Master Hydraulic Valve Sourcing: Your Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic valve
Navigating the intricate landscape of hydraulic valves is paramount for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Hydraulic valves serve as critical components in fluid power systems, controlling the flow, pressure, and direction of hydraulic fluids in various applications—from heavy machinery in construction to precision systems in aerospace. The quality and reliability of these valves directly influence operational efficiency, system integrity, and long-term profitability.
This comprehensive guide delves into the myriad aspects of hydraulic valves, equipping buyers with essential knowledge to make informed sourcing decisions. It explores various types of hydraulic valves, including OEM, ODM, and specialty manufacturers, and provides insight into selecting the right materials for specific applications. Furthermore, it addresses the manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and certifications that can help identify reputable suppliers.
Buyers will also benefit from an analysis of cost considerations, market trends, and logistical challenges unique to their regions. With detailed guidance on navigating supplier relationships and answers to frequently asked questions, this guide empowers B2B buyers to approach the global hydraulic valve market with confidence, ensuring that their procurement strategies align with their operational goals and technical requirements. By leveraging this knowledge, businesses can enhance their supply chain resilience and drive sustainable value across their operations.
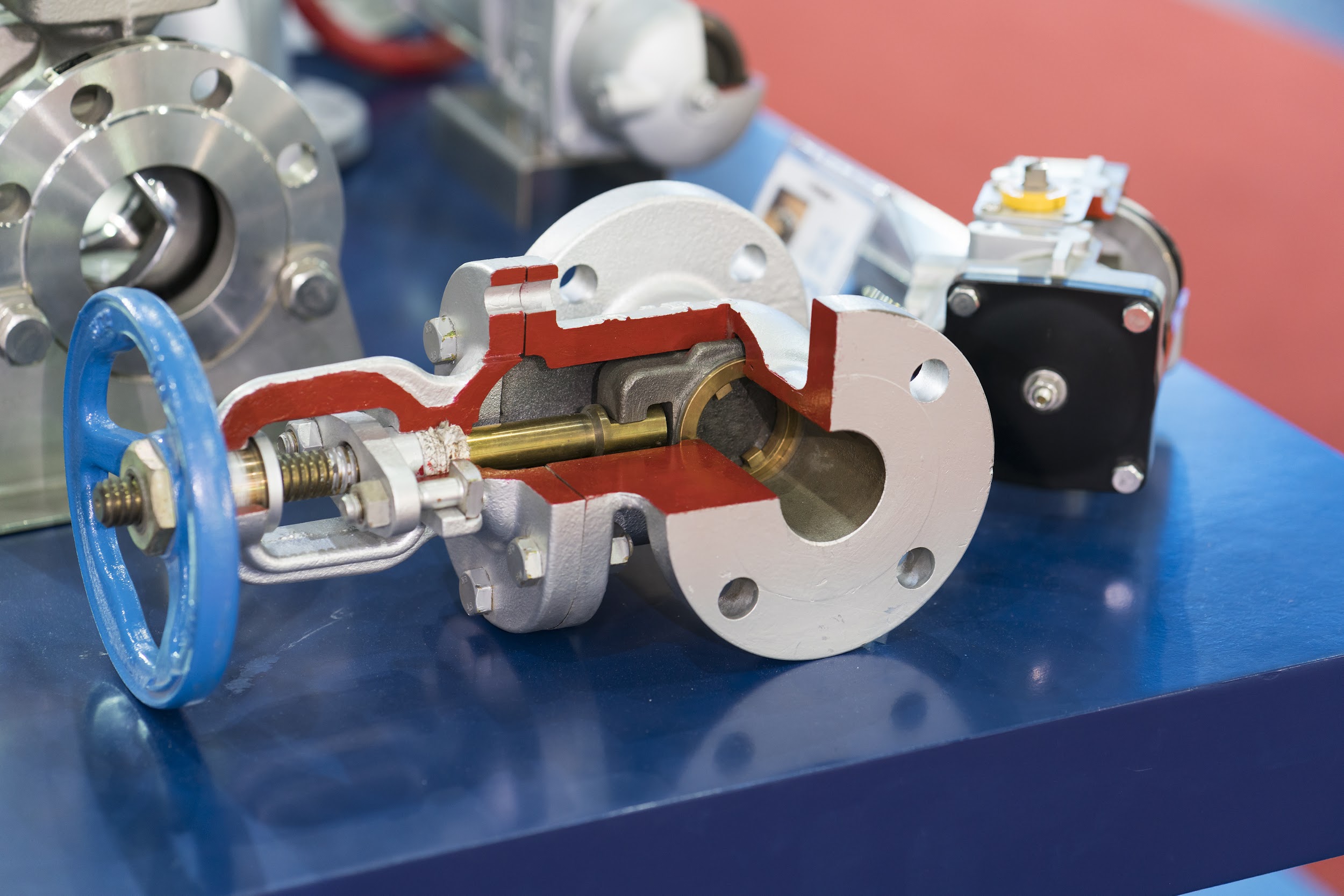
Understanding hydraulic valve Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Directional Control Valve | Controls the direction of hydraulic fluid flow; often features multiple ports | Construction, agriculture, manufacturing | Versatile for various applications; complex design may require expert installation |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Automatically releases excess pressure to protect systems | Oil & gas, chemical processing | Essential for safety; may require regular maintenance to ensure reliability |
| Flow Control Valve | Regulates the flow rate of hydraulic fluid; often adjustable | Manufacturing, automotive, aerospace | Provides precise control; potential for wear over time, affecting performance |
| Check Valve | Allows flow in one direction only, preventing backflow | Water treatment, pumping systems | Simple design enhances reliability; must be properly sized to avoid pressure drops |
| Solenoid Valve | Electromechanical valve that controls fluid flow using an electric current | Robotics, automation, HVAC | Fast operation and remote control capabilities; may require electrical compatibility |
Directional Control Valve
Directional control valves are fundamental in hydraulic systems, determining the path of fluid flow. They are essential in sectors like construction and agriculture, where precise control over hydraulic actuators is crucial. B2B buyers should consider factors such as port configuration, actuation method (manual, hydraulic, or pneumatic), and compatibility with existing systems. Selecting the right directional control valve can significantly enhance operational efficiency and response times in machinery.
Pressure Relief Valve
Pressure relief valves play a critical role in safeguarding hydraulic systems from excessive pressure that could lead to catastrophic failures. Commonly used in oil and gas and chemical processing applications, these valves automatically open to release pressure when it exceeds a preset limit. Buyers should evaluate the valve’s set pressure range, materials, and maintenance requirements to ensure reliability and compliance with safety standards. Regular checks and maintenance are essential for optimal functioning.
Flow Control Valve
Flow control valves are designed to regulate the flow rate of hydraulic fluids, making them vital in manufacturing, automotive, and aerospace sectors. They allow for precise adjustments to flow, which can optimize the performance of hydraulic systems. When purchasing, buyers should assess the valve’s flow characteristics, adjustability, and pressure drop implications. Understanding the specific application requirements is crucial to ensure the selected flow control valve meets operational demands without compromising efficiency.
Check Valve
Check valves prevent backflow in hydraulic systems, ensuring that fluid flows in only one direction. They are widely used in water treatment and pumping systems. Buyers must consider factors like size, pressure rating, and material compatibility when selecting check valves. Their simple, robust design enhances reliability, but proper sizing is critical to avoid unnecessary pressure drops. Regular inspections can help maintain their functionality and prevent system inefficiencies.
Solenoid Valve
Solenoid valves are electromechanical devices that control fluid flow through an electric current, making them integral in robotics, automation, and HVAC systems. Their ability to operate quickly and remotely offers significant advantages in modern applications. When sourcing solenoid valves, B2B buyers should focus on voltage compatibility, response time, and the valve’s suitability for specific hydraulic fluids. Ensuring that the electrical system can support these valves is also essential for seamless integration.
Related Video: Hydraulic flow control valve operation, uses, and types
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic valve
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic valve | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Control of heavy machinery operations | Enhances operational efficiency and safety | High-pressure ratings, durability, and compliance standards |
| Agriculture | Automation in irrigation systems | Increases water conservation and crop yield | Corrosion resistance, size compatibility, and adaptability |
| Oil & Gas | Flow regulation in drilling and extraction processes | Ensures safety and efficiency in high-pressure environments | Material specifications, certifications, and supply chain reliability |
| Manufacturing | Integration in assembly line automation | Improves production speed and reduces downtime | Customization options, quality control processes, and support services |
| Marine and Offshore | Control of hydraulic systems in vessels | Enhances reliability and performance under extreme conditions | Resistance to seawater corrosion, compliance with marine standards, and testing protocols |
Construction
In the construction industry, hydraulic valves are crucial for controlling the operation of heavy machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. These valves regulate the flow of hydraulic fluid, allowing precise movements and lifting capabilities. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and the Middle East, sourcing high-quality valves that can withstand harsh environmental conditions is essential. Buyers must ensure that the valves meet high-pressure ratings and are durable enough to avoid costly breakdowns, which can halt project timelines.
Agriculture
Hydraulic valves play a vital role in modern agricultural practices, particularly in automating irrigation systems. By controlling the flow of water to crops, these valves help optimize water usage, contributing to better crop yields and sustainability. For buyers in South America, where agriculture is a key economic driver, selecting valves that are resistant to corrosion and compatible with various irrigation systems is critical. Additionally, ensuring adaptability to local conditions will enhance the effectiveness of irrigation strategies.
Oil & Gas
In the oil and gas sector, hydraulic valves are employed to regulate fluid flow during drilling and extraction processes. These valves must operate reliably under extreme pressure and temperature conditions, ensuring both safety and efficiency. International buyers, particularly in regions like the Middle East, should prioritize sourcing valves made from high-grade materials that can withstand corrosive environments. Certifications and compliance with international safety standards are also crucial to mitigate risks associated with operational failures.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, hydraulic valves are integral to assembly line automation, controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid in machinery. This enhances production speed and reduces downtime, ultimately improving profitability. Buyers in Europe should focus on valves that offer customization options to fit specific machinery requirements. Additionally, manufacturers should have robust quality control processes to ensure consistent performance and reliability, which are vital for maintaining competitive advantage in the market.
Marine and Offshore
Hydraulic valves are essential in marine applications, controlling hydraulic systems in vessels such as ships and offshore platforms. These valves ensure reliable performance under extreme conditions, including high pressure and exposure to seawater. For international buyers in regions like the UAE, it is crucial to source valves that are resistant to corrosion and comply with marine safety standards. Comprehensive testing protocols should also be a priority to guarantee that valves can withstand the unique challenges of marine environments.
Related Video: Hydraulic Valve Body Inspection
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic valve
When selecting materials for hydraulic valves, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and suitability for specific applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic valve manufacturing: cast iron, stainless steel, brass, and specialized alloys. Each material presents distinct characteristics that can significantly impact operational efficiency and long-term reliability.
Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent wear resistance and ability to withstand high pressures. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 400°F (204°C) and can handle moderate corrosive environments.
Pros & Cons: Cast iron valves are durable and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for general applications. However, they are prone to corrosion in aggressive environments, which can limit their lifespan. Additionally, cast iron is heavier than other materials, which may affect installation and maintenance costs.
Impact on Application: Cast iron valves are suitable for water, steam, and non-corrosive fluids. They are commonly used in municipal water systems and industrial applications. Buyers should ensure compatibility with the specific media to avoid premature failure.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN is crucial. Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should consider the availability of cast iron valves that meet local regulations to ensure long-term reliability.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, temperature ratings up to 1,200°F (649°C), and high strength. It is particularly effective in harsh environments where other materials might fail.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for applications involving aggressive fluids. However, it is generally more expensive than cast iron and requires more complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are suitable for a wide range of fluids, including corrosive chemicals and high-pressure steam. They are commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical industries, where hygiene and reliability are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must verify compliance with international standards such as ASTM A312 for stainless steel piping. In Europe and the Middle East, certifications related to food safety and chemical compatibility are also critical.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its good corrosion resistance and moderate strength. It typically operates effectively at temperatures up to 400°F (204°C) and is suitable for low to medium-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: Brass valves are lightweight and easy to machine, making them cost-effective for smaller applications. However, they are less durable than stainless steel and may corrode in high-temperature or highly acidic environments.
Impact on Application: Brass is commonly used in plumbing, heating, and low-pressure hydraulic systems. It is ideal for applications involving water and non-corrosive gases.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding lead content in brass, particularly in Europe, where stringent limits are enforced. Ensuring compliance with standards such as JIS or ASTM is essential for market acceptance.
Specialized Alloys
Key Properties: Specialized alloys, such as Inconel or Monel, provide exceptional resistance to extreme temperatures and corrosive environments. They can handle pressures exceeding 10,000 psi and are designed for specialized applications.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of specialized alloys is their durability and performance in extreme conditions. However, they are significantly more expensive and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, leading to longer lead times.
Impact on Application: These materials are ideal for aerospace, marine, and chemical processing industries, where standard materials may fail. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions makes them suitable for high-stakes applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must evaluate the cost-benefit ratio of using specialized alloys, especially in emerging markets where budget constraints are common. Compliance with international standards is critical, especially for industries with strict regulatory oversight.
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic valve | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Municipal water systems | Cost-effective and durable | Prone to corrosion in aggressive media | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Food and pharmaceutical industries | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Brass | Plumbing and low-pressure systems | Lightweight and easy to machine | Less durable in high-temperature environments | Medium |
| Specialized Alloys | Aerospace and chemical processing | Exceptional performance in extreme conditions | Very high cost and longer lead times | High |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic valve
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for hydraulic valves are critical elements that directly influence the performance, reliability, and longevity of these essential components. For international B2B buyers, understanding these processes can enhance procurement decisions, ensuring that the selected valves meet operational demands and compliance standards.
Manufacturing Processes for Hydraulic Valves
The production of hydraulic valves involves several key stages, each crucial for ensuring the final product’s quality and functionality.
Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing hydraulic valves is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Common materials include:
- Cast Iron: Used for its strength and durability.
- Stainless Steel: Preferred for its corrosion resistance, especially in challenging environments.
- Alloy Steel: Offers high strength and toughness, suitable for high-pressure applications.
During material preparation, suppliers must ensure that the materials meet specific standards and specifications through rigorous inspections. B2B buyers should verify the supplier’s material certifications and traceability to ensure compliance with industry standards.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage is forming. This involves several techniques:
- Casting: A primary method for creating valve bodies, where molten metal is poured into molds to achieve desired shapes.
- Machining: After casting, components may require machining to achieve precise dimensions and tolerances. This can include processes such as turning, milling, and grinding.
- Forging: For high-strength applications, forging is used to shape metal through compressive forces, ensuring a denser and more durable product.
Quality at this stage is critical. Buyers should inquire about the machinery used and the expertise of the workforce to ensure high-quality production.
Assembly
The assembly stage involves combining various components, such as bodies, seats, and actuators, into a complete valve. This process may include:
- Integration of Seals and Gaskets: Essential for preventing leaks and ensuring the valve’s integrity under pressure.
- Installation of Actuators: For automated valves, actuators must be precisely aligned to function correctly.
A focus on precision during assembly is paramount. B2B buyers should assess the manufacturer’s assembly protocols, including any automated systems that enhance consistency and reduce human error.
Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing is finishing, which includes surface treatments such as:
- Coating: Protective coatings can enhance corrosion resistance and improve wear resistance.
- Polishing: Ensures smooth surfaces that reduce friction and improve flow characteristics.
Finishing processes can significantly impact the longevity and performance of hydraulic valves. Buyers should verify that manufacturers adhere to industry standards for surface treatments.
Quality Assurance in Hydraulic Valve Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is essential to ensure that the manufactured valves meet specific performance and safety standards. This includes adherence to international standards, rigorous testing protocols, and continuous monitoring throughout the manufacturing process.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should look for manufacturers that comply with recognized international standards, including:
- ISO 9001: This certification indicates a robust quality management system, focusing on consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute provides standards for valves used in oil and gas applications, focusing on safety and performance.
These certifications serve as a benchmark for reliability and quality in the manufacturing process.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control typically involves several key checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to catch defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product before it is shipped.
Each checkpoint plays a vital role in maintaining product integrity. Buyers should inquire about the specifics of the QC process, including the tools and techniques used.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods for hydraulic valves can include:
- Pressure Testing: Ensures that the valve can withstand operational pressures without leaking.
- Flow Testing: Assesses the valve’s performance under various flow conditions to ensure it meets design specifications.
- Durability Testing: Simulates long-term use to identify potential failure points.
These tests provide critical insights into the valve’s reliability and performance, helping buyers make informed decisions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take several steps:
- Audits: Conduct on-site audits to evaluate manufacturing processes and quality control measures firsthand. This can provide invaluable insights into a supplier’s operational capabilities.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality control reports, including test results and compliance certifications.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage independent inspection agencies to assess product quality before shipment, ensuring unbiased evaluation.
These measures help mitigate risks associated with supplier quality and enhance confidence in procurement decisions.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
For international B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is crucial.
- Regional Compliance: Ensure that the supplier’s certifications align with regional regulations and standards, as these can vary significantly.
- Language Barriers: Work with suppliers who can provide documentation and support in the buyer’s preferred language, facilitating better communication and understanding.
- Cultural Considerations: Be aware of different business practices and expectations in various regions, which can affect negotiation and partnership dynamics.
By focusing on these aspects, international buyers can enhance their sourcing strategy, ensuring that the hydraulic valves they procure are of the highest quality, reliable, and suited for their specific operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing Production Process with Modern Machines and Skilful Workers
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic valve Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of hydraulic valves is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The intricate interplay of various cost components and price influencers can significantly impact sourcing decisions and overall profitability.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly influences the cost of hydraulic valves. Common materials include cast iron, stainless steel, and specialized alloys. The higher the quality and corrosion resistance of the material, the greater the cost. Additionally, sourcing materials from different regions can vary in price due to local market conditions.
-
Labor: Labor costs include wages for skilled workers involved in the design, manufacturing, and assembly of valves. Regions with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing; however, this can sometimes come at the expense of quality if not managed properly.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the fixed and variable costs associated with the manufacturing process, such as utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient production techniques and economies of scale can help reduce these costs.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tooling: Initial setup costs for molds and specialized tools can be significant, especially for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over larger production runs, making them less impactful on unit pricing for high-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential for ensuring product reliability, particularly for hydraulic valves used in high-stakes applications. Testing protocols, certifications, and compliance with industry standards can add to the overall cost but are critical for maintaining operational integrity.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary widely depending on the geographical location of the supplier and buyer. Factors such as transportation mode, distance, and import/export duties can significantly affect total costs.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure sustainability. This margin can fluctuate based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic valves:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders usually result in better pricing due to economies of scale. Understanding the minimum order quantities (MOQs) can help in negotiating favorable terms.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-designed valves may incur additional costs for engineering and production. Standardized valves tend to be less expensive, so buyers should assess their needs carefully.
-
Materials: The choice of materials impacts not only the initial cost but also the durability and maintenance expenses over the valve’s lifecycle.
-
Quality and Certifications: Valves that meet rigorous quality standards and possess relevant certifications (like ISO) may command higher prices but offer better reliability and lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and financial stability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge premium prices due to their perceived reliability.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for calculating total landed costs. These terms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and insurance, affecting overall pricing.
Buyer Tips
For international buyers, especially from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Leverage volume commitments to negotiate better pricing and terms. Establish long-term relationships with suppliers to enhance negotiation power.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Assess the Total Cost of Ownership rather than just the purchase price. Consider maintenance, operational efficiency, and reliability when evaluating costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to local economic conditions, tariffs, and trade agreements. Researching local market dynamics can provide insights into fair pricing.
-
Supplier Diversity: Engage with multiple suppliers to compare costs, quality, and lead times. This can also mitigate risks associated with supplier dependency.
Disclaimer
Prices for hydraulic valves can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. It is advisable for buyers to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing and avoid unexpected costs.
Spotlight on Potential hydraulic valve Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘hydraulic valve’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic valve
When navigating the procurement of hydraulic valves, understanding key technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Below are essential specifications and commonly used terms that every B2B buyer should know.
Critical Technical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the type of material used in the construction of the hydraulic valve, typically stainless steel, cast iron, or brass.
– B2B Importance: Material selection affects durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for specific fluid types. Buyers must match material grades to their operational environment to prevent premature failure and costly downtime. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: The maximum pressure that a hydraulic valve can safely handle, often expressed in PSI (pounds per square inch).
– B2B Importance: Understanding pressure ratings is vital to ensure that the valve can withstand the demands of the specific application. Choosing a valve with an inadequate rating can lead to leaks or catastrophic failures.
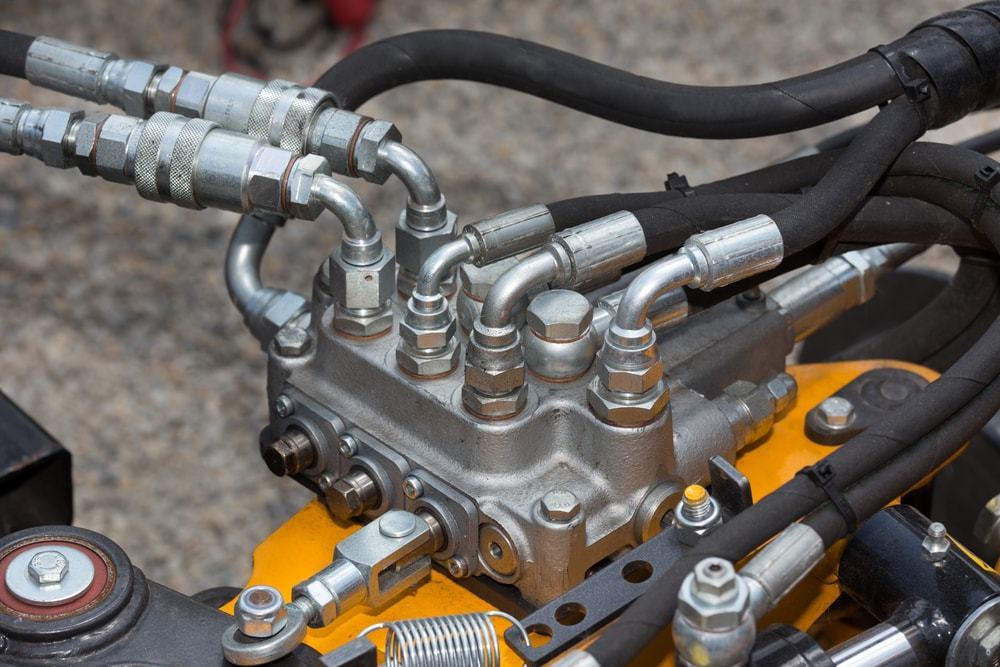

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a valve’s dimensions, which ensures proper fit and function.
– B2B Importance: Tight tolerances are critical for achieving optimal performance and preventing leaks. Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to industry standards to ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
Flow Rate
– Definition: The volume of fluid that can pass through the valve in a given time, typically measured in GPM (gallons per minute).
– B2B Importance: Knowing the flow rate is essential for ensuring that the hydraulic system operates efficiently. An improperly sized valve can lead to reduced performance or excessive energy consumption. -
Seal Type
– Definition: The type of sealing mechanism used to prevent leaks, such as O-rings, lip seals, or custom gaskets.
– B2B Importance: Seal materials must be compatible with the fluids being used and capable of withstanding pressure and temperature variations. Proper sealing is vital for maintaining system integrity and preventing contamination. -
Actuation Type
– Definition: The method by which the valve is operated, including manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic actuation.
– B2B Importance: The choice of actuation affects responsiveness and control. Buyers must consider the operational context to choose the most effective actuation method for their systems.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: OEM valves are designed for specific applications, ensuring compatibility and performance. Understanding OEM offerings is critical for maintaining system integrity. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers assess budget constraints and inventory requirements, especially for international transactions. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare multiple suppliers’ offerings, facilitating informed decision-making in the procurement process. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of rules that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Understanding Incoterms helps buyers clarify shipping responsibilities, costs, and risks, ensuring smoother logistics and compliance in international trade. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the product.
– Importance: Awareness of lead times is crucial for planning and managing supply chain logistics, especially in industries where downtime can be costly. -
Certification
– Definition: Official recognition that a product meets specific standards, such as ISO or CE certifications.
– Importance: Certifications assure buyers of quality and compliance with safety standards, particularly in regulated industries, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they select the most suitable hydraulic valves for their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hydraulic valve Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The hydraulic valve market is experiencing significant growth driven by several global factors. The increasing demand for automation in industries such as construction, agriculture, and manufacturing is propelling the need for efficient fluid control systems. As international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek to enhance operational efficiency, hydraulic valves are becoming crucial components in their machinery and systems.
Emerging technologies are reshaping sourcing strategies. The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) in hydraulic systems allows for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which reduces downtime and improves reliability. Additionally, the rise of digital procurement platforms is streamlining the sourcing process, enabling buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and products. These platforms often incorporate advanced analytics to help buyers make informed decisions based on market trends and supplier performance.
Market dynamics are also influenced by geopolitical factors and trade policies. For instance, tariffs and trade agreements can significantly impact pricing and availability, particularly for buyers in South America and the Middle East. Understanding these dynamics is essential for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and identify the most reliable suppliers. Furthermore, a focus on customization and specialized solutions is growing, as industries demand hydraulic valves tailored to specific applications and operational conditions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming increasingly critical in the procurement process for hydraulic valves. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, including resource consumption and waste generation, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who adopt environmentally friendly manufacturing techniques and utilize recyclable or sustainably sourced materials.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers should ensure their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and maintain transparency in their operations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management) are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices.
In terms of materials, the use of ‘green’ certifications, such as those from the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) for wood-based components or adherence to RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) standards for electronic components, is becoming essential. This not only helps in reducing the carbon footprint but also enhances the marketability of products in regions with stringent environmental regulations, particularly in Europe.
Brief Evolution/History
The hydraulic valve industry has evolved significantly over the past century, transitioning from rudimentary mechanical designs to highly sophisticated electronic and automated systems. Initially, hydraulic valves were primarily used in heavy machinery and industrial applications. However, advancements in technology have broadened their applications across various sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and renewable energy.
The introduction of proportional and servo-controlled valves marked a pivotal shift, allowing for more precise control of fluid dynamics. This evolution has been driven by the increasing complexity of industrial systems and the demand for higher efficiency and reliability. As the industry continues to innovate, international B2B buyers are presented with new opportunities to enhance their operations through cutting-edge hydraulic solutions.
Related Video: Incoterms for beginners | Global Trade Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic valve
-
What criteria should I use to vet hydraulic valve suppliers?
When vetting hydraulic valve suppliers, prioritize industry certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental practices. Investigate the supplier’s track record in your specific industry, looking for testimonials and case studies. Technical capabilities are also crucial; assess their R&D department’s strength and their ability to customize products to meet your needs. Lastly, examine their quality control processes to ensure they adhere to rigorous testing standards, which is vital for maintaining system reliability and performance. -
Can I customize hydraulic valves to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for hydraulic valves. This may include alterations in size, material, and functionality to suit specific applications. When approaching suppliers, clearly outline your technical specifications and operational challenges. A strong supplier will provide engineering support to help develop a solution that meets your needs. Keep in mind that customization may impact lead times and costs, so discuss these factors upfront to ensure alignment with your project timelines and budgets. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for hydraulic valves?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly among manufacturers and depend on the type of valve and customization level. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard products to hundreds for specialized designs. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by the complexity of the order and current production schedules. For urgent needs, inquire about expedited services or stock availability. Discussing these details early in the procurement process will help you plan your project timelines effectively. -
What quality assurance certifications should I look for in suppliers?
Key certifications to consider include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, which indicates a commitment to continuous improvement, and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Additionally, CE marking is crucial for products sold in Europe, ensuring compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Manufacturers may also hold industry-specific certifications relevant to your sector, which can further validate their expertise and commitment to quality. Always request documentation to verify these certifications during the supplier evaluation process.
-
How should I approach logistics when sourcing hydraulic valves internationally?
Logistics can be complex when sourcing hydraulic valves internationally. Start by identifying the shipping terms (Incoterms) that will govern your order, as these define responsibilities for shipping costs, risks, and insurance. Choose a reliable freight forwarder familiar with your product type and destination. Customs clearance is another critical aspect; ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation to facilitate a smooth import process. Planning for potential delays in shipping or customs will help you mitigate risks and keep your project on track. -
What steps should I take if there is a dispute with my supplier?
In the event of a dispute with your supplier, first attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication, outlining your concerns clearly. If informal discussions fail, refer to the terms laid out in your contract, including any dispute resolution clauses. Consider involving a neutral third party for mediation if necessary. Document all communications and agreements, as this can support your case if the dispute escalates. For significant issues, consulting with legal counsel experienced in international trade law may be advisable to explore your options. -
What payment terms are common for international B2B transactions in hydraulic valve sourcing?
Common payment terms for international transactions include letter of credit (LC), which offers security for both parties, and wire transfers, which can be faster but riskier without guarantees. Some suppliers may offer open account terms for established relationships, allowing payment after delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that protect your interests while considering the supplier’s requirements. Always verify the payment process and any fees associated with currency exchange, especially when dealing with suppliers in different regions. -
How can I ensure the hydraulic valves I purchase are compliant with local regulations?
To ensure compliance with local regulations, first research the specific standards applicable to hydraulic valves in your region. This may include safety, environmental, and performance regulations. Work closely with your supplier to verify that their products meet these standards and request certification documents as proof. Additionally, consider consulting with local regulatory bodies or industry associations for guidance on compliance requirements. Staying informed about regulations can prevent costly delays and ensure your operations remain within legal frameworks.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic valve
In conclusion, effective strategic sourcing for hydraulic valves is paramount for international B2B buyers aiming to enhance operational efficiency and mitigate risks in their supply chains. Key takeaways include understanding the diverse types of manufacturers—OEM, ODM, contract, specialty, and large-scale producers—and their respective advantages. Prioritizing manufacturers with robust quality control processes, industry certifications, and innovative R&D capabilities will ensure long-term reliability and performance of hydraulic systems.
As global markets become increasingly interconnected, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must leverage strategic sourcing to navigate complexities and capitalize on opportunities. By fostering strong supplier relationships and emphasizing compliance with regional standards, businesses can secure not only the best products but also sustainable competitive advantages.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced hydraulic solutions will only grow, driven by technological advancements and evolving industry needs. Now is the time for international buyers to refine their sourcing strategies and embrace innovation, ensuring they remain at the forefront of their respective sectors. Engage with suppliers who share your vision for quality and performance, and take proactive steps towards optimizing your procurement processes today.