Your Ultimate Guide to Sourcing Cleantech Environmental
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for cleantech environmental
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the demand for sustainable solutions is more pressing than ever. The cleantech environmental sector stands at the forefront of this movement, offering innovative technologies and practices that not only protect our planet but also enhance operational efficiency and profitability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the ability to navigate this complex market is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse aspects of the cleantech environmental industry, covering essential topics such as types of technologies, materials used, manufacturing and quality control, key suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends. Each section is designed to empower buyers with actionable insights, enabling them to identify the most effective solutions tailored to their specific needs.
Moreover, this guide addresses common FAQs to demystify the cleantech landscape, ensuring that decision-makers are equipped with the knowledge necessary to implement sustainable practices within their organizations. By harnessing the information provided, buyers can confidently engage with suppliers and leverage cleantech innovations to drive both environmental and economic benefits. Embrace the future of sustainable business and unlock the potential of cleantech environmental solutions today.
Understanding cleantech environmental Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Utilizes natural resources to generate energy (solar, wind, etc.) | Power generation, energy management systems | Pros: Reduces energy costs; Cons: High initial investment. |
| Energy Storage Solutions | Technologies that store energy for later use (batteries, etc.) | Grid stabilization, backup power solutions | Pros: Enhances energy reliability; Cons: Maintenance costs can be high. |
| Waste Management Technologies | Systems for recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy processes | Industrial waste management, municipal services | Pros: Reduces landfill waste; Cons: Regulatory complexities. |
| Water Purification Technologies | Advanced systems for treating and recycling water | Industrial water treatment, agricultural use | Pros: Ensures compliance with regulations; Cons: High operational costs. |
| Sustainable Agriculture | Practices that promote eco-friendly farming methods | Organic farming, agro-tech solutions | Pros: Improves soil health; Cons: Lower yields initially. |
Renewable Energy
Renewable energy encompasses technologies that harness natural resources such as sunlight, wind, and water to generate electricity. For B2B buyers, investing in renewable energy solutions can significantly reduce long-term energy costs and enhance sustainability credentials. However, the initial capital required for installation can be substantial, necessitating careful financial planning and analysis of potential return on investment.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions, including advanced battery technologies, allow businesses to store excess energy for later use, ensuring a reliable power supply. These systems are crucial for industries that rely heavily on uninterrupted energy, such as manufacturing and data centers. While they provide enhanced energy reliability and efficiency, buyers must consider ongoing maintenance costs and the lifespan of the storage systems when making purchasing decisions.
Waste Management Technologies
Innovative waste management technologies are designed to optimize the recycling process, convert waste to energy, and minimize landfill use. These solutions are particularly relevant for industries generating significant waste, such as construction and manufacturing. Although they can lead to substantial waste reduction and compliance with environmental regulations, potential buyers should be aware of the regulatory complexities and costs associated with implementing these systems.
Water Purification Technologies
Water purification technologies offer advanced methods for treating and recycling water, making them essential for industries with high water usage, such as agriculture and manufacturing. These systems help businesses comply with environmental regulations and improve water quality. However, buyers should evaluate the high operational costs and the need for regular maintenance when considering these technologies.
Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture focuses on environmentally friendly farming practices that enhance soil health and reduce chemical usage. This approach is increasingly important for businesses in the food supply chain looking to meet consumer demand for organic and sustainably sourced products. While it can lead to improved soil and crop health over time, initial yields may be lower, requiring careful planning and a long-term commitment to sustainability.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of cleantech environmental
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of cleantech environmental | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Solar Power Systems | Reduced energy costs and enhanced sustainability | Quality of solar panels, local regulations, installation support |
| Waste Management | Waste-to-Energy Technologies | Decreased landfill use and generation of renewable energy | Technology efficiency, compliance with environmental laws, operational costs |
| Agriculture | Precision Agriculture Solutions | Improved yield and resource efficiency | Technology integration, training for staff, local support services |
| Water Treatment | Advanced Filtration and Purification Systems | Enhanced water quality and reduced operational costs | System reliability, compliance with health standards, maintenance support |
| Manufacturing | Eco-Friendly Production Processes | Lower emissions and resource consumption | Supplier certifications, technology compatibility, lifecycle costs |
Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, solar power systems are a prime application of cleantech environmental solutions. These systems help businesses reduce their energy expenses while promoting sustainability. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, understanding local solar panel quality and installation support is crucial, as these factors can significantly impact the effectiveness and longevity of the investment.
Waste Management
Waste-to-energy technologies represent a significant cleantech application in waste management. This process converts non-recyclable waste materials into usable forms of energy, thus reducing landfill reliance and generating renewable energy. B2B buyers must consider the technology’s efficiency, compliance with local environmental regulations, and the overall operational costs associated with these systems to ensure a viable and sustainable solution.
Agriculture
Precision agriculture solutions leverage cleantech innovations to optimize farming practices. By using technologies such as IoT sensors and data analytics, businesses can enhance crop yields while minimizing resource use, including water and fertilizers. Buyers in this sector should focus on technology integration capabilities, the training required for their staff, and the availability of local support services to ensure successful implementation and operation.
Water Treatment
Advanced filtration and purification systems are essential applications of cleantech environmental in the water treatment sector. These systems improve water quality and can lead to significant operational cost reductions for businesses. For international buyers, particularly from the Middle East where water scarcity is a critical issue, it is vital to assess system reliability, compliance with health and safety standards, and the availability of maintenance support.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, eco-friendly production processes are increasingly adopted to reduce emissions and resource consumption. Implementing cleantech solutions not only helps businesses meet regulatory requirements but also enhances their marketability as environmentally responsible entities. Buyers should prioritize supplier certifications, technology compatibility with existing processes, and an analysis of lifecycle costs to ensure that their investments yield long-term benefits.
Related Video: From Waste to Wonder: The Surprising Uses of Carbon Dioxide
Strategic Material Selection Guide for cleantech environmental
When selecting materials for cleantech environmental applications, it is essential to consider their properties, advantages, limitations, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in the cleantech sector: Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Polypropylene, and Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP). Each material has unique characteristics that impact its suitability for various applications.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, has excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand temperatures up to 600°F (315°C). Its high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor applications. However, it can be more expensive than other metals and may require specialized welding techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is compatible with various media, including water and air, making it ideal for heat exchangers and structural components in solar energy systems.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should be aware of local availability and import duties. Compliance with standards such as ASTM B209 for aluminum sheet and plate is crucial for ensuring quality.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel exhibits high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and can withstand high temperatures (up to 1500°F or 815°C). It is also non-reactive, making it suitable for applications involving chemicals.
Pros & Cons: Its durability and resistance to rust make stainless steel a preferred choice for many cleantech applications. However, it is heavier than aluminum and can be more costly, particularly grades like 316 that offer superior corrosion resistance.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is particularly effective in applications involving corrosive environments, such as wastewater treatment and chemical processing.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel sheets. Understanding local market conditions in the Middle East, where stainless steel is often used in construction, can help in sourcing the right grade.
Polypropylene
Key Properties: Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer with excellent chemical resistance, low density, and a melting point of approximately 320°F (160°C). It is lightweight and flexible.
Pros & Cons: Its low cost and ease of manufacturing make polypropylene an attractive option for various applications. However, it has lower temperature resistance compared to metals, which may limit its use in high-heat environments.
Impact on Application: Polypropylene is often used in water filtration systems and as liners in biogas digesters due to its chemical resistance and lightweight nature.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards like ASTM D638 for tensile properties is essential. Buyers should consider local recycling capabilities, as polypropylene can be recycled, aligning with sustainability goals.
Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP)
Key Properties: GFRP is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with glass fibers. It offers high strength, low weight, and excellent corrosion resistance, with a temperature tolerance of up to 300°F (150°C).
Pros & Cons: GFRP is ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet strong materials. Its main disadvantage is the higher manufacturing complexity and cost compared to traditional materials.
Impact on Application: GFRP is commonly used in wind turbine blades and solar panel frames, where strength and weight are critical.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards such as ASTM D3039 for tensile testing is vital. Buyers in Europe may find GFRP more readily accepted due to its use in renewable energy applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for cleantech environmental | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Heat exchangers, structural components | Lightweight, corrosion-resistant | Higher cost, complex welding | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Wastewater treatment, chemical processing | Durable, high-temperature tolerance | Heavier, more expensive | High |
| Polypropylene | Water filtration systems, biogas digesters | Low cost, easy to manufacture | Limited temperature resistance | Low |
| Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic | Wind turbine blades, solar panel frames | Lightweight, strong | Higher manufacturing complexity | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for cleantech applications, emphasizing the importance of aligning material properties with specific application requirements and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for cleantech environmental
Manufacturing Processes in Cleantech Environmental Solutions
In the rapidly evolving cleantech sector, the manufacturing processes play a crucial role in ensuring that products meet the stringent demands of sustainability and efficiency. Understanding these processes is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Below is a breakdown of the typical stages involved in the manufacturing of cleantech solutions.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Sustainable Materials: The process begins with sourcing eco-friendly materials that align with sustainability goals. Common materials include recycled metals, bio-based plastics, and renewable resources.
– Pre-Processing Techniques: Materials undergo various pre-processing steps, such as cleaning, cutting, and treating, to ensure they meet specifications and are ready for forming. -
Forming
– Techniques: Common forming methods include extrusion, injection molding, and 3D printing. Each method is chosen based on the product design and material properties.
– Efficiency Considerations: Manufacturers often utilize energy-efficient machines and processes, reducing waste and energy consumption during this stage. -
Assembly
– Modular Design: Many cleantech products are designed modularly, allowing for easier assembly and maintenance. This approach enhances flexibility and scalability in production.
– Automation: Increasingly, manufacturers are employing automation technologies to streamline assembly processes, improve precision, and reduce labor costs. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatments: This stage may involve processes such as coating, painting, or polishing to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal while also providing additional protection against environmental factors.
– Quality Control Integration: Finishing processes are often integrated with quality control checks to ensure that products meet all required specifications before they reach the market.
Quality Assurance in Cleantech Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is paramount in the cleantech industry, where products must not only perform efficiently but also comply with international standards. Below are key aspects of QA that B2B buyers should consider.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system (QMS). It ensures that manufacturers consistently provide products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: Essential for products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates that a product complies with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For products related to the oil and gas sector, the American Petroleum Institute (API) sets standards that ensure safety and reliability.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified quality standards before entering the production process. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– Continuous monitoring during manufacturing helps identify defects early in the process. This may involve real-time data collection and analysis. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– Completed products undergo rigorous testing and inspection to ensure they meet all specifications and standards before shipping to clients.
Common Testing Methods
- Performance Testing: Evaluates how well the product functions under various conditions.
- Durability Testing: Assesses the lifespan and resilience of products against environmental factors.
- Safety Testing: Ensures compliance with safety regulations and standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, especially those from diverse regions, verifying supplier quality is critical. Here are effective strategies:
-
Supplier Audits
– Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes, quality control systems, and compliance with international standards. -
Requesting Quality Reports
– Suppliers should provide documentation of quality tests, certifications, and compliance with relevant standards. Reviewing these reports can offer insights into the supplier’s commitment to quality. -
Third-Party Inspections
– Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
For B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in different regions is essential:
- Cultural Differences: Recognize that quality expectations and manufacturing practices can vary significantly across regions. It’s vital to communicate specific requirements clearly.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions may have distinct regulatory requirements. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations that apply to cleantech products.
- Sustainability Standards: As sustainability becomes a global priority, ensure that suppliers adhere to international environmental standards and practices.
Conclusion
A thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices in the cleantech sector is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on sustainable materials, efficient manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control, businesses can ensure that they are sourcing high-quality, environmentally friendly products. Additionally, implementing robust verification processes will help mitigate risks and foster successful partnerships in this dynamic industry.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for cleantech environmental Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure in Cleantech Environmental Sourcing
When navigating the complex landscape of cleantech environmental sourcing, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to grasp the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing of products and services. A comprehensive understanding of these components allows buyers to make informed decisions and effectively negotiate contracts.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the cost structure. Sustainable materials often come with higher initial costs but can lead to long-term savings and environmental benefits. Buyers should evaluate the lifecycle of materials to assess their true cost.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and can be influenced by local wage standards and workforce skill levels. Countries with a skilled labor force may present higher upfront costs but can enhance quality and reduce errors, ultimately leading to cost savings.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, rent, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize overhead costs. Buyers should inquire about the supplier’s production capabilities and any technological advancements they employ.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront investment. However, investing in high-quality tooling can lead to better production efficiency and product quality. Buyers should assess whether the tooling costs are justified based on their volume requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures can increase costs, but they are essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance with environmental standards. Buyers should prioritize suppliers with robust QC practices to mitigate risks.
-
Logistics: Transporting cleantech products can be costly, especially when dealing with international shipments. Buyers must consider shipping costs, insurance, and potential delays in their budget. Understanding Incoterms can aid in clarifying responsibilities and reducing unexpected expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the perceived value of their offerings. Buyers should benchmark against industry standards to ensure they are receiving competitive pricing.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence pricing within the cleantech sector, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQs) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders typically yield lower per-unit costs. Buyers should assess their needs and negotiate MOQs that align with their purchasing capacity.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom solutions often come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against additional costs and consider whether off-the-shelf options could meet their needs.
-
Materials: The type and quality of materials directly impact pricing. Sustainable materials may be more expensive but can enhance product longevity and performance.
-
Quality/Certifications: Certifications such as ISO or environmental standards can add to costs but are crucial for compliance and market acceptance. Buyers should consider these certifications as indicators of product quality.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their reliability and proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining who bears the costs and risks during shipping. This knowledge can help buyers negotiate better terms and avoid unexpected fees.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
-
Negotiate: Always be prepared to negotiate pricing and terms. Leverage your understanding of the market and competitor pricing to secure favorable conditions.
-
Consider Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy use, and disposal. Sustainable solutions often provide better TCO in the long run.
-
Research Market Prices: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. This knowledge can empower you to make strategic purchasing decisions.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms over time. Trust and open communication can yield long-term benefits.
-
Be Aware of Regional Nuances: Pricing can vary significantly across regions due to local regulations, tariffs, and market dynamics. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should consider these factors when sourcing.
Disclaimer
The prices and cost components discussed are indicative and can fluctuate based on market conditions, supplier capabilities, and geopolitical factors. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate pricing tailored to their specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential cleantech environmental Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘cleantech environmental’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for cleantech environmental
When engaging with the cleantech environmental sector, international B2B buyers must familiarize themselves with critical technical properties and industry terminology. This knowledge ensures informed decision-making and successful negotiations.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: This refers to the classification of materials based on their properties and intended use, such as steel grades (e.g., stainless steel vs. carbon steel).
– B2B Importance: Understanding material grades is crucial when sourcing components for renewable energy technologies (like solar panels or wind turbines) to ensure durability and performance under environmental conditions. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation from a standard dimension or measurement in manufacturing.
– B2B Importance: Precise tolerances are vital in cleantech applications, where even minor deviations can affect efficiency and safety. Buyers must ensure suppliers can meet these specifications to avoid costly production errors. -
Energy Efficiency Rating
– Definition: This rating assesses how effectively a technology converts energy input into useful output, often expressed as a percentage.
– B2B Importance: Buyers should prioritize products with high energy efficiency ratings, as they indicate lower operational costs and reduced environmental impact, aligning with sustainability goals. -
Lifecycle Assessment (LCA)
– Definition: LCA evaluates the environmental impacts of a product throughout its lifecycle, from raw material extraction through production and use to disposal.
– B2B Importance: Understanding LCA helps businesses select products that minimize environmental harm, essential for compliance with regulations and corporate sustainability commitments. -
Capacity Factor
– Definition: This is the ratio of actual output over a period of time to the maximum possible output if the system operated at full capacity continuously.
– B2B Importance: For renewable energy projects, a high capacity factor indicates reliability and efficiency, crucial for justifying investment and ensuring long-term viability.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for components that meet quality and regulatory standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ helps buyers manage inventory levels and cash flow, especially when dealing with suppliers in different regions. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers requesting a quote for specific products or services.
– Importance: Issuing an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive procurement. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that delineate responsibilities between buyers and sellers.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand shipping responsibilities, risks, and costs, which is essential for international transactions. -
Sustainability Metrics
– Definition: Quantitative measures used to assess the environmental performance of products or processes.
– Importance: Using sustainability metrics allows buyers to evaluate suppliers on their commitment to environmental stewardship, critical for maintaining a sustainable supply chain.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the cleantech environmental sector can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring they make informed decisions that align with their sustainability objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the cleantech environmental Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The cleantech environmental sector is experiencing significant growth driven by a global shift towards sustainability and the urgent need to combat climate change. Key drivers include increasing regulatory pressures, rising energy costs, and the demand for cleaner technologies among consumers and businesses alike. For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed sourcing decisions.
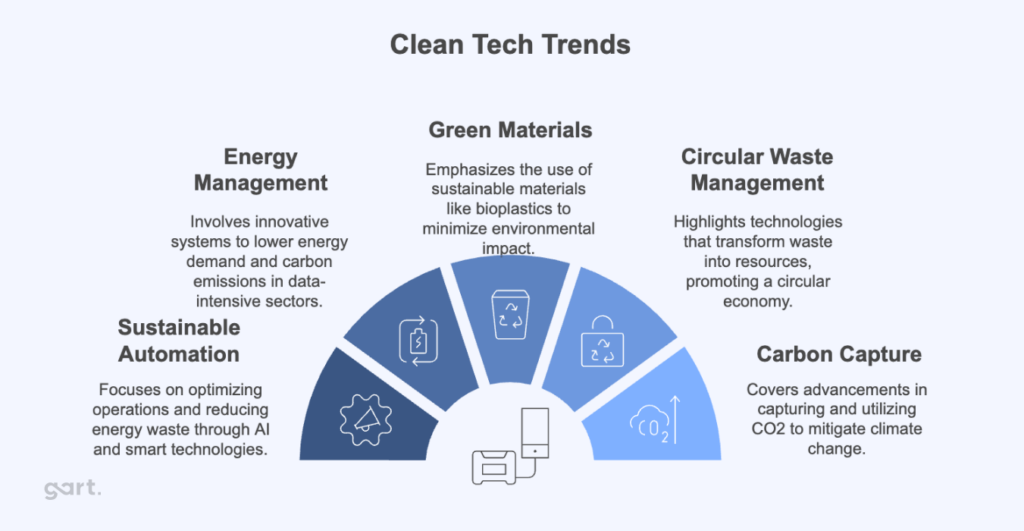
Emerging trends in B2B technology within the cleantech sector include the rise of renewable energy solutions, such as solar, wind, and bioenergy, which are becoming more accessible and affordable. Additionally, digital solutions like energy management systems and IoT applications are enhancing operational efficiencies and enabling real-time monitoring of energy consumption. Buyers should pay attention to innovations in waste management technologies and sustainable materials, which are gaining traction as companies seek to minimize their environmental footprint.
Furthermore, the market dynamics are influenced by a growing emphasis on circular economy principles, where businesses are encouraged to design products for longevity, reuse, and recyclability. This shift not only reduces waste but also creates new business opportunities. Buyers in emerging markets must be proactive in identifying suppliers that align with these trends, ensuring they are not only compliant with local regulations but also positioned to leverage global sustainability initiatives.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
In the cleantech environmental sector, sustainability and ethical sourcing have become pivotal considerations for B2B buyers. The environmental impact of sourcing decisions is profound; therefore, companies are increasingly held accountable for their supply chain practices. Ethical sourcing ensures that materials are obtained responsibly, minimizing harm to the environment and local communities.
Buyers should prioritize suppliers who demonstrate commitment to sustainability through certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). Utilizing materials that are certified as environmentally friendly, like recycled plastics or sustainably sourced wood, not only supports responsible practices but also resonates with increasingly eco-conscious consumers.
Moreover, the importance of transparency in supply chains cannot be overstated. B2B buyers are encouraged to engage with suppliers who provide clear documentation of their sourcing processes and environmental impact assessments. By fostering relationships with ethical suppliers, companies can not only enhance their brand reputation but also mitigate risks associated with sustainability compliance.
Brief Evolution/History
The cleantech sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from niche innovations to mainstream solutions. The 1970s oil crisis marked a pivotal moment, spurring interest in renewable energy sources. By the 1990s, advancements in technology led to increased investment in clean technologies, driven by both environmental concerns and economic opportunities.
The 2000s saw the rise of regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions, which further accelerated the adoption of cleantech solutions across various industries. Today, the sector is characterized by a diverse array of players, from startups innovating in energy storage to established corporations transitioning to greener practices. For B2B buyers, this evolution underscores the importance of staying informed about market developments to identify strategic partnerships and investment opportunities in sustainable technologies.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of cleantech environmental
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers in the cleantech sector?
When vetting suppliers, consider their industry experience, reputation, and certifications relevant to cleantech solutions. Look for suppliers with a proven track record in delivering quality products or services. Request case studies or references from previous clients to evaluate their reliability. Additionally, assess their compliance with international standards, such as ISO certifications, which can indicate adherence to quality management and environmental sustainability practices. -
Can cleantech products be customized to meet specific needs?
Yes, many cleantech suppliers offer customization options to align their products with your unique requirements. Engage in early discussions to outline your specific needs and the challenges you aim to address. Customization can include adjustments in product design, functionality, or integration with existing systems. Ensure that the supplier has the capacity and expertise to deliver tailored solutions while maintaining quality and performance standards. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for cleantech products?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly based on the supplier and product type. Generally, MOQs may range from a few units for specialized products to larger quantities for standard offerings. Lead times also depend on factors such as product complexity and supplier location. Always discuss these details upfront to align expectations and facilitate better planning for your project timelines. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for cleantech products?
Request documentation that verifies the quality assurance processes used by your supplier. Look for certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management and ISO 14001 for environmental management. Ask about their testing procedures and quality control measures, including third-party inspections. Establishing a clear QA agreement can help ensure that the products meet your specifications and international standards before shipment. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing cleantech products?
Logistics in international trade can be complex, especially for cleantech products that may require special handling or storage conditions. Evaluate shipping methods, customs regulations, and potential tariffs or duties that could impact costs. Collaborate with a logistics partner experienced in handling cleantech products to navigate these challenges effectively. Ensure proper documentation is prepared to minimize delays during customs clearance. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers in the cleantech sector?
Dispute resolution should be outlined in your contract with the supplier, specifying procedures for addressing conflicts. Start by communicating openly with the supplier to resolve issues amicably. If necessary, escalate to formal mediation or arbitration, especially if the dispute involves significant financial implications. Document all communications and agreements related to the dispute to maintain a clear record, which can be crucial if further action is required.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What payment terms are common in the cleantech industry?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers but often include options such as upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or installment payments based on milestones. Common practices may involve a 30% deposit upon order confirmation, with the balance due before shipment. Ensure that payment terms are clearly defined in your contract to prevent misunderstandings and ensure a smooth transaction process. -
Are there specific certifications that cleantech products should have for international trade?
Yes, various certifications can enhance the credibility of cleantech products in international markets. Look for certifications such as CE marking for products sold in Europe, which indicates compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards. Additionally, certifications like ENERGY STAR or the Global Renewable Energy Certification can provide assurance of energy efficiency and sustainability. Verify that your supplier’s products comply with the necessary certifications for your target market to facilitate smoother trade.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for cleantech environmental
In summary, effective strategic sourcing within the cleantech environmental sector is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking sustainable and innovative solutions. Understanding local market dynamics in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe is essential for tailoring approaches that meet specific environmental needs. By investing in a clear and compelling core message, businesses can enhance their brand recognition and resonate with stakeholders committed to sustainability.
B2B buyers should prioritize partnerships with cleantech companies that demonstrate a commitment to transparent practices and effective communication. Utilizing digital marketing strategies, such as SEO and organic content marketing, can facilitate greater engagement and reach, ensuring that your sustainability goals align with market demands.
As we look to the future, the cleantech sector will continue to expand, driven by increasing global awareness of environmental issues. Now is the time for international buyers to embrace this momentum, seek out innovative partnerships, and leverage sustainable technologies that not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute positively to the planet. Engage with the cleantech community, explore new opportunities, and be part of the transformation towards a greener economy.