Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Blow Molding Companies
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for blow molding companies
In today’s fast-paced global economy, blow molding companies play a pivotal role in various industries, from packaging to automotive components. As businesses seek to innovate and streamline production processes, understanding the intricacies of blow molding is essential for maintaining a competitive edge. This guide aims to equip international B2B buyers—especially those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—with the knowledge necessary to navigate this specialized market effectively.
Blow molding, a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts, is integral to producing high-quality, durable products. This guide covers a comprehensive range of topics, including the various types of blow molding techniques, commonly used materials, manufacturing and quality control practices, supplier selection, and cost considerations. Additionally, it addresses market trends and common FAQs, ensuring that buyers have access to critical insights that facilitate informed sourcing decisions.
By leveraging the knowledge presented in this guide, B2B buyers will be empowered to identify reliable suppliers, negotiate better pricing, and enhance product quality. Understanding the dynamics of the blow molding industry not only helps in optimizing procurement strategies but also fosters long-term partnerships that can drive innovation and growth in diverse markets. Embrace this opportunity to deepen your understanding of blow molding companies and take your sourcing strategy to the next level.
Understanding blow molding companies Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extrusion Blow Molding | Uses a continuous tube of plastic; high production rates | Bottles, containers, and large parts | Pros: Cost-effective for large volumes. Cons: Limited design flexibility. |
| Injection Blow Molding | Combines injection and blow molding; precise control over thickness | High-precision containers and complex shapes | Pros: Excellent surface finish. Cons: Higher initial setup costs. |
| Stretch Blow Molding | Utilizes a preform that is stretched during the blow molding process | PET bottles and containers | Pros: Lightweight products with high strength. Cons: More complex machinery required. |
| Reheat Blow Molding | Involves reheating preforms before blowing; suitable for recycling materials | Large containers and specialty products | Pros: Can utilize recycled materials. Cons: Slower cycle times compared to other methods. |
| Multi-layer Blow Molding | Creates products with multiple layers for added barrier properties | Food packaging and medical containers | Pros: Enhanced product protection. Cons: More expensive due to complexity. |
Extrusion Blow Molding
Extrusion blow molding (EBM) is characterized by its use of a continuous tube of plastic that is inflated into a mold. This method is highly efficient for producing large volumes of products, making it ideal for items such as bottles and containers. B2B buyers should consider EBM when looking for cost-effective solutions for high-volume needs. However, the design flexibility is limited, which may not suit projects requiring intricate shapes or details.
Injection Blow Molding
Injection blow molding (IBM) integrates both injection and blow molding processes, allowing for precise control over wall thickness and product dimensions. This method is particularly suitable for high-precision applications, including pharmaceutical and cosmetic containers. Buyers should note that while IBM offers superior surface finishes and design capabilities, the initial setup costs can be higher compared to other methods, which may impact budget constraints.
Stretch Blow Molding
Stretch blow molding (SBM) involves stretching a preform before blowing it into shape, resulting in lightweight yet strong products. This technique is predominantly used for producing PET bottles and containers. B2B buyers looking for durability combined with weight efficiency will find SBM advantageous. However, the machinery involved can be more complex, which may require additional training or investment.
Reheat Blow Molding
Reheat blow molding (RBM) is a process that involves reheating preforms before they are blown into the final shape. This method is particularly beneficial for recycling materials, making it an environmentally friendly option. RBM is suitable for large containers and specialty products. Buyers should be aware that while this method allows for the use of recycled materials, it typically results in slower production cycles compared to other blow molding techniques.
Multi-layer Blow Molding
Multi-layer blow molding creates products with multiple layers, enhancing barrier properties and overall product protection. This method is commonly utilized in food packaging and medical containers where product integrity is crucial. B2B buyers will appreciate the added benefits of durability and protection, but should also consider the higher costs associated with the complexity of multi-layer designs. Understanding these factors is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Related Video: ASB-150 Series 1-Step Injection Stretch Blow Molding Machines from Nissei ASB
Key Industrial Applications of blow molding companies
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of blow molding companies | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Packaging | Production of bottles and containers | Reduces material costs while enhancing product protection | Ensure compliance with local regulations and sustainability standards |
| Automotive | Manufacturing of fuel tanks and components | Lightweight solutions that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions | Evaluate durability and resistance to environmental factors |
| Consumer Goods | Creation of household items like toys | Customization options that cater to diverse markets and increase consumer appeal | Look for suppliers with advanced design capabilities and quality certifications |
| Medical Devices | Production of medical containers and tools | Ensures safety and compliance with health regulations, enhancing patient care | Prioritize suppliers with experience in medical-grade materials and certifications |
| Construction | Fabrication of pipes and fittings | Cost-effective solutions that ensure durability and reliability in infrastructure | Assess the supplier’s ability to meet specific size and pressure requirements |
Packaging
Blow molding companies play a vital role in the packaging industry by manufacturing a wide range of bottles and containers. These products are essential for various sectors including food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. The primary value lies in reducing material costs while providing superior protection for the contents. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to ensure that suppliers comply with local regulations and sustainability standards, which can vary significantly across markets.
Automotive
In the automotive sector, blow molding is utilized to produce components such as fuel tanks and various lightweight parts. This application is particularly beneficial as it enhances fuel efficiency and reduces overall emissions, aligning with global trends towards sustainability. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should focus on sourcing from companies that can provide durable materials capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term performance and safety.
Consumer Goods
The consumer goods industry leverages blow molding for creating diverse products, including toys and household items. This method allows for significant customization, catering to specific market demands and enhancing consumer appeal. B2B buyers, especially in Europe and Africa, should seek suppliers with advanced design capabilities and quality certifications to ensure that products meet regional safety standards and consumer preferences.
Medical Devices
Blow molding is critical in the medical sector for producing containers and tools that require stringent safety and compliance measures. These products directly impact patient care and must adhere to rigorous health regulations. International buyers, particularly from South America and the Middle East, should prioritize suppliers with proven expertise in medical-grade materials and relevant certifications to ensure product reliability and safety.
Construction
In the construction industry, blow molding is used for fabricating pipes and fittings, offering cost-effective solutions that provide durability and reliability for infrastructure projects. For B2B buyers in Africa and Europe, it is essential to assess suppliers’ capabilities to meet specific size and pressure requirements, as well as their experience in producing high-quality, long-lasting products that can withstand environmental stresses.
Related Video: What Is blow molding process?? Applications, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
Strategic Material Selection Guide for blow molding companies
When selecting materials for blow molding applications, international B2B buyers must consider several factors that influence product performance, cost, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in blow molding, along with their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Polyethylene (PE)
Key Properties: Polyethylene is known for its excellent chemical resistance, flexibility, and low-temperature performance. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 80°C (176°F) and can withstand moderate pressure.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PE is lightweight, cost-effective, and easy to process. It also offers good impact resistance and is recyclable.
– Disadvantages: Its lower temperature resistance compared to other materials can limit its application in high-heat environments. Additionally, it may not be suitable for certain chemical applications.
Impact on Application: PE is commonly used for packaging, containers, and automotive parts. Its compatibility with a wide range of chemicals makes it suitable for various applications, but buyers should confirm specific chemical resistance for their intended use.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is essential for buyers in regions like Europe and the Middle East. In Africa and South America, local regulations regarding recycling and environmental impact may also influence material selection.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene offers a higher temperature resistance (up to 100°C or 212°F) and excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: It is durable, has a high strength-to-weight ratio, and is resistant to fatigue and stress. PP is also recyclable and has a lower density than PE.
– Disadvantages: The manufacturing process can be more complex, and it may be more expensive than PE. It can also be sensitive to UV exposure unless treated.
Impact on Application: PP is ideal for automotive parts, industrial containers, and household goods. Its strength and thermal resistance make it suitable for applications that require durability under stress.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with DIN standards in Europe and JIS standards in Japan. In regions like Africa and South America, understanding local market preferences and regulations is crucial for successful sourcing.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties: PVC is recognized for its rigidity and excellent durability. It can withstand temperatures up to 60°C (140°F) and offers good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PVC is very versatile, cost-effective, and has good weather resistance. It is commonly used in construction and plumbing applications.
– Disadvantages: The environmental impact of PVC production and disposal can be a concern. It is also less flexible than PE and PP, which may limit its applications.
Impact on Application: PVC is widely used in the construction industry for pipes, fittings, and profiles. Its durability makes it suitable for long-lasting applications, but buyers should be aware of its limitations in high-temperature environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe should be aware of REACH regulations concerning chemical safety. In regions like the Middle East and Africa, local environmental regulations may impact the use of PVC.
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
Key Properties: PET is known for its excellent strength, thermal stability, and barrier properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C (248°F) and is highly resistant to moisture.
Pros & Cons:
– Advantages: PET is lightweight, recyclable, and offers superior clarity and strength, making it ideal for packaging applications.
– Disadvantages: The cost can be higher than other materials, and its processing requires more energy, which can impact sustainability.
Impact on Application: PET is commonly used for beverage bottles and food containers due to its excellent barrier properties. Its compatibility with food-grade applications makes it a preferred choice in the packaging industry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with food safety standards is critical for buyers in Europe and North America. In Africa and South America, understanding local recycling regulations is essential for PET products.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for blow molding companies | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | Packaging, containers, automotive parts | Cost-effective and recyclable | Limited high-temperature use | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Automotive parts, industrial containers | High strength-to-weight ratio | More complex manufacturing | Medium |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Construction pipes, fittings | Versatile and durable | Environmental impact concerns | Low |
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Beverage bottles, food containers | Excellent barrier properties | Higher processing cost | High |
By carefully evaluating these materials based on their properties and regional compliance requirements, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and market expectations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for blow molding companies
Overview of Blow Molding Manufacturing Processes
Blow molding is a widely used manufacturing process for creating hollow plastic parts. Understanding the stages involved can help B2B buyers from diverse regions—like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—make informed sourcing decisions. Here’s an in-depth look at the typical manufacturing processes and the quality assurance measures that are vital for international B2B transactions.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Resin Selection: The process begins with selecting the appropriate resin. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The choice of resin affects the end product’s strength, flexibility, and resistance to chemicals.
– Pelletizing: The resin is typically in pellet form, which must be dried and heated to the correct temperature before processing. This step is crucial to avoid defects in the final product. -
Forming
– Extrusion Blow Molding: In this technique, a parison (a tube of molten plastic) is extruded and then inflated into a mold. This method is ideal for larger parts like containers and bottles.
– Injection Blow Molding: This involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to form a preform, which is then transferred to a blow mold for inflation. This technique offers better dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
– Stretch Blow Molding: Used primarily for producing PET bottles, this technique stretches the preform while blowing, enhancing strength and clarity. -
Assembly
– Component Joining: If the product consists of multiple parts, assembly may involve mechanical fastening, adhesive bonding, or ultrasonic welding. Each method has its advantages, depending on the application and material compatibility. -
Finishing
– Trimming and Surface Treatment: Once molded, parts may require trimming to remove excess material and surface treatments like painting or coating for aesthetic and functional purposes.
– Quality Control Integration: Quality checks are often integrated into the finishing stage, ensuring that products meet specifications before packaging.
Quality Assurance in Blow Molding
Quality assurance is critical in blow molding to ensure product consistency and compliance with international standards. Here’s how quality control is typically structured.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS) and is essential for manufacturers aiming to demonstrate their ability to consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For products used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to API specifications is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet predefined specifications. This step often includes testing for physical and chemical properties. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process is essential to catch defects early. This may involve real-time measurements of temperature, pressure, and material flow. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Before products leave the factory, a final inspection is conducted. This includes dimensional checks, visual inspections, and functional testing to verify that the product meets all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
- Dimensional Inspection: Utilizing calipers and micrometers to ensure products meet dimensional tolerances.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing properties such as tensile strength and impact resistance using standardized tests.
- Environmental Testing: Evaluating how products perform under different conditions (e.g., temperature extremes, humidity) to ensure durability.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality assurance practices of their suppliers. Here are some actionable strategies:
-
Conduct Audits
– Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This includes reviewing documentation, interviewing staff, and observing production. -
Request Quality Reports
– Ask suppliers for their quality management reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC. A transparent supplier will readily share this information. -
Utilize Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices. These agencies can conduct random checks and provide detailed reports. -
Certifications and Compliance
– Verify that suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) and that they comply with industry-specific regulations. This can be cross-checked with issuing bodies.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
When sourcing blow molding products internationally, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, and the Middle East, buyers should be aware of several nuances:
- Cultural Differences: Understanding local business practices and communication styles can facilitate smoother interactions and negotiations.
- Regulatory Variations: Compliance with local regulations may differ significantly. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers are aware of and adhere to both local and international standards.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Considerations: Evaluate the logistics capabilities of suppliers, including shipping times and costs, as these factors can impact the overall supply chain efficiency.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in blow molding is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on these aspects, buyers can mitigate risks and ensure they source high-quality products that meet their specific needs.
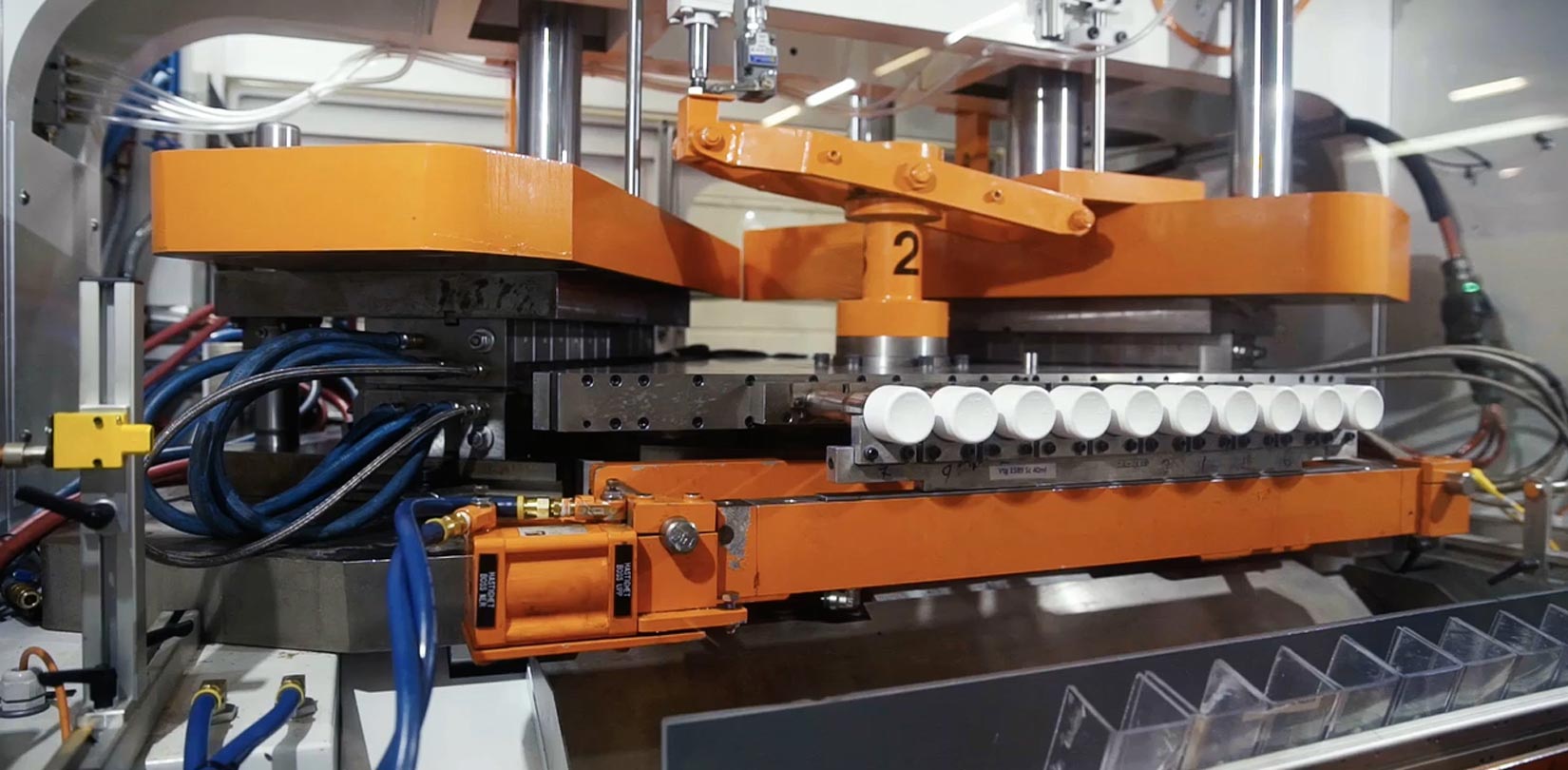

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for blow molding companies Sourcing
When sourcing from blow molding companies, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis will equip you with actionable insights to navigate the complexities of sourcing in this industry, specifically targeting buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences the overall cost. Common materials used in blow molding include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Prices can fluctuate based on global oil prices and supply chain disruptions, so it’s crucial to stay informed about market trends.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, sourcing from countries with lower labor costs can be advantageous, but consider the trade-off with quality and expertise. Countries like Kenya may offer competitive labor costs, while European nations might have higher wages but also greater expertise in manufacturing processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, rent, and maintenance of machinery. Efficient operations can lower these costs, so assess the manufacturing capabilities and technology used by potential suppliers.
-
Tooling: Tooling costs can be substantial in blow molding. These costs depend on the complexity of the molds required for production. Buyers should inquire about the tooling fees and whether they are included in the quoted price or charged separately.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing robust QC processes ensures that the products meet the required standards. This can involve additional costs, but it is critical for maintaining quality and compliance, especially when exporting to stringent markets in Europe.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary significantly based on the shipping method (air vs. sea), distance, and customs duties. Understanding the logistics framework in the supplier’s region is vital for accurate pricing.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a margin into their pricing, which can vary widely based on their market positioning and competition. Understanding the margin expectations of different suppliers can help in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to discounts. However, ensure that your order volume aligns with your demand to avoid excess inventory.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specifications can drive up costs. Be clear about your requirements to avoid unexpected price increases.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher-quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO) may incur additional costs but are crucial for compliance in certain markets, particularly in Europe.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, experience, and reliability can influence pricing. A well-established supplier may charge a premium for their expertise and proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) affects shipping costs and responsibilities. Understanding these terms can help in negotiating better deals and avoiding unexpected costs.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Approach negotiations with a clear understanding of the cost components. Leverage your position as a bulk buyer to negotiate better pricing terms and payment conditions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate suppliers not just on price but on total cost of ownership (TCO). This includes considering quality, delivery reliability, and after-sales service, which can impact long-term costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations and their impact on pricing. When sourcing from diverse regions, consider the economic stability and trade agreements that could affect costs.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: Prices in blow molding can vary significantly based on the factors mentioned. Always request detailed quotes and clarify what is included to avoid misinterpretations.
By understanding these cost components and pricing influencers, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ultimately leading to more strategic sourcing and better financial outcomes in their operations.
Spotlight on Potential blow molding companies Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘blow molding companies’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for blow molding companies
Key Technical Properties in Blow Molding
Understanding the essential technical properties related to blow molding is critical for B2B buyers to ensure they select the right materials and processes for their specific applications. Here are some of the most important specifications:
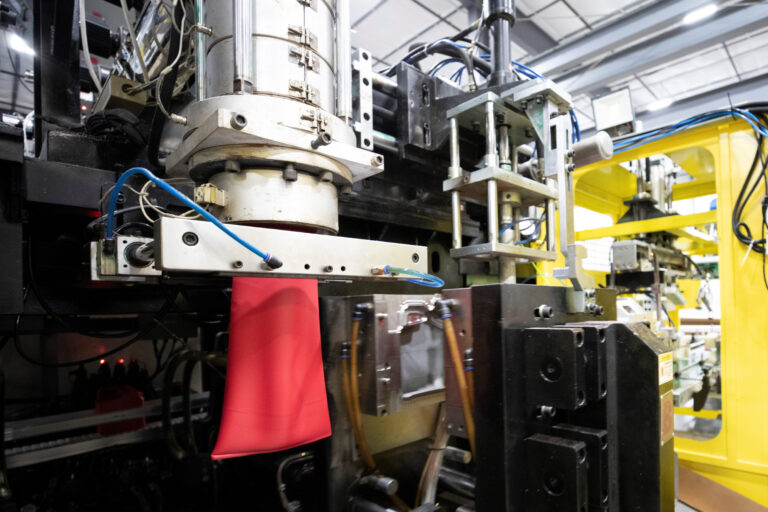
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade
The type of plastic used in blow molding significantly impacts the final product’s performance. Common materials include High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), Polypropylene (PP), and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). Each material has unique properties such as chemical resistance, impact strength, and temperature tolerance, making it crucial for buyers to choose the right grade based on their product requirements. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during manufacturing. In blow molding, maintaining tight tolerances is essential for ensuring that parts fit together correctly, especially in applications like automotive or medical devices. Understanding the tolerance levels required for a project can help buyers avoid costly reworks or product failures. -
Wall Thickness
The wall thickness of blow-molded products affects both durability and material cost. Thicker walls can provide greater strength and resistance to deformation but may also increase material usage and production costs. Buyers should balance the need for strength against budget constraints when specifying wall thickness. -
Surface Finish
The surface finish of blow-molded items can influence aesthetics and functionality. Options range from smooth finishes that enhance visual appeal to textured surfaces that improve grip. For buyers, specifying the desired surface finish is critical for ensuring the product meets both branding and practical requirements. -
Color Consistency
Color consistency is vital for branding and consumer recognition. Inconsistent coloring can lead to customer dissatisfaction and affect product perception. Buyers should discuss color specifications with manufacturers to ensure that color matching and consistency are part of the production process.
Common Trade Terms in Blow Molding
Familiarity with trade terminology is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the blow molding industry. Here are some key terms that international B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In blow molding, OEMs are critical partners for buyers seeking custom solutions tailored to their specific needs. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the minimum number of units a supplier is willing to produce for a single order. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers, as it can affect inventory management and overall project costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their production needs and market demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to solicit pricing for specific products or services. It should include detailed specifications, quantities, and delivery timelines. A well-crafted RFQ can help buyers receive accurate quotes and streamline the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with these terms helps buyers understand shipping costs, risk allocation, and delivery obligations, which are crucial for effective supply chain management. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product. In blow molding, lead times can vary based on complexity and production capacity. Buyers should consider lead times when planning their projects to avoid delays in product launches or inventory shortages.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions in the blow molding sector, ensuring alignment with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the blow molding companies Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The blow molding industry is currently experiencing significant transformation, driven by globalization, technological advancements, and evolving consumer preferences. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe engage with this sector, they must be aware of key market dynamics. Global drivers include the increasing demand for lightweight packaging solutions, particularly in the food and beverage, personal care, and pharmaceutical industries. This trend is fueled by the need for cost-effective, durable, and eco-friendly packaging options.
Emerging B2B tech and sourcing trends are reshaping the landscape. Automation and smart manufacturing technologies, such as Industry 4.0 solutions, are enhancing production efficiency and reducing lead times. Additionally, the integration of advanced materials like bio-resins and recycled plastics is gaining traction, aligning with the push for sustainability. Furthermore, digital platforms for sourcing are becoming increasingly popular, allowing buyers to easily compare suppliers, evaluate capabilities, and streamline procurement processes.
For buyers in regions such as France and Kenya, understanding the market dynamics is crucial. The rise of regional players and local manufacturing initiatives is creating opportunities for partnerships that can lead to reduced shipping costs and enhanced supply chain resilience. However, buyers must also navigate challenges, such as fluctuating raw material prices and geopolitical tensions, which can impact supply chains. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers and leveraging local insights can help mitigate these risks and create a competitive advantage.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of strategic sourcing in the blow molding sector. The environmental impact of plastic production and waste is under scrutiny, prompting companies to adopt more sustainable practices. For international B2B buyers, prioritizing ethical sourcing is essential. This involves selecting suppliers that implement environmentally responsible practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing waste during production.
Buyers should also look for green certifications that indicate a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and participation in initiatives like the Sustainable Packaging Coalition are positive indicators of a supplier’s dedication to reducing their environmental footprint. Additionally, sourcing materials that are biodegradable or derived from renewable resources can enhance the sustainability profile of products.
Engaging with suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains and environmental practices not only aligns with corporate social responsibility goals but also resonates with increasingly environmentally-conscious consumers. This approach not only helps in building a positive brand image but also ensures compliance with emerging regulations aimed at reducing plastic waste across different regions.
Brief Evolution/History
The blow molding industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, the process was limited to simple, single-layer containers. However, advancements in technology have led to the development of multi-layer and complex shapes, catering to diverse industries. The introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer numerical control (CNC) machinery has further revolutionized the sector, enhancing precision and production capabilities.
As global trade expanded, so did the blow molding market, with manufacturers seeking to meet the demands of international buyers. Today, the industry is characterized by a focus on sustainability, innovation, and efficiency, making it essential for B2B buyers to stay informed about the latest trends and practices to remain competitive. Understanding the historical context of blow molding can provide valuable insights into current market dynamics and future opportunities.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of blow molding companies
-
How can I effectively vet blow molding suppliers?
Vetting suppliers is crucial for ensuring quality and reliability. Start by checking their certifications, such as ISO 9001, which indicates a commitment to quality management. Request references from previous clients, and consider visiting their facilities if possible. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or industry-specific directories to gauge their reputation. Additionally, verify their production capacity and technology to ensure they can meet your needs, especially if you require complex or custom designs. -
What customization options are available when sourcing blow molded products?
Many blow molding companies offer extensive customization options, including size, shape, color, and material. It’s important to discuss your specific requirements upfront, including any design specifications or regulatory standards relevant to your market. Some suppliers may provide design services or assist with prototyping. Ensure you clarify the limits of customization, as some suppliers may have constraints based on their machinery and processes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times?
MOQs can vary significantly depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, you can expect MOQs ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 units for standard products. Lead times can also differ; typical production times range from 4 to 12 weeks. Always discuss these factors during initial negotiations, and consider building a buffer into your timeline, especially if shipping internationally, to account for potential delays. -
What payment terms should I expect when dealing with international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Common methods include wire transfers, letters of credit, or payment through secure platforms like PayPal. Ensure to negotiate terms that protect your interests, such as a deposit upfront and the balance upon delivery. Be aware of currency fluctuations and consider locking in exchange rates if necessary. Establishing clear payment milestones can also help manage cash flow and mitigate risks. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and compliance with certifications?
Quality assurance is critical in maintaining product standards. Request documentation of quality control processes, including any relevant certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe. It’s advisable to conduct pre-shipment inspections through third-party services, which can verify compliance with your specifications. Establishing a clear communication channel with your supplier regarding quality expectations is essential for minimizing disputes. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind?
Logistics play a vital role in the success of your sourcing strategy. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, including Incoterms that define who is responsible for shipping costs and risks. Consider the shipping method (air vs. sea) based on your budget and urgency. Additionally, familiarize yourself with customs regulations in your country and the country of origin to avoid delays and additional costs. Partnering with a reliable freight forwarder can also streamline the process. -
How can I handle disputes with my supplier effectively?
Disputes can arise from misunderstandings or unmet expectations. Establish clear communication from the outset and document all agreements in writing. If a dispute occurs, try to resolve it amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, refer to the contract terms regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Having a local legal advisor familiar with international trade laws can also provide guidance on navigating complex situations. -
What are the key factors to consider when evaluating supplier performance?
Evaluating supplier performance should be an ongoing process. Key metrics include product quality, adherence to delivery schedules, responsiveness to inquiries, and flexibility in handling changes. Regularly soliciting feedback from your team and conducting formal reviews can help identify areas for improvement. Additionally, maintaining a good relationship with your supplier encourages transparency and can lead to better service and innovation in future projects.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for blow molding companies
In the competitive landscape of blow molding, strategic sourcing emerges as a pivotal element for international B2B buyers. By understanding the intricacies of the supply chain and leveraging global partnerships, businesses can enhance product quality while optimizing costs. Engaging with suppliers from diverse regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, allows companies to tap into unique market strengths and innovations.
Key Takeaways:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Expanding your supplier base not only mitigates risks but also opens avenues for innovation and cost savings.
- Quality Assurance: Establishing clear quality benchmarks and compliance standards is essential to maintain product integrity across borders.
- Cultural Competence: Building relationships with suppliers requires an understanding of cultural nuances, which can facilitate smoother negotiations and collaborations.
As the blow molding industry continues to evolve, the emphasis on sustainability and technological advancements will shape future sourcing strategies. International buyers are encouraged to stay proactive, continuously assess market trends, and cultivate strategic partnerships. By embracing these practices, businesses can position themselves advantageously in the global marketplace, ensuring long-term success and resilience.