Master Hydraulic Control Valve Types for Optimal B2B
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic control valve types
In today’s competitive global marketplace, understanding the various types of hydraulic control valves is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations. These valves are integral components in hydraulic systems, regulating fluid flow and pressure to ensure efficient machinery performance. For B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, selecting the right hydraulic control valve can significantly impact operational efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
This comprehensive guide delves into the diverse types of hydraulic control valves, including their materials, manufacturing processes, and quality control standards. It also provides insights into reputable suppliers, cost considerations, and market trends, making it an essential resource for informed sourcing decisions. Whether you are looking for pressure relief valves, flow control valves, or specialized options like electric control valves, this guide equips you with the knowledge needed to navigate the complexities of the hydraulic valve market.
Moreover, we address frequently asked questions to clarify common uncertainties and enhance your purchasing strategy. By leveraging the insights provided, international B2B buyers can make data-driven decisions, ensuring they choose the most suitable hydraulic control valves to meet their specific operational needs while fostering long-term partnerships with reliable suppliers. Empower your business with this essential knowledge and stay ahead in the dynamic hydraulic market.
Understanding hydraulic control valve types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Control Valve | Stabilizes outlet pressure regardless of inlet fluctuations. | Hydraulic systems in manufacturing and construction. | Pros: Ensures consistent pressure; Cons: Requires regular maintenance for accuracy. |
| Flow Control Valve | Maintains constant flow rate despite pressure changes. | Industrial piping systems, water treatment. | Pros: Precise flow management; Cons: Can be complex to install and adjust. |
| Directional Control Valve | Directs fluid flow in specific directions, often electrically controlled. | Robotics, automotive, and mobile machinery. | Pros: Enhances automation; Cons: Higher initial costs and complexity. |
| Check Valve | Allows flow in one direction while preventing backflow. | Pumps, compressors, and pipeline systems. | Pros: Protects equipment from damage; Cons: Limited control over flow rate. |
| Emergency Shut-off Valve | Automatically cuts off flow in emergencies to prevent accidents. | Safety systems in industrial settings. | Pros: Enhances safety; Cons: May require frequent testing to ensure reliability. |
Pressure Control Valve
Pressure control valves are essential for maintaining a stable outlet pressure, even when the inlet pressure varies. These valves are commonly used in hydraulic systems within manufacturing and construction sectors. When purchasing, buyers should consider the valve’s pressure rating, compatibility with existing systems, and the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Flow Control Valve
Flow control valves automatically adjust to maintain a consistent flow rate, regardless of pressure changes. They are vital in industrial piping systems and water treatment facilities, where precise flow management is critical. B2B buyers should evaluate the complexity of installation, the required adjustments, and the long-term operational costs associated with these valves.
Directional Control Valve
Directional control valves manage the flow of hydraulic fluid in specific directions and can often be operated electronically. This feature makes them ideal for applications in robotics, automotive systems, and mobile machinery. Buyers should assess the initial investment, installation complexity, and the potential for enhanced automation when considering these valves.
Check Valve
Check valves are designed to allow fluid to flow in one direction while preventing backflow, making them crucial in protecting pumps and compressors from damage. They are widely used in various pipeline systems. Buyers must consider the valve’s material compatibility with the fluid, installation location, and the simplicity of maintenance when making their purchase.
Emergency Shut-off Valve
Emergency shut-off valves play a crucial role in safety systems by automatically stopping fluid flow during emergencies, thus preventing accidents. These valves are particularly important in industrial settings where hazardous materials are handled. When purchasing, buyers should prioritize reliability, ease of testing, and compliance with safety standards to ensure effective operation during critical situations.
Related Video: Hydraulic flow control valve operation, uses, and types
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic control valve types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic control valve types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Use in hydraulic excavators for precise movement control | Enhances operational efficiency and safety on site | Ensure compatibility with existing machinery; check for local support and service availability. |
| Agriculture | Control of irrigation systems to regulate water flow | Optimizes water usage, improving crop yield and sustainability | Consider valve durability against environmental conditions; assess local availability of parts for maintenance. |
| Manufacturing | Integration in automated assembly lines for fluid control | Increases production speed and reduces manual labor costs | Evaluate the technology’s adaptability to existing systems; prioritize suppliers with a strong warranty and support services. |
| Oil & Gas | Pressure control in drilling operations | Ensures safety and efficiency in high-pressure environments | Look for certifications and compliance with international safety standards; assess supplier’s experience in the sector. |
| Mining | Use in hydraulic systems for ore extraction machinery | Improves operational reliability and reduces downtime | Focus on sourcing valves that withstand harsh conditions; ensure suppliers can deliver on time to avoid project delays. |
In the construction sector, hydraulic control valves are integral to the operation of machinery like excavators. They facilitate precise movement control, allowing for efficient digging and lifting operations. This precision enhances safety and operational efficiency, which is crucial in high-stakes construction environments. Buyers should ensure that valves are compatible with existing machinery and consider the availability of local support and service to mitigate downtime.
In agriculture, hydraulic control valves regulate water flow in irrigation systems, ensuring optimal water usage. This not only conserves water but also enhances crop yields and promotes sustainability. Buyers should evaluate the valve’s durability against environmental conditions, such as soil corrosiveness and temperature fluctuations. Additionally, access to local parts for maintenance is vital to maintain system efficiency.
The manufacturing industry benefits from hydraulic control valves in automated assembly lines, where they manage fluid control for various processes. This integration speeds up production and reduces reliance on manual labor, ultimately lowering operational costs. Buyers need to assess how adaptable the valve technology is to their existing systems and prioritize suppliers that offer robust warranties and support services to ensure ongoing operational efficiency.
In the oil and gas industry, hydraulic control valves are essential for managing pressure in drilling operations. They ensure safety and efficiency in high-pressure environments, which is critical for preventing accidents and equipment failures. Buyers should look for suppliers that offer valves certified for compliance with international safety standards and have a proven track record in the sector, as this can significantly impact operational success.
Finally, in mining, hydraulic control valves are used in machinery for ore extraction, where they enhance operational reliability and reduce downtime. This is essential in a sector where efficiency directly translates to profitability. Buyers should focus on sourcing valves that can withstand harsh mining conditions and ensure that suppliers have a reliable delivery schedule to avoid project delays and associated costs.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic control valve types
When selecting materials for hydraulic control valves, international B2B buyers must consider the specific properties, advantages, and limitations of each material. The choice of material not only affects the performance and durability of the valve but also its compatibility with various operating environments and media. Here, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic control valves: Cast Iron, Stainless Steel, Brass, and Plastic.
Cast Iron
Key Properties: Cast iron is known for its excellent compressive strength and good wear resistance. It typically operates well under moderate temperature and pressure conditions, making it suitable for various hydraulic applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of cast iron is its durability and cost-effectiveness. However, it is relatively heavy and can be prone to corrosion if not properly coated or maintained. Its manufacturing process is straightforward, which keeps costs low, but it may not be suitable for high-pressure applications.
Impact on Application: Cast iron valves are often used in water and wastewater applications due to their ability to handle moderate pressures. However, they may not be ideal for corrosive environments without protective coatings.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN for cast iron materials, especially in industries like mining or agriculture where durability is critical.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers high corrosion resistance, strength, and the ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. It is often used in applications requiring sanitary conditions.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its longevity and resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for harsh environments. However, it is more expensive than cast iron and can be more complex to manufacture, which may increase lead times.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel valves are ideal for chemical processing, food and beverage, and pharmaceutical industries where cleanliness and durability are paramount. They are compatible with a wide range of fluids, including aggressive chemicals.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East should prioritize compliance with standards such as JIS and ASTM, particularly in sectors that demand high hygiene standards.
Brass
Key Properties: Brass is a copper-zinc alloy known for its good machinability and moderate corrosion resistance. It can handle moderate pressures and is typically used in low to medium temperature applications.
Pros & Cons: The advantages of brass include its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion, particularly in water applications. However, brass can be more expensive than cast iron and may not perform well in high-pressure environments.
Impact on Application: Brass valves are commonly used in plumbing, HVAC, and low-pressure hydraulic systems. They are particularly effective in applications involving water and air.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like South America should be aware of the potential for lead content in brass alloys, necessitating compliance with health regulations and standards to ensure safety.
Plastic
Key Properties: Plastic materials, such as PVC or polypropylene, are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and suitable for low-pressure applications. They can handle a range of temperatures depending on the specific type of plastic used.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of plastic valves is their resistance to corrosion and chemical attack, making them ideal for aggressive media. However, they are generally not suitable for high-pressure applications and can be less durable than metal options.
Impact on Application: Plastic valves are commonly used in chemical processing and irrigation systems where weight and resistance to corrosion are critical. They are suitable for non-pressurized systems or low-pressure applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Africa and the Middle East should consider the environmental impact of plastic materials and ensure compliance with local regulations regarding plastic use in industrial applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic control valve types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron | Water and wastewater applications | Durable and cost-effective | Heavy and prone to corrosion | Low |
| Stainless Steel | Chemical processing and food industries | High corrosion resistance and durability | More expensive and complex to manufacture | High |
| Brass | Plumbing and HVAC systems | Excellent thermal conductivity | Not suitable for high pressure | Med |
| Plastic | Chemical processing and irrigation systems | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Limited high-pressure applications | Low |
This strategic material selection guide provides B2B buyers with critical insights into the properties and applications of various materials used in hydraulic control valves. By understanding these factors, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic control valve types
The manufacturing processes for hydraulic control valves are critical to ensuring their functionality, reliability, and longevity. Understanding these processes can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing these components from international suppliers.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing of hydraulic control valves involves selecting the appropriate materials. Common materials include cast iron, stainless steel, and brass, chosen for their durability and resistance to corrosion and wear.
- Material Selection: Ensure that the material meets the specific requirements for pressure, temperature, and environmental conditions.
- Material Testing: Conduct tests such as tensile strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance to verify material integrity.
Forming
Once the materials are prepared, they undergo various forming processes to shape them into valve components.
- Casting: This is a prevalent method for creating complex shapes. For example, cast iron is often used for body components due to its strength and ability to absorb vibrations.
- Machining: After casting, components are machined to precise dimensions. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are commonly used for accuracy.
- Forging: For high-pressure applications, forging may be used to produce stronger components. This process aligns the grain structure of the metal, enhancing its strength.
Assembly
The assembly stage combines the various components into a complete hydraulic control valve.
- Sub-assembly: Individual components like the valve body, seat, and actuator are first assembled separately.
- Final Assembly: The sub-assemblies are then combined. This stage often includes the installation of seals and gaskets to prevent leaks.
- Calibration: After assembly, the valves are calibrated to ensure they function correctly under specified conditions.
Finishing
Finishing processes enhance the surface properties and prepare the valves for service.
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as electroplating, powder coating, or painting may be used to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal.
- Testing: Each valve undergoes a series of tests, including pressure testing, to ensure it meets operational specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) is an integral part of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every valve meets international standards and customer specifications.
International Standards
For B2B buyers, understanding the relevant international and industry-specific quality standards is essential.
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines a framework for quality management systems, ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, this marking indicates compliance with safety and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: The American Petroleum Institute (API) provides specifications for valves used in the oil and gas industry, focusing on safety and performance.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are established at various stages of the manufacturing process.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspects raw materials upon arrival to verify they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Conducted during the manufacturing process to identify and rectify defects early. This includes monitoring machining tolerances and assembly accuracy.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection phase, where completed valves undergo comprehensive testing for functionality, pressure, and leak testing.
Common Testing Methods
Testing is crucial to ensure that hydraulic control valves operate safely and effectively. Common testing methods include:
- Hydraulic Pressure Testing: Verifies the valve’s ability to withstand pressure without leaking.
- Functional Testing: Checks the valve’s operational performance under simulated working conditions.
- Endurance Testing: Assesses the valve’s long-term reliability by simulating extended use.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
When sourcing hydraulic control valves from international suppliers, buyers should implement strategies to verify the supplier’s quality control processes.
- Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality systems.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Suppliers should be able to provide documented evidence of their quality assurance practices, including inspection reports and compliance certificates.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspection agencies can offer an unbiased evaluation of product quality before shipment.
Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers
For buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality control in the context of local regulations and standards is vital.
- Regional Compliance: Ensure that suppliers are aware of and comply with local regulations and industry standards relevant to your region.
- Documentation: Verify that all quality assurance documentation is complete and properly archived, as this can facilitate smoother customs clearance and reduce delays.
- Cultural Considerations: Recognize that quality assurance practices may vary significantly across different cultures and regions. Building relationships with suppliers based on trust and transparency can enhance communication regarding quality expectations.
By familiarizing themselves with the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for hydraulic control valves, B2B buyers can make more informed decisions, ensuring they procure reliable and high-quality components that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: Amazing Production Process with Modern Machines and Skilful Workers
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic control valve types Sourcing
When sourcing hydraulic control valves, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The cost of hydraulic control valves is influenced by multiple components and factors that must be considered to optimize procurement strategies.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary raw materials used in hydraulic control valves include metals such as steel, brass, and aluminum, along with seals and other polymers. The choice of material directly impacts the valve’s durability, performance, and cost. For example, stainless steel valves generally cost more but offer better corrosion resistance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly based on the region and skill level required for manufacturing. Countries with lower labor costs can offer competitive pricing, but quality control must be ensured.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses expenses related to factory operations, including utilities, maintenance, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce overhead, thereby lowering the overall cost.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling may be necessary for specific valve designs or specifications. The initial investment in tooling can be significant, but it is often amortized over a larger production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance processes are essential to ensure reliability and compliance with international standards. The costs associated with QC can vary based on the complexity of the testing procedures.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary greatly depending on the location of the supplier and the destination. Incoterms selected (like FOB, CIF, or DDP) will affect who bears these costs and how they are calculated.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a profit margin to their costs. Understanding typical margins within the industry can help buyers gauge fair pricing.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Pricing often benefits from economies of scale. Higher order volumes can lead to significant discounts, making it essential for buyers to consider minimum order quantities (MOQ) to achieve cost efficiency.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom valves tailored to specific applications generally cost more than standard models. It is crucial to balance the need for customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials: The choice of materials not only affects the initial cost but also influences long-term performance and maintenance. Investing in higher-quality materials can reduce Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) by minimizing replacement frequency.
-
Quality/Certifications: Valves that meet international quality standards (like ISO or API certifications) may have higher upfront costs but can offer better reliability and lower operational risks.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact pricing. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their proven track record, while emerging suppliers might offer competitive rates to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms affect the total landed cost. Buyers should consider all logistics implications, including insurance and customs duties, when negotiating terms.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to explore flexible pricing options, especially when ordering in bulk. Building relationships with suppliers can lead to better terms and conditions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of the Total Cost of Ownership, including maintenance and operational costs, not just the purchase price. This will provide a clearer picture of the long-term value.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences, as local economic conditions can influence costs. For instance, fluctuations in currency exchange rates may affect pricing for international transactions.
-
Supplier Diversification: Consider multiple suppliers to enhance competition and secure the best possible pricing. This approach can also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
In summary, international B2B buyers must navigate a complex landscape of cost components and pricing influencers when sourcing hydraulic control valves. By understanding these dynamics and employing strategic procurement practices, buyers can optimize their sourcing decisions and achieve better value.
Disclaimer: Prices mentioned in the analysis are indicative and can vary based on market conditions and specific supplier negotiations. Always consult with suppliers for accurate quotes tailored to your requirements.
Spotlight on Potential hydraulic control valve types Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘hydraulic control valve types’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic control valve types
Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Control Valves
When selecting hydraulic control valves, international B2B buyers should be aware of several critical technical properties that influence performance, compatibility, and reliability. Understanding these specifications can lead to better purchasing decisions and ensure optimal functionality in various applications.
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The material from which the valve is constructed, typically stainless steel, brass, or plastic.
– Importance: The choice of material affects durability, corrosion resistance, and temperature tolerance. For instance, stainless steel valves are preferred in corrosive environments, while brass may be sufficient for less demanding applications. -
Pressure Rating
– Definition: The maximum pressure that the valve can safely handle, often specified in pounds per square inch (PSI) or bar.
– Importance: Selecting a valve with an appropriate pressure rating is crucial to avoid failures or leaks in high-pressure systems. This specification directly impacts safety and operational efficiency. -
Flow Rate
– Definition: The volume of fluid that can pass through the valve per unit of time, usually measured in liters per minute (LPM) or gallons per minute (GPM).
– Importance: Understanding the required flow rate is essential for system design. A valve that does not meet the flow requirements can lead to inadequate performance or system inefficiencies. -
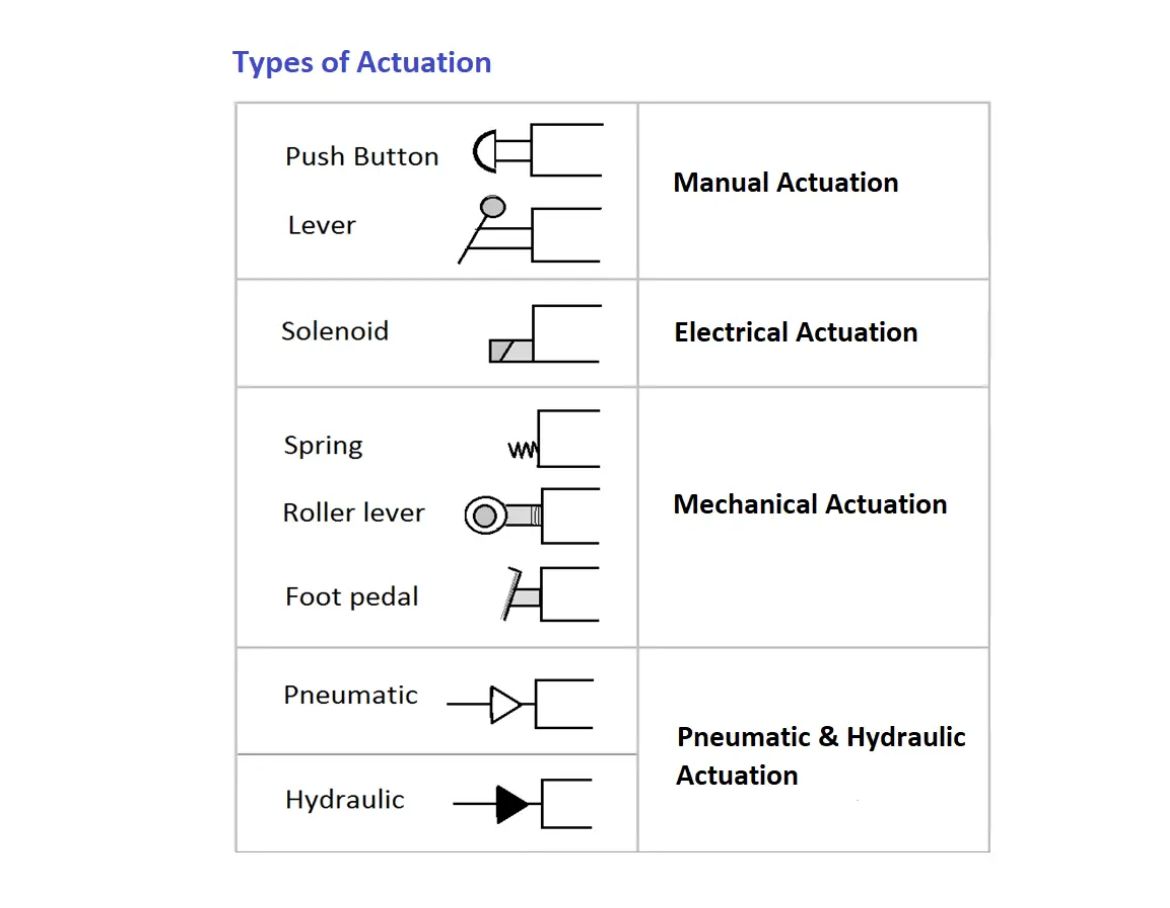
Actuation Type
– Definition: The mechanism used to operate the valve, which can be manual, pneumatic, or electric.
– Importance: The actuation type impacts the valve’s responsiveness and ease of integration into automated systems. Buyers must consider the existing infrastructure and operational needs when selecting the actuation type. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The acceptable variations in dimensions and performance parameters of the valve.
– Importance: Tighter tolerances often indicate higher quality and better performance. In precision applications, such as in robotics or aerospace, understanding tolerance levels can prevent malfunctions and ensure compatibility with other components. -
Temperature Range
– Definition: The range of temperatures within which the valve can operate effectively, often specified in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
– Importance: Selecting a valve that can withstand the operating temperature of the system is vital for maintaining performance and longevity. For example, valves in hydraulic systems subject to extreme temperatures must be able to handle those conditions without degradation.
Common Trade Terminology
Navigating the procurement process for hydraulic control valves involves understanding specific trade terms that facilitate communication and ensure clarity in transactions.
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Knowing whether a valve is sourced from an OEM can assure buyers of quality and compatibility with existing systems. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Understanding MOQ is crucial for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should assess whether the MOQ aligns with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document sent to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ helps buyers compare offers from multiple suppliers, ensuring they receive the best price and terms for hydraulic control valves. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international rules that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for understanding shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order to the delivery of the product.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time helps buyers plan their operations and manage inventory effectively. Delays can impact project timelines and operational efficiency. -
Certification Standards
– Definition: Industry standards that a product must meet to ensure quality and safety.
– Importance: Certifications provide assurance that the valves comply with international safety and performance standards, which is particularly important for industries such as aerospace and oil and gas.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terminologies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, optimize their procurement processes, and enhance the reliability of their hydraulic systems.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hydraulic control valve types Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The hydraulic control valve market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand across various industrial applications, including construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. The global market is projected to expand due to the rise in automation and the need for efficient fluid control systems. Key trends include the adoption of advanced technologies such as IoT-enabled valves and predictive maintenance solutions, which enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note the emerging trend of modular valve designs. These designs allow for easy customization and integration into existing systems, catering to diverse operational needs. Additionally, the shift towards digitalization in hydraulic systems is encouraging suppliers to offer more sophisticated control options, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and remote monitoring capabilities.
Sourcing strategies are also evolving. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers that can provide comprehensive solutions, including technical support and after-sales service, to ensure smooth operations. In regions like Vietnam and Colombia, where infrastructure development is paramount, the demand for reliable and high-performance hydraulic control valves is surging. Thus, understanding local market dynamics and building strong relationships with suppliers can yield significant competitive advantages.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a cornerstone of procurement strategies in the hydraulic control valve sector. Buyers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions, making it essential to prioritize suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices. This includes opting for manufacturers that utilize eco-friendly materials and processes, thus reducing the carbon footprint associated with production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important. International buyers should ensure that their suppliers comply with labor standards and promote fair trade practices throughout their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety can serve as benchmarks for evaluating supplier commitments to sustainability.
Moreover, the integration of recycled materials in hydraulic control valve manufacturing is gaining traction. This not only minimizes waste but also appeals to environmentally conscious buyers. By prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the increasing consumer demand for responsible manufacturing practices.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of hydraulic control valves reflects the broader advancements in hydraulic technology. Initially designed for simple on/off control, these valves have transformed into complex systems capable of precise flow and pressure regulation. The introduction of electronic control systems in the late 20th century marked a significant turning point, enabling remote operation and automation.
As industries have become more focused on efficiency and sustainability, the demand for advanced hydraulic control valves has surged. The latest developments emphasize modularity and integration with digital technologies, allowing for real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making. This historical context is crucial for B2B buyers aiming to understand the current landscape and future potential of hydraulic control valve technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic control valve types
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers of hydraulic control valves?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, certifications, and customer references. Assess their production capabilities, including technology and equipment used. Ensure they comply with international standards relevant to your region, such as ISO certifications. Request samples to evaluate product quality, and consider the supplier’s ability to provide timely support and after-sales service, which is crucial for maintenance in diverse operating conditions across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. -
Can hydraulic control valves be customized to fit specific operational needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for hydraulic control valves. Buyers can specify design features such as size, pressure ratings, and material compatibility based on their operational environment. Discuss your requirements early in the procurement process and provide technical specifications. Ensure the supplier has experience with similar custom projects, and request prototypes or CAD drawings to validate the design before mass production. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for hydraulic control valves?
MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and product type, typically ranging from 50 to several hundred units. Lead times usually depend on the complexity of the order and customization levels, ranging from a few weeks to several months. For international buyers, it’s essential to clarify these details upfront and factor in additional time for shipping and customs clearance, particularly for regions with less reliable logistics networks. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing hydraulic control valves internationally?
Common payment terms include advance payment, letter of credit, or payment upon delivery. Many suppliers may require a deposit (usually 30-50%) before production, with the balance due upon completion or delivery. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that provide security while ensuring cash flow flexibility. Consider using escrow services for large transactions to safeguard your investment, particularly when dealing with new suppliers in international markets. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for hydraulic control valves?
Request copies of quality certifications such as ISO 9001 or specific industry standards relevant to hydraulic systems. Suppliers should provide test reports and certificates of compliance for their products. Conducting periodic audits or third-party inspections can further ensure adherence to quality standards. For international transactions, check if the supplier has a robust quality management system in place to mitigate risks associated with product failures. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing hydraulic control valves?
Consider the shipping method (air vs. sea), which affects cost and delivery time. Ensure the supplier is experienced in handling international shipments and can provide all necessary documentation for customs clearance. Discuss insurance options to protect against damage during transit. Additionally, familiarize yourself with local import regulations, tariffs, and duties that may apply to hydraulic control valves in your country. -
How should disputes with suppliers be managed in international transactions?
Establish clear communication channels and document all agreements in writing, including specifications, timelines, and payment terms. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it through direct communication first. If necessary, refer to a mutually agreed-upon mediation or arbitration service, as outlined in your contract. Consider including a clause that specifies the governing law and jurisdiction to streamline resolution processes and avoid prolonged disputes. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing hydraulic control valves internationally?
Challenges include language barriers, cultural differences, and varying regulatory standards. Time zone differences can complicate communication, leading to delays. To mitigate these risks, invest time in establishing strong relationships with suppliers and consider employing local representatives or agents who understand the market dynamics. Additionally, conducting thorough due diligence and maintaining clear documentation can help navigate complexities in international sourcing effectively.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic control valve types
In the evolving landscape of hydraulic control valves, strategic sourcing remains paramount for international B2B buyers. Understanding the diverse types—ranging from pressure relief valves to flow control valves—enables organizations to optimize their operational efficiency. Key takeaways include the importance of selecting valves that align with system requirements, such as pressure conditions and flow rates, as well as the necessity for regular maintenance to prolong valve life and ensure reliability.
Moreover, as industry standards evolve, such as the recent updates to CJ/T219, staying informed about these changes is crucial for compliance and performance. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can offer not only high-quality products but also expertise in navigating these standards.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced hydraulic control solutions will only increase as industries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe strive for greater automation and efficiency. Engaging with reliable manufacturers and distributors will empower businesses to leverage cutting-edge technology in their operations. Now is the time to reassess your sourcing strategies and invest in hydraulic control valve solutions that drive your business forward.