Unlock Cost-Efficient Sourcing for Your 3-Phase Transformer
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for 3-phase transformer
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial power systems, three-phase transformers are essential for reliable and efficient energy management. These devices not only facilitate the transmission of electricity across vast distances but also ensure that industrial operations run smoothly and cost-effectively. For B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of three-phase transformers is critical for optimizing their energy infrastructure and enhancing productivity.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad aspects of three-phase transformers, including their types, materials, and manufacturing processes. It also covers crucial topics such as quality control measures, supplier evaluation, cost considerations, and prevailing market trends. By addressing frequently asked questions, this resource demystifies the complexities surrounding transformer selection and integration.
Armed with this knowledge, international B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic objectives. Whether you are seeking to expand your supplier network or to comprehend the latest technological advancements, this guide empowers you to navigate the global market for three-phase transformers with confidence. With the right insights, your organization can enhance its energy efficiency and drive substantial cost savings, ensuring a competitive edge in today’s dynamic marketplace.
Understanding 3-phase transformer Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta Transformer | Windings connected in a triangular shape | Industrial machinery, HVAC systems | Pros: Simplicity, lower cost; Cons: Higher starting current, less efficient at low loads. |
| Wye (Star) Transformer | Windings connected in a star formation | Power generation, large motors | Pros: Lower phase voltage, better for long-distance transmission; Cons: More complex, higher initial cost. |
| Autotransformer | Single winding with taps for voltage adjustment | Power distribution, voltage regulation | Pros: Compact size, cost-effective; Cons: Less isolation, potential safety risks. |
| Isolation Transformer | Provides electrical isolation between circuits | Sensitive equipment, medical applications | Pros: Enhances safety, reduces noise; Cons: Higher cost, larger footprint. |
| Phase-Shifting Transformer | Adjusts phase angles to improve system efficiency | Power quality improvement, renewable energy | Pros: Enhances power quality, reduces losses; Cons: Complex design, higher maintenance needs. |
Delta Transformer
The Delta transformer features a triangular winding configuration, making it a popular choice in industrial settings. Its design allows for higher starting currents, which can be advantageous in applications requiring significant power at startup, such as HVAC systems. However, buyers should be cautious of its reduced efficiency at lower loads. When considering a Delta transformer, assess the specific load demands and operational needs to ensure alignment with performance expectations.
Wye (Star) Transformer
Wye transformers utilize a star formation for their windings, resulting in lower phase voltages and making them ideal for long-distance power transmission. They are particularly suited for large motors and power generation systems. While they offer improved efficiency and reduced voltage drop, their complexity and higher initial costs may be a concern for some buyers. It is essential to evaluate the long-term benefits against upfront investments when considering this transformer type.
Autotransformer
Autotransformers consist of a single winding that serves as both the primary and secondary winding, with taps for voltage adjustment. Their compact design and cost-effectiveness make them suitable for power distribution and voltage regulation. However, they provide less electrical isolation compared to traditional transformers, which can pose safety risks. B2B buyers should weigh the advantages of space and cost savings against the potential need for additional safety measures.
Isolation Transformer
Isolation transformers are designed to provide electrical isolation between circuits, which is crucial for sensitive equipment and applications in medical settings. They enhance safety and reduce electrical noise, making them an excellent choice for critical applications. However, they tend to be more expensive and require more space than other transformer types. When evaluating isolation transformers, consider the specific safety and noise reduction needs of your operations.
Phase-Shifting Transformer
Phase-shifting transformers are specialized devices that adjust phase angles to improve system efficiency and power quality. They are particularly beneficial in applications involving renewable energy sources and power quality improvement. While these transformers can enhance efficiency and reduce losses, their complex design may lead to higher maintenance requirements. Buyers should assess their operational goals and the potential for improved power quality when considering this transformer type.
Related Video: What Is 3 Phase Transformer | How It Works?
Key Industrial Applications of 3-phase transformer
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of 3-phase transformer | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Power Supply for Heavy Machinery | Ensures stable and efficient operation of machinery, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. | Buyers should consider voltage requirements, load capacity, and efficiency ratings. |
| Renewable Energy | Integration with Solar and Wind Farms | Facilitates the step-up of voltage for grid compatibility, enhancing energy distribution efficiency. | Assess compatibility with existing systems and certifications for renewable energy standards. |
| Mining and Minerals | Power Distribution in Mining Operations | Supports heavy equipment operation, ensuring reliability and minimizing energy losses. | Evaluate ruggedness and durability suited for harsh environments, along with local regulations. |
| Commercial Buildings | HVAC Systems and Lighting | Provides reliable power for essential services, optimizing energy consumption and operational costs. | Consider energy efficiency ratings and scalability options for future expansions. |
| Transportation and Logistics | Rail and Metro Systems | Supplies consistent power for trains and transit systems, improving service reliability. | Focus on compliance with safety standards and the ability to handle peak load demands. |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, three-phase transformers are vital for supplying power to heavy machinery. These transformers ensure a stable and efficient power supply, which is crucial for reducing downtime and maintenance costs associated with machinery failures. Buyers in this sector should carefully consider the voltage requirements and load capacity needed for their specific applications, as well as the efficiency ratings of the transformers to optimize operational costs.
Renewable Energy
Three-phase transformers play a significant role in integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind farms, into the power grid. They facilitate the step-up of voltage, making energy distribution more efficient and compatible with existing grid systems. International buyers, particularly in regions focused on renewable initiatives, should assess the compatibility of transformers with their current systems and ensure they meet the necessary certifications for renewable energy standards.
Mining and Minerals
In the mining industry, three-phase transformers are essential for the power distribution needed to operate heavy equipment reliably. They help in minimizing energy losses and ensuring that the power supply remains stable under varying loads. Buyers should evaluate the ruggedness and durability of transformers to withstand harsh mining environments, as well as compliance with local regulations and standards to ensure safe operations.
Commercial Buildings
For commercial buildings, three-phase transformers are crucial in powering HVAC systems and lighting. They provide a reliable power supply for essential services, which helps optimize energy consumption and reduce operational costs. Buyers should focus on energy efficiency ratings and consider scalability options for future expansions, ensuring that the transformers can accommodate increased power demands as the business grows.
Transportation and Logistics
In the transportation and logistics sector, three-phase transformers are integral to rail and metro systems, supplying consistent power that enhances service reliability. These transformers must comply with stringent safety standards and be capable of handling peak load demands during busy operational periods. Buyers should prioritize sourcing transformers that meet these requirements to ensure uninterrupted service and operational efficiency.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for 3-phase transformer
When selecting materials for three-phase transformers, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with regional standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in three-phase transformers, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for specific markets.
1. Silicon Steel
Key Properties:
Silicon steel is known for its excellent magnetic properties, particularly its high permeability and low hysteresis loss. It can typically withstand temperatures up to 150°C and has good corrosion resistance.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of silicon steel is its high efficiency in reducing energy losses during operation, which translates to lower operational costs. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes, increasing overall production complexity.
Impact on Application:
Silicon steel is ideal for high-frequency applications due to its magnetic characteristics. It is compatible with various cooling mediums, including oil and air, making it versatile for different transformer designs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should ensure compliance with ASTM and DIN standards for silicon steel. Additionally, evaluating suppliers based on their ability to provide high-quality silicon steel can significantly impact the efficiency and longevity of transformers.
2. Copper
Key Properties:
Copper is highly conductive, with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and can operate effectively at temperatures up to 200°C. It also exhibits good corrosion resistance, especially when treated.
Pros & Cons:
Copper’s high conductivity ensures minimal energy loss, making it a preferred choice for windings in transformers. However, its cost is relatively high compared to aluminum, and it can be more challenging to work with due to its weight and malleability.
Impact on Application:
Copper is particularly suited for applications requiring high efficiency and performance, such as industrial power systems. Its compatibility with various insulating materials also enhances its application versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the availability of copper in their regions and potential fluctuations in pricing. Compliance with international standards such as JIS and ASTM for copper quality is crucial to ensure reliability and performance.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has decent electrical conductivity, operating effectively at temperatures up to 150°C. It is less resistant to corrosion compared to copper but can be treated to enhance its durability.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and lighter weight, making it easier to handle and install. However, its conductivity is lower than that of copper, which may lead to higher energy losses in some applications.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is suitable for medium-voltage transformers and applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in mobile or portable transformer units.
Considerations for International Buyers:
When sourcing aluminum, buyers should ensure that the material meets local and international standards, including ISO and ASTM. Additionally, understanding the local market for aluminum can help in negotiating better prices and securing reliable supply chains.
4. Insulation Materials (e.g., Paper, Resin)
Key Properties:
Insulation materials like paper and resin provide critical electrical insulation and thermal stability. They can withstand temperatures ranging from 90°C to 200°C, depending on the type and treatment.
Pros & Cons:
High-quality insulation materials enhance the reliability and safety of transformers. However, they can add to the overall cost and complexity of manufacturing, especially if specialized treatments are required.
Impact on Application:
Insulation materials are essential for ensuring the safe operation of transformers, particularly in environments with high humidity or temperature fluctuations. They also play a role in the overall thermal management of the transformer.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should assess insulation materials for compliance with IEC and UL standards, particularly in regions with stringent safety regulations. Understanding the local availability of these materials can facilitate smoother procurement processes.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for 3-phase transformer | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon Steel | Core material for transformers | High efficiency, low energy loss | Higher cost, complex manufacturing | High |
| Copper | Windings in high-performance transformers | Excellent conductivity, low energy loss | High cost, heavier than aluminum | High |
| Aluminum | Medium-voltage transformers | Lightweight, lower cost | Lower conductivity, higher energy loss | Medium |
| Insulation Materials | Electrical insulation in transformers | Enhances reliability and safety | Adds to cost and manufacturing complexity | Medium |
This analysis provides actionable insights for international B2B buyers, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding material selection for three-phase transformers. Understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of each material will help optimize performance and ensure compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for 3-phase transformer
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for three-phase transformers are critical elements that international B2B buyers must understand to ensure they acquire reliable and efficient products. This section delves into the main stages of manufacturing, quality control measures, relevant international standards, and best practices for verifying supplier quality, particularly for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of three-phase transformers generally involves several key stages:
1. Material Preparation
The first step in transformer manufacturing is the preparation of raw materials. High-quality electrical steel sheets are used for the core to minimize energy losses. These sheets are cut into specific shapes and sizes according to the design specifications. Copper or aluminum is used for the windings, chosen based on conductivity and cost considerations. Insulation materials such as paper, resin, or oil are prepared to ensure safety and efficiency.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the core is assembled. This involves stacking the laminated steel sheets to form the core, which is crucial for efficient magnetic flux transfer. The windings are then fabricated, typically using automated winding machines to ensure precision. The winding process must maintain specific turns ratios to achieve the desired voltage transformation.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage combines the core and windings. The windings are placed onto the core, and insulation materials are applied to prevent short circuits. Afterward, the entire assembly is encased in a protective housing made from materials like steel or fiberglass, which also aids in cooling. Various connection configurations, such as Delta or Wye, are implemented at this stage based on the application requirements.
4. Finishing
The final stage involves testing and finishing the transformer. This includes applying protective coatings, installing cooling systems (air, oil, or forced cooling), and conducting initial quality tests. Proper labeling and documentation are also part of this stage to ensure compliance with international standards.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is vital in transformer manufacturing to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability. International standards, such as ISO 9001, play a significant role in guiding manufacturers toward maintaining high-quality production processes. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like CE (European Conformity) and API (American Petroleum Institute) may be necessary depending on the application and market.
Key Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. Any non-compliant materials are rejected or returned.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, regular checks are performed at various stages. This includes verifying dimensions, checking winding resistance, and ensuring proper insulation is applied.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the transformer undergoes rigorous testing to verify performance and safety. This includes dielectric strength tests, temperature rise tests, and load tests to ensure the transformer operates as intended.
Common Testing Methods
- Dielectric Testing: Assesses the insulation’s ability to withstand electrical stress.
- Temperature Rise Testing: Measures how much the transformer heats up under load conditions.
- Short Circuit Testing: Evaluates the transformer’s response to fault conditions.
- Efficiency Testing: Determines how effectively the transformer converts input power to output power.
Verifying Supplier Quality
For B2B buyers, especially those operating in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality is essential. Here are practical steps to ensure that suppliers adhere to quality standards:
-
Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can provide insight into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include reviewing their compliance with ISO standards and industry-specific certifications.
-
Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality assurance reports from suppliers can help buyers understand their quality control processes and outcomes. These reports should include test results and any corrective actions taken.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies to assess the manufacturing process and final products can provide an unbiased view of quality compliance. These agencies can conduct on-site inspections and tests, ensuring adherence to international standards.
Quality Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers must be aware of specific quality certification nuances when sourcing transformers. For instance, while ISO 9001 is a global standard, regional certifications may also be required depending on local regulations. Buyers should familiarize themselves with the certification requirements of their respective markets. In Europe, CE marking is often mandatory, indicating compliance with safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
In regions like Africa and South America, local regulatory bodies may have their own certification processes. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers are compliant with these regulations to avoid operational disruptions and legal issues.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for three-phase transformers is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, assembly techniques, and rigorous quality control, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to international quality standards and conducting thorough verification processes will ultimately lead to successful sourcing and enhanced operational efficiency.
Related Video: Porsche 911 ENGINE PRODUCTION 🛠️ 991 vs 992 🚘 Which is BETTER?
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for 3-phase transformer Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of three-phase transformers is essential for international B2B buyers. Here’s a comprehensive analysis tailored for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components of Three-Phase Transformers
-
Materials: The primary materials include high-quality steel for the core, copper or aluminum for the windings, and insulation materials. The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost; for instance, copper is generally more expensive than aluminum but offers better conductivity.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region, influenced by local wage standards and expertise availability. Skilled labor is crucial for assembling transformers correctly, as improper assembly can lead to inefficiencies and failures.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses costs related to facility maintenance, utilities, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for specialized tools and machinery can be substantial, particularly for customized transformers. Buyers should consider these costs when evaluating suppliers.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that transformers meet international standards requires rigorous QC processes. This may involve testing and certification fees, which should be factored into the total cost.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely depending on the transformer size, weight, and destination. International buyers must consider freight, insurance, and customs duties in their budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their operational costs and profit. Understanding market rates can help buyers negotiate better deals.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Ordering in bulk often results in lower per-unit costs. Suppliers may offer discounts for large orders, so negotiating Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ) can be beneficial.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized transformers tailored to specific applications generally incur higher costs due to additional engineering and design work. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can dramatically influence pricing. High-grade materials may lead to higher upfront costs but can enhance performance and longevity, impacting Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Quality/Certifications: Transformers that meet international quality standards (e.g., ISO, IEC) may come at a premium. However, these certifications can be crucial for ensuring reliability and safety in industrial applications.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record may charge more, but they often provide better assurance of quality and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the delivery terms outlined in Incoterms (e.g., CIF, FOB) is essential. These terms dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and customs duties, affecting the overall pricing strategy.
Buyer Tips for Cost Efficiency
-
Negotiate Wisely: Always engage in negotiations. Suppliers often have room for price adjustments, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Consider not just the initial purchase price but also maintenance, operation, and replacement costs. A slightly higher upfront cost for a more efficient transformer can lead to significant savings over time.
-
Stay Informed on Pricing Trends: Regularly review market conditions and material costs. Changes in global supply chains or material shortages can impact pricing and availability.
-
Leverage Regional Differences: Buyers from different regions may encounter varying costs based on local manufacturing capabilities and labor costs. Exploring suppliers in different regions can yield cost benefits.
-
Request Detailed Quotations: Ensure that quotes include a breakdown of all costs. This transparency allows for better comparisons and informed decision-making.
Disclaimer
Prices for three-phase transformers can vary widely based on the factors discussed above. The insights provided are indicative and should be used as a guideline rather than fixed rates. Always conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain the best possible pricing.
Spotlight on Potential 3-phase transformer Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘3-phase transformer’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for 3-phase transformer
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with three-phase transformers is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also enhances operational efficiency in various industrial applications.
Key Technical Properties of Three-Phase Transformers
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality of materials used in the construction of the transformer, particularly the core and windings, affects performance and durability.
– B2B Importance: Higher-grade materials reduce energy losses and improve overall efficiency, leading to lower operational costs. Buyers should inquire about the specific grades used to ensure compliance with industry standards. -
Winding Configuration
– Definition: The arrangement of the primary and secondary windings, typically in either Delta (Δ) or Wye (Y) configurations.
– B2B Importance: Each configuration has distinct advantages and applications. Understanding the implications of each can help buyers select the right transformer for their power distribution needs, optimizing both efficiency and cost. -
Voltage Rating
– Definition: The maximum voltage the transformer can handle safely without risking damage.
– B2B Importance: Proper voltage ratings are crucial for compatibility with existing electrical systems. Buyers must ensure that the transformer meets their specific voltage requirements to avoid operational failures. -
Power Rating (kVA)
– Definition: The apparent power capacity of the transformer, measured in kilovolt-amperes (kVA).
– B2B Importance: This specification indicates how much load the transformer can support. Selecting a transformer with the appropriate power rating is vital to prevent overloading and ensure reliable operation in industrial settings.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Efficiency Rating
– Definition: The ratio of output power to input power, expressed as a percentage.
– B2B Importance: Higher efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operational costs. Buyers should seek transformers with high efficiency ratings to maximize return on investment. -
Cooling Method
– Definition: The technique used to dissipate heat generated during operation, which can include air, oil, or forced cooling.
– B2B Importance: The cooling method affects the transformer’s performance and longevity. Understanding cooling requirements can help buyers select a transformer suited to their environmental conditions and operational demands.
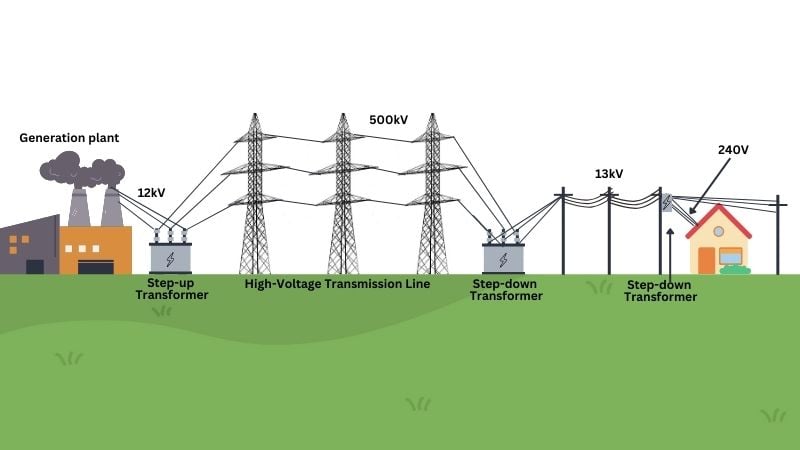
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: When sourcing transformers, buyers should consider OEMs for high-quality products that meet specific industry standards, ensuring reliability in their operations. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Importance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers plan their purchases and manage inventory effectively. It can also influence negotiations and pricing strategies. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for a specific product or service.
– B2B Importance: Utilizing RFQs allows buyers to compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and favorable terms, which is crucial for budget management. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– B2B Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their responsibilities regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs, which is essential for smooth cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– B2B Importance: Knowing lead times is critical for planning and ensuring that projects are not delayed due to equipment shortages. -
Warranty and Service Agreements
– Definition: Contracts that outline the terms of service and support provided by the manufacturer.
– B2B Importance: These agreements provide assurance regarding the quality and longevity of the transformer, making them a key consideration for buyers concerned about long-term reliability.
By familiarizing themselves with these essential properties and terminologies, B2B buyers can enhance their decision-making processes, ensuring that they select the right three-phase transformers for their operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the 3-phase transformer Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for three-phase transformers is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for reliable and efficient power distribution systems across various industries. Key factors fueling this demand include urbanization, industrial expansion, and the transition towards renewable energy sources. As international B2B buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to recognize the significance of these trends in shaping procurement strategies.
Emerging technologies, such as smart grid systems and IoT-enabled devices, are revolutionizing the way transformers are monitored and managed. These advancements allow for real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and enhanced operational efficiency. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who incorporate these technologies into their products, as this will contribute to long-term cost savings and improved reliability.
Additionally, there is a growing trend towards modular and scalable transformer designs, which enable businesses to adapt their energy infrastructure to evolving needs. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for companies in rapidly developing regions, where power demands may fluctuate significantly. Buyers should assess their specific energy requirements and consider suppliers offering customizable solutions that align with their operational goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the three-phase transformer sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes and the lifecycle of transformers cannot be overlooked. It is essential for companies to engage with suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using recyclable materials and minimizing waste during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important; buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and contribute positively to their local communities. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and social responsibility.
Moreover, integrating ‘green’ materials into transformer production, such as environmentally friendly insulation oils and high-efficiency core materials, can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of electrical systems. Buyers should actively seek out suppliers that offer products certified by recognized organizations, as these certifications not only enhance brand reputation but also meet increasing regulatory requirements in various markets.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of three-phase transformers dates back to the late 19th century when the need for efficient power distribution systems arose alongside industrialization. Initially designed for large-scale applications, these transformers have undergone significant advancements in materials and technology, improving their efficiency and reliability over time.
Today, the focus is on enhancing energy efficiency, reducing operational costs, and integrating digital technologies for smarter management. As global energy demands continue to rise, the development of three-phase transformers will play a pivotal role in supporting sustainable industrial growth and energy transition initiatives. B2B buyers must remain informed about these historical developments to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with future industry trends.
Related Video: US Strikes On Iran Add to Market Uncertainty | Bloomberg: The Asia Trade, 6/23/25
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of 3-phase transformer
-
What key factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for 3-phase transformers?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience in manufacturing 3-phase transformers and their compliance with international standards such as ISO and IEC certifications. Request customer references and reviews to gauge their reliability and service quality. Additionally, assess their production capacity, delivery times, and responsiveness to inquiries. It’s also beneficial to visit their facilities, if possible, to inspect quality control processes and manufacturing conditions. -
Can I customize the specifications of a 3-phase transformer to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for 3-phase transformers. You can specify parameters such as voltage levels, power ratings, and connection types (Delta or Wye). It’s crucial to communicate your requirements clearly and work closely with the supplier’s engineering team. Customization may affect lead times and pricing, so ensure you discuss these factors upfront to align expectations. -
What is the typical minimum order quantity (MOQ) and lead time for 3-phase transformers?
The MOQ for 3-phase transformers varies by supplier but often ranges from 5 to 10 units for standard models. For customized transformers, the MOQ may be higher. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production schedule. Always confirm these details during negotiations to plan your procurement timeline effectively. -
What payment terms are usually offered for purchasing 3-phase transformers internationally?
Payment terms for international purchases can vary significantly. Common options include advance payment, letters of credit, and payment upon delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate favorable terms that protect your interests, such as partial payments based on milestones. Ensure that the payment method aligns with your cash flow management and is secure against potential disputes. -
What quality assurance measures should I expect from a reputable 3-phase transformer supplier?
A reputable supplier should have robust quality assurance (QA) processes in place, including regular testing of transformers for performance and safety standards. Look for certifications such as CE, UL, or CSA that indicate compliance with international quality standards. Request detailed QA documentation, including test reports and inspection certificates, to ensure that the transformers meet your operational requirements. -
How do logistics and shipping factors impact my purchase of 3-phase transformers?
Logistics play a critical role in the procurement of 3-phase transformers, especially for international shipments. Consider factors such as shipping methods (air vs. sea), customs clearance, and associated costs. Work with suppliers who have experience in international logistics to ensure timely delivery. Additionally, discuss packaging requirements to prevent damage during transit, which can affect performance upon installation. -
What steps should I take if I encounter a dispute with a transformer supplier?
In the event of a dispute, start by addressing the issue directly with the supplier through clear and constructive communication. Document all interactions and agreements to establish a record. If the issue remains unresolved, refer to the terms of your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. In international transactions, consider involving legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to navigate complex issues. -
What certifications should I look for to ensure the quality and safety of 3-phase transformers?
When sourcing 3-phase transformers, look for certifications that demonstrate compliance with international safety and quality standards. Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, IEC 60076 for power transformers, and UL or CE marks for safety compliance. These certifications indicate that the transformers meet stringent performance criteria and are safe for use in industrial applications, providing peace of mind for your investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for 3-phase transformer
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of three-phase transformers presents a significant opportunity for B2B buyers in diverse markets, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various configurations—Delta and Wye connections—as well as the specific applications of these transformers is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and ensuring reliable power distribution.
Buyers should prioritize supplier evaluation, focusing on quality assurance processes, technological capabilities, and after-sales support to align with their operational goals. The long-term benefits of investing in high-quality three-phase transformers include reduced energy costs, improved system reliability, and enhanced productivity.
Looking ahead, as industries globally shift towards more sustainable and efficient energy solutions, the demand for advanced three-phase transformers is expected to rise. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about market trends and technological advancements to make strategic decisions that not only meet current needs but also position their businesses for future growth. Engaging with reputable suppliers and investing in innovative transformer solutions will be key to navigating this evolving landscape successfully.