden force or shock without breaking.
– Importance: Materials with high impact resistance are crucial for applications where durability is paramount, such as automotive and consumer electronics. Buyers must assess this property to ensure their products can endure the expected environmental stresses. -
Thermal Stability
– Definition: The capability of a thermoplastic to maintain its properties at elevated temperatures without degradation.
– Importance: Thermal stability is vital for applications exposed to heat. Buyers should consider this property to prevent product failure in high-temperature environments, ensuring longevity and reliability.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships is critical for buyers looking to source components for their products. It can influence pricing, quality assurance, and supply chain dynamics. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for buyers to manage inventory and cash flow effectively. It also impacts negotiations and sourcing strategies, especially for smaller companies or startups. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare pricing and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating informed purchasing decisions. This process is crucial for budget management and cost control. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms that outline the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and risks in international transactions, enabling smoother logistics and clearer agreements. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order until the product is delivered.
– Importance: Understanding lead times is crucial for inventory management and production planning. Buyers need to factor this into their schedules to avoid production delays and maintain supply chain efficiency.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance their procurement processes and ultimately contribute to their operational success.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the thermoplastic injection molding Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The thermoplastic injection molding sector is experiencing significant transformation driven by several global factors. Technological advancements in manufacturing processes, such as automation and Industry 4.0 technologies, are enhancing production efficiency and reducing costs. International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who leverage these innovations. Sourcing trends are shifting towards suppliers that can provide rapid prototyping services and customized solutions, allowing companies to adapt swiftly to market demands.
Additionally, the growing emphasis on lightweight materials is reshaping product design in sectors like automotive and aerospace, where fuel efficiency is paramount. The adoption of bio-based and recycled thermoplastics is on the rise, driven by sustainability goals and consumer demand for environmentally friendly products. Moreover, buyers are keen on understanding the total cost of ownership (TCO) of their sourcing decisions, focusing not only on the initial purchase price but also on the long-term benefits and impacts of materials used.
The market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors, which can affect trade regulations and tariffs. Buyers must remain vigilant about changing policies in key regions, particularly as trade agreements evolve. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for B2B buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing in an increasingly interconnected global market.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of sourcing strategies in the thermoplastic injection molding sector. The environmental impact of plastic production is substantial, prompting businesses to consider their role in reducing waste and promoting responsible sourcing practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 or the Cradle to Cradle certification, which indicate adherence to environmental management standards.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their suppliers for compliance with social responsibility standards, ensuring that labor practices are fair and that materials are sourced responsibly. Utilizing green materials, such as recycled thermoplastics or bioplastics, not only reduces the carbon footprint but also appeals to a growing segment of eco-conscious consumers.
Moreover, companies that invest in sustainable practices often enjoy enhanced brand loyalty and competitive advantage. By aligning procurement strategies with sustainability goals, international B2B buyers can foster long-term partnerships that are not only economically viable but also environmentally responsible.
Brief Evolution/History
The thermoplastic injection molding industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially dominated by traditional materials such as polystyrene and polyethylene, the sector began to expand with the introduction of engineering thermoplastics in the 1960s. These materials offered enhanced properties, such as higher strength and thermal stability, making them suitable for more demanding applications.
In recent decades, the focus has shifted towards innovation and sustainability, with advancements in material science leading to the development of high-performance thermoplastics. This evolution has allowed manufacturers to meet the increasing demands for lightweight, durable, and recyclable products, particularly in industries like automotive and consumer electronics. As the market continues to advance, understanding its historical context can provide valuable insights for B2B buyers navigating current trends and future opportunities.
Related Video: Global Trends Tutorial: Chapter 3: IPE
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of thermoplastic injection molding
-
How do I vet suppliers for thermoplastic injection molding?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with industry certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and a proven track record in thermoplastic injection molding. Request references and case studies from past clients to assess quality and reliability. Additionally, visit their facilities if possible, or conduct virtual audits to evaluate their production capabilities and quality control processes. Consider suppliers who are familiar with international standards and regulations relevant to your market, as this can significantly impact compliance and logistics. -
Can I customize products during the injection molding process?
Yes, customization is a significant advantage of thermoplastic injection molding. You can specify dimensions, material types, colors, and surface finishes to meet your unique requirements. Discuss your needs early in the design phase with the supplier to ensure they can accommodate your specifications. It’s also crucial to understand the implications of customization on lead times and costs, as complex designs may require additional resources and extended production schedules. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the parts. Generally, MOQs for injection molded parts can range from 1,000 to 10,000 units, but some suppliers may offer lower quantities for prototypes or smaller runs. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on factors such as tooling requirements, material availability, and production schedules. Always clarify these details upfront to plan your inventory and project timelines accordingly. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing from international suppliers?
Payment terms will vary by supplier and region but typically include options like upfront deposits (20-50%) with the balance due upon completion or shipment. It’s crucial to negotiate terms that are favorable to both parties while ensuring security. Consider using letters of credit or escrow services for larger orders to protect against potential disputes. Be aware of any international banking fees and currency exchange rates, which can impact overall costs. -
What quality assurance measures should I look for in suppliers?
Seek suppliers that implement robust quality assurance (QA) protocols throughout the injection molding process. This includes in-process inspections, final product testing, and adherence to international standards. Ask for certifications that demonstrate their commitment to quality, such as ISO certifications or compliance with specific industry regulations. Additionally, request detailed documentation of QA processes and ask about their procedures for handling defective products or non-conformities. -
How should I handle logistics and shipping when sourcing internationally?
Logistics can be complex in international trade, so it’s essential to work closely with your supplier to coordinate shipping methods that align with your timeline and budget. Discuss Incoterms to clarify responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Ensure that your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation to facilitate smooth customs clearance. Consider partnering with a freight forwarder who specializes in your target regions to streamline the process. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear contracts that outline expectations regarding quality, timelines, and payment terms. If issues arise, communicate directly with the supplier to address concerns promptly. Consider implementing a formal dispute resolution process, such as mediation or arbitration, to handle conflicts professionally and efficiently. Maintain thorough documentation of all communications and agreements to support your position if a dispute escalates. -
What certifications should my supplier have to ensure compliance with international standards?
Ensure that your supplier possesses relevant certifications that demonstrate compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems or ISO 14001 for environmental management. Depending on your industry, additional certifications may be necessary, such as FDA approval for medical devices or UL certification for electrical components. Verify these certifications with the issuing bodies and ask for documentation to ensure that your products meet the necessary regulatory requirements in your market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for thermoplastic injection molding
In conclusion, strategic sourcing in thermoplastic injection molding is essential for international B2B buyers looking to optimize their manufacturing processes. By prioritizing the selection of high-quality engineering thermoplastics, businesses can achieve significant improvements in product durability, performance, and cost efficiency. The versatility of thermoplastic materials allows for innovative designs that cater to diverse industry needs, from automotive to consumer electronics.
Key takeaways include:
- Material Selection: Understand the properties and benefits of various thermoplastics to choose the right material for your applications.
- Supplier Relationships: Establish strong partnerships with reliable suppliers who can provide consistent quality and support throughout the production process.
- Process Optimization: Invest in advanced injection molding technologies to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve product quality.
As the global market continues to evolve, staying informed about trends and innovations in thermoplastic injection molding will be crucial. International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should actively engage with suppliers and industry experts to leverage the full potential of this manufacturing process. Embrace the future of injection molding to drive growth and competitive advantage in your respective markets.