Master Chemical Milling: A Comprehensive Guide for B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for chemical milling
In today’s competitive landscape, chemical milling stands out as a vital manufacturing process that allows businesses to achieve precision in material shaping while minimizing waste. This technique, integral to various industries including aerospace, automotive, and electronics, employs chemical solutions to selectively etch materials, offering unparalleled control over component dimensions and surface finishes. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of chemical milling is essential for making informed sourcing decisions.
This guide comprehensively explores the chemical milling process, covering essential topics such as types of chemical milling techniques, the materials used, and the critical aspects of manufacturing and quality control. It also highlights the landscape of suppliers, delves into cost considerations, and examines the broader market dynamics. Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section addresses common queries, ensuring that buyers have access to all necessary information to streamline their procurement processes.
By empowering stakeholders with knowledge and insights into chemical milling, this guide serves as a strategic resource for making well-informed sourcing choices. Whether you are based in Mexico, Kenya, or elsewhere, the actionable insights provided herein will enhance your capability to navigate the global market effectively, fostering stronger partnerships and driving operational excellence in your supply chain.
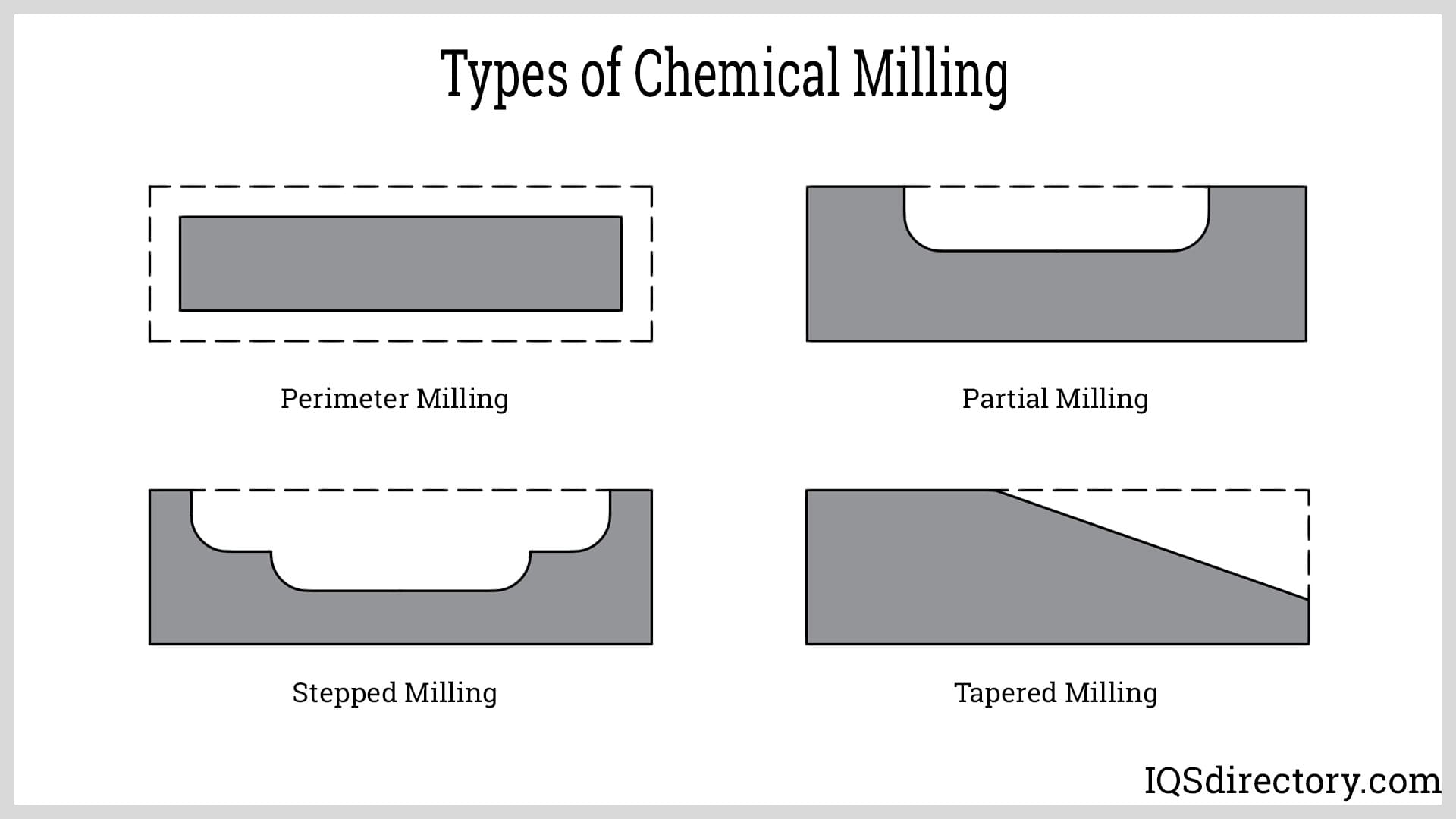
Understanding chemical milling Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline Chemical Milling | Utilizes alkaline solutions for etching and surface preparation. | Aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries. | Pros: Effective for complex geometries; Cons: May require post-treatment for surface finish. |
| Acidic Chemical Milling | Involves the use of acidic solutions, often for metals and alloys. | Metal finishing, jewelry manufacturing, and tooling. | Pros: Quick processing time; Cons: Higher environmental impact and safety concerns. |
| Photo-Chemical Milling | Uses photochemical processes to selectively etch materials. | Electronics, microfabrication, and precision engineering. | Pros: High precision and repeatability; Cons: More expensive setup costs. |
| Electrochemical Milling | Combines electrolysis with chemical milling for enhanced control. | Aerospace, medical devices, and precision parts. | Pros: Reduces material wastage; Cons: Requires specialized equipment and expertise. |
| Biochemical Milling | Employs biological agents to facilitate material removal. | Sustainable manufacturing and eco-friendly applications. | Pros: Environmentally friendly; Cons: Slower process and limited material compatibility. |
Alkaline Chemical Milling
Alkaline chemical milling employs alkaline solutions, such as sodium hydroxide, to etch and prepare surfaces. This method is particularly effective for materials that require complex geometries, making it suitable for aerospace and automotive applications. Buyers should consider the need for post-treatment processes to achieve the desired surface finish, which may add to overall production time and costs.
Acidic Chemical Milling
This variation utilizes acidic solutions, like hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, to etch metals and alloys. It is widely used in metal finishing, jewelry manufacturing, and tooling industries due to its rapid processing capabilities. However, buyers must be aware of the environmental impact and safety concerns associated with handling hazardous materials, which may necessitate additional safety equipment and training.
Photo-Chemical Milling
Photo-chemical milling employs light-sensitive materials and photochemical processes to achieve high precision in etching. This method is ideal for applications in electronics and microfabrication, where accuracy is paramount. Although it offers excellent repeatability, the initial setup costs can be significant, making it a consideration for buyers looking for long-term investment in precision manufacturing.
Electrochemical Milling
Combining electrolysis with chemical milling, electrochemical milling offers enhanced control over the etching process. It is particularly beneficial in industries like aerospace and medical devices, where precision is critical. Buyers should evaluate the investment in specialized equipment and expertise required for this method, as it can lead to reduced material wastage and more efficient production cycles.
Biochemical Milling
Biochemical milling utilizes biological agents to facilitate material removal, positioning itself as a sustainable manufacturing option. This method is gaining traction in eco-friendly applications but is generally slower and may have limited compatibility with certain materials. Buyers interested in sustainability should weigh the benefits of reduced environmental impact against the potential drawbacks of longer processing times.
Related Video: CS 198-126: Lecture 12 – Diffusion Models
Key Industrial Applications of chemical milling
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of chemical milling | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Precision component manufacturing for aircraft parts | Enhanced accuracy and reduced material waste | Supplier certifications and compliance with aerospace standards |
| Automotive | Lightweight structural components in vehicles | Improved fuel efficiency and performance | Availability of specialized chemical milling equipment and expertise |
| Electronics | Fabrication of intricate circuit boards | High precision in microfabrication leading to better performance | Technology compatibility and rapid prototyping capabilities |
| Medical Devices | Production of custom implants and surgical instruments | Tailored solutions for patient-specific applications | Regulatory compliance and material traceability |
| Defense | Manufacturing of specialized weaponry and parts | High durability and reliability under extreme conditions | Security clearances and adherence to defense procurement standards |
Aerospace Applications
In the aerospace sector, chemical milling is utilized for the precision manufacturing of aircraft components, such as brackets, panels, and other structural elements. This process enables the production of complex geometries while minimizing material waste, which is crucial in an industry where weight savings can significantly impact fuel efficiency. International buyers, especially from regions like Africa and South America, should seek suppliers with certifications that comply with stringent aerospace standards, ensuring quality and safety.
Automotive Applications
The automotive industry employs chemical milling for creating lightweight structural components, which contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance. This technique allows for the production of parts that are both strong and lightweight, addressing the industry’s ongoing push toward sustainability. Buyers from Europe and the Middle East should prioritize suppliers with advanced chemical milling capabilities, ensuring they can meet the rigorous demands of automotive manufacturing, including adherence to environmental regulations.
Electronics Applications
In the electronics sector, chemical milling is essential for the fabrication of intricate circuit boards. This application requires high precision in microfabrication, which chemical milling provides through its ability to create fine features and complex shapes. B2B buyers in regions like Europe and Africa should consider suppliers that offer state-of-the-art technology and rapid prototyping services, enabling them to stay competitive in the fast-paced electronics market.
Medical Device Applications
Chemical milling is increasingly used in the medical device industry to produce custom implants and surgical instruments tailored to specific patient needs. This application ensures that devices meet unique anatomical requirements, improving patient outcomes. Buyers should focus on suppliers that demonstrate regulatory compliance and material traceability, particularly in regions like South America and the Middle East, where healthcare standards may vary significantly.
Defense Applications
The defense sector benefits from chemical milling in the manufacturing of specialized weaponry and parts that require high durability and reliability under extreme conditions. This process allows for the creation of components that can withstand harsh environments, which is crucial for defense applications. Buyers must consider suppliers who hold necessary security clearances and adhere to defense procurement standards, particularly in regions with stringent regulatory environments.
Related Video: Chemical Etching: A Tour Through The Process (3D Animation)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for chemical milling
When selecting materials for chemical milling, it is essential to consider various factors that can influence both the performance of the milling process and the quality of the final product. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in chemical milling, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, and ability to withstand high temperatures (up to 900°C). It also has good mechanical properties, making it suitable for various milling applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can withstand harsh chemical environments. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require specialized machining techniques, increasing manufacturing complexity.
Impact on Application:
Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of chemicals, making it ideal for applications involving acidic or alkaline substances. Its robustness ensures that it maintains integrity over prolonged use.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing local suppliers who meet these standards can reduce costs and lead times.
Aluminum
Key Properties:
Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, particularly when anodized. It can withstand moderate temperatures (up to 600°C) and is easy to machine.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce transportation costs. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not be suitable for high-stress applications or exposure to aggressive chemicals.
Impact on Application:
Aluminum is often used in applications where weight savings are critical, such as in aerospace components. Its compatibility with less corrosive media makes it a viable option for specific milling processes.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should consider the availability of aluminum grades that meet standards like ASTM B221. In regions like the Middle East, local sourcing can help mitigate import tariffs.
Polypropylene
Key Properties:
Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer known for its chemical resistance and low density. It can handle temperatures up to 100°C and is resistant to many acids and bases.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polypropylene is its excellent chemical resistance, making it suitable for corrosive environments. However, it has lower mechanical strength compared to metals and can deform under high temperatures.
Impact on Application:
Polypropylene is ideal for applications involving aggressive chemicals, particularly in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Its lightweight nature also contributes to lower shipping costs.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure that the polypropylene used conforms to relevant standards such as ASTM D4101. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is critical for chemical safety.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium boasts exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, high corrosion resistance, and can withstand extreme temperatures (up to 1,600°C). It is particularly resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Pros & Cons:
The durability and longevity of titanium make it a preferred choice for high-performance applications. However, it is one of the most expensive materials and can be challenging to machine, leading to increased manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is particularly suited for applications in the aerospace and medical industries where performance is critical. Its compatibility with various aggressive chemicals also enhances its appeal.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers should be aware of the high costs associated with titanium and ensure compliance with standards like ASTM B348. In regions with developing markets, the availability of titanium may be limited, necessitating careful supplier selection.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for chemical milling | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Aerospace components, chemical tanks | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost, complex machining | High |
| Aluminum | Lightweight structural components | Low weight, easy to machine | Less durable, limited chemical resistance | Medium |
| Polypropylene | Pharmaceutical and food packaging | Excellent chemical resistance | Lower mechanical strength | Low |
| Titanium | Aerospace, medical implants | Exceptional strength and durability | Very high cost, difficult to machine | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides insights into the materials commonly used in chemical milling, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on their specific needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for chemical milling
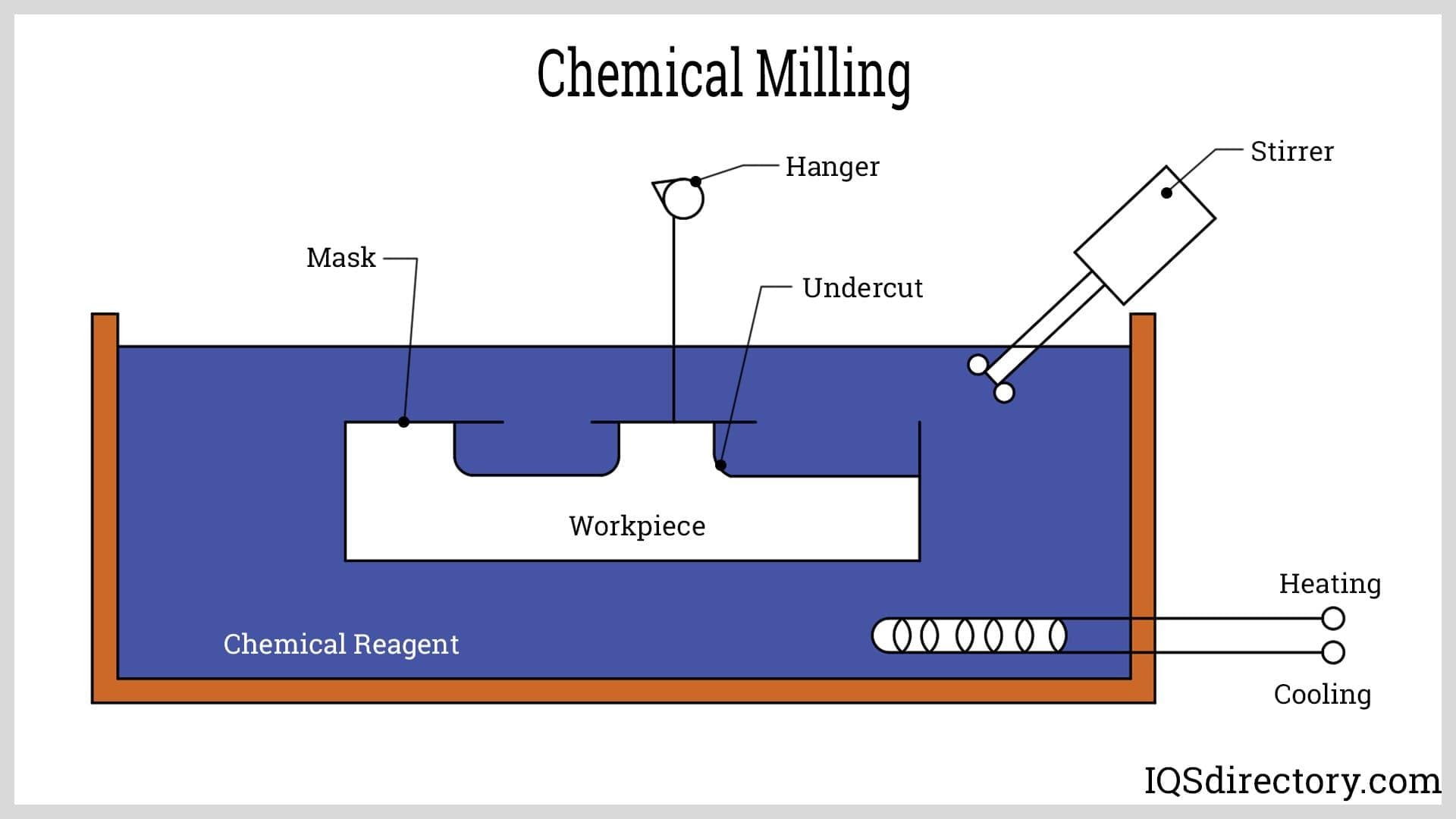
Chemical milling is a sophisticated manufacturing process that involves the selective removal of material from a substrate using chemical etching techniques. This process is essential in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics, where precision and quality are paramount. For international B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in chemical milling is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
The chemical milling process is typically divided into several main stages:
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Substrate: The choice of substrate material (often aluminum, titanium, or steel) is critical, as it affects the etching process and final product quality.
– Surface Cleaning: Before milling, substrates must be thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants. Techniques include ultrasonic cleaning and solvent degreasing.
– Masking: A protective mask is applied to areas that should not be etched. This can involve photoresist films or other masking materials that withstand the chemical processes. -
Forming
– Chemical Etching: The core of chemical milling involves immersing the masked substrate in a chemical solution that selectively removes material. This process can be finely controlled to achieve desired thicknesses and features.
– Control of Parameters: Key parameters such as temperature, concentration of chemicals, and immersion time must be tightly controlled to ensure uniformity and precision. -
Assembly
– Post-Etching Treatment: After the etching process, the components may undergo additional treatments, such as rinsing and drying, to remove any residual chemicals.
– Inspection: Components are inspected for compliance with design specifications before proceeding to the next stage. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Final surface treatments may include anodizing, passivation, or coating to enhance corrosion resistance and finish quality.
– Quality Checks: Final inspection involves checking dimensions, surface finish, and overall quality to ensure compliance with customer specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in chemical milling is vital to ensure that the final products meet international standards and customer expectations. Key aspects include:
- International Standards: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems is essential. This ensures a consistent approach to quality across processes.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Depending on the application, additional certifications may be required, such as:
- CE Marking: For products sold in the European Economic Area, ensuring compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: For components used in the oil and gas sector, ensuring adherence to specific industry standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is typically structured around several checkpoints:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC):
– Verification of incoming materials against specifications.
– Inspection of supplier certifications and quality reports. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC):
– Continuous monitoring during the chemical etching process.
– Use of statistical process control (SPC) to identify variances in production. -
Final Quality Control (FQC):
– Comprehensive inspection of finished products against specifications.
– Utilization of non-destructive testing methods, such as X-ray or ultrasonic testing, to identify any internal defects.
Common Testing Methods
To ensure the integrity and quality of the chemical milling process, various testing methods are employed:
- Dimensional Inspection: Using calipers and micrometers to verify dimensions.
- Surface Roughness Testing: To assess the finish of the milled surface.
- Chemical Composition Analysis: Spectroscopy techniques may be used to confirm material properties.
- Adhesion Testing: For coatings applied to ensure they bond effectively to the substrate.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those from diverse regions, verifying supplier quality control is essential. Here are some actionable steps:
- Audits: Conduct on-site audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes and quality management systems.
- Documentation Review: Request and review quality assurance documentation, including ISO certifications and quality manuals.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party inspection agencies to perform independent checks on supplier processes and products.
- Supplier Performance Metrics: Track supplier performance through key performance indicators (KPIs) related to quality, delivery times, and responsiveness.
Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers must navigate several nuances in quality control:
- Regulatory Variations: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are compliant with both local and international standards.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural attitudes towards quality and business practices can aid in smoother negotiations and collaborations.
- Language Barriers: Clear communication is vital. Buyers should ensure that all technical specifications and quality requirements are well-documented and communicated in a language understood by both parties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a thorough understanding of the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in chemical milling is essential for B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing processes, alongside rigorous quality control and testing methods, buyers can ensure they select reliable suppliers who meet their precise specifications. By implementing proactive verification strategies and understanding regional nuances, international buyers can mitigate risks and enhance their procurement processes.
Related Video: What is Electro-Chemical Machining Process??? ||Engineer’s Academy||
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for chemical milling Sourcing
In the chemical milling industry, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section provides a detailed breakdown of cost components, price influencers, and strategic tips for effective sourcing.
Cost Components of Chemical Milling
-
Materials: The primary input costs include chemicals, substrates, and any specialized materials required for milling. Prices can vary significantly based on global supply chain conditions and material quality.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for operating milling equipment and ensuring quality control. Labor costs can differ by region, influenced by local wage standards and availability of skilled workers.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Overhead can significantly impact the final pricing, especially in regions with higher operational costs.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be required for various milling processes, affecting initial investment costs. The amortization of these costs over production volume is a critical factor in pricing.
-
Quality Control (QC): Maintaining high standards through rigorous QC processes incurs additional costs. These may include testing materials and finished products to meet industry standards and certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation and shipping costs are vital, especially for international transactions. Factors such as distance, mode of transport, and customs duties can substantially influence overall costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically build a profit margin into their pricing. Understanding the average margin in your specific market can aid in negotiations.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable terms based on projected volumes can yield significant savings.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom milling processes or specialized specifications can raise prices. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly impacts pricing. Sustainable or high-performance materials may carry a premium but can enhance the final product’s value.
-
Quality/Certifications: Higher quality and specific certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can justify higher prices. Buyers should assess the necessity of these certifications against their quality requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and location can influence pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for pricing negotiations. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping costs, insurance, and delivery.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Leverage your purchasing volume and long-term relationships to negotiate better pricing terms. Understanding the supplier’s cost structure can provide leverage during discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes all costs associated with the product lifecycle, not just the purchase price. This approach can help identify the most cost-effective options.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations. For instance, suppliers in Africa or South America may have different pricing structures due to local market conditions and operational costs.
-
Conduct Market Research: Regularly analyze market trends and pricing benchmarks in your industry. This information can inform your purchasing strategy and help identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and service. Regular communication and feedback can enhance collaboration and lead to more favorable terms.
Disclaimer
Pricing in the chemical milling sector can vary widely based on multiple factors. The figures presented here are indicative and should be verified with suppliers to ensure accuracy. Always consider local market conditions and supplier capabilities when making sourcing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential chemical milling Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘chemical milling’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for chemical milling
In the chemical milling industry, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for international B2B buyers, especially those operating in diverse markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This knowledge not only aids in making informed purchasing decisions but also fosters effective communication with suppliers and partners.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Material grade refers to the classification of materials based on their chemical composition and mechanical properties.
– B2B Importance: Selecting the right material grade is vital for ensuring the durability and performance of the milled components. Different grades may exhibit varying resistance to corrosion, heat, and wear, which can significantly impact the longevity of the final product. -
Tolerance
– Definition: Tolerance is the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value.
– B2B Importance: Precise tolerances are essential in chemical milling to ensure that parts fit together correctly and function as intended. Poor tolerance can lead to assembly issues, increased wear, or even failure of the product. -
Surface Finish
– Definition: Surface finish describes the texture of a surface and is characterized by roughness, waviness, and lay.
– B2B Importance: A specific surface finish may be required for aesthetic purposes or to enhance the functionality of the part, such as reducing friction or improving adhesion. Understanding surface finish specifications can help buyers ensure compliance with product performance requirements. -
Thickness
– Definition: Thickness refers to the measurement of how thick a material is, usually expressed in millimeters or inches.
– B2B Importance: The thickness of the material can affect the strength and weight of the final product. Buyers must ensure that the thickness aligns with their application needs and industry standards.
- Chemical Resistance
– Definition: Chemical resistance indicates how well a material can withstand chemical exposure without degrading.
– B2B Importance: For industries that utilize harsh chemicals, selecting materials with appropriate chemical resistance is crucial to avoid premature failure and costly replacements.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Explanation: An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Significance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable sources for high-quality components that meet their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Explanation: MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Significance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management, especially for smaller businesses or those just entering a market. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Explanation: An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services.
– Significance: Utilizing RFQs can streamline the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers effectively. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Explanation: Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) related to international commercial law.
– Significance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for buyers to understand their responsibilities and liabilities during shipping and delivery, ensuring smoother international transactions. -
Lead Time
– Explanation: Lead time is the amount of time that passes from the initiation of a process until its completion.
– Significance: Knowing lead times helps buyers plan their production schedules and manage inventory levels, particularly in industries where timing is critical.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the chemical milling landscape more effectively, making informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the chemical milling Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The chemical milling sector is currently experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand from various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Global drivers include technological advancements, the need for precision manufacturing, and the rising emphasis on cost-effective production processes. In particular, international B2B buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are leveraging these advancements to enhance their operational efficiency.
Current and emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of automation and robotics, which streamline production processes and reduce labor costs. Additionally, the adoption of data analytics and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies is allowing manufacturers to monitor processes in real-time, optimizing performance and reducing waste. Sourcing trends are also evolving, with buyers increasingly favoring suppliers that can demonstrate agility and responsiveness to market changes.
Market dynamics are influenced by geopolitical factors, trade policies, and supply chain disruptions, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. For international buyers, understanding regional market conditions is essential. For instance, buyers in Africa may find opportunities in localizing supply chains to mitigate risks associated with global sourcing, while those in Europe might focus on suppliers that align with stringent regulatory standards and sustainability goals.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a paramount concern in the chemical milling sector, with increasing awareness of its environmental impact. The production processes often involve hazardous materials, necessitating a focus on minimizing emissions and waste. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices, such as recycling solvents and utilizing green chemistry principles.
The importance of ethical supply chains cannot be overstated. Buyers must ensure that their suppliers adhere to ethical labor practices and maintain transparency in their sourcing methods. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are critical indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the trend towards using green certifications and materials is gaining momentum. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer environmentally friendly alternatives, such as bio-based chemicals or recyclable materials. By opting for sustainable sourcing, companies not only enhance their corporate social responsibility (CSR) profile but also meet the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products.
Brief Evolution/History
The chemical milling process has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for the aerospace industry to produce lightweight components, the technique has expanded into various sectors, including automotive and electronics. Over the decades, innovations in chemical formulations and milling technologies have led to enhanced precision and efficiency.
The transition towards digital manufacturing and Industry 4.0 has further transformed the sector, allowing for greater customization and automation. As international B2B buyers navigate this evolving landscape, understanding the historical context of chemical milling can provide valuable insights into current trends and future developments. This historical perspective underscores the importance of continuous innovation and adaptation in meeting the demands of a dynamic global market.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of chemical milling
-
How do I vet potential suppliers for chemical milling?
Vetting suppliers is crucial to ensure quality and reliability. Start by researching the supplier’s history, reputation, and customer reviews. Request references from previous clients and verify their experience in your specific industry. Assess their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO 9001 or specific chemical safety regulations. Additionally, consider visiting their facilities if feasible, or use third-party audit services to evaluate their operational capabilities and quality control processes. -
Can chemical milling services be customized to meet my specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for chemical milling services. When engaging with potential suppliers, clearly outline your requirements, including material specifications, dimensions, and tolerances. Suppliers may have different capabilities, so it’s essential to discuss your needs upfront. Request samples or prototypes to validate that the customized solution meets your expectations before placing a larger order. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for chemical milling?
MOQs and lead times can vary significantly among suppliers and depend on the complexity of the project. Generally, MOQs can range from small batch sizes for specialized applications to larger quantities for mass production. Lead times may vary from a few days to several weeks, depending on the supplier’s capacity and your specific requirements. Always confirm these details during negotiations to avoid surprises and plan your procurement timeline accordingly. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing chemical milling services?
Payment terms can differ based on the supplier’s policies and your relationship with them. Common terms include upfront deposits, payment upon delivery, or net terms such as 30 or 60 days post-invoice. For international transactions, consider the currency exchange rates and any potential transaction fees. Establish clear payment terms in your contract to ensure mutual understanding and to protect against payment disputes. -
What quality assurance measures should suppliers provide?
Suppliers should have robust quality assurance (QA) processes in place. Request documentation on their QA protocols, including inspection methods, testing procedures, and compliance with industry standards. Certifications such as ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 (for medical applications) can indicate a commitment to quality. Additionally, inquire about their ability to provide material certifications and test reports for the chemical milling processes used. -
How can I ensure efficient logistics for my chemical milling orders?
Efficient logistics are vital for timely delivery. Discuss shipping options with your supplier, considering factors such as cost, speed, and reliability. Ensure that the supplier can handle customs documentation and international shipping regulations. For large orders, consider working with a freight forwarder who specializes in chemical products to streamline the process and mitigate potential delays.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- What should I do in case of a dispute with a supplier?
In the event of a dispute, first, attempt to resolve the issue directly with the supplier through open communication. If this fails, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration processes. Ensure that you document all communications and agreements. If necessary, consult legal counsel familiar with international trade laws to explore your options for resolution.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Are there specific certifications I should look for in chemical milling suppliers?
Yes, when sourcing chemical milling services, look for suppliers with relevant certifications that demonstrate their adherence to quality and safety standards. Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and OHSAS 18001 for occupational health and safety. Depending on your industry, additional certifications may be necessary, such as FDA approval for pharmaceutical applications or REACH compliance for chemical safety in the EU. Always verify these certifications to ensure compliance with international regulations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for chemical milling
In the evolving landscape of chemical milling, strategic sourcing remains a crucial element for international B2B buyers. By leveraging global supply chains, buyers can access a diverse range of materials and technologies that enhance their production capabilities. It’s essential to assess suppliers not only for their product offerings but also for their compliance with international standards and sustainability practices, which are increasingly important to consumers and regulatory bodies alike.
Key Takeaways for B2B Buyers:
- Diversity in Sourcing: Engage with suppliers across different regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to mitigate risks and capitalize on local expertise and innovation.
- Sustainability Focus: Prioritize suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, ensuring that your sourcing aligns with global environmental goals.
- Technology Integration: Embrace suppliers that utilize advanced technologies in their processes, which can lead to improved efficiency and product quality.
Looking ahead, the chemical milling sector is poised for growth driven by innovations and increased demand for customized solutions. Now is the time for international buyers to reassess their sourcing strategies and forge partnerships that will not only meet current needs but also position them advantageously for future developments in the industry. Engage with potential suppliers today to explore how strategic sourcing can drive your business forward.
