Master Blister Packaging: The Essential B2B Guide for Smart
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for blister packaging
In today’s competitive global marketplace, blister packaging has emerged as a cornerstone for industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to consumer goods. This versatile packaging solution not only ensures product safety and integrity but also enhances visibility and user convenience. As international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of blister packaging can significantly impact sourcing decisions and supply chain efficiency.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of blister packaging, covering essential topics such as types of blister packs, material selection, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. Each section is designed to equip buyers with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions, whether assessing suppliers or evaluating cost-effectiveness. The guide also addresses market trends and provides answers to frequently asked questions, ensuring that you are well-prepared to navigate this dynamic sector.
By leveraging the insights offered herein, B2B buyers can optimize their procurement strategies, mitigate risks associated with product integrity, and ultimately enhance their competitive edge. Whether you are sourcing for a startup or a large enterprise, the information presented will empower you to make strategic choices that align with your business objectives and consumer demands. Embrace the potential of blister packaging and position your company for success in the global market.
Understanding blister packaging Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermoformed Blister Packs | Made from heated plastic sheets molded into cavities; versatile and cost-effective. | Pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, medical devices | Pros: Cost-effective, customizable; Cons: Limited barrier protection compared to cold-formed packs. |
| Cold Formed Blister Packs | Utilizes aluminum laminate pressed into molds at room temperature; excellent barrier properties. | Sensitive pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals | Pros: Superior protection against moisture and oxygen; Cons: Higher production costs and slower manufacturing. |
| Blister Cards | Features a plastic cavity affixed to a paperboard backing; often used for medications. | Pharmaceuticals, over-the-counter drugs | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to print branding; Cons: Less durable than clamshell options. |
| Clamshell Blisters | Fully enclosed plastic shells that can be opened and closed multiple times; often re-sealable. | Electronics, toys, consumer goods | Pros: Reusable, excellent visibility; Cons: More expensive and may require complex machinery for sealing. |
| Child-Resistant Blister Packs | Designed with safety mechanisms to prevent access by children; often includes tamper-evidence features. | Pharmaceuticals, household chemicals | Pros: Enhances safety for sensitive products; Cons: Can be more expensive and less convenient for adult users. |
Thermoformed Blister Packs
Thermoformed blister packs are created by heating plastic sheets and molding them into specific shapes to hold products securely. This method is widely favored in various industries due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility. B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their products, as while thermoformed packs are suitable for many applications, they may not offer the same level of barrier protection as other types. Customization options allow for branding and product visibility, making them a popular choice for consumer goods.
Cold Formed Blister Packs
Cold formed blister packs are distinguished by their use of aluminum-based laminates, which are pressed into molds at room temperature. This method provides exceptional barrier properties, making these packs ideal for sensitive pharmaceuticals and nutraceuticals that require protection from moisture and oxygen. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of superior product protection against the higher costs associated with cold forming, as well as the potential for slower production times. This type of packaging is particularly suitable for high-value products requiring stringent safety measures.
Blister Cards
Blister cards combine a plastic cavity with a paperboard backing, creating an effective packaging solution for medications and over-the-counter drugs. They are cost-effective and easily customizable, allowing for printed branding and product information. However, B2B buyers should consider their durability, as blister cards may not withstand extensive handling compared to other options. This type is particularly suitable for products that do not require stringent environmental protection but benefit from visibility and ease of use.
Clamshell Blisters
Clamshell blisters are fully enclosed plastic shells that can be opened and closed multiple times, providing excellent visibility for the product inside. They are commonly used in the electronics and toy industries. While they offer the advantage of reusability and easy display, B2B buyers should be aware that clamshells can be more expensive to produce and may require specialized sealing equipment. Their design is ideal for products that benefit from robust packaging and consumer engagement.
Child-Resistant Blister Packs
Child-resistant blister packs are engineered with safety features to prevent children from accessing potentially harmful products. These packs often include tamper-evident seals, making them suitable for pharmaceuticals and household chemicals. B2B buyers should assess the balance between safety and user convenience, as these packs may pose challenges for adult users. This type of packaging is critical for ensuring compliance with safety regulations and enhancing consumer trust in sensitive product categories.
Related Video: Blister Packaging line in pharma
Key Industrial Applications of blister packaging
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of blister packaging | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Medication Blister Packs | Ensures precise dosage and protects against contamination | Compliance with health regulations; material safety data |
| Medical Devices | Packaging for Surgical Instruments | Provides sterility and tamper-evidence | Customization for device shape; high-quality materials |
| Consumer Electronics | Packaging for Small Electronics | Offers visibility while protecting sensitive components | Durability of materials; ease of opening for consumers |
| Food and Beverages | Single-Serve Food Packaging | Extends shelf life and maintains freshness | Food safety compliance; barrier properties against moisture |
| Cosmetics | Blister Packs for Makeup Products | Enhances product visibility and reduces waste | Aesthetic design options; compatibility with various formulations |
Pharmaceuticals
Blister packaging is widely employed in the pharmaceutical industry for medication packaging. Each blister pack allows for precise dosage control, which is critical for patient compliance and safety. The packaging protects against moisture and contamination, ensuring that medications remain effective until consumption. For international buyers, particularly in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing must comply with stringent health regulations. It’s essential to evaluate material safety data sheets and ensure that the packaging meets local regulatory standards.
Medical Devices
In the medical device sector, blister packaging is crucial for maintaining the sterility of surgical instruments and other sensitive products. The tamper-evident feature of blister packs ensures that the integrity of the device is preserved until it is ready for use, reducing the risk of contamination. Buyers should focus on sourcing materials that can be customized to fit the unique shapes of various devices, while also ensuring that the packaging meets health and safety standards applicable in their respective markets.
Consumer Electronics
Blister packaging is increasingly used for small electronics, such as batteries and mobile accessories. This application provides a dual benefit: it showcases the product clearly while offering protection against physical damage and environmental factors. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, considerations should include the durability of materials to withstand shipping and handling, as well as user-friendly designs that facilitate easy opening without damaging the product.
Food and Beverages
In the food and beverage industry, blister packaging is utilized for single-serve items like snacks and condiments. This method not only extends the shelf life of products by providing an effective barrier against moisture and oxygen but also enhances consumer convenience. Buyers must ensure that the materials used comply with food safety regulations and offer appropriate barrier properties to maintain freshness. Sourcing materials that are both functional and environmentally friendly can also be a significant consideration.
Cosmetics
Blister packaging is popular in the cosmetics industry for products like lipsticks and skincare samples. This type of packaging enhances product visibility while minimizing waste by providing the right amount of product per use. For international buyers, especially in markets like France and Mexico, sourcing considerations should include aesthetic design options that align with branding strategies, as well as compatibility with various cosmetic formulations to ensure product integrity.
Related Video: In-line thermoforming of trays and blister integrated into a packaging machine from Schubert
Strategic Material Selection Guide for blister packaging
When selecting materials for blister packaging, it is essential to consider various factors, including product protection, manufacturing capabilities, and compliance with international standards. Here, we analyze four common materials used in blister packaging, highlighting their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
Key Properties: PVC is known for its excellent clarity, making it ideal for showcasing products. It has a temperature resistance ranging from -10°C to 60°C and offers moderate barrier properties against moisture and oxygen.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PVC is its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing, which makes it a popular choice for high-volume production. However, it has lower thermal resistance compared to other materials and can be less suitable for products requiring stringent barrier protection.
Impact on Application: PVC is commonly used in pharmaceutical and consumer goods packaging. However, its limited barrier properties may not be adequate for sensitive products that need extended shelf life.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of regulatory compliance, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector, where standards like ASTM and DIN may apply. In regions like Europe, there is a growing preference for eco-friendly alternatives due to environmental concerns.
Polypropylene (PP)
Key Properties: Polypropylene has a higher temperature resistance than PVC, typically ranging from -20°C to 100°C. It also possesses good chemical resistance and is less prone to deformation.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of PP include its durability and higher barrier properties compared to PVC, making it suitable for a wider range of applications. However, it is generally more expensive and may complicate the manufacturing process due to its rigidity.
Impact on Application: PP is particularly effective for packaging products that require higher temperature stability, such as certain medical devices. Its chemical resistance makes it suitable for pharmaceuticals that may react with other materials.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the cost implications of using PP in regions where budget constraints are significant. Compliance with local standards and regulations is crucial, especially in the Middle East and Africa, where industry standards may vary.
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC)
Key Properties: COC offers excellent clarity and a high barrier to moisture and oxygen, making it ideal for sensitive pharmaceutical products. It can withstand temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The key advantage of COC is its superior barrier properties, which extend the shelf life of products. However, it is one of the more expensive materials and may require specialized manufacturing processes.
Impact on Application: COC is particularly suitable for high-value pharmaceuticals and products that require extended shelf life and protection from environmental factors.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must assess the cost-benefit ratio when considering COC, especially in markets with budget constraints. Compliance with stringent pharmaceutical regulations is essential, particularly in Europe, where standards are rigorously enforced.
Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
Key Properties: PETG is known for its excellent clarity and strength, with a temperature resistance of -40°C to 70°C. It also offers good barrier properties against moisture.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of PETG include its durability and recyclability, making it an attractive option for environmentally conscious buyers. However, it can be more expensive than PVC and may require specific processing conditions.
Impact on Application: PETG is commonly used in packaging for food and pharmaceuticals, where clarity and product visibility are essential.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the environmental impact of their packaging choices, especially in Europe, where sustainability is increasingly prioritized. Compliance with food safety standards is also critical in regions like South America.
| Material | Typical Use Case for blister packaging | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | Pharmaceuticals, consumer goods | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Limited barrier properties | Low |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Medical devices, pharmaceuticals | Higher temperature resistance and durability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | Medium |
| Cyclic Olefin Copolymer (COC) | Sensitive pharmaceuticals | Superior barrier properties | High cost and specialized manufacturing | High |
| Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG) | Food and pharmaceuticals | Excellent clarity and recyclability | Higher cost and specific processing needs | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding blister packaging materials, taking into account their unique market conditions and regulatory requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for blister packaging
Blister packaging has become an essential component across various industries, particularly in pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and medical devices. The manufacturing process and quality assurance measures are critical for ensuring the integrity and safety of packaged products. This section provides an in-depth overview of the key manufacturing stages, quality control measures, and actionable insights for international B2B buyers.
Manufacturing Process of Blister Packaging
The manufacturing process of blister packaging typically involves four main stages: Material Preparation, Forming, Assembly, and Finishing.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the blister packaging process is selecting and preparing the materials. The two primary components are the blister cavity, which is usually made from plastics such as PVC, PP, or PETG, and the backing material, which can be aluminum foil, paper, or a combination of both.
- Material Selection: Buyers should consider the product’s sensitivity to environmental factors. For example, aluminum foil provides excellent barrier properties for moisture-sensitive products, while PVC is cost-effective for general use.
- Supplier Verification: Ensure that suppliers adhere to international standards for material quality, such as ISO 9001.
2. Forming
The forming stage is crucial for creating the blister cavities. This typically involves two main techniques: Thermoforming and Cold Forming.
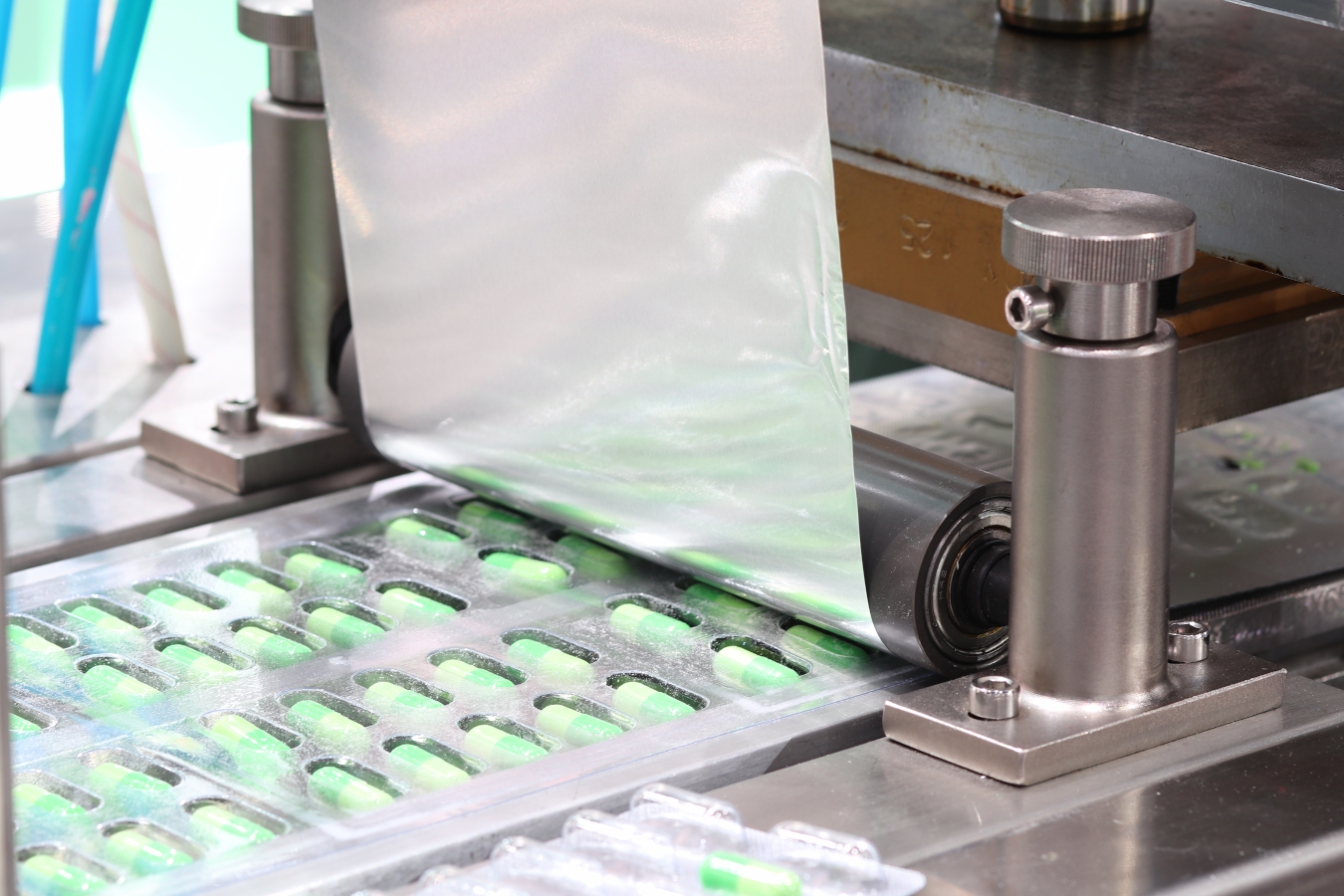
- Thermoforming: In this widely used method, a plastic sheet is heated and formed into a mold to create the blister cavities. Precise temperature control is essential to avoid material degradation.
- Cold Forming: This technique uses aluminum-based laminates pressed into molds at room temperature. It is ideal for sensitive products requiring high barrier properties.
Both methods require custom molds, which should be crafted from high-quality materials such as aluminum or steel to maintain precision throughout the production run.
3. Assembly
Once the blister cavities are formed, the next stage involves placing the product within the cavity and sealing it with the backing material.
- Product Placement: This can be done manually for smaller batches or automatically for larger volumes. Automation increases consistency and speed, reducing the likelihood of errors.
- Sealing Techniques: Common methods include heat sealing and cold sealing, depending on the materials used and the desired strength of the seal.
4. Finishing
The final stage of the manufacturing process focuses on quality checks and the preparation of the blister packs for distribution.
- Trimming and Packaging: Excess material is trimmed away, and the finished blister packs are packaged for shipment. Proper labeling and handling are essential to maintain product integrity during transportation.
Quality Assurance in Blister Packaging
Quality assurance is vital in blister packaging to ensure compliance with industry standards and to protect consumer safety. Various international and industry-specific standards govern these processes.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system and is applicable to any organization, regardless of its size or industry. It emphasizes a process approach to ensure consistent quality.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, compliance with CE marking regulations ensures that the products meet safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: In the pharmaceutical sector, Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) standards set specific requirements for the quality of materials used in blister packaging.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control in blister packaging can be categorized into several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assess the quality of raw materials before production begins. This includes testing samples for compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Monitor the manufacturing process in real-time to ensure adherence to established protocols and standards. This includes checking the dimensions of the blister cavities and the sealing strength.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Conduct thorough inspections of the finished products, including visual inspections for defects and functionality tests to ensure the seals are intact.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods used to ensure quality include:
- Visual Inspection: Manual checks for defects such as cracks, misalignments, or contamination.
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the strength of seals and the integrity of the packaging under stress.
- Barrier Testing: Evaluating the ability of the packaging to protect against moisture, oxygen, and light.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, ensuring that suppliers maintain rigorous quality control is paramount. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
- Conduct Audits: Perform regular audits of potential suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures.
- Request Quality Reports: Ask suppliers for detailed quality reports, including metrics on defect rates, compliance with standards, and any corrective actions taken.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilize third-party inspection services to independently verify the quality of the products and the manufacturing processes.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
When dealing with suppliers across different regions, buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Different countries may have varying regulations governing packaging materials, particularly in the pharmaceutical sector. Familiarize yourself with local regulations in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
- Sustainability Considerations: Increasingly, buyers are looking for suppliers who adopt eco-friendly materials and processes. Suppliers should provide documentation demonstrating compliance with environmental standards.
In summary, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in blister packaging is essential for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material selection, rigorous quality control, and supplier verification, buyers can ensure that they source high-quality blister packaging that meets their product requirements and regulatory standards.
Related Video: Blister Packaging: The Complete Guide
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for blister packaging Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Blister Packaging
When sourcing blister packaging, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex cost structure comprising various components. Key cost elements include:
-
Materials: The choice of materials (e.g., PVC, PET, aluminum) significantly influences the cost. High-quality, specialized materials for pharmaceuticals or sensitive products may carry a premium.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the manufacturing process. Automation can reduce labor costs but may require higher initial investment.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, maintenance, and depreciation of equipment, which can add up, especially for manufacturers with older machinery or less efficient processes.
-
Tooling: Custom molds and tooling can be a significant upfront expense. The complexity of the design and the materials used for tooling will affect this cost.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes is essential to ensure compliance with industry standards. This may include testing materials and inspecting final products, contributing to overall costs.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on distance, volume, and chosen logistics partners. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their costs and profit. This margin can fluctuate based on competition and demand.
Price Influencers in Blister Packaging
Several factors can influence the pricing of blister packaging, making it essential for buyers to understand their implications:
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often benefits from economies of scale. Higher order volumes can lead to reduced per-unit costs, while minimum order quantities (MOQs) can limit flexibility for smaller buyers.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized designs or materials tailored to specific products can increase costs. Standardized solutions may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials or certifications (like ISO or FDA compliance) can command premium prices. Buyers should balance quality against budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, production capabilities, and location can all impact pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge more but offer reliability.
-
Incoterms: The terms of shipping (e.g., FOB, CIF) can affect overall costs. Buyers should be aware of how these terms influence risk and responsibility for shipping costs.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
To maximize value when sourcing blister packaging, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate Terms: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate prices, terms, and conditions. Leverage your purchasing power, especially if you are committing to high volume.
-
Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial price. Consider long-term costs, including logistics, storage, and potential waste. A cheaper upfront cost may result in higher TCO due to quality issues.
-
Understand Regional Pricing Nuances: Pricing strategies can vary significantly across regions. For instance, buyers from Africa or South America may face different logistics and import tariffs than those in Europe. Familiarize yourself with local market conditions to negotiate effectively.
-
Consider Sustainable Options: Increasingly, suppliers are offering eco-friendly materials. While these may have a higher initial cost, they can enhance brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
-
Leverage Technology: Utilize online platforms and marketplaces to compare prices and supplier capabilities. This can provide a clearer picture of market rates and help in making informed decisions.
Disclaimer on Pricing
The prices associated with blister packaging can vary widely based on numerous factors discussed above. The information provided is indicative and should be used as a guideline rather than a definitive cost. Always conduct thorough market research and supplier evaluations to establish accurate pricing for your specific needs.
Spotlight on Potential blister packaging Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘blister packaging’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for blister packaging
Key Technical Properties of Blister Packaging
Understanding the technical specifications of blister packaging is crucial for international B2B buyers to ensure that the packaging meets product safety and regulatory standards. Here are some critical properties to consider:
-
Material Grade
– The grade of materials used in blister packaging significantly affects product protection and compliance. Common materials include PVC, PETG, and aluminum. Each material offers different attributes, such as clarity, barrier properties, and cost. Selecting the right grade can influence product shelf life and consumer safety. -
Tolerance
– Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the blister cavity. Precise tolerances are essential for ensuring that products fit securely within the package, preventing movement that could lead to damage. For manufacturers, maintaining tight tolerances minimizes waste and enhances production efficiency. -
Barrier Properties
– Barrier properties indicate the ability of the packaging to protect the product from external factors such as moisture, oxygen, and light. This is particularly important for pharmaceuticals and sensitive consumer goods. High barrier materials help maintain product integrity and extend shelf life, which is a key concern for buyers in diverse markets.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Sealing Strength
– Sealing strength is the measure of how well the blister pack is sealed, which is vital for tamper resistance and product safety. A strong seal prevents contamination and ensures that the product remains secure until it reaches the end-user. Buyers should verify that the sealing strength meets industry standards relevant to their products. -
Transparency and Aesthetics
– The visual clarity of the blister pack can enhance product appeal and consumer trust. Transparent materials allow for product visibility, which is particularly important in retail environments. Aesthetically pleasing designs can also support branding efforts, making this property vital for marketing strategies. -
Compatibility with Automation
– As manufacturing processes become increasingly automated, compatibility with machinery for product placement, sealing, and inspection is crucial. Buyers should consider how well the blister packaging integrates with existing production lines to ensure efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Common Trade Terminology in Blister Packaging
Familiarizing oneself with industry jargon is essential for effective communication and negotiation in the blister packaging market. Here are some key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– OEM refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In blister packaging, OEMs can provide custom solutions tailored to specific product requirements, making them valuable partners in the supply chain. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to manage inventory and budget effectively, especially when dealing with specialized blister packaging solutions. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to solicit price quotations for specific products or services. This is a critical step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and select the best supplier based on price and quality. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions, including shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand their obligations and minimize risks during shipping and delivery. -
Lead Time
– Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their inventory and production schedules, ensuring they meet market demands without overstocking. -
Sustainability Certification
– This term refers to certifications that indicate a product meets certain environmental standards. As sustainability becomes increasingly important, buyers should look for blister packaging options that are certified eco-friendly to align with consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring that their blister packaging solutions are both effective and compliant with industry standards.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the blister packaging Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The blister packaging market is undergoing significant transformation driven by advancements in technology, changing consumer preferences, and increasing regulatory scrutiny, particularly in the pharmaceutical and consumer goods sectors. International B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing a shift towards high-barrier packaging solutions, which enhance product protection against moisture, oxygen, and contamination. Emerging technologies such as smart packaging, which integrates QR codes and IoT capabilities, are also gaining traction, offering enhanced user engagement and traceability.
Key trends include the growing demand for eco-friendly materials and the rise of automation in manufacturing processes. Automation not only improves efficiency but also ensures consistency and quality, essential for meeting regulatory standards. Additionally, the global push for sustainability is leading manufacturers to explore biodegradable and recyclable materials, such as PLA (Polylactic Acid) and recycled PET, which align with environmental goals while maintaining product integrity.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the need for tamper-evident and hygienic packaging solutions, further solidifying the role of blister packs in the pharmaceutical industry. For international buyers, understanding local market dynamics, such as regulatory requirements and consumer preferences, is crucial for effective sourcing and implementation of blister packaging solutions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of blister packaging is a critical consideration for B2B buyers. Traditional materials like PVC and aluminum pose challenges in terms of recyclability and biodegradability, raising concerns about waste management and sustainability. As a result, many companies are prioritizing ethical sourcing and are committed to reducing their carbon footprint through the adoption of sustainable practices.
Importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated, especially in a global market where consumers are increasingly conscious of environmental issues. Buyers should seek suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as using certified materials and maintaining transparency throughout the supply chain. Certifications like FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) for paper materials and ISO 14001 for environmental management systems are indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
In response to the demand for greener solutions, the blister packaging industry is innovating with materials such as biodegradable plastics and recyclable laminates. These materials not only meet the protective needs of products but also contribute to a circular economy, enabling businesses to reduce waste and enhance their brand reputation. For B2B buyers, selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainability is essential for aligning with modern consumer values and regulatory trends.
Brief Evolution/History
Blister packaging has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Originally designed for consumer goods, its application expanded into the pharmaceutical sector due to its protective qualities and user-friendly design. The introduction of thermoforming processes in the 1960s revolutionized the industry, allowing for mass production of customizable blister packs.
As technology advanced, so did the materials used in blister packaging. The shift from traditional PVC to more advanced materials such as PET and COC reflects the industry’s response to the growing demand for high-performance packaging that meets stringent safety and regulatory standards. Today, blister packaging is not just a functional solution but also a strategic asset for brands aiming to enhance product visibility and consumer trust in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of blister packaging
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers for blister packaging?
When vetting suppliers, assess their industry experience, production capacity, and certifications (such as ISO and GMP). Request samples to evaluate quality and ensure they can meet your specific requirements. Additionally, inquire about their compliance with international regulations relevant to your product category, especially if you operate in the pharmaceutical or food sectors. Lastly, consider their geographic location and logistics capabilities to facilitate efficient shipping and reduce costs. -
Can blister packaging be customized for my specific product needs?
Yes, blister packaging is highly customizable. Suppliers can create unique cavity shapes, sizes, and materials tailored to your product’s requirements. Discuss your branding needs with potential suppliers, as they can often incorporate custom graphics and colors into the packaging design. Ensure that you provide detailed product specifications and any regulatory considerations to facilitate the customization process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for blister packaging?
Minimum order quantities vary by supplier, typically ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 units, depending on the complexity and customization level of the packaging. Lead times can also differ; standard production may take 4-6 weeks, while custom orders may require additional time for design and approval. It’s advisable to confirm these details upfront to align your production schedules and avoid delays in product launches. -
What quality assurance (QA) measures should I expect from blister packaging suppliers?
Reputable suppliers implement rigorous QA measures, including material testing, in-process inspections, and final product evaluations. Look for suppliers that provide certifications for their materials and processes, such as ISO 9001 or specific pharmaceutical standards. Additionally, inquire about their quality control protocols and whether they conduct regular audits or third-party inspections to ensure compliance with industry standards. -
What payment terms are commonly offered in international transactions for blister packaging?
Payment terms can vary widely; however, many suppliers offer options such as advance payment, letters of credit, or payment upon delivery. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and risk tolerance. Consider using escrow services for larger orders to protect your investment until you receive the goods as specified. Always ensure that the payment method complies with international trade regulations. -
How should I approach logistics and shipping for blister packaging orders?
When arranging logistics, consider both the shipping method and the supplier’s location. Air freight is faster but more expensive, while sea freight is cost-effective for larger volumes but may take longer. Confirm the supplier’s ability to handle export documentation and customs clearance. Additionally, clarify responsibilities for shipping costs and risks in your contract to avoid disputes later. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with blister packaging suppliers?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear contracts that outline product specifications, delivery timelines, payment terms, and quality expectations. If a dispute arises, initiate communication to address the issue directly. If necessary, refer to your contract’s dispute resolution clause, which may include mediation or arbitration. Maintaining a professional relationship can often lead to amicable solutions without escalating to legal action. -
Are there environmental considerations I should be aware of when sourcing blister packaging?
Yes, environmental sustainability is increasingly important in packaging. Inquire about the materials used in blister packaging, as some may be recyclable or biodegradable. Suppliers should ideally provide information about their environmental policies and practices. Additionally, consider sourcing from suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly materials and processes, as this can enhance your brand’s reputation and compliance with global sustainability standards.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for blister packaging
In conclusion, the landscape of blister packaging presents robust opportunities for international B2B buyers, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the intricacies of the blister packaging process—from material selection to quality control—buyers can make informed decisions that enhance product safety and marketability. Strategic sourcing is paramount; it enables companies to not only secure high-quality packaging solutions but also to foster sustainable practices that align with evolving consumer expectations.
Investing in blister packaging not only ensures the protection and visibility of products but also enhances brand integrity through tamper-evidence features. As the industry continues to evolve with innovations in materials and technology, buyers are encouraged to stay proactive and engaged.
Take action now: Evaluate your current packaging strategies and consider integrating advanced blister packaging solutions that meet your specific needs. By doing so, you will not only improve product delivery but also position your business favorably in a competitive global market. Embrace the future of packaging to drive growth and sustainability in your operations.