Master Aircraft Cables Sourcing: Your Comprehensive B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for aircraft cables
Navigating the global market for aircraft cables is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking reliable and high-performance solutions in the aerospace industry. Aircraft cables, engineered for exceptional strength and flexibility, play a vital role in numerous applications, from flight control systems to heavy lifting in maintenance operations. Their unique properties, including corrosion resistance and fatigue endurance, make them indispensable in both aviation and various industrial sectors, including agriculture, construction, and military applications.
This comprehensive guide serves as an essential resource for buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, including countries like Vietnam and Italy. It explores the diverse types of aircraft cables, detailing materials such as stainless steel and galvanized options, and their specific applications. Furthermore, the guide delves into manufacturing standards, quality control processes, and effective sourcing strategies to ensure that you make informed purchasing decisions.
Additionally, it covers critical market insights, including trends driving demand for aircraft cables, potential cost factors, and frequently asked questions to address common buyer concerns. By empowering you with the knowledge and tools necessary for effective sourcing, this guide aims to enhance your procurement strategy, ensuring you select the right aircraft cables that meet your operational needs and regulatory standards.
Understanding aircraft cables Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel Aircraft Cables | High corrosion resistance, long lifespan | Flight control systems, marine applications, architectural rigging | Pros: Durable, minimal maintenance; Cons: Higher cost compared to other options. |
| Galvanized Aircraft Cables | Economical, good corrosion resistance | General industrial use, agricultural applications, construction | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Limited corrosion resistance in harsh environments. |
| 7×7 and 7×19 Configurations | Stranding patterns that enhance flexibility | Rigging, safety cables, mechanical linkages | Pros: Excellent flexibility; Cons: May not handle as high loads as other configurations. |
| High-Strength Synthetic Cables | Lightweight, non-corrosive, flexible | Aerospace, military, and specialized industrial applications | Pros: Lightweight, resistant to environmental factors; Cons: May have lower tensile strength than steel cables. |
| Custom Engineered Cables | Tailored specifications for unique applications | Specialized aviation, military, and industrial projects | Pros: Meets specific needs; Cons: Longer lead times and potentially higher costs. |
Stainless Steel Aircraft Cables
Stainless steel aircraft cables are renowned for their exceptional corrosion resistance and durability, making them ideal for environments exposed to moisture and harsh conditions. Typically constructed from 316 or 302/304 alloys, these cables are often used in flight control systems, marine applications, and architectural rigging. When purchasing, buyers should consider the specific alloy grade required for their application, as well as the potential higher upfront costs compared to other materials. However, their longevity and minimal maintenance needs often justify the investment.
Galvanized Aircraft Cables
Galvanized aircraft cables are made from steel that has been coated with zinc to enhance corrosion resistance while remaining cost-effective. These cables are widely used in general industrial applications, agriculture, and construction, where extreme environmental conditions are not a primary concern. Buyers should weigh the cost benefits against potential limitations in harsh environments, as galvanized cables may corrode faster than stainless steel options. Their affordability and availability make them a popular choice for many businesses.
7×7 and 7×19 Configurations
The 7×7 and 7×19 configurations refer to the stranding patterns of the wires within the cable, which directly influence flexibility and load-bearing capacity. The 7×19 configuration offers greater flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring tight bends, such as rigging and safety cables. Buyers should assess the specific load requirements and flexibility needs of their application when selecting between these two configurations. While 7×19 cables can handle dynamic loads better, they may not support as high a static load as 7×7 cables.
High-Strength Synthetic Cables
High-strength synthetic cables are increasingly popular in aviation and military applications due to their lightweight and non-corrosive properties. These cables offer flexibility and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for specialized industrial applications. However, buyers should consider that while synthetic cables are lightweight, they may not match the tensile strength of traditional steel cables. This trade-off can be critical depending on the specific load requirements of the application.
Custom Engineered Cables
Custom engineered cables are designed to meet specific requirements for unique applications, particularly in specialized aviation, military, and industrial projects. These cables can be tailored in terms of material, diameter, and construction to fit precise operational needs. While they provide a perfect solution for niche applications, buyers should be prepared for longer lead times and potentially higher costs. Ensuring clear communication with suppliers about specifications and performance standards is crucial in the purchasing process.
Related Video: 003. Connectors: Basic overview of aircraft Dsub, Molex and Circular Connectors
Key Industrial Applications of aircraft cables
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Aircraft Cables | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Flight Control Systems | Ensures precise control and safety during flight operations. | Compliance with FAA and aerospace standards; high tensile strength. |
| Marine | Lifting and Rigging Applications | Facilitates safe handling of heavy loads in marine environments. | Corrosion resistance; ability to withstand harsh weather conditions. |
| Construction | Temporary and Permanent Lifting Solutions | Provides reliable support for lifting heavy materials and equipment. | Strength-to-weight ratio; flexibility for tight spaces. |
| Agriculture | Irrigation and Hoisting Systems | Enhances efficiency in agricultural operations and maintenance. | Durability against environmental factors; cost-effectiveness. |
| Military & Defense | Safety Cables and Rigging for Equipment | Increases operational safety and reliability in defense applications. | High fatigue resistance; compliance with military specifications. |
Aerospace: Flight Control Systems
Aircraft cables are crucial in flight control systems, where they connect various control surfaces to the cockpit. They ensure precise maneuverability and safety during flight operations. For international buyers, particularly from regions with stringent aviation regulations, sourcing cables that meet FAA and other aerospace standards is essential. High tensile strength and fatigue resistance are critical to withstand the stresses of flight, making quality assurance a priority in procurement.
Marine: Lifting and Rigging Applications
In marine settings, aircraft cables are used for lifting and rigging applications, such as hoisting heavy equipment and securing loads on vessels. Their corrosion-resistant properties make them ideal for exposure to saltwater and harsh weather conditions. Buyers from coastal regions need to prioritize sourcing options that offer superior corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity and reliability in demanding marine environments.
Construction: Temporary and Permanent Lifting Solutions
In the construction industry, aircraft cables are employed in both temporary and permanent lifting solutions, facilitating the movement of heavy materials and equipment. Their robust design provides the necessary strength while maintaining a lightweight profile, allowing for easier handling. Buyers should consider the strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility of the cables, especially in projects involving tight spaces or complex rigging setups.
Agriculture: Irrigation and Hoisting Systems
Agricultural applications leverage aircraft cables for irrigation systems and hoisting operations, enhancing the efficiency of farming practices. These cables can withstand environmental stresses and provide reliable performance over time. For international buyers in agriculture, cost-effectiveness and durability against environmental factors are crucial when selecting suppliers, especially in regions with varying climates.
Military & Defense: Safety Cables and Rigging for Equipment
In military and defense applications, aircraft cables are utilized as safety cables and rigging for equipment, ensuring operational safety under high-stress conditions. Their high fatigue resistance is essential for the rigorous demands of military operations. Buyers in this sector must focus on compliance with military specifications and the availability of cables that can withstand extreme conditions, ensuring reliability and safety in critical applications.
Related Video: How to use an aircraft control cables tensiometer.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for aircraft cables
Material Analysis for Aircraft Cables
When selecting aircraft cables, understanding the properties and applications of different materials is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in aircraft cables, focusing on their key properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
1. Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel aircraft cables are known for their high tensile strength and exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in marine environments. They typically come in grades 302, 304, and 316, with 316 offering superior protection against saltwater corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel cables makes them suitable for critical applications, such as flight control systems and safety barriers. However, they tend to be more expensive than other materials, which may be a concern for budget-conscious buyers. Manufacturing complexity can also be higher due to the need for precise fabrication techniques.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel cables are ideal for environments exposed to moisture and chemicals, such as coastal or industrial settings. Their strength and flexibility allow for versatile applications, including marine lifelines and architectural rigging.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Europe and the Middle East should ensure compliance with ASTM and MIL standards. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding corrosion resistance can influence material selection.
2. Galvanized Steel
Key Properties:
Galvanized aircraft cables are made from steel wires coated with zinc, providing a cost-effective solution with moderate corrosion resistance. They are generally available in various diameters and constructions, making them versatile for different applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of galvanized cables is their affordability, making them suitable for general industrial and agricultural applications. However, their corrosion resistance is not as robust as stainless steel, limiting their use in harsh environments. They also may require more frequent maintenance to prevent rust.
Impact on Application:
These cables are commonly used in applications such as winch cables and utility rigging, where extreme corrosion resistance is not critical. Their strength makes them suitable for lifting and support tasks.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers in Africa and South America should evaluate the local climate and environmental conditions when considering galvanized cables. Compliance with regional standards, such as DIN or JIS, is also essential for ensuring safety and performance.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum aircraft cables are lightweight and have good corrosion resistance, making them suitable for applications where weight savings are critical. They typically have a lower tensile strength compared to stainless steel but are easier to handle and install.
Pros & Cons:
The lightweight nature of aluminum cables allows for increased payload capacity in aircraft, which can enhance fuel efficiency. However, they may not be suitable for high-load applications due to their lower strength and can be more expensive than galvanized options.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum cables are often used in applications where weight is a significant factor, such as in lightweight aircraft or drones. Their corrosion resistance makes them suitable for various environments, although they may require protective coatings in harsh conditions.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific regulations governing the use of aluminum in aviation applications, particularly in Europe, where stringent standards apply. Understanding the local supply chain for aluminum products can also affect sourcing decisions.
4. Composite Materials
Key Properties:
Composite aircraft cables are made from a combination of materials, often incorporating high-strength fibers to enhance performance. They offer excellent fatigue resistance and are lightweight, making them ideal for advanced aerospace applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of composite cables is their high strength-to-weight ratio, which is critical for modern aircraft design. However, they can be more expensive to manufacture and may require specialized handling and installation techniques.
Impact on Application:
These cables are increasingly being used in next-generation aircraft, particularly in electric and urban air mobility applications, where weight and performance are paramount.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of composite materials in their region and the associated costs. Compliance with aerospace standards and certifications is crucial, particularly in markets with stringent regulations like Europe.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for aircraft cables | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Flight control cables | Exceptional corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Galvanized Steel | Winch cables | Cost-effective for general use | Moderate corrosion resistance | Low |
| Aluminum | Lightweight aircraft applications | Reduces overall weight | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Composite Materials | Advanced aerospace applications | High strength-to-weight ratio | Higher manufacturing costs | High |
This guide provides international B2B buyers with actionable insights to make informed decisions regarding aircraft cable material selection, ensuring compliance and optimal performance for their specific applications.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for aircraft cables
The manufacturing of aircraft cables involves several meticulous stages, each crucial to ensuring the final product meets stringent safety and performance standards. For B2B buyers, especially those in diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes can help in making informed purchasing decisions. Here’s an in-depth overview of the typical manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with aircraft cables.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in manufacturing aircraft cables is the selection and preparation of raw materials. Most aircraft cables are made from high-strength stainless steel or galvanized steel. The chosen material undergoes several processes:
- Material Inspection: Incoming materials are rigorously inspected for quality, composition, and compliance with specifications.
- Cutting and Stranding: Raw wires are cut to specified lengths and then stranded together. The most common configurations are 7×7 and 7×19, which provide the necessary flexibility and strength.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the next stage involves forming the cable. This includes:
- Stranding Process: Wires are twisted together to form strands, which are then bundled to create the cable. This process is critical for ensuring the cable maintains its strength while remaining flexible.
- Coating Application: For galvanized cables, a protective zinc coating is applied to enhance corrosion resistance. Stainless steel cables may undergo passivation to further improve their durability against environmental factors.
3. Assembly
After forming, the cables are assembled into the final product. This stage includes:
- Cable Laying: Strands are laid in specific patterns to ensure uniform load distribution and performance consistency.
- End Fittings Installation: Depending on the application, end fittings such as thimbles, swages, or terminals are attached to enable connection to aircraft systems.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage ensures that the cables meet all aesthetic and performance requirements:
- Surface Treatment: Final surface treatments may be applied to enhance corrosion resistance and overall durability.
- Marking and Identification: Each cable is marked with specifications, including size, material, and manufacturer details, to ensure traceability.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the aircraft cable manufacturing process. International standards and industry-specific regulations govern the quality checkpoints throughout the manufacturing cycle.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system and is crucial for ensuring consistent quality in manufacturing processes.
- MIL-DTL-83420: This military specification sets the standards for aircraft cables used in defense applications, ensuring they meet rigorous performance criteria.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints to ensure that the cables produced meet all specifications:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet the required standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Throughout the manufacturing process, various parameters such as dimensions, tensile strength, and flexibility are monitored.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The finished cables undergo comprehensive testing, including load tests and visual inspections, to verify that they meet all operational and safety standards.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of the various testing methods used to ensure product integrity:
- Tensile Testing: Measures the maximum load the cable can withstand before breaking.
- Fatigue Testing: Assesses how the cable performs under repeated stress to simulate operational conditions.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Evaluates the cable’s ability to withstand environmental factors.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is crucial. Here are some actionable steps:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and adherence to international standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports that outline the manufacturing process, testing results, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection services to validate the quality and compliance of the aircraft cables prior to shipment. This provides an additional layer of assurance.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances
Understanding the nuances of quality control and certification is essential for B2B buyers in different regions:
- Regional Compliance: Buyers should be aware of specific regional compliance requirements, such as CE marking in Europe, which indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- Documentation: Ensure that suppliers provide all necessary documentation, including certificates of compliance, test reports, and material safety data sheets (MSDS).
- Supplier Relationships: Building strong relationships with suppliers can enhance communication regarding quality expectations and facilitate smoother resolution of any quality issues that may arise.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices for aircraft cables is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, rigorous testing, and supplier verification, companies can ensure they procure high-quality aircraft cables that meet their operational needs and safety standards.
Related Video: How Cables are Made in Factories – Modern Manufacturing Process
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for aircraft cables Sourcing
In the sourcing of aircraft cables, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The overall cost of aircraft cables can be categorized into several components, each playing a crucial role in determining the final price.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts pricing. Stainless steel cables, particularly those made from 316 alloy, are typically more expensive due to their superior corrosion resistance and strength. Conversely, galvanized steel cables offer a more economical option but may not provide the same longevity.
-
Labor: Manufacturing aircraft cables requires skilled labor, especially for processes involving intricate stranding and assembly. Labor costs can vary based on the geographical location of the manufacturer, with regions having higher labor costs impacting the overall pricing.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, but they are still a significant factor in the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Specialized tooling and equipment are necessary for producing aircraft cables. These costs can be substantial, particularly for manufacturers who invest in advanced technology to enhance precision and efficiency.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential in aerospace applications to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. The costs associated with testing and certification can be reflected in the final price.
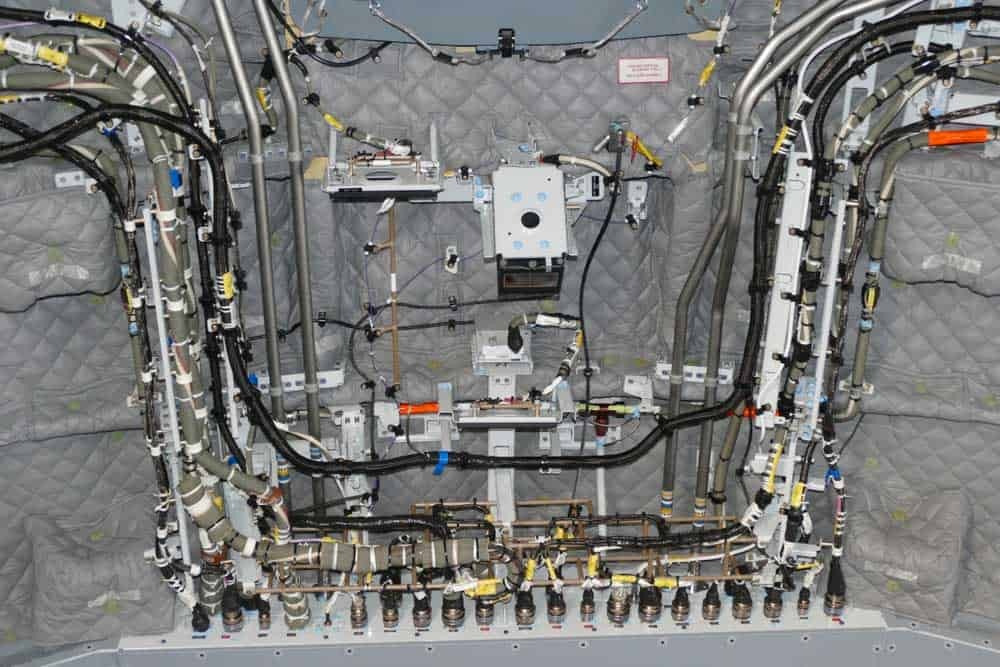

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Logistics: Transportation costs, including shipping and handling, can vary widely based on the Incoterms agreed upon in the contract. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and delivery timelines will influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a profit margin to cover their costs and ensure business sustainability. This margin can vary based on competition, market demand, and the perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of aircraft cables:
- Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchases often lead to discounts. Establishing a Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) can help negotiate better pricing.
- Specifications/Customization: Custom specifications or special features can increase costs. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these enhancements against their budget.
- Materials: As mentioned, the choice between stainless steel and galvanized options can affect pricing. Buyers should assess their application needs carefully.
- Quality/Certifications: Cables that meet stringent aviation standards (e.g., FAA, MIL) typically command higher prices due to the rigorous testing and certification processes.
- Supplier Factors: Established suppliers with a strong reputation may charge premium prices. However, their reliability can mitigate risks associated with quality and delivery.
- Incoterms: The agreed-upon Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can significantly affect the total landed cost, including shipping and insurance.
Buyer Tips
For international B2B buyers, particularly in regions with diverse economic conditions, here are actionable insights:
- Negotiation: Leverage volume purchases and long-term relationships to negotiate favorable terms. Be prepared to discuss your specific needs and how they align with the supplier’s capabilities.
- Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also maintenance, replacement, and operational costs over the product’s lifespan.
- Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional market conditions that might affect pricing, such as tariffs, import duties, and local sourcing capabilities. This knowledge can be a powerful tool during negotiations.
Disclaimer
Prices for aircraft cables can vary widely based on the above factors, and the information provided here is indicative. Buyers should conduct thorough market research and consult multiple suppliers to obtain accurate quotes tailored to their specific requirements.
Spotlight on Potential aircraft cables Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘aircraft cables’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for aircraft cables
Aircraft cables are crucial components in various aviation applications, and understanding their essential technical properties and trade terminology is vital for B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in selecting the right product but also ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations. Below are key specifications and terminology relevant to aircraft cables.
Critical Specifications
-
Material Grade
– Aircraft cables are commonly made from stainless steel (302, 304, 316) or galvanized carbon steel. The choice of material impacts corrosion resistance, strength, and application suitability. For instance, 316 stainless steel is ideal for marine environments due to its superior resistance to saltwater corrosion. Understanding material grades helps buyers select cables that meet specific environmental conditions. -
Construction Type
– Aircraft cables are typically constructed in configurations such as 7×7 or 7×19, which refer to the number of strands and wires per strand. A 7×19 construction provides greater flexibility and fatigue resistance compared to 7×7. This specification is crucial for applications requiring tight bends and repeated use, impacting the cable’s longevity and performance. -
Diameter
– The diameter of aircraft cables can range from 3/64″ to 3/8″ or more, depending on the application. A smaller diameter allows for easier routing in confined spaces but may limit load-bearing capacity. Buyers must assess load requirements and installation constraints to ensure the selected diameter aligns with their specific needs. -
Breaking Strength
– This refers to the maximum load the cable can withstand before failure. Breaking strengths vary based on diameter and construction type, often ranging from hundreds to thousands of pounds. Understanding breaking strength is essential for ensuring safety and compliance with operational requirements, particularly in critical applications like flight controls. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Given their use in various environments, corrosion resistance is a key property. Buyers should consider whether to opt for stainless steel or galvanized cables based on the expected exposure to moisture and chemicals. This choice affects maintenance costs and the longevity of the cables in service. -
Certification Standards
– Aircraft cables must meet specific regulatory standards, such as those set by the FAA and ASTM. Familiarity with these certifications ensures that buyers acquire products that comply with safety and quality requirements, which is particularly important for industries like aerospace and defense.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships is important for buyers to ensure they are sourcing high-quality components that meet industry standards. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– This term defines the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively, particularly in international transactions where shipping costs can be significant. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent by buyers to suppliers requesting pricing and terms for specific products. Issuing an RFQ is an effective way to gather competitive bids and ensure that suppliers understand the buyer’s requirements clearly. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are a series of predefined international sales terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms helps buyers manage risks associated with shipping, insurance, and customs, ensuring smooth cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the amount of time from placing an order to receiving the product. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for project planning and ensuring that operations are not disrupted due to delays. -
Certification
– This term refers to the process of verifying that a product meets specific standards and regulations. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that provide certifications to ensure compliance with safety and quality expectations.
By grasping these technical properties and terminology, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing aircraft cables, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and safety in their applications.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the aircraft cables Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The aircraft cables sector is witnessing a significant transformation driven by various global factors. The increasing demand for aircraft production, highlighted by Boeing’s forecast of nearly 44,000 new commercial aircraft in the next two decades, underscores the robust growth prospects for suppliers. This surge is further fueled by advancements in urban air mobility and electric aircraft programs, which require sophisticated wiring solutions. As the market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.9% from 2025 to 2034, international B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must stay abreast of emerging trends.
One notable trend is the shift towards high-voltage cable systems, essential for integrating advanced propulsion technologies and battery systems in next-generation aircraft. Additionally, there is a growing focus on lightweight and compact wiring systems, which enhance fuel efficiency and payload capacity. Buyers should also consider the digital transformation within the sector, as the integration of smart technologies into aircraft systems increases the demand for high-performance cables. This evolution necessitates a deeper understanding of the technological requirements and compliance standards of different markets, particularly in regions with stringent aviation regulations.
B2B buyers should be proactive in evaluating suppliers not just on price but on their ability to deliver innovative, compliant, and performance-oriented products. Engaging with manufacturers who are adapting to these trends can provide a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
As sustainability becomes a focal point in the aerospace industry, the demand for environmentally friendly aircraft cables is on the rise. The environmental impact of sourcing materials for aircraft cables, particularly the use of non-renewable resources and energy-intensive production processes, has prompted a shift towards more sustainable practices. B2B buyers should prioritize suppliers who are committed to reducing their carbon footprint and employing ethical sourcing practices. This includes transparent supply chains that ensure materials are obtained responsibly and sustainably.
The use of green certifications and sustainable materials is crucial for buyers looking to align with global sustainability goals. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and the use of recyclable materials in cable production can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the transition to alternative materials, such as lightweight alloys and fluoropolymer insulations, not only supports sustainability initiatives but also enhances the performance characteristics of aircraft cables.
By choosing suppliers who emphasize sustainability, international B2B buyers can contribute to a greener aviation industry while also meeting regulatory requirements and consumer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of aircraft cables has been marked by advancements in materials and manufacturing processes, driven by the need for enhanced performance and safety in aviation. Initially developed for flight control systems, aircraft cables have expanded their applications across various sectors, including military, agriculture, and construction. The introduction of high-strength steel and stainless steel compositions has significantly improved the tensile strength and corrosion resistance of these cables.
As the aviation industry has progressed, so too have the specifications and standards governing aircraft cables. Compliance with rigorous regulations set by organizations like the FAA and MIL-DTL has become essential for suppliers. This evolution has not only enhanced the safety and reliability of aircraft operations but has also paved the way for innovations in cable technology, addressing the growing demands of modern aviation. International B2B buyers can benefit from understanding this historical context, as it informs current trends and future directions in the aircraft cables market.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of aircraft cables
-
How do I vet suppliers of aircraft cables?
Vetting suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching the supplier’s reputation in the industry. Look for certifications that comply with international standards such as FAA, MIL-DTL-83420, and ASTM. Verify their production capabilities, quality control processes, and previous client references. Consider requesting samples to assess product quality firsthand. Additionally, check for experience in international trade, especially in your region, to ensure they understand local regulations and logistics. -
Can aircraft cables be customized to specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for aircraft cables, including variations in diameter, material grade, and construction type (e.g., 7×7, 7×19). When requesting customization, clearly outline your specifications, including tensile strength, corrosion resistance, and application environment. Discuss lead times and any additional costs associated with custom orders. Ensure that the manufacturer has the capability and experience to meet your specific needs without compromising quality.
-
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for aircraft cables?
Minimum order quantities can vary significantly among suppliers, often ranging from 100 meters to several kilometers, depending on the type and customization of the aircraft cable. Lead times typically span from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by factors such as customization, production capacity, and shipping logistics. When engaging suppliers, clarify these details upfront to align your procurement timelines with your project needs. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing aircraft cables internationally?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your negotiation. Common methods include letters of credit, wire transfers, or escrow services for larger orders. For initial transactions, suppliers may require full payment upfront or a deposit with the balance due upon shipment. Always discuss payment terms before finalizing agreements and consider using trade finance options to mitigate risks associated with international transactions. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for aircraft cables?
Request documentation that demonstrates compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ISO certifications, FAA regulations, and material specifications. A reputable supplier should provide certificates of compliance or test reports upon request. Establish a quality assurance process that includes inspections at various production stages and before shipment. Consider third-party inspection services if you’re unsure about the supplier’s claims. -
What logistical considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing aircraft cables?
Logistics play a critical role in international sourcing. Consider shipping options (air freight vs. sea freight) based on your urgency and budget. Discuss with suppliers about their logistics capabilities and partnerships with freight forwarders. Understand the import regulations in your country, including duties and taxes, to avoid unexpected costs. Ensure that the supplier provides appropriate packaging to prevent damage during transit. -
What should I do if there is a dispute with the supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. Document all correspondence and agreements. If resolution is not possible, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, such as mediation or arbitration. Consider involving legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to navigate complex issues. Maintain professionalism to preserve the business relationship wherever possible.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Are there any specific considerations for international buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe?
Each region has unique regulatory and economic considerations. Familiarize yourself with local import regulations, tariffs, and standards relevant to aircraft cables. Consider the currency fluctuations and payment methods preferred in your region to mitigate financial risks. It’s also beneficial to engage suppliers who have experience in your market to ensure they can navigate potential challenges effectively. Building strong relationships can lead to better service and terms in the long run.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for aircraft cables
Effective strategic sourcing in aircraft cables is pivotal for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Buyers should prioritize high tensile strength and corrosion resistance when evaluating suppliers, as these attributes ensure reliability and longevity in demanding applications. It’s essential to understand the specific needs of your industry—whether aerospace, agriculture, or construction—to select the most suitable cable type, such as stainless steel for corrosive environments or galvanized cables for general use.
Furthermore, staying informed about market trends, including the shift towards high-voltage systems and lightweight materials, can position your organization as a leader in innovation. As the global aircraft wire and cable market is projected to grow significantly, aligning your sourcing strategy with these trends will enhance your competitive advantage.
In conclusion, strategic sourcing is not merely a procurement function but a critical element that can drive operational excellence and sustainability. By leveraging the insights shared in this guide, international buyers are encouraged to forge strong partnerships with reliable suppliers and invest in advanced cable solutions that meet the future demands of the aviation industry. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategies and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient aerospace ecosystem.