Master Hydraulic Cylinder Types: Boost Efficiency and Cut
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for hydraulic cylinder types
In the ever-evolving landscape of global manufacturing and engineering, hydraulic cylinders stand as pivotal components, driving efficiency and precision across various sectors. For international B2B buyers, particularly those from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the diverse types of hydraulic cylinders is crucial for optimizing operations and enhancing productivity. These cylinders serve as the backbone of hydraulic systems, facilitating essential tasks such as lifting, moving, and controlling machinery with remarkable force and reliability.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of hydraulic cylinder types, offering an in-depth exploration of their classifications, materials, manufacturing quality control, and sourcing strategies. Buyers will find detailed insights into single-acting, double-acting, and specialized cylinders, alongside critical factors influencing their performance and longevity. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations and highlights reputable suppliers, ensuring that decision-makers are equipped with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing choices.
By navigating this guide, B2B buyers will not only enhance their understanding of hydraulic cylinder types but also empower their sourcing strategies, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re sourcing for construction, agriculture, or industrial applications, this resource is designed to facilitate your journey in selecting the right hydraulic solutions for your unique needs.
Understanding hydraulic cylinder types Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single Acting Cylinder | Operates in one direction; uses spring or external force for return | Jacks, construction equipment, automotive | Pros: Simple design, cost-effective. Cons: Limited force; prone to wear. |
| Double Acting Cylinder | Operates in both directions; fluid pressure applied on both sides | Industrial machinery, heavy-duty vehicles | Pros: Efficient, faster response. Cons: Requires more space, higher cost. |
| Tie-Rod Cylinder | Reinforced by threaded rods; seals fluid with end caps | Manufacturing, agricultural machinery | Pros: Easy assembly, economical. Cons: Shorter lifespan, limited designs. |
| Tandem Cylinder | Two or more cylinders working in unison | Heavy lifting applications, construction | Pros: Increased force and stability. Cons: Complex installation, higher maintenance. |
| Telescopic Cylinder | Multiple nested cylinders for extended stroke | Dump trucks, aerial lifts | Pros: Compact design, high stroke length. Cons: More complex, higher cost. |
Single Acting Cylinder
Single acting cylinders are designed to apply force in one direction only, typically using a spring or external force to return the piston to its original position. This simplicity makes them ideal for applications where space is limited and cost-effectiveness is crucial. However, buyers should consider that while these cylinders are economical, they can be prone to wear, particularly in the retractable spring mechanism. Applications include jacks and various construction equipment, making them suitable for industries focused on manual lifting and material handling.
Double Acting Cylinder
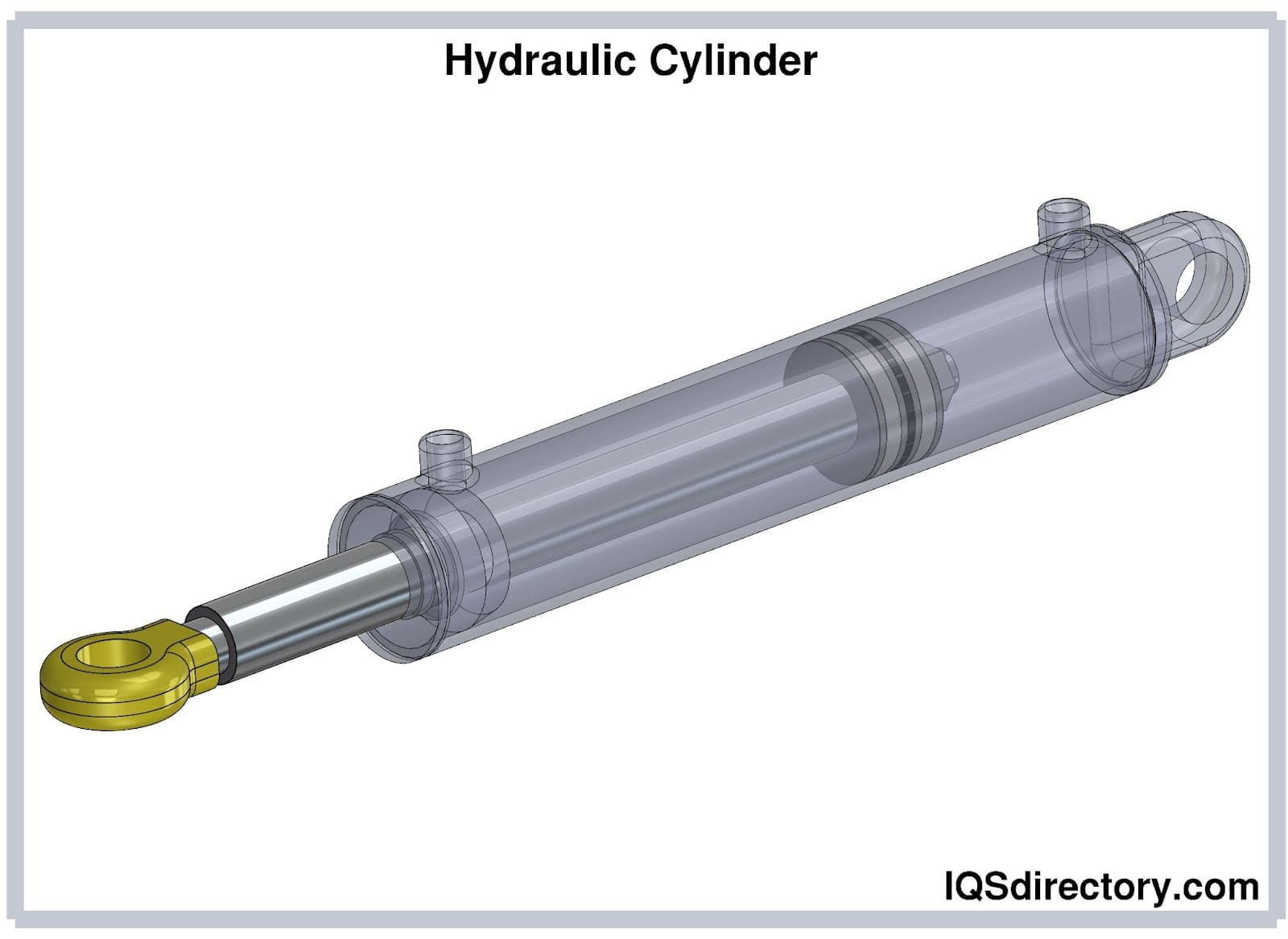
Double acting cylinders utilize fluid pressure to push and pull the piston in both directions, providing greater efficiency and control. Their design allows for quicker response times and better acceleration, which is essential for heavy-duty machinery and applications such as industrial manufacturing and automotive systems. While they offer significant advantages, buyers must account for the increased installation space and costs associated with these cylinders. Their versatility makes them a preferred choice for applications requiring precise movements and force control.
Tie-Rod Cylinder
Tie-rod cylinders are characterized by their threaded steel rods that reinforce the structure, providing durability and reliability for various applications. They are commonly used in manufacturing and agricultural machinery due to their ease of assembly and maintenance. However, buyers should be aware of their limited lifespan and design options, which may restrict their use in more demanding environments. This type of cylinder is a cost-effective solution for industries that require reliable performance without the need for extensive customization.
Tandem Cylinder
Tandem cylinders consist of two or more cylinders working together, allowing for increased force output and stability. They are particularly useful in heavy lifting applications, such as construction and industrial settings, where substantial force is required. While they provide enhanced performance, the complexity of installation and potential for higher maintenance needs should be considered by buyers. Tandem cylinders are ideal for projects that demand synchronized operations across multiple cylinders.
Telescopic Cylinder
Telescopic cylinders feature multiple nested cylinders, allowing for a significant stroke length while maintaining a compact design. This makes them particularly advantageous in applications like dump trucks and aerial lifts, where space is a premium. While they offer impressive reach and lifting capabilities, buyers should be mindful of the complexity and cost associated with their design. Telescopic cylinders are best suited for industries that require both compact equipment and extended reach, balancing functionality with spatial constraints.
Related Video: Types of Hydraulic Cylinder । Double Acting । Single Acting । Telescopic Type Uses & Applications.
Key Industrial Applications of hydraulic cylinder types
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of hydraulic cylinder types | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Lifting and lowering heavy construction materials | Improves efficiency and safety on job sites | Ensure compatibility with existing equipment; consider load capacity and cycle times. |
| Agriculture | Actuating equipment for planting and harvesting | Enhances productivity and reduces manual labor | Focus on durability and resistance to environmental factors; evaluate service and maintenance support. |
| Manufacturing | Precision positioning in assembly lines | Increases accuracy and speed in production processes | Assess the precision requirements; consider availability of replacement parts and service. |
| Transportation & Logistics | Loading and unloading cargo in shipping and freight | Streamlines operations and reduces handling time | Look for cylinders that offer reliability under heavy loads; consider local supplier capabilities. |
| Mining | Operating heavy machinery for material extraction | Maximizes operational efficiency and minimizes downtime | Evaluate performance in extreme conditions; prioritize suppliers with proven industry experience. |
Construction
In the construction industry, hydraulic cylinders are essential for lifting and lowering heavy materials such as steel beams and concrete blocks. They provide the necessary force to operate cranes and excavators, ensuring that tasks are completed efficiently and safely. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing cylinders that can withstand high load capacities and offer quick cycle times to enhance productivity on-site. Compatibility with existing machinery and easy maintenance are also critical considerations for ensuring smooth operations.
Agriculture
Hydraulic cylinders play a pivotal role in agricultural machinery, facilitating functions like planting, plowing, and harvesting. By automating these processes, they significantly enhance productivity and reduce the physical strain on operators. Buyers in this sector should prioritize cylinders that are durable and resistant to harsh environmental conditions, such as moisture and dust. Additionally, sourcing from suppliers that offer robust support and maintenance services can help mitigate downtime during peak farming seasons.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, hydraulic cylinders are used for precision positioning in assembly lines, where accuracy is paramount. They enable quick and reliable movement of components, contributing to faster production rates and improved quality control. International B2B buyers need to assess the precision requirements of their operations and ensure that the cylinders they source meet these specifications. Availability of replacement parts and after-sales support is also crucial to minimize disruptions in production.
Transportation & Logistics
Hydraulic cylinders are integral to loading and unloading cargo in the transportation and logistics sector. They facilitate the operation of forklifts and other material handling equipment, streamlining operations and significantly reducing handling times. Buyers should consider sourcing cylinders that are reliable under heavy loads and evaluate the capabilities of local suppliers to ensure timely support and service. This can enhance overall efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Mining
In the mining industry, hydraulic cylinders are critical for operating heavy machinery used in material extraction. They provide the force required to lift and maneuver large equipment, maximizing operational efficiency and minimizing downtime. B2B buyers should look for cylinders that can perform well under extreme conditions, such as high pressure and harsh environments. Prioritizing suppliers with proven experience in the mining sector can help ensure the reliability and longevity of the hydraulic systems used.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for hydraulic cylinder types
When selecting materials for hydraulic cylinders, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below, we analyze four common materials used in hydraulic cylinder construction, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and implications for specific applications.
Steel
Key Properties: Steel is renowned for its high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it suitable for high-pressure applications. It typically withstands temperatures up to 300°C and pressures exceeding 350 bar, depending on the grade.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of steel is its strength and resistance to deformation under load. However, it is susceptible to corrosion, especially in humid or chemically aggressive environments. Additionally, manufacturing steel cylinders can be complex due to the need for precise machining and welding.
Impact on Application: Steel’s compatibility with a variety of hydraulic fluids makes it versatile. However, in corrosive environments, protective coatings or stainless steel alternatives may be necessary.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should consider local availability and the cost of high-quality steel. Compliance with standards such as ASTM A36 or DIN 17100 is crucial for ensuring product reliability.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight and has good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is critical. It can handle pressures up to 200 bar and operates effectively at temperatures ranging from -40°C to 80°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which enhances the efficiency of mobile hydraulic systems. However, it has lower tensile strength compared to steel, which may limit its use in high-load applications. Manufacturing processes for aluminum can also be more expensive due to the need for specialized equipment.
Impact on Application: Aluminum’s corrosion resistance allows it to be used in marine or outdoor applications where exposure to moisture is a concern. However, compatibility with certain hydraulic fluids must be assessed to avoid chemical reactions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe and the Middle East may prefer aluminum for its lightweight properties in automotive and aerospace applications. Compliance with JIS H 2000 or similar standards is essential for quality assurance.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and can withstand high pressures (up to 400 bar) and temperatures (up to 600°C). Its chemical composition provides durability in harsh environments.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it suitable for aggressive fluids. However, it is more expensive than regular steel and can be challenging to machine, which may increase manufacturing costs.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is ideal for hydraulic systems in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and marine applications due to its hygienic properties. It is compatible with a wide range of hydraulic fluids.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from the Middle East and Europe should ensure compliance with ASTM A312 or EN 10088 standards. The higher cost may be justified by the longevity and reduced maintenance needs of stainless steel cylinders.
Composite Materials
Key Properties: Composite materials, such as carbon fiber reinforced polymers, provide excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can withstand moderate pressures (up to 150 bar) and temperatures (up to 120°C).
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of composites is their lightweight nature and resistance to corrosion. However, they are not as widely used in high-pressure applications due to their lower strength compared to metals. Manufacturing processes can also be complex and costly.
Impact on Application: Composites are suitable for specialized applications in aerospace and automotive industries where weight savings are critical. They may not be compatible with all hydraulic fluids, necessitating careful selection.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in advanced manufacturing regions like Europe may find composites appealing for innovative applications. Compliance with specific aerospace or automotive standards is crucial for ensuring performance.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for hydraulic cylinder types | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Heavy-duty industrial applications | High tensile strength | Susceptible to corrosion | Medium |
| Aluminum | Mobile hydraulic systems | Lightweight | Lower tensile strength | Medium |
| Stainless Steel | Food processing, pharmaceuticals | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost | High |
| Composite Materials | Aerospace, automotive | Lightweight and corrosion-resistant | Not suitable for high pressures | High |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview for international B2B buyers, enabling informed decisions based on performance requirements and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for hydraulic cylinder types
Hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in various industrial applications, and understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures is vital for international B2B buyers. This section delves into the main stages of manufacturing hydraulic cylinders, key techniques used, and the quality control (QC) standards that ensure reliability and performance.
Manufacturing Processes
The manufacturing of hydraulic cylinders involves several key stages, each critical to ensuring the final product meets the required specifications and performance standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is selecting and preparing the appropriate materials. Hydraulic cylinders are typically made from high-strength steel or aluminum alloys, chosen for their durability and resistance to deformation under pressure.
- Material Selection: Buyers should ensure that suppliers use materials compliant with international standards (e.g., ASTM, EN).
- Cutting: Raw materials are cut to size using precision cutting tools. This step requires accuracy to minimize waste and ensure proper fit during assembly.
2. Forming
Once the materials are prepared, the forming process begins, which shapes the components of the hydraulic cylinder.
- Machining: Components such as the cylinder barrel and end caps are machined to achieve precise dimensions and surface finishes. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines are often used for this purpose, ensuring high levels of accuracy.
- Welding: For certain designs, components may be welded together. Buyers should inquire about the welding techniques used (e.g., MIG, TIG) and the qualifications of the welders, as this can significantly affect the strength and integrity of the cylinder.
3. Assembly
The assembly phase involves putting together the various components of the hydraulic cylinder.
- Piston and Rod Assembly: The piston is inserted into the cylinder barrel, and the piston rod is attached. Proper alignment is critical to ensure smooth operation.
- Sealing: Seals are installed to prevent hydraulic fluid leakage, which is essential for maintaining pressure and performance. Buyers should understand the types of seals used and their compatibility with different hydraulic fluids.
4. Finishing
The final stage of manufacturing includes finishing processes that enhance the durability and appearance of the hydraulic cylinder.
- Surface Treatment: Processes like anodizing, plating, or painting can be applied to protect against corrosion. This is particularly important for buyers in humid or corrosive environments.
- Quality Inspection: Before the product is packaged, it undergoes rigorous quality checks to ensure it meets all specifications.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is a critical aspect of hydraulic cylinder manufacturing, ensuring that the final product is safe, reliable, and compliant with international standards.
International Standards
B2B buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to recognized quality standards, which may include:
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems and is essential for ensuring consistent product quality.
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
- API Standards: For hydraulic cylinders used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control involves several checkpoints throughout the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Ongoing inspections during the manufacturing process help identify defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): A comprehensive inspection of the completed product ensures it meets all design and performance criteria.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to verify the performance and safety of hydraulic cylinders:
- Hydrostatic Testing: This test checks for leaks and structural integrity by pressurizing the cylinder with fluid.
- Pneumatic Testing: Similar to hydrostatic testing but uses air to test for leaks and performance.
- Performance Testing: Evaluates the cylinder’s operational efficiency under load conditions.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must take proactive steps to verify the quality control processes of their suppliers:
- Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess their manufacturing processes, quality assurance practices, and compliance with international standards.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality reports and test certificates for each batch of hydraulic cylinders supplied.
- Third-Party Inspection: Engage independent inspection services to assess the quality and compliance of products before shipment.
QC/Certifications Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the nuances of quality certifications is essential:
- Regional Standards: Be aware of local regulations and standards that may affect the acceptance of hydraulic cylinders in your market.
- Documentation: Ensure that all quality assurance documentation is complete and readily available for customs and regulatory inspections.
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers who understand the importance of quality assurance and are willing to collaborate on meeting specific requirements.
By focusing on these manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing hydraulic cylinders, ensuring they receive high-quality products that meet their operational needs.
Related Video: What is Production? Types of Production, Factors of Production
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for hydraulic cylinder types Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of hydraulic cylinders is crucial for international B2B buyers. Here, we break down the cost components, price influencers, and provide actionable tips for effective sourcing.
Cost Components
The total cost of hydraulic cylinders encompasses several key components:
-
Materials: The choice of materials—such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials—directly impacts the cost. High-grade materials that enhance durability and performance will typically command higher prices.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary significantly by region. In countries with higher wage standards, such as those in Europe, labor can be a substantial portion of the overall cost. Conversely, regions like Africa or South America may benefit from lower labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with utilities, facility maintenance, and equipment depreciation. Efficient manufacturing processes can reduce overhead, affecting the final price.
-
Tooling: Initial tooling costs can be significant, especially for custom designs. The more specialized the cylinder, the higher the tooling costs. These costs are typically amortized over the production run.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC processes ensures product reliability, but adds to the overall cost. Certifications (e.g., ISO) can also influence pricing.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs depend on the weight and size of the cylinders, as well as the distance traveled. International shipping can significantly add to costs, especially with tariffs and customs duties.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence the pricing of hydraulic cylinders:
-
Volume/MOQ: Larger orders often qualify for discounts due to economies of scale. Buyers should inquire about minimum order quantities (MOQ) to optimize pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom-designed cylinders or those with unique specifications can be priced higher due to additional material and labor costs.
-
Materials and Quality: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., for high-pressure applications) will drive up costs. Buyers should weigh the benefits of investing in higher quality against their specific needs.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but offer better assurance of quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the agreed-upon Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) is essential, as they dictate who bears the cost and risk at various stages of the shipping process, influencing the total landed cost.
Buyer Tips
To maximize cost-efficiency and ensure a successful sourcing experience, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms with suppliers. Leverage volume commitments or long-term partnerships to secure better pricing.
-
Focus on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate not just the purchase price but also maintenance costs, lifespan, and efficiency of the hydraulic cylinders. A slightly higher upfront cost may lead to lower operating costs over time.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Be aware that international shipping and customs can add unforeseen costs. Factor these into your budget and timeline.
-
Research Local Markets: For buyers in regions like Africa and South America, exploring local suppliers may reveal cost advantages due to reduced shipping and tariffs.
-
Request Samples: Before placing large orders, request samples to assess quality and performance. This can prevent costly mistakes down the line.
Disclaimer
Prices for hydraulic cylinders can fluctuate based on market conditions, raw material costs, and supplier pricing strategies. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure competitive pricing tailored to your specific requirements.
Spotlight on Potential hydraulic cylinder types Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘hydraulic cylinder types’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for hydraulic cylinder types
Key Technical Properties of Hydraulic Cylinder Types
When selecting hydraulic cylinders for various applications, understanding the essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
Hydraulic cylinders are typically made from materials such as steel, aluminum, or composite materials. The choice of material affects strength, weight, corrosion resistance, and overall durability. For example, high-grade steel is often preferred for heavy-duty applications due to its strength and fatigue resistance, while aluminum can be beneficial in applications where weight reduction is critical. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measured value. In hydraulic cylinders, tight tolerances are essential to ensure proper fit and function, minimizing wear and enhancing performance. B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers can meet the necessary tolerances for their specific applications, as poor tolerances can lead to leaks and reduced efficiency. -
Pressure Rating
The pressure rating indicates the maximum pressure the hydraulic cylinder can withstand during operation. This property is vital for safety and efficiency, as operating above the specified pressure can lead to failure. Buyers must match the pressure rating to their application requirements to avoid potential hazards and ensure optimal performance. -
Bore and Stroke Length
The bore size (the internal diameter of the cylinder) and stroke length (the distance the piston travels) are critical dimensions that determine the force output and range of motion. Selecting the appropriate bore and stroke length based on the application’s load requirements ensures that the hydraulic system operates efficiently and effectively. -
Seal Type
The seals used in hydraulic cylinders prevent fluid leakage and contamination. Different seal types (e.g., O-rings, lip seals) offer varying levels of performance based on the application environment (temperature, pressure, and fluid type). Understanding seal specifications can help buyers select cylinders that offer optimal sealing performance for their specific needs. -
Mounting Style
The mounting style of a hydraulic cylinder (e.g., clevis, trunnion, flange) affects installation and alignment. Choosing the correct mounting style is important for ensuring that the cylinder operates smoothly and effectively within the system. Buyers should consider the available space and application requirements when selecting the appropriate mounting style.
Common Trade Terminology in Hydraulic Cylinder Procurement
Familiarity with industry jargon can facilitate smoother communication and negotiations between buyers and suppliers. Here are key terms to know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts and equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding the role of OEMs is crucial, as they often provide components that must meet specific industry standards and quality requirements. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest amount of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ helps buyers plan their orders effectively, especially when dealing with specialized hydraulic cylinders that may have higher production costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used by buyers to solicit price quotes from suppliers for specific products or services. It typically includes detailed specifications and quantities. Using RFQs helps buyers compare prices and terms from different suppliers, ensuring they receive the best value. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade, including the delivery of goods, risk management, and transportation costs. Understanding Incoterms is essential for B2B buyers to clarify their obligations and rights during transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. It is a critical consideration for project planning, as longer lead times can impact schedules and overall project delivery. Buyers should inquire about lead times when negotiating orders.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Hydraulic Fluid Compatibility
This term refers to the ability of hydraulic seals and materials to withstand various hydraulic fluids without degradation. Understanding fluid compatibility is essential for ensuring the longevity and reliability of hydraulic systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions and optimize their procurement processes for hydraulic cylinders, ensuring they meet their operational needs efficiently.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the hydraulic cylinder types Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The hydraulic cylinder market is experiencing significant growth driven by increasing demand across various industries, including construction, agriculture, and manufacturing. Global factors such as urbanization, infrastructure development, and the rise of automation technologies are propelling this demand. For international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, staying informed about emerging trends is crucial for strategic sourcing.
Current trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as IoT and AI in hydraulic systems, leading to improved efficiency and predictive maintenance capabilities. For instance, IoT-enabled hydraulic cylinders can provide real-time performance data, allowing businesses to optimize operations and reduce downtime. Furthermore, there is a growing shift towards customized solutions that cater to specific operational needs, enhancing product longevity and performance.
Buyers should also be aware of regional dynamics affecting sourcing strategies. For instance, suppliers in Europe may focus on innovation and quality, while those in Africa and South America could emphasize cost-effective solutions. Understanding these dynamics can help buyers align their procurement strategies with regional strengths and market demands.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the sourcing of hydraulic cylinders. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of energy consumption and waste generation, has prompted many companies to reevaluate their supply chains. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices, such as using renewable energy sources and minimizing emissions during production.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as it encompasses fair labor practices and responsible material sourcing. Buyers should look for suppliers who are transparent about their supply chains and adhere to international standards regarding labor rights and environmental regulations. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) can be indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Additionally, the use of ‘green’ materials—such as recyclable or biodegradable components—can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of hydraulic cylinders. By prioritizing suppliers with sustainable practices and certifications, buyers can not only enhance their corporate responsibility but also meet the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products.
Brief Evolution/History
The hydraulic cylinder industry has evolved significantly since its inception in the 19th century. Initially developed for steam-powered machinery, hydraulic cylinders have undergone extensive technological advancements, making them crucial components in modern industrial applications. The introduction of more robust materials and precision engineering techniques has improved their efficiency and durability. Today, hydraulic cylinders are integral to various sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and construction, reflecting a shift toward more complex and demanding applications. This evolution continues as manufacturers explore innovative designs and technologies to meet the diverse needs of global markets.
In summary, understanding market dynamics, sourcing trends, and sustainability practices is essential for B2B buyers navigating the hydraulic cylinder sector. By aligning procurement strategies with these insights, businesses can enhance operational efficiency and meet their sustainability goals.
Related Video: International Trade and Supply Chains
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of hydraulic cylinder types
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for hydraulic cylinders?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their experience and reputation in the hydraulic cylinder industry. Check for certifications such as ISO 9001, which indicates quality management systems. Additionally, assess their production capabilities, including technology and equipment used, to ensure they can meet your specifications. Request references from past clients and evaluate their responsiveness to inquiries. It’s also beneficial to understand their after-sales service and support, as this can impact long-term satisfaction. -
Can hydraulic cylinders be customized for specific applications?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for hydraulic cylinders to meet specific application needs. Common customizations include variations in size, stroke length, mounting configurations, and materials. When discussing customization, provide detailed specifications and performance requirements. Be sure to inquire about the supplier’s design capabilities and lead times for custom orders, as this can significantly affect project timelines and costs. -
What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for hydraulic cylinders?
MOQs for hydraulic cylinders can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the order. Standard cylinders may have lower MOQs, while specialized or custom cylinders could require larger quantities. Lead times also vary based on the supplier’s production capacity and your order specifics, typically ranging from a few weeks to several months. Always clarify these details upfront to align your project schedules and budget. -
What payment terms should I expect when sourcing hydraulic cylinders internationally?
Payment terms can differ significantly among suppliers and regions. Common arrangements include upfront payments, partial payments upon order confirmation, and balance payments before shipment. Consider using secure payment methods such as letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Always negotiate terms that align with your cash flow needs and ensure you understand any additional costs, such as taxes or tariffs, that may apply to international transactions. -
What quality assurance measures should suppliers have in place?
Reputable suppliers should implement rigorous quality assurance (QA) protocols throughout the manufacturing process. This includes material inspections, in-process testing, and final product evaluations. Request documentation of their QA processes, including certifications and test reports. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s warranty and return policy, as these are critical in resolving any quality issues that may arise post-purchase. -
How do logistics and shipping impact sourcing hydraulic cylinders internationally?
Logistics and shipping play a crucial role in international sourcing. Ensure the supplier has a reliable logistics partner to handle transportation, customs clearance, and delivery. Discuss shipping options and costs, as these can vary based on destination and urgency. It’s also wise to understand the implications of Incoterms, which define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping arrangements, to avoid unexpected costs or delays. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers?
To effectively resolve disputes with suppliers, start with clear communication to identify the issue. Document all correspondence and agreements related to the transaction. If direct negotiation fails, consider involving a third-party mediator or arbitrator to facilitate a resolution. Understanding the legal framework governing international trade in your contract can also help in enforcing your rights. Building a strong relationship with suppliers can prevent many disputes from arising in the first place. -
What certifications should I look for when sourcing hydraulic cylinders?
When sourcing hydraulic cylinders, look for certifications that ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations. Key certifications include ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental management, and CE marking for products sold in Europe. Additionally, certifications specific to hydraulic systems, such as those from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) or the National Fluid Power Association (NFPA), can provide assurance of performance and safety. Always request proof of certifications to verify supplier compliance.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for hydraulic cylinder types
As international B2B buyers explore the landscape of hydraulic cylinders, understanding the diverse types available is crucial for effective strategic sourcing. Each type, from single-acting to double-acting and tandem cylinders, offers unique functionalities tailored to specific applications. Key takeaways include recognizing the importance of selecting the right cylinder type based on operational needs, maintenance requirements, and economic feasibility.
Strategic sourcing not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives cost-effectiveness and innovation. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and suppliers, buyers can ensure access to high-quality hydraulic cylinders that meet industry standards and performance expectations.
Looking ahead, the demand for hydraulic systems will continue to rise, particularly in emerging markets across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. B2B buyers are encouraged to stay informed about advancements in hydraulic technology and to leverage market insights to make informed purchasing decisions. Act now to optimize your sourcing strategy and position your business for success in a competitive landscape. Embrace the future of hydraulic systems with confidence and foresight.