Master Fiberglass Fabrication: Your Ultimate B2B Sourcing
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for fiberglass fabrication
In today’s competitive global marketplace, fiberglass fabrication stands out as a crucial element across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, and marine. This versatile material is celebrated for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and adaptability, making it indispensable for B2B buyers seeking reliable solutions. As international demand for fiberglass products continues to grow, understanding the nuances of fabrication processes, material selection, and supplier networks becomes imperative for informed sourcing.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of fiberglass fabrication, offering insights into the types of fiberglass, materials used, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. It also highlights critical aspects of supplier selection, cost considerations, and market trends, providing a holistic view that empowers B2B buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including emerging markets like Thailand and Vietnam.
By leveraging the insights presented here, buyers can navigate the complexities of the fiberglass market with confidence. Whether you’re looking to optimize your supply chain, assess potential suppliers, or understand pricing dynamics, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to make strategic, informed decisions. Embrace the power of fiberglass fabrication as a cornerstone of innovation and efficiency in your business operations.
Understanding fiberglass fabrication Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Lay-Up | Manual application of resin and fiberglass layers. | Boat manufacturing, architectural features. | Pros: Low cost, flexibility in design. Cons: Labor-intensive, longer production times. |
| Spray-Up | Uses a spray gun to apply resin and chopped fibers. | Large composite parts, automotive components. | Pros: Faster production, good for large parts. Cons: Less control over fiber orientation. |
| Vacuum Infusion | Involves vacuum to draw resin into dry fibers. | Aerospace, high-performance marine applications. | Pros: Superior finish, reduced waste. Cons: Higher initial setup cost, requires skilled labor. |
| Filament Winding | Continuous fibers wound around a mandrel. | Pressure vessels, pipes, aerospace components. | Pros: Stronger structures, material efficiency. Cons: Limited shapes, higher equipment costs. |
| Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) | Involves injecting resin into a closed mold. | Automotive parts, wind turbine blades. | Pros: High precision, repeatability. Cons: Initial mold costs can be high, longer cycle times. |
Hand Lay-Up
Hand lay-up is one of the most traditional methods of fiberglass fabrication. This technique involves manually layering fiberglass cloth and applying resin, making it particularly suitable for complex shapes and custom designs. It is widely used in boat manufacturing and architectural applications due to its low material costs and flexibility. However, buyers should consider the labor-intensive nature of this process, which can lead to longer production times.
Spray-Up
The spray-up method utilizes a spray gun to apply a mixture of resin and chopped fiberglass. This technique is ideal for producing large composite parts quickly, making it popular in the automotive and marine industries. While it allows for rapid production, buyers should be aware that it can compromise control over fiber orientation, which may affect the final product’s strength.
Vacuum Infusion
Vacuum infusion is a sophisticated technique that employs a vacuum to draw resin into dry fiber layers. This method is especially favored in aerospace and high-performance marine applications due to its ability to produce high-quality finishes with minimal waste. Although it requires a higher initial investment in equipment and skilled labor, the benefits of reduced material waste and enhanced structural integrity make it a compelling option for B2B buyers focused on performance and sustainability.
Filament Winding
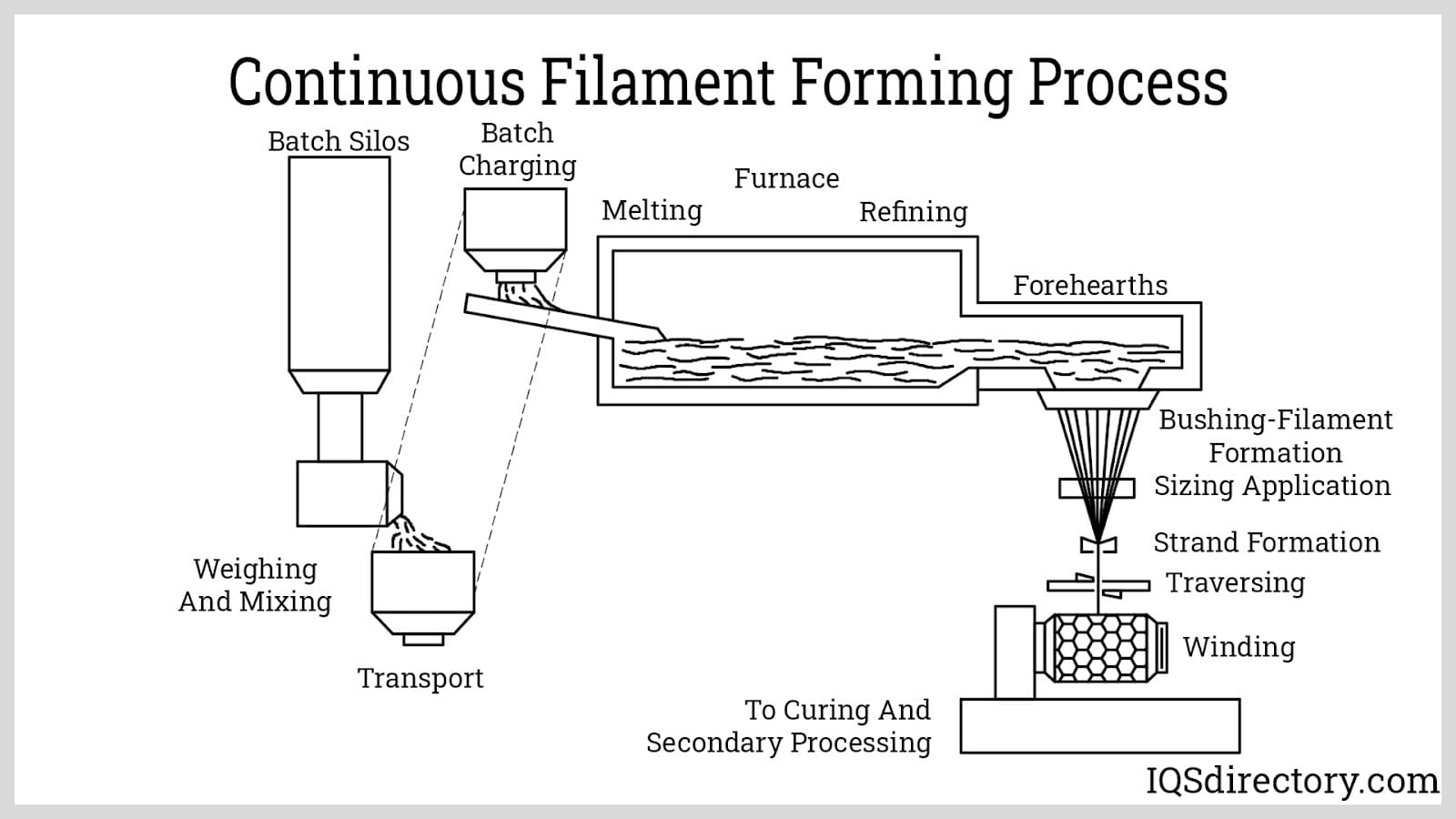
Filament winding involves winding continuous strands of fiberglass around a mandrel to create strong, lightweight structures. This method is commonly used in pressure vessels, pipes, and aerospace components, where strength-to-weight ratios are critical. While filament winding offers material efficiency and robust product characteristics, buyers should consider the higher equipment costs and limitations in geometric shapes.
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
RTM is a closed-mold process where resin is injected into a mold containing dry fibers. This method is known for its precision and repeatability, making it suitable for automotive parts and wind turbine blades. Despite its advantages, such as high-quality finishes and consistent production, the initial costs for molds can be significant, and the longer cycle times may impact production schedules. Buyers need to weigh these factors when considering RTM for their projects.
Related Video: The Basics of Fiberglass Fabric
Key Industrial Applications of fiberglass fabrication
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of fiberglass fabrication | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Lightweight aircraft components | Reduces fuel consumption and improves efficiency | Compliance with aerospace standards, sourcing from certified suppliers |
| Marine | Hulls and structural components of boats | Enhanced durability and resistance to corrosion | Quality assurance in material properties and environmental compliance |
| Construction | Insulated panels for buildings | Improved energy efficiency and thermal insulation | Local regulations on fire safety and insulation standards |
| Automotive | Body panels and interior components | Weight reduction leading to better fuel economy | Material compatibility and compliance with automotive industry standards |
| Oil and Gas | Storage tanks and piping systems | Corrosion resistance and lower maintenance costs | Supplier reliability and capability for large-scale production |
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, fiberglass fabrication is utilized to create lightweight aircraft components such as wing structures and fuselage parts. The primary benefit of using fiberglass is its strength-to-weight ratio, which helps reduce fuel consumption and enhances overall aircraft performance. International buyers must ensure that their suppliers meet stringent aerospace standards and certifications, as quality and reliability are paramount in this highly regulated industry.
Marine
Fiberglass fabrication plays a crucial role in the marine industry, particularly in constructing hulls and structural components of boats. This material is favored for its exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, which is vital for vessels operating in harsh marine environments. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that can guarantee high-quality materials and have proven experience in marine applications, as compliance with safety and performance standards is critical.
Construction
In the construction industry, fiberglass is commonly used for insulated panels that enhance energy efficiency in buildings. These panels provide excellent thermal insulation, helping to reduce energy costs and improve comfort for occupants. B2B buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding fire safety and insulation standards when sourcing fiberglass products, ensuring that their suppliers comply with these requirements to avoid legal and operational challenges.
Automotive
Fiberglass fabrication is increasingly being used in the automotive sector for body panels and interior components. The lightweight nature of fiberglass contributes to significant weight reduction, leading to improved fuel economy and performance. Buyers must consider material compatibility and ensure that suppliers adhere to automotive industry standards, as this will directly impact product performance and safety.
Oil and Gas
In the oil and gas industry, fiberglass is used for constructing storage tanks and piping systems due to its corrosion resistance and low maintenance requirements. This application is particularly valuable in environments where traditional materials may fail due to harsh conditions. International buyers should focus on supplier reliability and their capability to produce fiberglass products at scale, as consistent quality and timely delivery are essential for operational efficiency.
Related Video: Learn Fiberglass Fabrication Without Molds In 15 Minutes
Strategic Material Selection Guide for fiberglass fabrication
When selecting materials for fiberglass fabrication, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence the performance, cost, and suitability of the final product. Here, we analyze four common materials used in fiberglass fabrication: polyester resin, epoxy resin, vinyl ester resin, and glass fibers. Each material has distinct properties, advantages, and limitations that can significantly impact the choice for specific applications.
Polyester Resin
Key Properties:
Polyester resin is known for its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to UV light. It typically has a temperature rating of up to 80°C (176°F) and offers moderate corrosion resistance against water and some chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of polyester resin is its cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for large-scale projects. However, it has lower durability compared to epoxy resins and can be more susceptible to environmental stress cracking. The manufacturing complexity is relatively low, which aids in faster production cycles.
Impact on Application:
Polyester resin is well-suited for applications in marine environments and automotive parts, where cost is a critical factor. However, it may not be suitable for high-performance applications requiring superior strength and chemical resistance.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with local regulations regarding emissions and waste disposal, as polyester resins can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Familiarity with standards such as ASTM D638 for tensile properties is essential.
Epoxy Resin
Key Properties:
Epoxy resin exhibits superior adhesion, chemical resistance, and a temperature rating of up to 120°C (248°F). It is also known for its excellent mechanical strength and durability.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of epoxy resin is its high performance in demanding applications, including aerospace and automotive industries. However, it is typically more expensive than polyester resin and requires more complex manufacturing processes, which can increase lead times.
Impact on Application:
Epoxy resin is ideal for applications requiring high strength and resistance to harsh chemicals, such as in industrial tanks and pipelines. Its compatibility with a wide range of media makes it versatile for various sectors.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific curing agents and hardeners used, as these can affect performance and compliance with international standards. Understanding local regulations regarding chemical handling is also crucial.
Vinyl Ester Resin
Key Properties:
Vinyl ester resin combines the advantages of both polyester and epoxy resins, offering excellent corrosion resistance and a temperature rating of up to 100°C (212°F). It is particularly effective against aggressive chemicals.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of vinyl ester resin is its superior resistance to corrosion and stress cracking, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is generally more expensive than polyester resin and can be more challenging to process.
Impact on Application:
This resin is often used in chemical processing industries and marine applications where exposure to corrosive substances is a concern. Its durability makes it a preferred choice for long-term applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers must ensure that the selected vinyl ester resin meets specific industry standards, such as DIN 16945 for chemical resistance. Knowledge of local environmental regulations regarding resin disposal is also important.
Glass Fibers
Key Properties:
Glass fibers are integral to fiberglass fabrication, providing reinforcement and enhancing the mechanical properties of the composite material. They are lightweight, have high tensile strength, and can withstand temperatures up to 200°C (392°F).
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of glass fibers is their ability to significantly improve the strength-to-weight ratio of fiberglass products. However, they can be brittle and may not perform well under high-impact conditions.
Impact on Application:
Glass fibers are widely used in construction, automotive, and aerospace applications where weight reduction without compromising strength is critical. Their compatibility with various resins makes them versatile.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should consider the type of glass fiber (E-glass or S-glass) based on the application requirements. Compliance with standards such as ASTM D578 for glass fiber reinforcement is essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for fiberglass fabrication | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester Resin | Marine parts, automotive components | Cost-effective | Lower durability | Low |
| Epoxy Resin | Aerospace, industrial tanks | High performance and durability | Higher cost and complexity | High |
| Vinyl Ester Resin | Chemical processing, marine applications | Excellent corrosion resistance | More expensive and challenging to process | Medium |
| Glass Fibers | Construction, automotive, aerospace | Improves strength-to-weight ratio | Brittle and impact-sensitive | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials commonly used in fiberglass fabrication, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for fiberglass fabrication
Manufacturing Processes for Fiberglass Fabrication
Fiberglass fabrication is a multi-stage process that involves the transformation of raw materials into high-quality fiberglass products. Understanding these stages is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those from regions with varying industrial standards and practices. Below is an overview of the typical manufacturing processes involved in fiberglass fabrication.
1. Material Preparation
The first stage in fiberglass fabrication is the preparation of materials, which primarily consists of fiberglass reinforcements (glass fibers) and resin systems.
- Key Techniques:
- Glass Fiber Selection: Different types of glass fibers (e.g., E-glass, S-glass) are chosen based on required properties like strength, flexibility, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Resin Formulation: The resin (usually polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy) is selected based on the desired application and performance characteristics. Proper mixing and handling are critical to ensure optimal curing and bonding.
2. Forming
In the forming stage, the prepared materials are shaped into the desired forms. This can be achieved through various techniques, each with its own advantages.
- Key Techniques:
- Hand Lay-up: A manual process where layers of resin and fiberglass mat are laid into a mold. This method is cost-effective for small production runs.
- Spray-Up: Involves spraying a mixture of resin and chopped fiberglass onto a mold, allowing for quicker production times.
- Filament Winding: Continuous strands of fiberglass are wound around a rotating mandrel, ideal for producing cylindrical parts like pipes and tanks.
- Compression Molding: Pre-measured amounts of resin and fiberglass are placed into a heated mold, then compressed to form the final shape. This method is effective for high-volume production.
3. Assembly
After forming, the individual components may need to be assembled into a final product. This stage often requires additional bonding techniques.
- Key Techniques:
- Adhesive Bonding: Specialized adhesives may be used to join parts, ensuring strength and durability.
- Mechanical Fastening: Bolts, screws, and other hardware can be employed to secure components together, particularly in structural applications.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage enhances the aesthetic and functional aspects of the fiberglass products.
- Key Techniques:
- Trimming and Grinding: Excess material is removed to achieve the desired shape and smoothness.
- Surface Coating: Protective coatings, paints, or gel coats are applied to improve weather resistance and appearance.
- Quality Inspection: Final checks are essential to ensure compliance with specifications and standards.
Quality Assurance in Fiberglass Fabrication
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component of fiberglass fabrication, ensuring that products meet both international standards and specific client requirements.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be familiar with several key international standards that govern quality in fiberglass manufacturing:
- ISO 9001: A widely recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS) that outlines best practices for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates that products conform to health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
- API Standards: For fiberglass products used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) specifications is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Effective quality control (QC) involves multiple checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Assessing raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify any issues promptly.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A thorough inspection of the finished products to ensure they meet all specifications and standards.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods can be employed to verify the quality of fiberglass products:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluates strength, flexibility, and durability through tensile, compression, and shear tests.
- Thermal Testing: Assesses how materials respond to heat exposure, important for applications in extreme environments.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: Determines how well fiberglass products withstand exposure to various chemicals.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
International B2B buyers must ensure that their suppliers maintain rigorous quality control standards. Here are actionable steps to verify supplier QC:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can help assess their compliance with quality standards and processes. Consider both on-site visits and virtual audits.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide detailed QC reports, including test results and certifications. This documentation should reflect compliance with relevant international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent third-party inspectors to conduct assessments of the manufacturing processes and final products. This adds an extra layer of verification.
-
Quality Certifications: Ensure suppliers hold relevant certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, CE) as evidence of their commitment to quality.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of the following nuances when it comes to quality assurance and certification:
- Regional Standards Variation: Different regions may have varying standards and regulations. Understanding local requirements can prevent compliance issues.
- Cultural Differences in Quality Expectations: Quality perceptions may vary by region, so it is crucial to establish clear expectations with suppliers from the outset.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Buyers should seek suppliers who are transparent about their manufacturing processes and quality control measures, as this can lead to better collaboration and trust.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices involved in fiberglass fabrication, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers who meet their quality expectations and regulatory requirements.
Related Video: Fiberglass Manufacturing How Fiberglass Is Made
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for fiberglass fabrication Sourcing
The cost structure of fiberglass fabrication is multifaceted, encompassing various components that significantly influence pricing. Understanding these elements is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Cost Components in Fiberglass Fabrication
-
Materials: The primary material in fiberglass fabrication is glass fiber, which varies in cost based on type (E-glass, S-glass) and quality. Additives, resins, and coatings also contribute significantly to the material cost. Buyers should consider sourcing materials locally to mitigate import tariffs and shipping costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate depending on the region and skill level required. In regions like Southeast Asia, labor may be less expensive, impacting overall pricing. However, skilled labor is essential for quality assurance, particularly in custom fabrication.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facilities, utilities, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, allowing suppliers to offer competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be substantial, particularly for custom designs. These costs are often amortized over the production run, meaning larger orders can yield lower per-unit costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Investing in robust QC processes ensures product reliability and compliance with international standards. While this increases upfront costs, it can lead to long-term savings by reducing defects and returns.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs, customs duties, and insurance are critical factors in the total cost of fiberglass products. Buyers should negotiate Incoterms that align with their logistical capabilities to avoid unexpected expenses.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Margin: Suppliers will typically add a margin to cover their business risks and profit expectations. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge the fairness of pricing.
Price Influencers
Several factors influence the pricing of fiberglass products:
-
Volume/MOQ: Higher order volumes generally lead to lower prices per unit due to economies of scale. Establishing minimum order quantities (MOQ) can be advantageous for both suppliers and buyers.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom designs or specific performance requirements can significantly increase costs. Buyers should clearly define their specifications to avoid unnecessary modifications during production.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, ASTM) come at a premium but are essential for applications requiring durability and safety. Buyers should weigh the benefits of certified products against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: A supplier’s reputation, reliability, and experience can affect pricing. Established suppliers may command higher prices due to their proven track record.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms can impact logistics costs and risk exposure. Buyers should select terms that align with their shipping capabilities and cost management strategies.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Effective negotiation can yield better pricing and terms. Buyers should be prepared to discuss their purchasing strategy, including potential for volume increases.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Focus on total cost of ownership rather than just initial pricing. Consider long-term savings from quality products that require less maintenance and fewer replacements.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences, especially when sourcing from different continents. Economic conditions, local labor costs, and material availability can lead to significant price variations.
-
Build Relationships: Establishing long-term relationships with suppliers can lead to better pricing and terms as suppliers may offer discounts for repeat business or loyalty.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and pricing fluctuations. Utilizing resources like industry reports can provide valuable insights into cost structures and pricing strategies.
Disclaimer
Pricing for fiberglass fabrication can vary widely based on numerous factors. The information provided here is indicative and should not be considered as fixed pricing. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and obtain multiple quotes before making purchasing decisions.
Spotlight on Potential fiberglass fabrication Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘fiberglass fabrication’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for fiberglass fabrication
Key Technical Properties of Fiberglass Fabrication
Understanding the technical specifications of fiberglass materials is crucial for international B2B buyers to ensure quality and compliance with project requirements. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Material Grade:
– Fiberglass comes in various grades, such as E-glass and S-glass. E-glass is commonly used for general applications due to its excellent electrical insulation properties, while S-glass offers higher strength and thermal resistance. Choosing the right grade affects durability and performance, which can impact overall project success. -
Tensile Strength:
– This property measures the maximum stress a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing. High tensile strength is crucial for applications that experience significant stress, such as in automotive or aerospace components. For B2B buyers, understanding tensile strength helps in selecting the right fiberglass for specific applications, ensuring safety and reliability. -
Flexural Modulus:
– The flexural modulus indicates a material’s ability to resist deformation under load. It is essential for structural applications where rigidity is required. A higher flexural modulus means the material will maintain its shape better under stress, which is vital for long-lasting products. -
Thermal Conductivity:
– Fiberglass has low thermal conductivity, making it an excellent insulator. This property is particularly important for applications requiring temperature control, such as in piping or storage tanks. Buyers should consider thermal conductivity to ensure energy efficiency and compliance with industry standards. -
Moisture Absorption:
– The ability of fiberglass to resist moisture is critical, especially in humid environments. High moisture absorption can lead to material degradation, impacting performance. Understanding this property helps buyers choose the right fiberglass for specific environmental conditions. -
Tolerance Levels:
– Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In fiberglass fabrication, tight tolerances are often required for components that must fit precisely. Understanding tolerance levels is essential for buyers to ensure compatibility and functionality in assembled products.
Common Trade Terminology in Fiberglass Fabrication
Familiarity with industry jargon can streamline communication and enhance negotiation processes. Here are several key terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer):
– An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. For buyers, understanding OEM relationships can help ensure that they are sourcing high-quality components that meet their specifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity):
– This term indicates the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is vital for buyers to assess whether they can meet procurement needs without incurring excess costs or inventory. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation):
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It is a critical step in the procurement process, enabling buyers to compare costs and negotiate better deals. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms):
– These are a series of international sales terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Understanding Incoterms is essential for navigating shipping costs, risk, and delivery obligations. -
Lead Time:
– This term refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Awareness of lead times helps buyers plan their projects effectively and manage inventory levels. -
Certification:
– Certification refers to the formal verification that a product meets specific standards or regulations. For buyers, ensuring that fiberglass products are certified can provide confidence in their quality and compliance, reducing risk in procurement.
By grasping these technical properties and terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize sourcing strategies, and enhance collaboration with suppliers in the fiberglass fabrication industry.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the fiberglass fabrication Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The fiberglass fabrication market is experiencing a transformative phase, driven by several global factors. Increasing demand for lightweight, durable materials in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and renewable energy is propelling growth. Emerging economies in Africa and South America are witnessing a surge in infrastructure projects, which further fuels the need for fiberglass products. Additionally, advancements in manufacturing technologies, such as automated processes and digitalization, are enhancing efficiency and reducing costs for B2B buyers.
International buyers are increasingly focusing on sourcing strategies that leverage digital procurement tools and data analytics. These technologies allow for better spend analysis, supplier collaboration, and real-time monitoring of market dynamics. Notably, the rise of e-commerce platforms is reshaping supplier-buyer interactions, facilitating access to a wider range of suppliers and products, particularly in regions like the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
Moreover, sustainability is becoming a central theme in sourcing decisions. Buyers are encouraged to consider not only cost but also the environmental footprint of materials. This shift is reflected in the growing preference for suppliers who demonstrate eco-friendly practices and certifications. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics will be crucial for international buyers seeking competitive advantages.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability in fiberglass fabrication is gaining traction as environmental concerns become paramount. The production of fiberglass can have significant environmental impacts, including energy consumption and waste generation. Therefore, international buyers must prioritize suppliers who adopt sustainable practices and materials.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are increasingly held accountable for the social and environmental implications of their supply chains. Ensuring that suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and environmental regulations can enhance brand reputation and customer trust.
Buyers should also look for certifications that signify a commitment to sustainability, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) for sustainable building practices. Additionally, utilizing recycled fiberglass or bio-based resin materials can further minimize environmental impacts and align with global sustainability goals.
Incorporating these principles into sourcing strategies not only supports corporate responsibility but also meets the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Brief Evolution/History
The fiberglass fabrication sector has undergone significant evolution since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially developed for its lightweight and durable properties, fiberglass quickly found applications in various industries, from marine to automotive. Over the decades, technological advancements have refined production processes, enhancing material properties and reducing costs.
The introduction of resin infusion and filament winding techniques has improved production efficiency and product performance. In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainability and innovation, with a growing emphasis on recycling and the use of bio-based materials. This evolution reflects broader industry trends, positioning fiberglass as a versatile and sustainable choice for future applications in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
By understanding these historical trends and their implications, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with both current market demands and future sustainability goals.
Related Video: The Inside Story of the Ship That Broke Global Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of fiberglass fabrication
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers for fiberglass fabrication?
When vetting suppliers for fiberglass fabrication, focus on their experience, certifications, and previous projects. Evaluate their production capacity and technology capabilities. Request references from past clients and assess their financial stability. Check if they comply with international quality standards such as ISO 9001. Additionally, consider their ability to provide customized solutions that meet your specific requirements, as this can greatly impact project success. -
Can I customize fiberglass products to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many fiberglass fabrication suppliers offer customization options. You can specify dimensions, shapes, colors, and performance characteristics tailored to your project needs. Ensure you communicate your requirements clearly and ask for prototypes or samples to assess the quality before full-scale production. Discuss any additional costs associated with customization and confirm the supplier’s capability to deliver within your timeline. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for fiberglass fabrication?
Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can vary significantly by supplier and project type. Commonly, suppliers may set MOQs ranging from a few hundred to several thousand units. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity and scale of the order. Always clarify these terms upfront and consider negotiating MOQs if you require smaller quantities, especially for initial projects or testing phases. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing fiberglass fabrication?
Payment terms can vary widely among suppliers. Standard practices include a deposit (often 30-50%) upfront with the balance due upon completion or delivery. Some suppliers may offer payment upon receipt or extended terms for established relationships. It’s crucial to discuss payment methods, such as letters of credit or wire transfers, and ensure transparency to avoid misunderstandings. -
How can I ensure quality assurance (QA) and certifications for fiberglass products?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of the supplier’s QA processes and certifications. Look for suppliers with ISO certifications or those adhering to ASTM standards for fiberglass products. Ask for test results or reports from third-party labs if necessary. Regular audits and inspections during production can also help maintain quality, so consider including these in your contract. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing fiberglass products?
Logistics can be complex when importing fiberglass products, particularly regarding shipping methods, customs clearance, and delivery timelines. Ensure your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation for customs. Discuss packaging to prevent damage during transit and consider working with a freight forwarder to streamline the process. Be aware of import duties and taxes applicable in your country. -
How should I handle disputes or issues with a fiberglass supplier?
To handle disputes effectively, first, ensure clear communication with your supplier to resolve issues amicably. Document all correspondence and agreements to support your case if necessary. If the issue persists, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Building a good relationship with your supplier can also help prevent conflicts from escalating. -
What are the common applications for fiberglass products in various industries?
Fiberglass products are versatile and used across multiple industries, including construction, automotive, marine, and aerospace. Common applications include tanks, pipes, insulation, and structural components. Understanding these applications can help you identify potential suppliers with relevant expertise and products. When sourcing, consider how the specific properties of fiberglass, such as strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, align with your project requirements.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for fiberglass fabrication
In summary, effective strategic sourcing in fiberglass fabrication is essential for international B2B buyers aiming to optimize costs and enhance supply chain resilience. By leveraging diagnostic tools, should-cost modeling, and fostering collaborative relationships with suppliers, businesses can unlock significant savings while ensuring quality and sustainability in their procurement processes. Understanding market dynamics and raw material volatility are crucial for making informed decisions that can mitigate risks associated with price fluctuations.
As the global demand for fiberglass products continues to grow, particularly in sectors such as construction, automotive, and aerospace, buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must prioritize strategic sourcing practices. This not only enhances competitiveness but also positions companies to capitalize on emerging opportunities in new markets.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Looking ahead, the integration of digital procurement technologies will further streamline sourcing processes, making it imperative for buyers to stay abreast of these advancements. Engage with reliable suppliers, invest in data analytics, and embrace innovative strategies to ensure your business remains agile and responsive to market changes. The future of fiberglass fabrication sourcing is bright—take the proactive steps now to secure your position in this dynamic landscape.