Master Sourcing Strategies for Your Etching Company Needs
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for etching company
In an era where precision and quality dictate competitive advantage, the role of etching companies has become paramount for businesses across various sectors. These specialized firms utilize advanced techniques to create intricate designs and patterns on materials ranging from metals to glass, essential for everything from electronics to automotive applications. For international B2B buyers, understanding the nuances of etching services can directly influence product quality and overall project success.
This comprehensive guide serves as an invaluable resource for decision-makers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including key markets like the UK and Italy. It covers a broad spectrum of topics, including the different types of etching processes, the materials commonly used, and the significance of manufacturing and quality control standards. Furthermore, it highlights how to identify reputable suppliers, evaluate cost factors, and analyze market trends that impact sourcing decisions.
By empowering buyers with detailed insights and practical knowledge, this guide aims to facilitate informed sourcing decisions. With a clear understanding of the etching landscape, businesses can leverage the right partnerships to enhance their product offerings, ensuring they remain competitive in a global marketplace.
Understanding etching company Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Etching | Utilizes chemical solutions to remove material. | Electronics, automotive, aerospace | Pros: Cost-effective for intricate designs. Cons: Limited to specific materials. |
| Laser Etching | Employs laser technology for precision and speed. | Medical devices, consumer products | Pros: High precision and speed. Cons: Higher initial costs. |
| Photo Etching | Involves light-sensitive materials for detailed designs. | Semiconductor manufacturing, optics | Pros: Excellent detail and repeatability. Cons: More complex setup. |
| Plasma Etching | Uses plasma to etch surfaces, ideal for thin films. | Microelectronics, MEMS fabrication | Pros: Uniform etching on complex geometries. Cons: Requires specialized equipment. |
| Mechanical Etching | Involves physical removal of material using tools. | Industrial parts, signage, decorative items | Pros: Versatile for various materials. Cons: Slower process compared to chemical methods. |
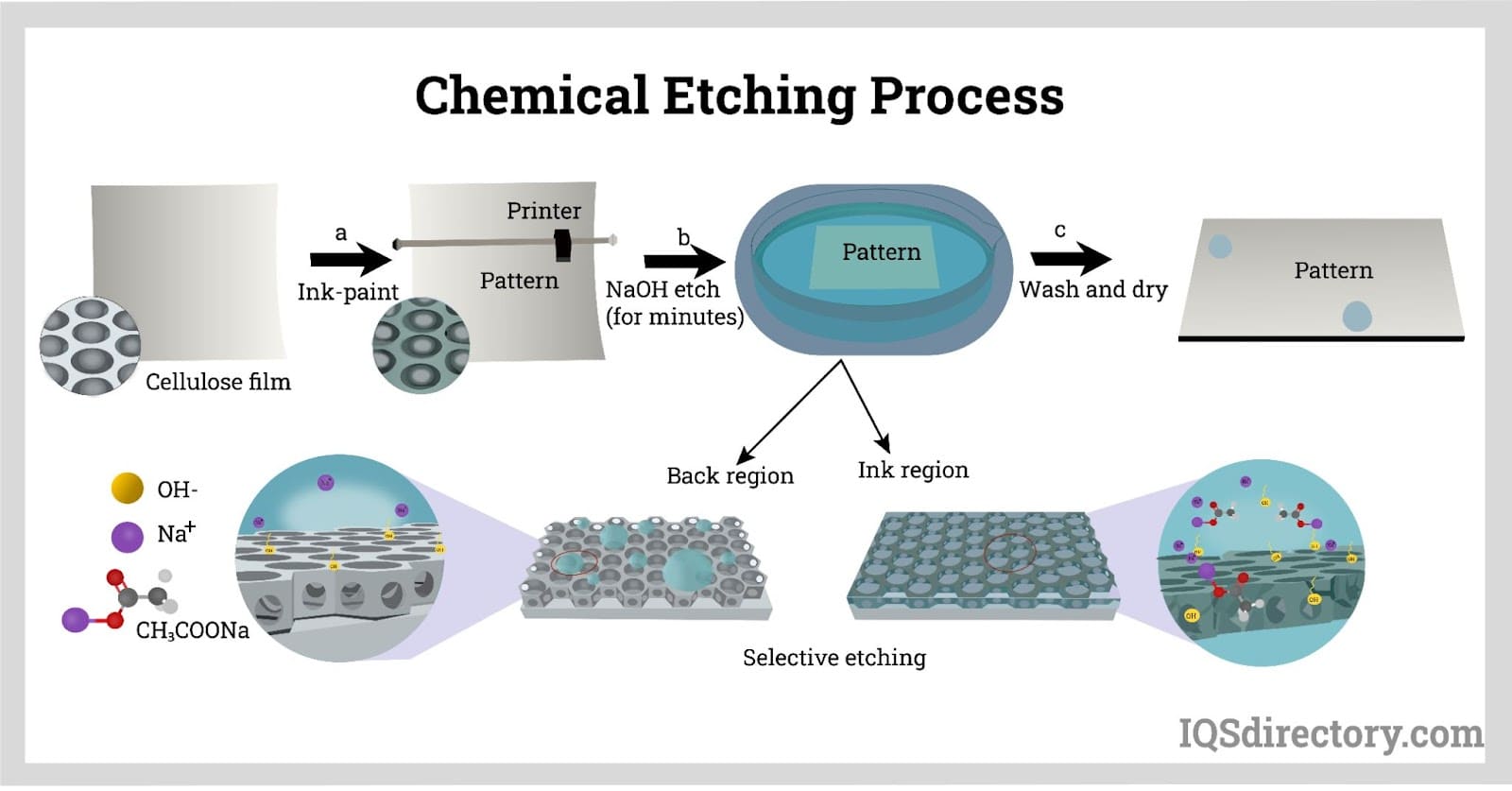
Chemical Etching
Chemical etching is a subtractive manufacturing process that utilizes corrosive chemicals to remove material from a substrate. This method is particularly well-suited for producing intricate designs on metals, making it a popular choice in industries such as electronics and aerospace. When considering chemical etching, buyers should evaluate the types of materials available, the desired precision, and the overall cost-effectiveness, especially for large production runs.
Laser Etching
Laser etching employs focused laser beams to engrave or mark materials with high precision. This technique is favored for its speed and ability to produce detailed designs on various substrates, including metals and plastics. Buyers should consider the upfront investment in laser technology, as well as the operational costs associated with maintenance and energy consumption. The ability to quickly adapt designs makes laser etching ideal for industries like medical devices and consumer products.
Photo Etching
Photo etching, or photochemical etching, uses light-sensitive materials to create highly detailed patterns. This method excels in applications requiring high precision, such as semiconductor manufacturing and optics. Companies interested in photo etching should weigh the complexity of the setup against the benefits of achieving intricate designs with consistent quality. The initial investment in technology and materials can be significant, but the potential for high-volume production may justify the costs.
Plasma Etching
Plasma etching is a dry etching technique that utilizes plasma to remove material from a surface. This method is particularly effective for creating thin films and is widely used in microelectronics and MEMS fabrication. Buyers should assess the need for specialized equipment and the potential for uniform etching across complex geometries. The precision of plasma etching can lead to superior product performance, making it a valuable option for high-tech applications.
Mechanical Etching
Mechanical etching involves physically removing material using tools such as routers or milling machines. This versatile method is applicable to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites. While mechanical etching can be slower than chemical processes, it allows for direct control over the etching process and is often used in industrial parts production and decorative items. Buyers should consider the trade-off between speed and the variety of materials that can be processed when selecting this method.
Related Video: Lecture 1 Two compartment models
Key Industrial Applications of etching company
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of etching company | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronics | Circuit Board Manufacturing | Enhanced precision in producing intricate designs | Quality of etching process, turnaround time, scalability |
| Automotive | Component Fabrication | Improved performance and durability of parts | Material compatibility, technology used, cost efficiency |
| Aerospace | Lightweight Structural Components | Reduced weight without compromising strength | Compliance with aviation standards, lead times |
| Medical Devices | Custom Tooling and Implants | High precision leading to better patient outcomes | Regulatory compliance, customization capabilities |
| Renewable Energy | Solar Cell Production | Increased efficiency of energy conversion | Material sourcing, technology integration, sustainability |
Electronics
In the electronics sector, etching companies play a crucial role in circuit board manufacturing. The etching process allows for the precise removal of material to create intricate pathways for electrical connections. This precision is vital for the functionality of modern electronics, where even minor defects can lead to significant failures. International buyers, particularly from Africa and South America, should prioritize suppliers with advanced etching technologies and a proven track record of quality assurance to ensure reliable performance in their products.
Automotive
Etching is extensively used in the automotive industry for the fabrication of various components, such as sensors and brackets. The ability to create complex shapes while maintaining tight tolerances enhances the performance and durability of automotive parts. Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should consider sourcing etching services that offer advanced material compatibility and rapid prototyping capabilities to streamline their production processes and reduce lead times.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on etching for the production of lightweight structural components that meet strict safety and performance standards. Etched parts can significantly reduce the weight of aircraft, contributing to fuel efficiency without compromising structural integrity. Buyers in Europe, especially in countries like Italy and the UK, should ensure that their etching partners comply with aerospace regulations and can demonstrate a robust quality control process to mitigate risks associated with flight safety.
Medical Devices
Etching companies are vital in producing custom tooling and implants in the medical device industry. The high precision achieved through etching leads to better-fitting devices, which can improve patient outcomes. For international buyers from regions like Africa and South America, it is crucial to partner with etching companies that understand the regulatory landscape and can provide documentation to support compliance with health standards.
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, etching is used in the production of solar cells, where it enhances the efficiency of energy conversion. The etching process allows for the creation of microstructures that optimize light absorption. Buyers should focus on sourcing from companies that prioritize sustainable practices and can provide innovative solutions to improve the performance of solar technologies, particularly in regions where renewable energy adoption is increasing rapidly.
Related Video: Self-Etching Primers – Types & Applications – Weld Thru & High Build from Eastwood
Strategic Material Selection Guide for etching company
Common Materials for Etching Applications
When selecting materials for etching processes, it is essential to consider the specific properties and performance characteristics that will influence the quality and efficiency of the final product. Below, we analyze four common materials used in etching applications, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Silicon
Key Properties: Silicon is known for its excellent thermal stability and electrical properties. It typically withstands temperatures up to 1,000°C and exhibits good corrosion resistance in certain chemical environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of silicon is its high durability and suitability for semiconductor applications. However, it can be expensive to manufacture and requires complex processing techniques, which may increase production costs.
Impact on Application: Silicon is often used in microelectronics and photovoltaic cells. Its compatibility with various etching media, such as hydrofluoric acid, makes it a preferred choice for high-precision applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM and JIS, especially in regions like Europe and the Middle East, where stringent regulations are common.
2. Glass
Key Properties: Glass offers excellent chemical resistance and can withstand high temperatures (up to 600°C). It is also non-conductive, making it suitable for applications where electrical insulation is necessary.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of glass is its inertness, which minimizes contamination during etching. However, it is relatively brittle, which can pose challenges during handling and processing.
Impact on Application: Glass is widely used in optical applications and in the production of microfluidic devices. Its compatibility with various etching solutions, including alkaline and acidic media, enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the specific grades of glass required for their applications and ensure that suppliers can meet these specifications. Compliance with local regulations regarding glass production and recycling is also crucial.
3. Metals (e.g., Stainless Steel)
Key Properties: Stainless steel is renowned for its excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength. It can withstand temperatures exceeding 800°C and is highly durable in various environments.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and ability to be recycled. However, it can be more challenging to etch compared to softer metals, requiring specialized techniques and equipment.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is often used in industrial applications, including manufacturing and food processing. Its compatibility with a range of etching media, including acids and bases, makes it a versatile choice.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the specific grade of stainless steel needed for their applications, as different grades have varying corrosion resistance levels. Compliance with international standards such as ASTM and DIN is essential, especially in Europe.
4. Polymers (e.g., PTFE)
Key Properties: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is known for its outstanding chemical resistance and low friction properties. It can withstand temperatures up to 260°C and is non-reactive with most chemicals.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PTFE is its exceptional resistance to chemical attack, making it ideal for harsh environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized etching techniques.
Impact on Application: PTFE is commonly used in applications where chemical resistance is critical, such as in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Its compatibility with various etching solutions enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the PTFE grade meets their specific application requirements and that suppliers adhere to relevant international standards for safety and quality.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for etching company | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silicon | Microelectronics, photovoltaic cells | High durability and thermal stability | Expensive and complex processing | High |
| Glass | Optical applications, microfluidic devices | Excellent chemical resistance | Brittle and challenging to handle | Medium |
| Metals (Stainless Steel) | Industrial manufacturing, food processing | Excellent corrosion resistance | Difficult to etch, requires special techniques | Medium |
| Polymers (PTFE) | Pharmaceutical, food industries | Outstanding chemical resistance | Higher cost and specialized etching | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for etching applications, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for etching company
Manufacturing Processes for Etching Companies
The manufacturing process for an etching company typically involves several key stages. Each stage is critical for ensuring the quality and precision of the etched products. Below is an overview of the main stages involved in the manufacturing process, along with the key techniques utilized.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the etching process is material preparation. This involves selecting the appropriate substrates, which may include metals, glass, or plastics.
- Material Selection: Choose materials based on the final application and required properties, such as conductivity, strength, or thermal resistance.
- Surface Treatment: Clean and prepare surfaces to ensure adhesion and uniform etching. This may include chemical cleaning, sanding, or applying primers.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves creating the initial shapes that will be etched.
- Laser Cutting: A precise method for cutting materials into specific shapes. It allows for high accuracy and minimal waste.
- Photolithography: This technique involves applying a photoresist material to the substrate, which is then exposed to light to create a pattern that will guide the etching process.
3. Etching
The etching process itself is where the material is selectively removed to create the desired patterns or features.
- Wet Etching: Involves immersing the substrate in a chemical solution that dissolves the exposed areas. It is suitable for larger areas but can lead to undercutting.
- Dry Etching: This method uses plasma to remove material and is more precise than wet etching. It is particularly useful for intricate designs and smaller features.
4. Assembly
After etching, the products may require assembly, especially if they are components of a larger system.
- Bonding: Techniques such as adhesive bonding or soldering are employed to join different parts together.
- Integration: Ensure that all components work seamlessly together, which may involve additional testing for compatibility.
5. Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which enhances the product’s appearance and functionality.
- Coating: Applying protective coatings can improve resistance to corrosion and wear.
- Polishing: This step enhances the surface finish, making it smoother and more aesthetically pleasing.
Quality Assurance in Etching Companies
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the etching industry, especially for international B2B buyers who require consistency and compliance with various standards. Here’s an overview of relevant QA practices.
International Standards
To ensure high-quality products, etching companies often adhere to several international standards:
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard that focuses on quality management systems. Companies certified under ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: Relevant for companies supplying products to the oil and gas industry, ensuring that materials meet specific performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to maintaining standards throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspect raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitor processes during manufacturing to detect and rectify any deviations from quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conduct comprehensive testing of finished products before shipment to verify they meet all specifications.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is crucial to verify that products meet quality standards:
- Dimensional Inspection: Use tools like calipers and micrometers to measure critical dimensions.
- Functional Testing: Assess the product’s performance in real-world applications.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic or X-ray testing to detect internal flaws without damaging the product.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s QC practices is essential to mitigate risks associated with quality issues.
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to evaluate their adherence to quality standards and processes.
- Reports: Request detailed QC reports that outline testing results, methodologies, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent third-party organizations to conduct inspections and testing to ensure objectivity in quality assessment.
Nuances for International B2B Buyers
When sourcing from etching companies, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, buyers should be aware of the following:
- Cultural Considerations: Understand regional practices and communication styles to foster better relationships with suppliers.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Factor in transportation and potential delays when sourcing materials internationally. Local regulations may also impact shipping and import processes.
- Compliance with Local Standards: In addition to international standards, ensure that products comply with local regulations in the buyer’s country, which may differ significantly from international norms.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in the etching industry is crucial for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, etching, assembly, and finishing, alongside stringent QC practices, buyers can ensure they partner with reliable suppliers that meet their quality expectations. Verifying supplier capabilities through audits, reports, and third-party inspections further strengthens confidence in the sourcing process, enabling successful international trade relationships.
Related Video: Etching | Multi-layer PCB Manufacturing Process – 09
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for etching company Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Etching Companies
When sourcing from etching companies, it’s crucial to analyze the comprehensive cost structure that affects pricing. The key components include:
-
Materials: The quality and type of materials used for etching significantly influence costs. Higher-grade materials may increase the price but can enhance the final product’s durability and performance.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for precision in etching processes. Labor costs vary by region, with higher wages in developed markets like Europe compared to some regions in Africa or South America.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. Understanding the overhead can help buyers identify suppliers with efficient operations, potentially leading to better pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, especially for custom projects. Buyers should clarify whether these costs are included in the quotes they receive.
-
Quality Control (QC): Stringent QC processes ensure the final product meets specifications, which may add to the cost. Buyers should inquire about the QC measures in place to assess their value.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, mode of transport, and Incoterms. Accurate logistics planning is essential for total cost estimation.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding typical margins in the industry can aid negotiation.
Key Influencers on Pricing
Several factors can affect the pricing strategy of etching companies:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing strategy.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom projects may incur additional costs. Clearly defining specifications upfront can prevent unexpected charges later in the process.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products that require specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the importance of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reliability, reputation, and financial stability can influence pricing. Conducting due diligence on potential suppliers can lead to better long-term partnerships.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the implications of Incoterms can help buyers anticipate additional costs related to shipping, customs, and insurance. Choosing the right Incoterm can optimize total landed costs.
Buyer Tips for Effective Sourcing
International B2B buyers should consider the following strategies to maximize value when sourcing from etching companies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing. Highlighting long-term relationships can encourage suppliers to provide better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. This includes considering maintenance, potential delays, and the quality of the final product.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing trends. For example, buyers from Europe may face different cost structures compared to those in Africa or South America due to varying labor and material costs.
-
Local Insights: Leverage local expertise when entering new markets. Understanding cultural and economic factors can enhance negotiation strategies and supplier selection.
-
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices: Always remember that quoted prices are often indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, material availability, and other factors. It’s prudent to request updated quotes regularly.
By comprehensively understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of etching companies, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they achieve both quality and cost-effectiveness in their sourcing endeavors.
Spotlight on Potential etching company Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘etching company’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for etching company
Critical Technical Properties of Etching Services
When selecting an etching company, understanding specific technical properties is vital for ensuring that the products meet your operational needs. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
-
Material Grade: The quality of the material used for etching significantly impacts the durability and performance of the final product. Common materials include stainless steel, aluminum, and copper, each with distinct properties. For B2B buyers, selecting the appropriate material grade ensures compatibility with end-use applications and adherence to industry standards.
-
Tolerance: This refers to the allowable variation in dimensions during the etching process. Tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.001 inches) are crucial for precision applications such as electronics or aerospace components. Understanding tolerance levels helps buyers ensure that the final product fits within their assembly requirements and minimizes the need for rework.
-
Etch Depth: This specification indicates how deep the etching penetrates into the material. Different applications require varying etch depths; for instance, deeper etching might be needed for intricate designs or functional features. Buyers must communicate their specific needs to ensure the etching company can achieve the desired results.
-
Surface Finish: The finish of the etched surface affects both aesthetic and functional aspects. Common finishes include matte, polished, or textured. A superior surface finish can enhance adhesion for coatings or improve the part’s overall performance. Buyers should specify their finish requirements to align with product functionality and brand standards.
-
Chemical Resistance: Depending on the application, the etched materials may need to withstand exposure to various chemicals. Understanding the chemical resistance of materials can prevent premature failure in environments such as laboratories or manufacturing plants. Buyers should inquire about the chemical compatibility of the etched products to ensure longevity.
-
Lead Time: This refers to the time required to complete an etching project from order to delivery. Lead times can vary based on complexity and volume. For international buyers, understanding lead times is essential for effective project planning and inventory management.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terms in the Etching Industry
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication between buyers and suppliers. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that are marketed by another company. For B2B buyers, working with an OEM can ensure that the products meet specific standards and specifications required for their applications.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure that their orders align with production schedules.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document that solicits pricing and terms from suppliers for a specific quantity of goods or services. This term is vital for buyers who are looking to compare options and negotiate pricing with multiple etching companies.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms): These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the shipping process. Knowing the relevant Incoterms can help buyers understand shipping costs, insurance responsibilities, and risk management during international transactions.
-
Prototype Development: This term refers to the initial creation of a product to test its functionality and design before mass production. For B2B buyers, engaging in prototype development can help identify potential issues early in the manufacturing process and ensure that the final product meets specifications.
-
Lead Time: As mentioned earlier, lead time is the period from order placement to product delivery. It is a crucial factor for B2B buyers to consider when planning inventory and project timelines.
Understanding these technical properties and trade terms empowers international B2B buyers to make informed decisions when partnering with etching companies, ultimately enhancing project success and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the etching company Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The etching company sector is currently experiencing significant growth driven by technological advancements and increasing demand across various industries, including electronics, automotive, and aerospace. Global drivers such as digital transformation and the shift towards miniaturization in manufacturing are reshaping how businesses operate. For international B2B buyers, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
Emerging B2B tech trends include the adoption of automation and artificial intelligence in etching processes, which enhance precision and reduce lead times. Additionally, there is a growing trend towards collaborative sourcing models, where companies are forming strategic partnerships with suppliers to foster innovation and streamline supply chains. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who can offer not just products, but also integrated solutions that encompass design, production, and logistics.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regional factors. For instance, European buyers may prioritize suppliers with robust quality assurance processes, while African and South American companies might focus on cost-effectiveness and scalability. It’s essential for buyers to evaluate suppliers based on their capability to meet specific regional regulations and standards, ensuring compliance and minimizing risk.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a core consideration for buyers in the etching company sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste generation and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize ethical sourcing and environmentally friendly practices.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Companies that demonstrate a commitment to sustainability not only enhance their brand reputation but also build stronger relationships with eco-conscious customers. Buyers should look for suppliers that hold green certifications such as ISO 14001, which indicates effective environmental management systems, or those using sustainable materials in their etching processes.
Furthermore, utilizing recycled materials and implementing waste reduction strategies can significantly lower the environmental footprint. Buyers are encouraged to inquire about the sustainability practices of potential suppliers and consider those that are transparent about their sourcing and production methods.
Brief Evolution/History
The etching industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 20th century. Initially used primarily for decorative purposes, etching technology has advanced to become a critical process in the manufacturing of intricate components across various sectors. With the introduction of computer-aided design (CAD) and laser etching technologies, precision and efficiency have drastically improved.
Today, the etching sector is not only about traditional methods but also encompasses innovative techniques that cater to the demands of modern manufacturing. As a result, international B2B buyers must stay informed about these technological advancements to leverage the best solutions available in the market. Understanding the historical context can provide valuable insights into current trends and future developments in the industry.
Related Video: International Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of etching company
-
What criteria should I use to vet etching suppliers?
When vetting etching suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and customer reviews. Request references and case studies to assess their capabilities. Verify their certifications, such as ISO or industry-specific standards, to ensure compliance with quality and safety regulations. Additionally, evaluate their production capacity and technological capabilities to meet your specific requirements. Engaging in initial discussions can also provide insights into their responsiveness and willingness to collaborate. -
Can etching services be customized for my project?
Yes, many etching companies offer customization options tailored to your project needs. Discuss your design specifications, materials, and desired finishes with potential suppliers. It is crucial to provide detailed drawings or prototypes to facilitate accurate quotes and timelines. Be clear about your expectations regarding tolerances and quality standards. A collaborative approach in the initial stages can enhance the customization process and lead to better outcomes. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for etching services?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among etching suppliers, often ranging from small batch sizes to larger quantities based on their operational capabilities. Lead times are influenced by factors such as complexity, materials, and current workload. It’s advisable to communicate your project timeline upfront to ensure that the supplier can meet your deadlines. For ongoing projects, consider negotiating flexible MOQs and lead times to accommodate future needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when dealing with etching companies?
Payment terms can vary by supplier, but common practices include upfront deposits (typically 30-50%) followed by the balance upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer credit terms based on your relationship and order history. Ensure you clarify the payment methods accepted, such as wire transfers, letters of credit, or online payment systems. It’s also wise to discuss any potential penalties for late payments or incentives for early settlements. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications from my etching supplier?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s quality management system, including their certifications (ISO, AS9100, etc.). Ask about their quality control processes, such as inspections and testing protocols throughout production. Conducting audits or site visits can further validate their practices. Establishing clear quality expectations in the contract can help mitigate risks and ensure compliance with your standards. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from an etching company?
Logistics play a critical role in international sourcing. Consider shipping options, customs regulations, and potential tariffs that may affect your overall costs. Verify the supplier’s ability to handle logistics, including packaging, labeling, and documentation for international shipping. Discuss delivery schedules and any potential delays that could arise from customs clearance. Collaborating with a logistics partner can streamline the process and minimize risks.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How should I handle disputes with my etching supplier?
Dispute resolution should be outlined in your contract, specifying preferred methods such as mediation or arbitration. Maintain clear communication with your supplier to address issues as they arise. Document all interactions and agreements to ensure transparency. If a dispute escalates, consider involving a third-party mediator to facilitate discussions. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can help prevent conflicts and foster a cooperative environment. -
What role does after-sales support play in my relationship with an etching supplier?
After-sales support is essential for addressing any issues post-delivery, such as defects or additional needs. Inquire about the supplier’s policies regarding product warranties, returns, and customer support availability. A reliable supplier will provide ongoing assistance and be responsive to your inquiries. Establishing a strong after-sales relationship can enhance satisfaction and encourage long-term collaboration, making it easier to resolve future issues.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for etching company
The landscape of strategic sourcing for etching companies is evolving rapidly, driven by globalization and technological advancements. For international B2B buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of this process is crucial. Key takeaways include:
- Value of Strategic Partnerships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers can enhance reliability and innovation, ultimately leading to improved product quality and cost efficiency.
- Importance of Local Market Insight: Buyers should leverage local expertise to navigate regulatory environments and cultural nuances, facilitating smoother transactions and better alignment with market demands.
- Emphasis on Sustainability: As global focus shifts toward sustainable practices, aligning with suppliers who prioritize environmental responsibility can enhance brand reputation and meet consumer expectations.
Looking ahead, the future of sourcing in the etching industry will be shaped by advancements in technology and an increasing emphasis on agility and responsiveness. International B2B buyers are encouraged to embrace these changes and actively seek partnerships that align with their strategic goals. By prioritizing collaboration and adaptability, companies can position themselves at the forefront of a competitive market landscape, driving innovation and growth.