Master Control Solenoid Sourcing: Key Insights for Global
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for control solenoid
In the rapidly evolving landscape of industrial automation, control solenoids stand out as pivotal components that enhance operational efficiency across various applications. These electromechanical devices facilitate the precise control of fluid and gas flow, making them indispensable in sectors ranging from manufacturing and food processing to HVAC and medical equipment. As businesses in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for greater automation and productivity, understanding the intricacies of control solenoids becomes crucial for informed procurement decisions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of control solenoids, exploring their specific applications and material compositions. Buyers will gain insights into manufacturing standards, quality control practices, and effective supplier evaluation methods, ensuring compliance with local regulations and industry benchmarks. Additionally, the guide will address cost considerations and the current market dynamics, equipping international B2B buyers with the knowledge needed to navigate potential challenges in sourcing.
By leveraging the expertise contained within this guide, procurement professionals from regions like Nigeria, Brazil, Saudi Arabia, and Italy will be empowered to make strategic sourcing decisions. With a focus on reliability, compliance, and cost-effectiveness, this resource aims to optimize your procurement strategy, ensuring that your operations remain robust and competitive in a global market that demands excellence.
Understanding control solenoid Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct-Acting Solenoid | Directly actuated by the solenoid coil | Low flow systems, general automation | Quick response; suitable for low pressure. Limited to low flow rates. |
| Pilot-Operated Solenoid | Uses system pressure to assist in operation | High flow, industrial applications | Efficient for large flows; lower energy consumption. Requires pressure differential. |
| Normally Closed (NC) | Closed by default when not energized | Safety systems, fluid control | Fail-safe operation; prevents unintended flow. Not suitable for all applications. |
| Normally Open (NO) | Open by default when not energized | Venting applications, pneumatic systems | Allows immediate flow; useful in specific applications. Can lead to unintended operation if power fails. |
| Proportional Solenoid | Varies flow rate based on input signal | Precision control in manufacturing | Allows fine-tuning of flow; ideal for automated processes. More complex and costly than standard solenoids. |
Direct-Acting Solenoid
Direct-acting solenoids are notable for their straightforward design, where the solenoid coil directly opens or closes the valve. This type is ideal for low flow applications and is commonly used in general automation processes across various industries. B2B buyers should consider the quick response time and simplicity of installation, but must also be aware that their use is limited to low-pressure systems, which may not suit all operational needs.
Pilot-Operated Solenoid
Pilot-operated solenoids leverage the pressure of the fluid to assist in valve actuation, making them suitable for high flow applications. This design is prevalent in industrial settings, where efficiency is paramount. Buyers should appreciate the lower energy consumption and ability to handle larger flows. However, the requirement for a pressure differential can complicate installation and operation, making it critical to assess the specific conditions of use.
Normally Closed (NC)
Normally closed solenoids are designed to remain closed when not energized, offering a fail-safe solution in various applications. They are widely used in safety systems and fluid control scenarios where unintended flow must be prevented. B2B buyers benefit from their reliability in critical operations, but must also consider that these solenoids may not be suitable for all applications, particularly where constant flow is required.
Normally Open (NO)
Normally open solenoids allow fluid flow when de-energized, making them suitable for applications such as venting and pneumatic systems. This design enables immediate flow upon energization, which can be advantageous in specific scenarios. However, B2B buyers must be cautious as power failure can lead to unintended operation, potentially causing system malfunctions in sensitive environments.
Proportional Solenoid
Proportional solenoids offer advanced control by varying the flow rate based on an input signal. These solenoids are ideal for precision applications in manufacturing where fine-tuning of fluid dynamics is necessary. B2B purchasers should weigh the benefits of enhanced control against the increased complexity and cost, ensuring that their investment aligns with operational requirements for automation and process efficiency.
Related Video: How Solenoid Valves Work – Basics actuator control valve working principle
Key Industrial Applications of control solenoid
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of Control Solenoid | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated assembly lines | Increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs | Ensure compatibility with existing automation systems and verify response times. |
| Food and Beverage | Fluid control in processing and packaging | Ensures hygienic handling and precise dosing of liquids | Look for FDA-compliant materials and certifications to meet safety standards. |
| HVAC Systems | Temperature regulation | Improves energy efficiency and maintains comfort levels | Source valves that withstand high humidity and have appropriate IP ratings for environmental conditions. |
| Oil and Gas | Control of gas and liquid flow | Enhances safety and reliability in hazardous environments | Focus on valves with corrosion-resistant materials and certifications for explosive atmospheres. |
| Medical Equipment | Oxygen concentrators and dialysis machines | Critical for patient safety and operational reliability | Prioritize sourcing from suppliers with proven track records in medical-grade components. |
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, control solenoids are integral to automated assembly lines, where they facilitate the precise control of pneumatic cylinders and robotic arms. By enabling rapid actuation, these solenoids increase production efficiency and minimize labor costs. International B2B buyers must ensure that the solenoids they source are compatible with existing automation systems and meet specific response time requirements to avoid bottlenecks in production.
Food and Beverage
Control solenoids play a vital role in the food and beverage industry, particularly in fluid control during processing and packaging. They ensure hygienic handling and precise dosing of liquids, which is essential for maintaining product quality and safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing solenoids made from FDA-compliant materials and ensure that they possess the necessary certifications to meet stringent safety standards, especially in regions with strict food safety regulations.
HVAC Systems
In HVAC systems, control solenoids are utilized for temperature regulation, allowing for the efficient flow of refrigerants and air. This functionality is crucial for improving energy efficiency and maintaining comfort levels in commercial and residential buildings. Buyers should focus on sourcing solenoids that can withstand high humidity and have appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings to ensure durability in various environmental conditions.
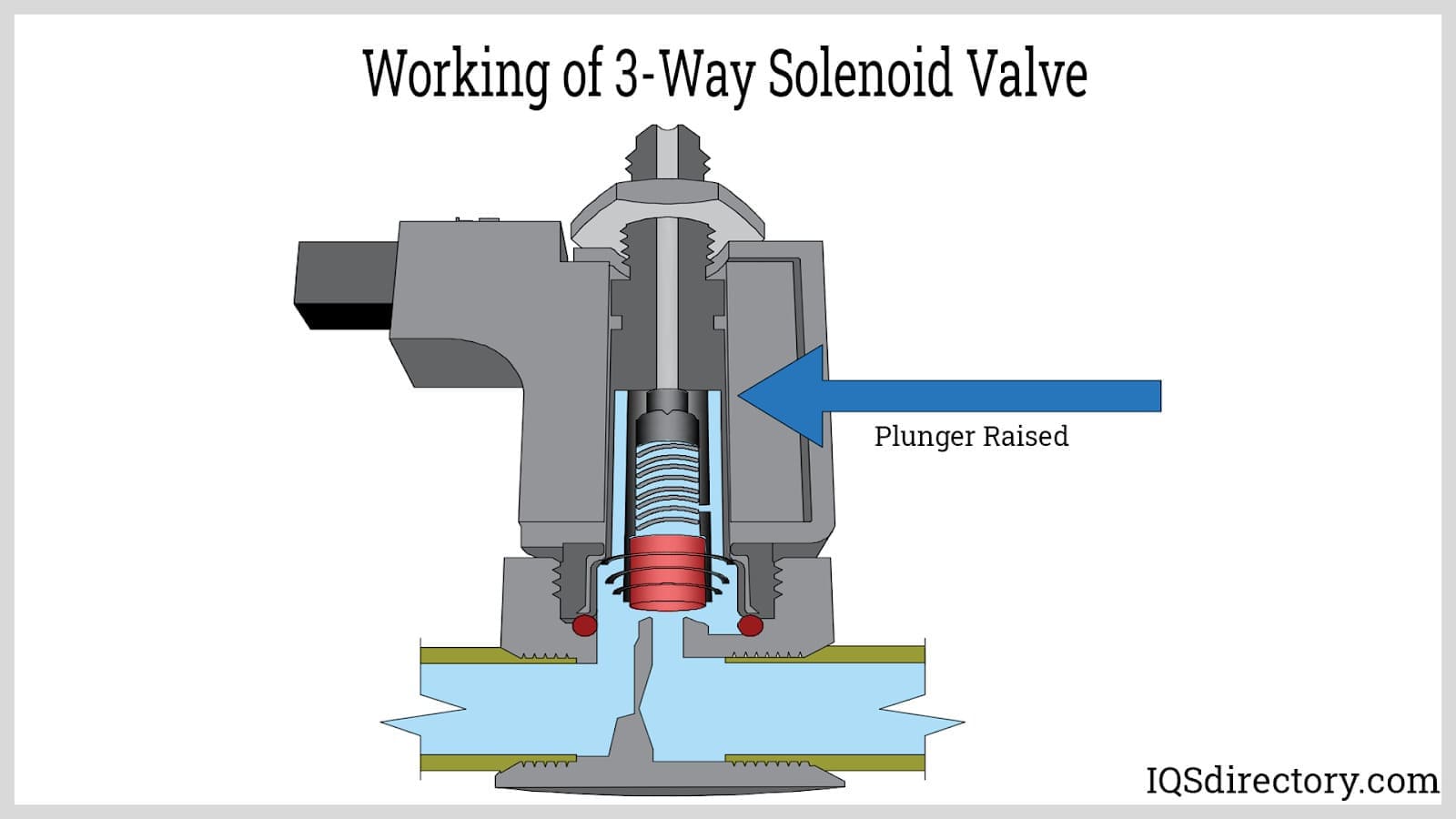
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Oil and Gas
The oil and gas industry relies on control solenoids for the safe and reliable management of gas and liquid flow. These solenoids are essential in environments that pose significant hazards, enhancing operational safety. B2B buyers in this sector should focus on sourcing solenoids made from corrosion-resistant materials and ensure that they have the necessary certifications for use in explosive atmospheres, as required by regional regulations.
Medical Equipment
In medical equipment, control solenoids are crucial components in devices such as oxygen concentrators and dialysis machines, where they ensure reliable fluid switching essential for patient safety. Buyers should prioritize sourcing from suppliers with a proven track record in providing medical-grade components, ensuring that the solenoids meet rigorous safety and performance standards required in healthcare applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for control solenoid
Material Analysis for Control Solenoids
When selecting materials for control solenoids, international B2B buyers must consider the specific requirements of their applications, including temperature and pressure ratings, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with the media being controlled. Below, we analyze four common materials used in the construction of solenoids, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations relevant to buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
1. Stainless Steel (316L)
Key Properties: Stainless steel 316L is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, particularly in saline and acidic environments. It can withstand high temperatures (up to 800°F or 427°C) and high pressures, making it suitable for demanding applications.
Pros & Cons: The durability of 316L stainless steel ensures a long lifespan and reduced maintenance costs. However, it is more expensive than other materials, which may impact budget constraints. The manufacturing complexity is moderate, requiring specialized tooling and processes.
Impact on Application: This material is ideal for applications involving corrosive fluids, such as in petrochemical or marine environments. Its robustness allows for reliable operation under challenging conditions.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM A240 for stainless steel. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding corrosion resistance can aid in selecting the right material.
2. Brass
Key Properties: Brass offers good corrosion resistance and can operate effectively at moderate temperatures (up to 350°F or 177°C). It has a decent pressure rating, making it suitable for various fluid control applications.
Pros & Cons: Brass is relatively cost-effective and easy to machine, which can lower manufacturing costs. However, it may not perform well in highly corrosive environments or with certain chemicals, limiting its use in specific applications.
Impact on Application: Commonly used in water and gas applications, brass solenoids are effective for general-purpose use. However, they may not be suitable for aggressive media, which could lead to premature failure.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with standards such as ASTM B36 for brass materials. Understanding the chemical compatibility of brass with the intended media is crucial to avoid failures.
3. Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and offers good resistance to corrosion, particularly when anodized. It can handle moderate temperatures (up to 300°F or 149°C) and is suitable for low to medium-pressure applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its lightweight nature, which can reduce shipping costs and ease installation. However, it has lower strength compared to stainless steel and brass, which may limit its use in high-stress applications.
Impact on Application: Aluminum solenoids are often used in HVAC systems and pneumatic applications. They are not recommended for high-pressure or corrosive environments, as they may degrade over time.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should verify that aluminum components meet regional standards, such as DIN 17615. Additionally, understanding the environmental conditions where the solenoid will operate is essential for longevity.
4. Plastic (Polyamide or Nylon)
Key Properties: Plastic materials like polyamide (Nylon) offer excellent chemical resistance and can operate at moderate temperatures (up to 185°F or 85°C). They are lightweight and provide good insulation properties.
Pros & Cons: The low cost and ease of manufacturing make plastic solenoids an attractive option for many applications. However, their mechanical strength is lower than metals, and they may not withstand high temperatures or pressures.
Impact on Application: Plastic solenoids are suitable for applications involving water and non-aggressive chemicals. They are ideal for lightweight, low-cost solutions but may not be appropriate for high-demand environments.
Considerations for Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ISO 9001 is important for quality assurance. Buyers should also consider the specific chemical compatibility of the plastic with the media being controlled.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for Control Solenoid | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel 316L | Petrochemical, marine environments | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Brass | Water and gas applications | Cost-effective, easy to machine | Poor performance in corrosive media | Med |
| Aluminum | HVAC systems, pneumatic applications | Lightweight, reduces shipping costs | Lower strength, not for high-stress | Low |
| Plastic (Nylon) | Water and non-aggressive chemicals | Low cost, good insulation | Limited mechanical strength | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with the necessary insights to make informed decisions regarding control solenoids, ensuring compatibility with specific applications and compliance with regional standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for control solenoid
In the manufacturing of control solenoids, the processes involved are crucial for ensuring both performance and reliability. For B2B buyers from diverse regions—including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—understanding these processes and the accompanying quality assurance measures is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes
1. Material Preparation
The first stage of manufacturing control solenoids involves selecting and preparing high-quality raw materials. Common materials include:
- Copper: Used for the wire coils due to its excellent electrical conductivity.
- Steel or Aluminum: The valve body is often made from these materials for their strength and durability.
- Elastomers: Various types of rubber (e.g., Nitrile, Viton) are chosen for sealing components, depending on the fluid they will control.
Before manufacturing, materials undergo inspection to ensure they meet specified standards. This includes checking for purity, tensile strength, and compatibility with the intended application.
2. Forming
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This typically includes:
- Coiling: Copper wires are wound into coils, which generate a magnetic field when electrical current is applied. The number of turns and gauge of wire directly influence the solenoid’s performance.
- Machining: The valve body is machined to precise dimensions. This may involve CNC machining to achieve the necessary tolerances for proper fit and function.
The forming process must adhere to strict tolerances to ensure the solenoid operates effectively within its designed parameters.
3. Assembly
The assembly stage integrates all components into the final product. This includes:
- Coil Assembly: The wound copper coil is positioned within the solenoid body, along with the armature or plunger that will move to open or close the valve.
- Sealing: O-rings and other sealing elements are installed to prevent leaks. The choice of elastomer here is critical, as it must withstand the specific fluids and temperatures involved.
During assembly, it is essential to maintain a clean environment to avoid contamination that could affect performance.
4. Finishing
The final stage is finishing, which may involve:
- Surface Treatment: Applying coatings to protect against corrosion, especially for solenoids intended for harsh environments.
- Testing and Calibration: Each solenoid is tested to ensure it meets operational specifications. This includes checking the response time, leak testing, and functional tests under simulated operating conditions.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in the manufacturing of control solenoids is paramount, especially for international B2B buyers who require reliability and compliance with various standards.
International Standards
Manufacturers typically adhere to recognized international standards, which may include:
- ISO 9001: Focuses on quality management systems and continuous improvement.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: Relevant for solenoids used in oil and gas applications, ensuring they meet industry-specific requirements.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with specific checkpoints including:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Initial inspection of raw materials to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing checks during production to monitor process parameters and ensure consistency.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of the finished product, including functional tests and visual inspections.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods employed in the quality assurance of control solenoids may include:
- Electrical Testing: Verifies coil resistance and functionality.
- Pressure Testing: Checks for leaks under operational pressures.
- Temperature Cycling: Assesses performance across a range of temperatures.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers can take several steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of the manufacturing facility can provide insights into their processes, quality management systems, and adherence to standards.
- Quality Reports: Requesting detailed quality reports, including test results and compliance certifications, can help verify the reliability of the solenoids.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can add an extra layer of assurance, particularly for large orders or critical applications.
Regional Considerations
When sourcing control solenoids, B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must consider regional standards and conditions. For example, solenoids used in harsh environments may require additional protective features or specific certifications (such as ATEX for explosive atmospheres in Europe). Understanding local regulations and market needs can help buyers make better-informed decisions.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers, comprehending the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for control solenoids is essential for ensuring product reliability and compliance. By focusing on material selection, precise manufacturing techniques, and rigorous quality control, buyers can confidently procure solenoids that meet their operational demands and regional requirements. Engaging with suppliers who prioritize these aspects will further enhance supply chain reliability and performance.
Related Video: Factory IO – Production Line Project ( Programmed using Control IO and Tia Portal )
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for control solenoid Sourcing
When it comes to sourcing control solenoids, understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. The cost of control solenoids is influenced by various components and factors that can significantly affect the total expenditure.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in manufacturing control solenoids include metals (like stainless steel), plastics (such as PA66), and elastomers (like Nitrile or Viton). Material choice impacts both the performance and cost of the solenoid. For example, solenoids made with high-grade materials that offer better durability and resistance to harsh environments typically command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher wages, such as those in Europe, labor costs can be a substantial portion of the total price. Conversely, sourcing from regions with lower labor costs can help reduce overall expenses.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to factory operations, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes and economies of scale can reduce overhead costs, which may be reflected in the pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs for custom or specialized solenoids can be significant. Buyers should consider whether the investment in tooling will yield a favorable return, especially if high volumes are anticipated.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring that control solenoids meet required standards involves rigorous quality control processes. Costs associated with testing and certification can be substantial but are crucial for ensuring reliability and compliance, particularly in regulated industries.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs play a critical role in the overall cost structure. Factors such as shipping distance, method (air vs. sea), and any tariffs or duties can affect pricing. Buyers should consider logistics as a key component of the total cost of ownership (TCO).
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely based on market conditions, competition, and the exclusivity of the product. Understanding the typical margin within a specific market can help buyers gauge whether they are getting a fair price.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often lead to better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate minimum order quantities (MOQs) to secure more favorable pricing structures.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom solenoids tailored to specific applications may come at a premium. Clearly defining requirements upfront can help manage costs.
-
Materials: The choice of materials directly affects pricing. Buyers should balance the need for high-performance materials with budget constraints.
-
Quality/Certifications: Products with specific certifications (e.g., ISO, ATEX) usually come at a higher price. Buyers must assess the necessity of these certifications based on application requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and service level of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a strong track record may charge more but offer better support and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is vital for determining the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and logistics. Terms like FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the final landed cost of the solenoids.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate pricing and payment terms. Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better deals and discounts over time.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership, which includes acquisition, operational, and maintenance costs. This will provide a clearer picture of the investment value.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing variations due to local market conditions. Prices for solenoids may fluctuate based on geopolitical factors, currency exchange rates, and supply chain disruptions.
-
Supplier Assessment: Evaluate potential suppliers not only on price but also on quality, service, and reliability. A slightly higher upfront cost can lead to significant savings in downtime and maintenance.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends, material costs, and emerging technologies that could impact pricing and availability.
Disclaimer
The prices discussed in this analysis are indicative and can vary based on several factors including market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific project requirements. Always conduct due diligence and seek multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential control solenoid Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘control solenoid’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for control solenoid
Understanding the technical properties and terminology associated with control solenoids is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to make informed purchasing decisions. This section outlines essential specifications and common trade terms that can enhance procurement processes and facilitate effective communication with suppliers.
Key Technical Properties of Control Solenoids
-
Material Grade
– The material of a solenoid valve directly affects its durability and compatibility with various media. Common materials include stainless steel, brass, and various plastics. For example, stainless steel is preferred in corrosive environments, while brass is often used in general applications. Selecting the right material can prevent premature failure and reduce maintenance costs. -
Voltage Rating
– Control solenoids are available in different voltage ratings, typically 12V, 24V, or 110V. The voltage rating impacts the solenoid’s power consumption and suitability for specific applications. Ensuring the correct voltage matches the system’s electrical design is vital for optimal performance and reliability. -
Operating Pressure
– This specification defines the maximum pressure at which the solenoid can operate. Different applications—such as water systems versus pneumatic controls—may require solenoids with varying pressure ratings. Understanding the operating pressure ensures that the solenoid can handle the demands of the intended application without risk of failure. -
Response Time
– The response time of a solenoid valve is the time it takes to open or close after being energized. Quick response times are critical in applications requiring precise control, such as automated manufacturing or medical devices. Buyers should evaluate response times to ensure they meet the operational requirements of their systems. -
Flow Rate
– This specification indicates the volume of fluid that can pass through the solenoid valve per unit of time, usually measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM). Understanding the flow rate is essential for selecting a solenoid that meets the demands of the specific application, ensuring efficiency and performance. -
Duty Cycle
– The duty cycle refers to the ratio of time a solenoid can be energized versus the time it needs to cool down. Solenoids with a continuous duty cycle can remain energized for extended periods, while those with intermittent duty cycles require downtime to avoid overheating. Selecting a solenoid with the appropriate duty cycle is crucial for applications with varying operational demands.
Common Trade Terms in Solenoid Procurement
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
-
This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM specifications is essential for buyers looking to source compatible solenoids for their existing systems.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
-
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is vital for buyers to understand, as it affects purchasing decisions and inventory management. Knowing the MOQ helps in budgeting and planning for future needs.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
-
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers requesting pricing information for specific products or services. This process allows buyers to compare offers and negotiate terms. Crafting a clear RFQ can streamline the procurement process and ensure better pricing and service terms.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
-
Incoterms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Understanding Incoterms is crucial for buyers engaged in international trade, as they define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
-
Lead Time
- Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order until it is delivered. For B2B buyers, understanding lead times is essential for planning and ensuring that projects remain on schedule. It helps in aligning procurement with production timelines.
Familiarity with these technical properties and trade terminology not only aids in making informed decisions but also enhances communication with suppliers, ultimately leading to more efficient and successful procurement processes.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the control solenoid Sector
In the rapidly evolving control solenoid market, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape influenced by multiple factors. Global drivers such as the push for automation, advancements in smart technology, and the demand for efficient fluid control systems are redefining sourcing strategies. Emerging markets in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are witnessing significant growth in sectors like manufacturing, HVAC, and oil and gas, which rely heavily on solenoid valves for operational efficiency.
Current and emerging B2B tech trends include the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) capabilities into solenoid systems, enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This technological shift not only enhances reliability but also reduces downtime, which is critical for maintaining competitive advantage. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on modular designs, allowing for easier upgrades and repairs, which can be particularly beneficial for buyers in regions with limited access to specialized maintenance services.
Market dynamics also reflect a shift toward local sourcing to mitigate supply chain disruptions, particularly in the wake of recent global events. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who can offer flexible manufacturing capabilities and shorter lead times. As such, establishing strong relationships with local manufacturers or distributors can provide a strategic advantage, ensuring timely access to critical components while reducing transportation costs.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
The environmental impact of manufacturing processes for control solenoids is an area of increasing scrutiny. B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize ethical supply chains that minimize carbon footprints and waste. This includes sourcing from manufacturers that employ sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and renewable energy sources in production.
Moreover, certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems) and the use of green materials—like bio-based plastics or elastomers with lower environmental impacts—are becoming essential considerations for procurement professionals. Emphasizing sustainable practices not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances brand reputation and can lead to cost savings through improved efficiency and reduced regulatory risks.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of control solenoids has been marked by technological advancements that have broadened their applications and enhanced performance. Initially developed for basic on/off control, modern solenoids now incorporate sophisticated features such as proportional control and energy-efficient designs. This transformation has been fueled by the increasing complexity of industrial processes and the need for precise fluid control, particularly in sectors like food processing and pharmaceuticals. As a result, buyers today benefit from a wide array of options tailored to specific operational needs, reflecting the ongoing innovation within the industry.
By understanding these market dynamics, sourcing trends, and sustainability imperatives, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that not only meet their operational requirements but also contribute to a more sustainable future.
Related Video: Global Trade & Logistics – What is Global Trade?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of control solenoid
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers for control solenoids?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their industry experience, production capabilities, and quality certifications. Verify their adherence to international standards such as ISO 9001 and relevant local regulations. Request references from previous clients in your region to assess reliability and performance. Additionally, evaluate their customer service responsiveness and support for customization, which can be crucial for meeting specific operational needs. -
Can I customize control solenoids to fit my specific application?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for control solenoids, including changes in size, material, and operational features. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications about your application, including environmental conditions and compatibility with media. This helps the supplier to recommend the best design modifications. Always request prototypes or samples to validate the performance of customized products before full-scale production. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for control solenoids?
MOQs for control solenoids can vary significantly based on the supplier and product specifications. Typically, they range from 100 to 1,000 units. Lead times also depend on customization levels and supplier capacity, generally ranging from 4 to 12 weeks. To optimize your supply chain, discuss your requirements upfront and consider establishing long-term agreements for better pricing and reduced lead times. -
What quality assurance measures and certifications should I look for?
Seek suppliers that adhere to international quality assurance standards such as ISO 9001 for manufacturing processes. Certifications specific to your industry, like ATEX for hazardous environments or FDA compliance for food applications, are also essential. Request documentation that demonstrates testing protocols, including pressure tests and material certifications, to ensure the solenoids meet the required specifications for safety and performance. -
How should I manage logistics when importing control solenoids?
Managing logistics involves selecting a reliable freight forwarder experienced in international shipping regulations. Ensure that your supplier provides all necessary documentation, including customs declarations and certificates of origin. It’s essential to consider shipping costs, lead times, and potential tariffs. Establish clear communication with your logistics partner to track shipments and address any potential delays proactively. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
To resolve disputes, maintain clear and documented communication throughout the procurement process. If issues arise, first attempt direct negotiation with the supplier to find a mutually acceptable solution. If necessary, refer to the contractual terms regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration clauses. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can also facilitate smoother negotiations and conflict resolution. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing control solenoids internationally?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include a deposit (typically 30-50%) upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or after passing quality inspections. Using methods like letters of credit can provide security for both parties. Always clarify payment terms before placing orders and consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow needs while ensuring supplier confidence. -
How can I ensure the solenoids I receive are compliant with local regulations?
To ensure compliance with local regulations, engage suppliers who understand the specific requirements of your region, such as safety and environmental standards. Request relevant certifications and test reports for the solenoids. Additionally, consider consulting with local regulatory bodies or industry associations to verify compliance and avoid potential issues upon importation.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for control solenoid
In the complex landscape of control solenoid sourcing, strategic decision-making is paramount for B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By understanding the diverse types of solenoids, their applications, and the critical factors influencing performance and reliability, buyers can mitigate risks associated with procurement and enhance operational efficiency. Emphasizing the importance of material compatibility, response times, and environmental adaptability will empower businesses to make informed choices that align with their specific industry needs.
Moreover, leveraging a global supplier network fosters competitive pricing and access to cutting-edge technologies that can drive innovation within operations. As supply chain dynamics continue to evolve, maintaining agility and responsiveness in sourcing strategies is essential.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers are encouraged to prioritize partnerships with reputable suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to quality and compliance with regional standards. Embrace the opportunities presented by advancements in solenoid technology and the growing demand for automation. By doing so, companies can ensure not only the reliability of their fluid control systems but also their position at the forefront of industry advancements. Take the next step in your sourcing journey—invest in strategic partnerships that will pave the way for sustainable growth and operational excellence.