Master AC Power Sourcing: Essential Insights for B2B Buyers
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for ac power
In an increasingly interconnected global marketplace, AC power stands as a cornerstone of industrial efficiency and technological advancement. As international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Spain and Argentina—navigate the complexities of sourcing, understanding the nuances of AC power is crucial. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of AC power, covering essential topics such as types of power supplies, materials used in their construction, and the manufacturing and quality control processes that underpin reliability.
AC power is not merely a utility; it is the lifeblood of diverse industries, from manufacturing to telecommunications, enabling the seamless operation of machinery and equipment. By delving into the various categories of AC power supplies, including single-phase and three-phase systems, this guide equips buyers with the knowledge to make informed decisions. Furthermore, it offers insights into supplier evaluations, cost considerations, and current market trends that can significantly influence procurement strategies.
With an extensive FAQ section addressing common concerns, this resource empowers B2B buyers to optimize their sourcing decisions. By leveraging this knowledge, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, mitigate risks, and secure a competitive edge in the dynamic landscape of AC power solutions.
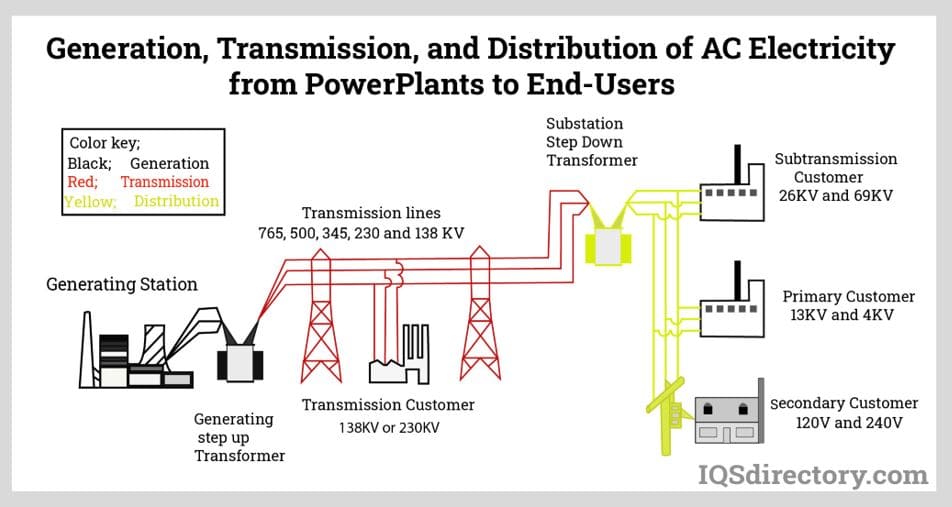
Understanding ac power Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Phase AC | Utilizes two wires; common in residential use | Homes, small businesses | Pros: Simple installation; Cons: Limited power capacity. |
| Three-Phase AC | Consists of three conductors; high efficiency | Industrial motors, large facilities | Pros: Efficient power delivery; Cons: More complex setup. |
| Delta Connection | No neutral wire; compact design | Heavy machinery, industrial applications | Pros: High starting torque; Cons: Risk of unbalanced loads. |
| Wye (Star) Connection | Includes a neutral wire; stable voltage | Commercial buildings, lighting systems | Pros: Stable voltage output; Cons: Increased wiring complexity. |
| Open Delta Connection | Uses two transformers instead of three | Smaller industrial applications | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Less efficient under heavy loads. |
Single-Phase AC
Single-phase AC power is commonly used in residential and small commercial settings. It operates with two wires, making it straightforward to install and maintain. However, its limited power capacity can be a drawback for businesses that require higher energy demands. B2B buyers should consider their current and future power needs, as this type may not be suitable for larger operations.
Three-Phase AC
Three-phase AC power is essential for industries that operate heavy machinery and require efficient power distribution. This system consists of three conductors, allowing for a continuous flow of electricity and reducing the likelihood of voltage drops. While it is more complex to install, the benefits of improved efficiency and the ability to handle larger loads make it a preferred choice for B2B buyers in sectors like manufacturing and logistics.
Delta Connection
The Delta connection is characterized by its lack of a neutral wire, which allows for a compact design and high starting torque. It is particularly well-suited for heavy machinery and industrial applications. However, buyers must be cautious of potential unbalanced loads that can arise, leading to operational inefficiencies. When considering this option, businesses should assess their load requirements and the potential impacts on equipment longevity.
Wye (Star) Connection
The Wye connection includes a neutral wire, providing a stable voltage output that is ideal for commercial buildings and sensitive lighting systems. This configuration can accommodate a variety of loads, but the increased complexity in wiring may result in higher initial costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of stable voltage against installation challenges, ensuring that their infrastructure can support this type of power supply.
Open Delta Connection
Open Delta connections utilize only two transformers instead of three, offering a cost-effective solution for smaller industrial applications. While this setup reduces equipment costs, it is less efficient under heavy loads, which could hinder performance in demanding environments. B2B buyers should evaluate their specific power needs and consider whether the cost savings justify the potential limitations in efficiency and reliability.
Key Industrial Applications of ac power
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of ac power | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Powering industrial motors and machinery | Ensures high efficiency and reliability in production processes | Voltage compatibility, motor specifications, energy ratings |
| Agriculture | Operating irrigation systems | Enhances crop yield through reliable watering solutions | Power requirements, energy efficiency, local regulations |
| Healthcare | Running medical equipment | Critical for patient safety and operational effectiveness | Compliance with health standards, voltage stability, backup solutions |
| Construction | Supplying power to heavy machinery | Facilitates timely project completion and reduces downtime | Equipment compatibility, power capacity, durability |
| Data Centers | Supporting server operations | Maintains uptime and prevents data loss | Power redundancy, cooling requirements, efficiency ratings |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, AC power is essential for powering industrial motors and machinery. These systems require a stable and efficient power supply to operate continuously and effectively. By utilizing three-phase AC power, businesses can achieve higher efficiency and reliability, significantly reducing production downtime. International buyers must consider voltage compatibility and motor specifications to ensure that the equipment meets local standards and operational requirements.
Agriculture
In agriculture, AC power is vital for operating irrigation systems. Reliable power supply is crucial for ensuring consistent watering, which directly affects crop yield and quality. Advanced irrigation systems often require specific voltage and power ratings, making it essential for international buyers to understand local energy regulations and infrastructure. Energy efficiency is also a key consideration, as it can lead to cost savings and sustainability.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector relies heavily on AC power for running critical medical equipment, such as imaging devices and life-support systems. A stable power supply is imperative to ensure patient safety and operational effectiveness. International buyers must prioritize compliance with health standards and seek solutions that offer voltage stability. Additionally, backup power solutions are crucial to prevent equipment failure during outages, which can have serious consequences.
Construction
In construction, AC power is used to supply energy to heavy machinery and tools. This application is critical for facilitating timely project completion and minimizing downtime. Buyers in this sector need to ensure that the power supply can handle the demands of various equipment types. Considerations include equipment compatibility and the power capacity required to support multiple machines simultaneously.
Data Centers
Data centers depend on AC power to support server operations and maintain uptime. A reliable power supply is essential to prevent data loss and ensure continuous service. International buyers must focus on power redundancy to safeguard against outages and evaluate cooling requirements to maintain optimal operating conditions. Efficiency ratings are also important, as they can significantly impact operational costs and sustainability efforts.
Related Video: SCADA Systems for electric power industry
Strategic Material Selection Guide for ac power
When selecting materials for AC power applications, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in AC power systems, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Copper
Key Properties: Copper exhibits excellent electrical conductivity, making it a preferred choice for wiring and electrical components. It has a high melting point (1,984°F or 1,085°C) and good resistance to corrosion, particularly when coated with protective materials.
Pros & Cons: Copper is highly durable and can withstand high temperatures, which is crucial in AC applications. However, it is more expensive compared to alternatives like aluminum. Manufacturing processes can be complex due to the need for precise handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Copper is ideal for high-performance applications where efficiency is paramount, such as in transformers and motors. Its compatibility with various media and environments enhances its utility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international standards like ASTM and IEC is essential. Buyers should also consider the cost implications in regions where copper prices fluctuate significantly, such as in Africa and South America.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good electrical conductivity, though not as high as copper. It has a melting point of around 1,221°F (660°C) and offers decent corrosion resistance, especially when anodized.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lower cost and weight, making it easier to handle and install. However, it is less durable than copper and may require larger cross-sections to achieve the same conductivity, which can complicate design and installation.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is commonly used in overhead power lines and large-scale distribution systems. Its weight advantage makes it suitable for applications where structural support is limited.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local standards and regulations regarding aluminum use, particularly in Europe where strict guidelines on material quality and performance exist.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is known for its strength and durability, with a high melting point around 2,500°F (1,370°C). It is often coated to enhance corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: Steel’s strength makes it suitable for structural applications, such as in power poles and frames. However, its weight can be a disadvantage in mobile applications. The manufacturing process can also be complex, requiring specialized techniques for handling and installation.
Impact on Application: Steel is typically used in supporting structures for power systems. Its robustness is vital in regions prone to extreme weather conditions, ensuring reliability.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as DIN and JIS is crucial for ensuring quality. Buyers in the Middle East and Africa should also consider the availability of steel and associated costs in their regions.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials, often made from a combination of fibers and resins, offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and corrosion resistance. Their thermal stability can vary based on the specific composition.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to environmental degradation. However, they can be more expensive and complex to manufacture, which may limit their use in some applications.
Impact on Application: Composites are increasingly used in applications requiring high strength and low weight, such as in wind turbine components and specialized electrical enclosures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the specific certifications and standards applicable to composites in their regions, especially in Europe where regulations on material safety are stringent.
| Material | Typical Use Case for ac power | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper | Wiring and electrical components | Excellent conductivity and durability | Higher cost compared to alternatives | High |
| Aluminum | Overhead power lines | Lightweight and cost-effective | Less durable than copper | Medium |
| Steel | Structural applications (e.g., poles) | High strength and durability | Heavy and complex to install | Medium |
| Composite | Wind turbine components | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Expensive and complex manufacturing | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material selection for AC power applications, emphasizing the importance of understanding material properties, advantages, and limitations. By considering these factors, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for ac power
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for AC power systems are critical for ensuring reliability and performance in a variety of applications. B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must understand these processes to make informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines the key stages of manufacturing and the quality control measures that should be in place.
Manufacturing Processes for AC Power Systems
The production of AC power systems typically involves several main stages: material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing. Each stage incorporates specific techniques that contribute to the overall quality and performance of the final product.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in manufacturing AC power systems is the preparation of raw materials. This involves sourcing high-quality materials such as copper for windings, silicon steel for transformers, and other essential components.
- Sourcing: Buyers should ensure that suppliers have established relationships with reputable material providers to guarantee the quality of raw materials.
- Inspection: Materials should undergo incoming quality control (IQC) checks to verify specifications and detect any defects before they are used in production.
2. Forming
The forming stage includes processes such as winding, stamping, and molding.
- Winding: For transformers and inductors, copper wire is precisely wound around a core to create the necessary inductance. Automated winding machines are often employed to ensure uniformity and precision.
- Stamping: Steel sheets are stamped into core shapes for transformers. This process must be performed with high accuracy to minimize losses and improve efficiency.
3. Assembly
Once components are formed, they are assembled into the final product. This stage typically involves:
- Integration of Components: All electrical components, including capacitors, resistors, and circuit boards, are assembled into the housing.
- Connection Techniques: Soldering and crimping techniques are commonly used to ensure reliable electrical connections.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on ensuring that the product meets aesthetic and functional standards.
- Coating and Painting: Protective coatings are applied to prevent corrosion and enhance durability.
- Final Inspection: Each unit undergoes a final quality check to confirm that it meets design specifications and is free from defects.
Quality Assurance in AC Power Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is essential to ensure that AC power systems meet international standards and customer expectations. The QA process typically includes adherence to relevant international standards and industry-specific regulations.
International Standards
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Manufacturers should be certified to ISO 9001 to demonstrate their commitment to quality and continuous improvement.
-
CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, compliance with CE marking requirements ensures that the product meets health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
-
API Standards: For applications involving power generation and transmission, adherence to API (American Petroleum Institute) standards may be necessary, particularly in industries such as oil and gas.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral to the QA process. They typically include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves checking the quality of raw materials upon arrival at the manufacturing facility.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): This step monitors the manufacturing process at various stages to ensure that production remains within specified tolerances.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final product is rigorously tested to ensure it meets all specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the various testing methods that manufacturers utilize to ensure product quality, including:
-
Electrical Testing: This includes testing for voltage output, frequency, and waveform stability.
-
Thermal Testing: Ensures that products can operate under specified temperature ranges without failure.
-
Load Testing: Verifies that the product can handle its rated load without overheating or malfunctioning.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
To ensure that suppliers maintain high-quality standards, B2B buyers can take the following steps:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Buyers should request audit reports and certifications.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation detailing their QC processes, including records of IQC, IPQC, and FQC.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can offer an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality control practices and product reliability.
Quality Control Considerations for International Buyers
For buyers from different regions, understanding the nuances of quality control is vital.
-
Regional Standards: Familiarize yourself with the specific quality standards applicable in your region (e.g., IEC standards in Europe, ANVISA regulations in South America).
-
Supply Chain Logistics: Consider the implications of international shipping on product quality. Products may be exposed to varying environmental conditions, so ensure that packaging and transportation methods are robust.
-
Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware that business practices and quality expectations may differ across cultures. Establish clear communication channels with suppliers to mitigate misunderstandings.
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for AC power systems is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material quality, manufacturing techniques, and effective quality control measures, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers capable of meeting their operational needs.
Related Video: How It’s Made Air Conditioner In Factories | Air Conditioner Manufacturing Process @Techmachine_
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for ac power Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of AC Power Sourcing
When sourcing AC power solutions, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure that includes several key components. Understanding these costs is crucial for effective budgeting and negotiation. The primary cost components involved in AC power sourcing include:
-
Materials: The cost of raw materials, such as copper and aluminum for wiring, transformers, and circuit components, can significantly impact pricing. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can lead to variations in overall costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs encompass the wages of skilled technicians and engineers involved in manufacturing, assembly, and installation. Regions with higher labor costs may see increased pricing for AC power solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative support. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these overhead costs, directly influencing the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tools and machinery necessary for production can be substantial. Suppliers may pass these costs onto buyers, particularly in highly customized orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that AC power solutions meet industry standards and certifications involves rigorous testing and quality assurance processes. These QC measures are essential for reliability but also contribute to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as distance, shipping method, and customs duties can add to the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically apply a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary significantly depending on the supplier’s market position and the competitive landscape.
Key Price Influencers in AC Power Sourcing
Several factors influence pricing in the AC power market, including:
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to leverage better pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized solutions generally incur higher costs due to the additional design and manufacturing processes involved. Standardized products may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Materials: The choice of materials can drastically affect the cost. High-quality materials may result in higher upfront costs but can lead to lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) through improved efficiency and longevity.
-
Quality and Certifications: Products with recognized certifications (e.g., ISO, CE) may be priced higher due to the added assurance of quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can influence pricing. Suppliers with established track records may command higher prices but also offer better service and support.
-
Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms can affect the final pricing by determining who bears the responsibility for shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Buyers should negotiate terms that minimize their risk and exposure.
Strategic Buyer Tips
To optimize sourcing decisions, B2B buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Engage suppliers in discussions to explore pricing flexibility, especially for larger orders or long-term contracts. Highlighting the potential for ongoing business can motivate suppliers to offer better terms.
-
Focus on Cost-Efficiency: Look beyond initial purchase prices and evaluate the TCO, which includes installation, maintenance, and energy consumption over the product’s lifespan.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may vary significantly between regions. For instance, buyers in Africa may face different logistical challenges compared to those in Europe, influencing overall costs.
-
Leverage Local Suppliers: Whenever possible, engage local suppliers to reduce logistics costs and lead times. Local suppliers may also have a better understanding of regional regulations and standards.
-
Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market trends, including material price fluctuations and regulatory changes, to better anticipate potential impacts on pricing.
Disclaimer
Prices and cost structures discussed herein are indicative and may vary based on specific requirements, market conditions, and supplier negotiations. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to obtain accurate pricing information tailored to their needs.
Spotlight on Potential ac power Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘ac power’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for ac power
Key Technical Properties of AC Power
Understanding the essential technical properties of AC power is crucial for B2B buyers, especially when evaluating products or systems for industrial applications. Here are some critical specifications to consider:
-
Voltage Rating
The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that an AC power source can safely supply. It is essential to match this rating with the operational requirements of equipment to prevent damage. Incorrect voltage levels can lead to operational inefficiencies or equipment failure, making this a vital specification for procurement decisions. -
Frequency
AC power frequency, typically measured in Hertz (Hz), determines the oscillation rate of the current. Common frequencies include 50 Hz in Europe and Africa and 60 Hz in the Americas. Understanding frequency requirements is crucial for ensuring compatibility with both local power grids and specific equipment, as mismatched frequencies can lead to operational issues. -
Power Factor
The power factor measures the efficiency of power usage in an AC system, expressed as a ratio between real power (used for work) and apparent power (total power supplied). A power factor close to 1 indicates efficient power usage. For B2B buyers, selecting equipment with a high power factor can lead to reduced energy costs and improved system performance. -
Load Capacity
Load capacity refers to the maximum load that an AC power source can handle without compromising performance. This specification is critical for ensuring that systems can manage peak demand without overheating or failing. Buyers should assess the load capacity in relation to their operational needs to ensure reliability. -
Harmonic Distortion
Harmonic distortion occurs when the waveform of the AC power deviates from its ideal sine wave shape. High levels of distortion can lead to inefficiencies and damage sensitive equipment. Buyers must evaluate harmonic distortion levels, especially in environments where power quality is paramount, such as data centers or manufacturing facilities. -
Efficiency Rating
The efficiency rating of an AC power supply indicates how well it converts input power into usable output power. Higher efficiency ratings translate to lower operational costs and reduced energy waste, making this a key factor for B2B buyers focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the B2B landscape. Here are some common terms related to AC power:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable suppliers and ensure compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Buyers must consider MOQs when planning purchases, as they can impact inventory management and cash flow. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document issued by a buyer to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific goods or services. This process is critical for securing competitive pricing and ensuring all specifications are met. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in the delivery of goods. Familiarity with these terms is essential for understanding shipping costs, risks, and logistics when sourcing AC power equipment globally. -
KVA (Kilovolt-Ampere)
KVA is a unit of measurement used to express the apparent power in an AC circuit. It is crucial for understanding the capacity of transformers and generators, especially in large-scale industrial applications. -
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply)
A UPS is a device that provides backup power to critical systems during outages. Understanding UPS options is vital for B2B buyers concerned about maintaining operational continuity in the face of power disruptions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that enhance operational efficiency and support strategic sourcing initiatives in the global market for AC power.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the ac power Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The AC power sector is undergoing significant transformations driven by global economic shifts, technological advancements, and an increasing focus on sustainability. For international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial for strategic sourcing.
One of the primary drivers is the rising demand for reliable and efficient power solutions to support industrial growth. Regions like Africa and South America are investing heavily in infrastructure development, which creates opportunities for suppliers of AC power systems, particularly three-phase solutions that cater to high-load applications. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies and IoT in power management systems is reshaping sourcing strategies. This shift enables real-time monitoring and optimization of energy use, enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
Emerging trends include the increased adoption of modular power systems, which allow businesses to scale their power solutions according to demand. This flexibility is particularly appealing in volatile markets where energy needs can fluctuate. Furthermore, buyers should be aware of the importance of compliance with international standards and certifications, which can influence sourcing decisions and supply chain reliability.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the AC power sector, as businesses increasingly recognize the environmental impact of their operations. B2B buyers are now prioritizing ethical sourcing practices, ensuring that their suppliers adhere to environmentally friendly standards. This includes selecting vendors who utilize sustainable materials and processes in the production of AC power equipment.
The significance of ‘green’ certifications, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Energy Star ratings for energy efficiency, cannot be overstated. These certifications not only demonstrate a commitment to sustainability but also enhance a company’s reputation and marketability. For buyers, sourcing from companies that hold these credentials can lead to a reduction in operational costs through energy savings and improved efficiency.
Moreover, the transition towards renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, is influencing AC power solutions. This shift requires buyers to consider suppliers who are capable of integrating renewable technologies into their offerings, thereby aligning with global sustainability goals. By embracing ethical sourcing and sustainable practices, businesses can contribute to a greener future while simultaneously enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of AC power systems dates back to the late 19th century, with Nikola Tesla’s innovations laying the groundwork for alternating current as a viable power distribution method. Over the decades, AC power has become the standard for electrical systems worldwide due to its efficiency in transmitting electricity over long distances.
The development of three-phase systems in the early 20th century further transformed the landscape, allowing for greater efficiency in industrial applications. Today, advancements in technology, such as smart grids and renewable energy integration, continue to shape the AC power sector, presenting new opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers. Understanding this historical context is essential for making informed sourcing decisions that align with current market trends and future developments.
Related Video: Understanding Basics of the Power Market
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of ac power
-
How can I effectively vet suppliers for AC power products?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize those with a proven track record in the AC power sector. Check their certifications, such as ISO standards, which indicate quality management systems. Request references from other international buyers and assess their responsiveness and communication. Utilize platforms like Alibaba or Global Sources to review supplier ratings and feedback. Consider visiting manufacturing facilities or attending trade shows to build relationships and evaluate capabilities firsthand. -
What customization options are typically available for AC power solutions?
Many suppliers offer customization options, such as voltage specifications, frequency settings, and power capacity tailored to your specific needs. Discuss your requirements upfront to determine the extent of customization available. Some manufacturers may also provide options for form factors, control interfaces, and additional features like surge protection. Ensure that any custom solutions undergo rigorous testing to maintain reliability and compliance with local regulations. -
What are the common minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for AC power products?
MOQs for AC power products can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Generally, MOQs can range from a few units for standard items to hundreds for customized solutions. Lead times may also vary; standard products often ship within 4-6 weeks, while custom orders can take longer. Always clarify these details during negotiations to avoid delays in your procurement schedule and ensure timely project execution. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certifications for AC power products?
Request documentation of quality assurance processes from suppliers, including their testing methods and certification compliance (e.g., CE, UL). It’s crucial to verify that products meet international standards relevant to your region. Conducting audits or requiring third-party testing can further ensure product quality. Establishing a clear quality control agreement before finalizing the purchase will help mitigate risks associated with faulty products. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing AC power products internationally?
When sourcing internationally, consider shipping methods, costs, and timelines. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is economical for larger shipments but takes longer. Additionally, understand customs regulations in your country to avoid delays. Collaborating with a logistics provider experienced in handling electrical equipment can streamline the shipping process, ensuring your products arrive safely and on time. -
What should I do in case of disputes with suppliers?
In the event of a dispute, start by addressing the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. Document all communications and agreements to provide clarity. If the issue cannot be resolved amicably, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution. Consider mediation or arbitration as alternatives to litigation, as these methods can be less costly and time-consuming. Always consult legal counsel familiar with international trade laws for guidance. -
How can I manage payment risks when sourcing AC power products?
To mitigate payment risks, use secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services, which protect both parties during transactions. Establish clear payment terms in your contract, specifying milestones for payments based on delivery or inspection. Consider using trade finance solutions to facilitate payments without exposing your capital. Conducting thorough due diligence on your supplier’s financial stability can also help reduce risks.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What are the key factors to consider when evaluating the total cost of ownership (TCO) for AC power systems?
TCO encompasses not just the initial purchase price but also installation, maintenance, and operational costs. Evaluate energy efficiency ratings, as more efficient systems can lead to significant savings over time. Consider the costs associated with potential downtime due to equipment failures and the need for spare parts. Including warranties and service agreements in your assessment can also provide financial protection and enhance the overall value of your investment.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for ac power
As we conclude this guide on AC power, it’s essential to recognize the strategic advantages of informed sourcing practices for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of AC power systems, including single-phase and three-phase options, empowers businesses across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to optimize their operations. Key considerations such as voltage stability, equipment compatibility, and supplier reliability are critical in mitigating risks and enhancing efficiency.
Strategic sourcing not only ensures access to high-quality AC power solutions but also fosters long-term partnerships with suppliers who understand regional challenges and opportunities. As industries continue to evolve, staying ahead of market trends and technological advancements will be paramount.
Looking forward, B2B buyers are encouraged to leverage this knowledge to make proactive decisions that drive innovation and sustainability. Embrace the complexities of AC power sourcing as an opportunity to enhance your operational capabilities and maintain a competitive edge in your respective markets. The time to act is now—invest in reliable AC power solutions that will support your business growth for years to come.